Apush Unit 5
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Westward Expansion Causes: opportunities
california Gold Rush (mineral wealth)
Mormons settle Utah (religious freedom)
Improved transportation - Oregon trail, transcontinental railroad
Westward Expansion Causes: Manifest Destiny
spread what US defines as civilization
justification to replace people, spread civilization
racist concept
Westward Expansion Causes: Legislation
land treaties →creates more land
-Texas
-Homestead Act
-Transcontinental railroad
Effects of Westward Expansion
Western women gain more rights (some)
Native Americans suffered more
Racial Conflict in California (Chinese)
Expanded Trade with Asia
Causes of Mexican American War
New president big ideas for expansion to buy California
Manifest Destiny Ideal
Spread Slavery
disputed territory
Effects of the Mexican American War
Territorial Expansion
Increased Conflict
-Mangas Coloradas and Geronimo
-California Land Claims
Continued debates over slavery in the Mexican Cession, and the Compromise of 1850
Compromise of 1850: North Benefits
California admitted as free state
Slave trade prohibited in Washington D.C.
Texas loses boundary dispute with New Mexico
Compromise of 1850: South Benefits
Slavery holding permitted in Washington D.C.
Texas gets $10 million
Fugitive Slave Law
No slavery restrictions in Utah or New Mexico territories
The Compromise of 1850 is a _________ solution. In many ways, it sets up the debates about _____ to get more intense
temporary
slavery
Fugitive Slave Act
Popularly Sovereignty
Increased Immigration
Irish Potato Famine is happening (1846-1851)
German Revolution (1848)
Nativism
Know-Nothing Party (anti-immigration)
Chinese immigration because of Railroad work, Gold Rush
Effects of Increased Immigration
Nativism
anti-immigration ideology
know nothing party (American party) - political party with nativist ideals
Ethnic Neighborhoods
creation of them
Example: China Town (SF)
Free Soil Party (North)
Goal: Abolish slavery, or just stop the spread
Abolitionists (North)
Goal: Abolish slavery in USA
Frederick Douglass
Defenders of Slavery (South)
Goal: Keep slavery and expand it
Political Causes of the Civil War: Failed Attempts to Resolve Slavery
Kansas Nebraska Act (1854)
repealed Missouri compromise
created two new territories
allowed for popular sovereignty regarding the status of slavery
Dred Scott v. Sandford
Supreme Court case
upheld slavery in the terriotires
Denied citizenship to African Americans
Declared Missouri Compromise unconstiutional
Political Causes of the Civil War: End of the 2nd Party System Causes
Sectionalism ends second party system
Regional differences become more important than political ideology
whigs can’t agree on slavery
southern whigs become democrats
whigs fall apart
New Republican party takes its place
Political Causes of the Civil War: End of the 2nd Party System: Republican Party (1854)
Made up of:
Free Soilers
Northern Wigs who opposed slavery
some nativists
Primarily Northerners
GOP = Grand Ol’ Party
AKA Whigs against slavery support Federal power union to stay together
Election of 1860
Most free states vote Lincoln
Shows sectionalism
north vs. south (big divide)
before election, people are threatening secession to keep slavery
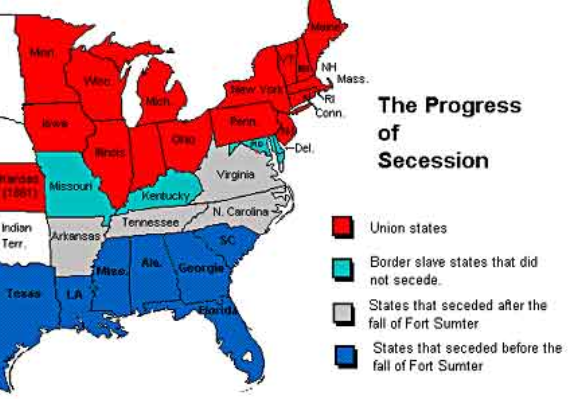
Secession
First Group:
South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas
Second Group:
Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, North Carolina
The Lost cause myth
Romanticizes the Confederate Cause (celebrates those who fought for the south)
Downplays the role of slavery as a cause for Secession
Reason for Confederate statues in the south, and works of literature such as “Gone with the Wind”
Cause of Secession
Cornerstone Address
New government foundation laid
“Negro is not equal to the white man: slavery subordinate to superior race natural normal condition” etc.
Based on white supremacy
War Begins
Lincoln elected Nov. 1860
Secession of first group early 1861
Lincolns inaugural address: will use force to keep union together
Fort Sumter is attacked by Confederate states in South Carolina
Topic 5.6 KNA
Kansas-Nebraska Act led to increased tension/violence
Whig party breaks up over slavery issue
Republicans Rise
Abraham Lincoln
Coalition of: - Free Soilers - abolitionists - nativists
Topic 5.7
The election of Lincoln triggers secession
southern states believe that he will move to end slavery, and start seceding
The Civil war was about slavery, its written into the Confederate founding documents
War begins with the attack on Fort Sumter
The Civil War: North Strengths
Industrialized = can produce more war materials
Wealthier (see industrialization)
Larger population (Urbanization + immigration)
Strong Government
Extensive Railroad networks (able to move people and goods around quicker)
The Civil War: North Weaknesses
Lacked Military Leadership (military schools are in the South)
Not as unified (not everyone is down for the cause)
The Civil War: Southern Strengths
Capable Military Leadership (Lee)
Defensive war at home (their turf)
Very unified (everyone is on board)
The Civil War: Southern Weaknesses
less resources (not industrialized, smaller population)
weak central government (its brand new, and they love States rights)
Border States
Slave holding States that did not secede from the Union
Delaware
Maryland
Kentucky
Missouri
(soon to be W. Virginia in 1863)
How did the Union mobilize for war in the face of opposition at home?
Lincoln’s Suspension of Habeas Corpus (1861)
Habeas Corpus allows a prisoner to appeal for release if they can prove they’re being held unlawfully
Lincoln suspended this right for individuals in the border states, because he wanted to stop the spread of secessionist ideas
Northern Conscription Act (1863)
same basic idea as the South
allowed people to buy their way out
resulted in draft riots of NYC
How did the Confederacy mobilize for war in the face of opposition at home?
Southern Conscription Act (1862)
required anyone between the ages of 18-35 to serve in the army for 3 years
some resisted
Causes of Union Victory: Industrialized North
The Union had:
More people
higher manufacturing capacity
more railroads
more wealth
Causes of Union Victory: The Anaconda Plan (1861)
The Union strategy to beat the South, created at the start of the war
naval blockade of the southern ports
take control of the Mississippi River, to split the south
Although importance of the plan is the outcome of the war is debated, Union control of the Mississippi River would prove to be a turning point in the war
Causes of Union Victory: Antietam (1862)
Bloodiest day in American Military history
Union “strategic victory”
Effects:
First major union victory
stopped Lee’s invasion of Maryland, put south on the defensive (for now)
Gave Lincoln an opportunity to issue the Emancipation Proclamation, changing the purpose of the war
Prevented European countries allying with the Confederates
Causes of Union Victory: Battle of Gettysburg (1863)
Between 46K and 51K casualties between both sides (over several days)
Lee gambled on invading he North and ended the war
Union Victory - Lee’s army retreated from Pennsylvania back to Virginia, would never invade North again
Effects:
Confederates losses would make it impossible for the south to ever win the war outright, only if they could hold on long enough for the north to quit
The Gettysburg Address
Causes of Union Victory: Battle of Vicksburg (1863)
47 day siege of the town of Vicksburg by Union Army, along the Mississippi River
Union Victory
Effects:
Union takes control of the Mississippi River, which splits Confederate states in two
Ulysses Grand gets Lincoln’s attention, and would become leader of Union Armies, eventually leading them to victory
Causes of Union Victory: “Hard War” Strategy
The systematic destruction of everything in the Confederate states that could aid their war effort (including civilian property)
The biggest example was “Sherman’s March to the Sea”
A Union Army, lead by General Sherman, blazed a trail of destruction through Georgia, destroying Atlanta along the way
Still hated in the South
“I intend to make Georgia howl” - Sherman
5.9 Key takeaways
emancipation proclamation changes the reason for the war to one about ending slavery, rather than about politics
Gettysburg Address convinces Americans that the fight against slavery is the fulfillment of the ideals set out in the country’s founding
Plans for Reconstruction: Lincoln
required 10% of a state’s voters to take an oath of loyalty to the Union in order to for a new government and rejoin the Union
required states to accept emancipation of slaves
offered full pardons to all former Confederates
Plans for Reconstruction: Johnson
required former Confederates with property worth $20,000 or more to obtain presidential pardon in order to vote or hold office; gave full pardons to others
required ratification of the 13th amendment
Plans for Reconstruction: Radical Republican
required 50% of a state’s voters to take an oath of loyalty to the Union in order to call a constitutional convention and elect a new government
divided south into five military districts
required state legislatures to adopt new constitutions guaranteeing African American suffrage
required states to ratify the 14th Amendment in order to seat representatives in Congress
Debates about voting rights: Women’s rights movement
Division:
National Woman Suffrage Association
Stanton
argued that women should get the right to vote first
American Woman Suffrage Association
Stone
Argued that Black men should get the right to vote first and women can fight for suffrage after
Reconstruction Amendments
13th Amendment
Abolishes slavery (unless you’re in prison)
14th Amendment
makes freedmen citizens
further defines citizenship
And a lot more
15th Amendment
says all MEN can vote (regardless of race)
Other effects of reconstruction debates
Increase in Federal Power (vs. States)
Rules of voting rights
Rules on Slavery
Violence
Klu Klux Klan
Lost Cause
South tries to revise the history of the civil war
Carpetbaggers
a political candidate who seeks election in an area where they have no local connections