HA&P Integumentary System Ch. 6
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
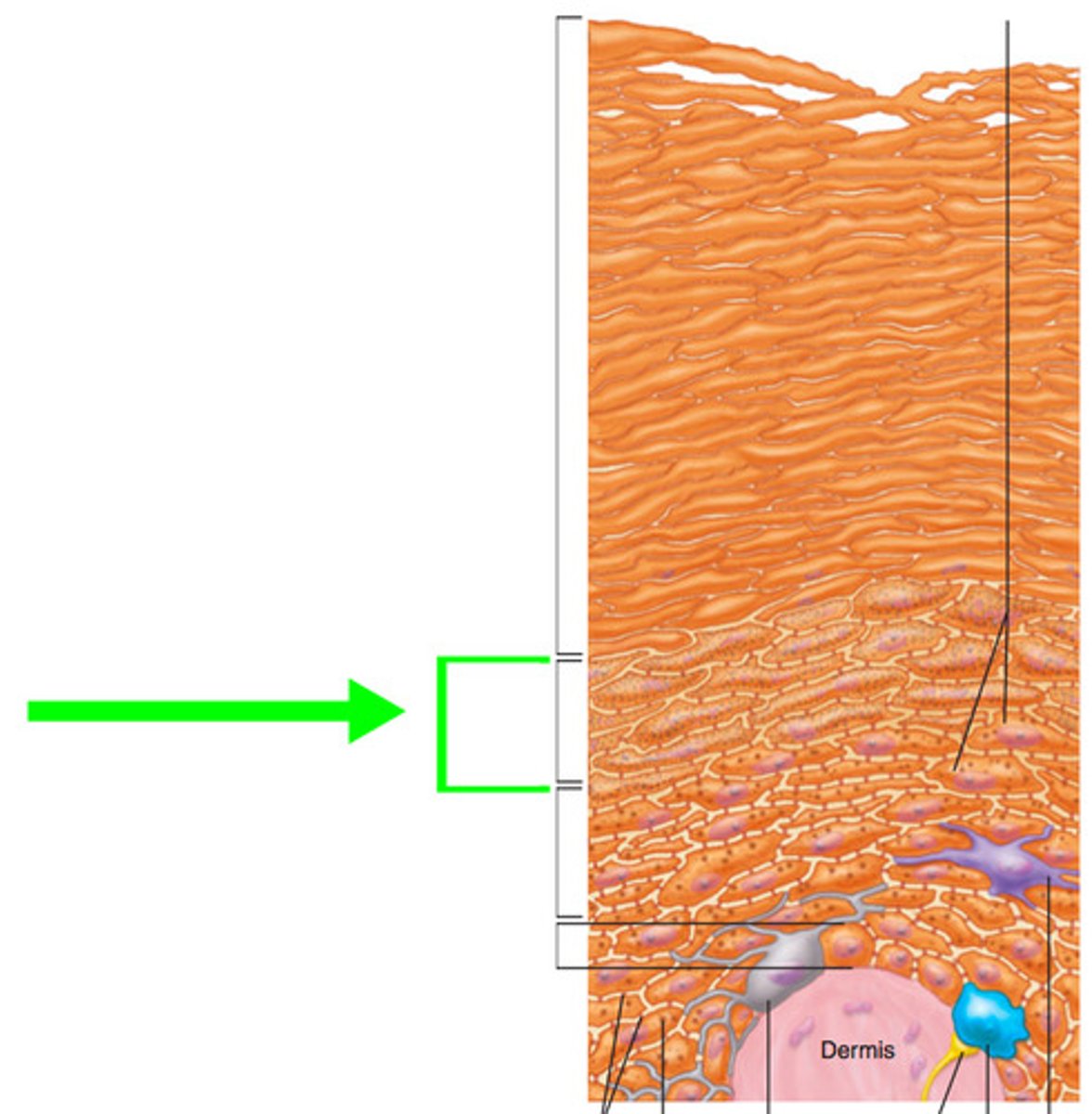
Epidermis
Superficial layer of the skin. Composed of keratinized, stratified squamos epithelium. Provides a thick, water-proof, protective covering over the underlying layers of the skin.
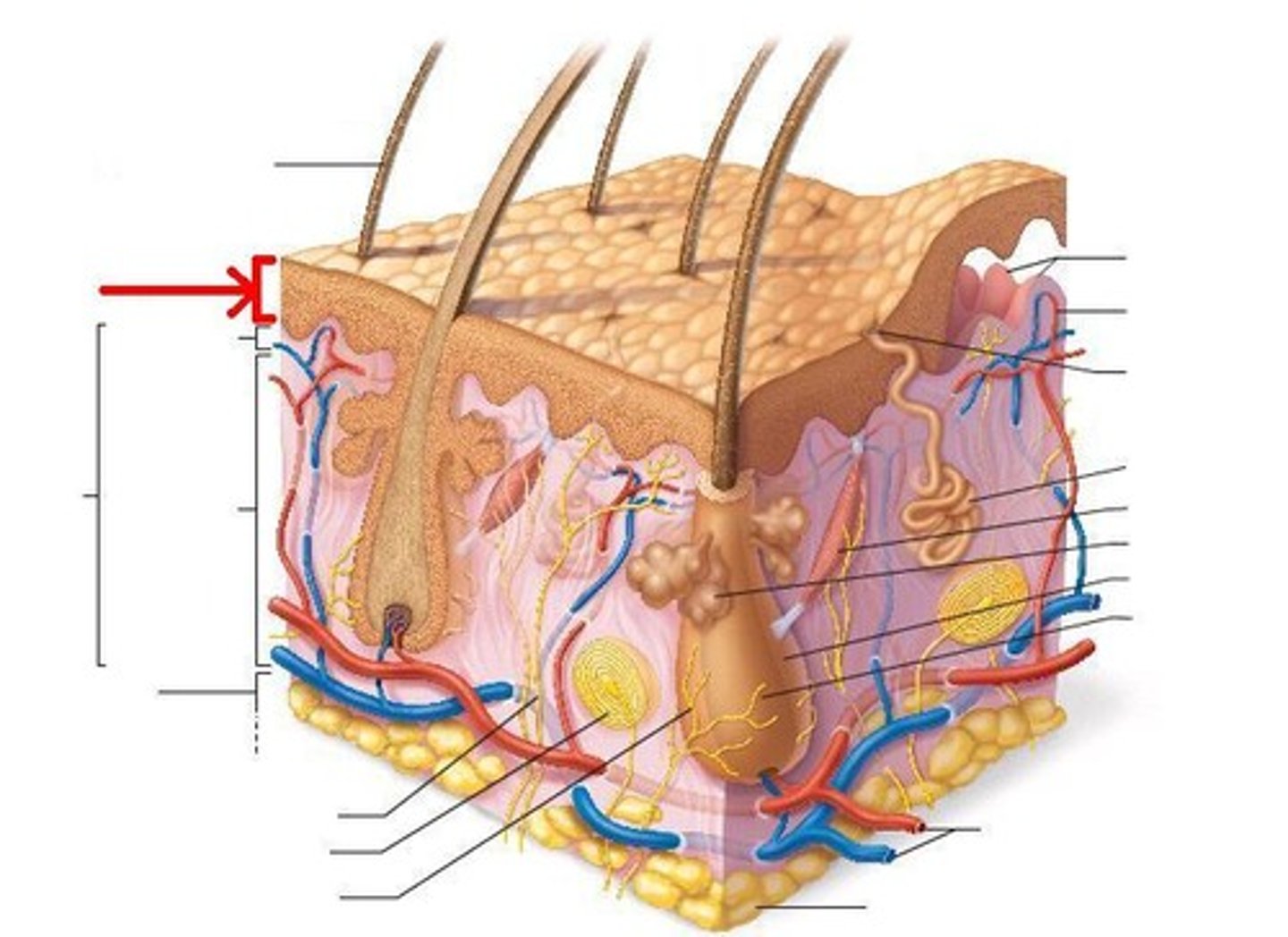
Dermis
Composed of connective tissue. Contains blood vessels, nerve endings, and epidermally derived cutaneous organs such as sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and hair follicles
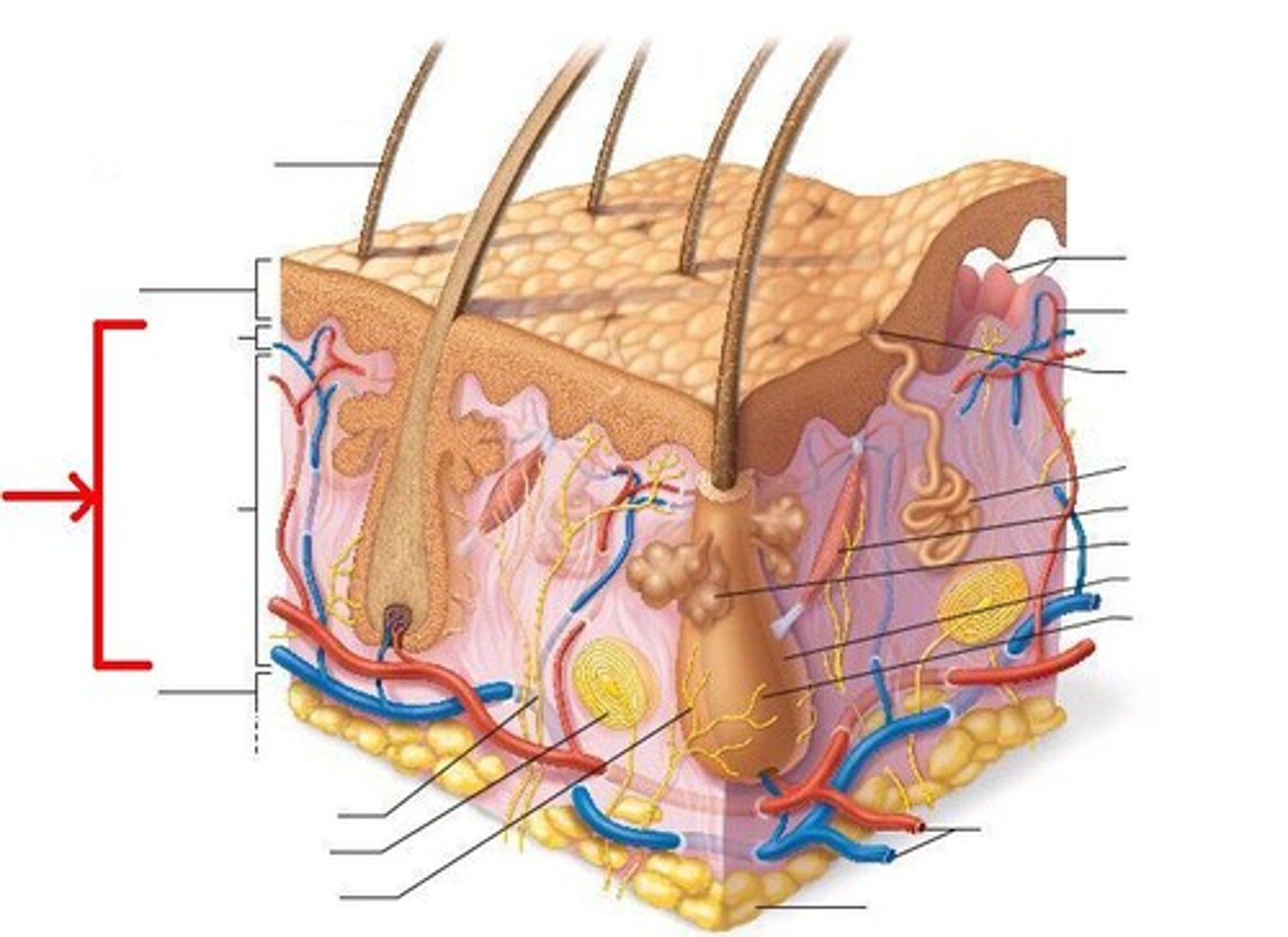
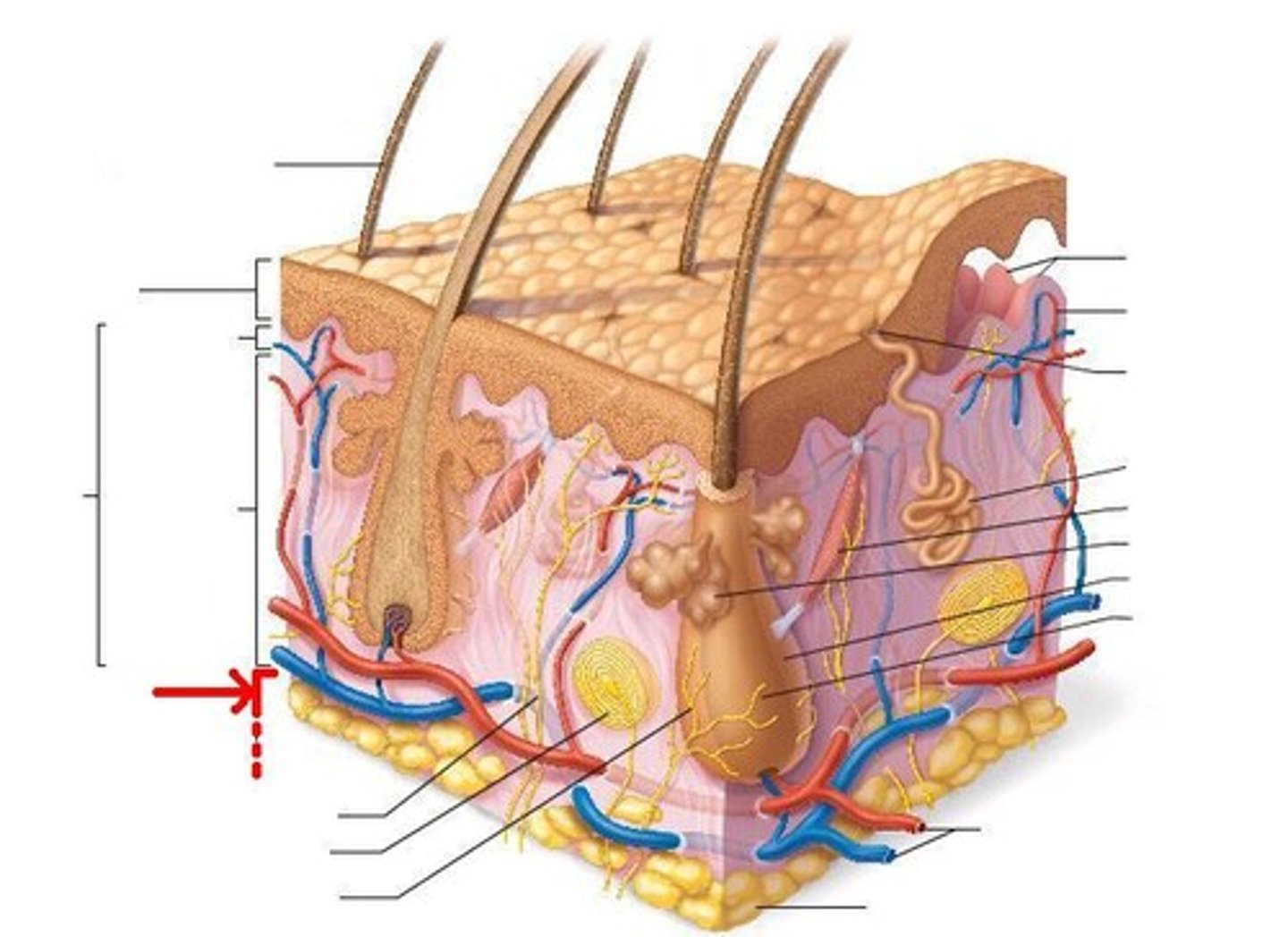
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer)
Composed of adipose and aerolar connective tissue. The fat layer provides mechanical cushioning and a thermal insulation layer for underlying organs
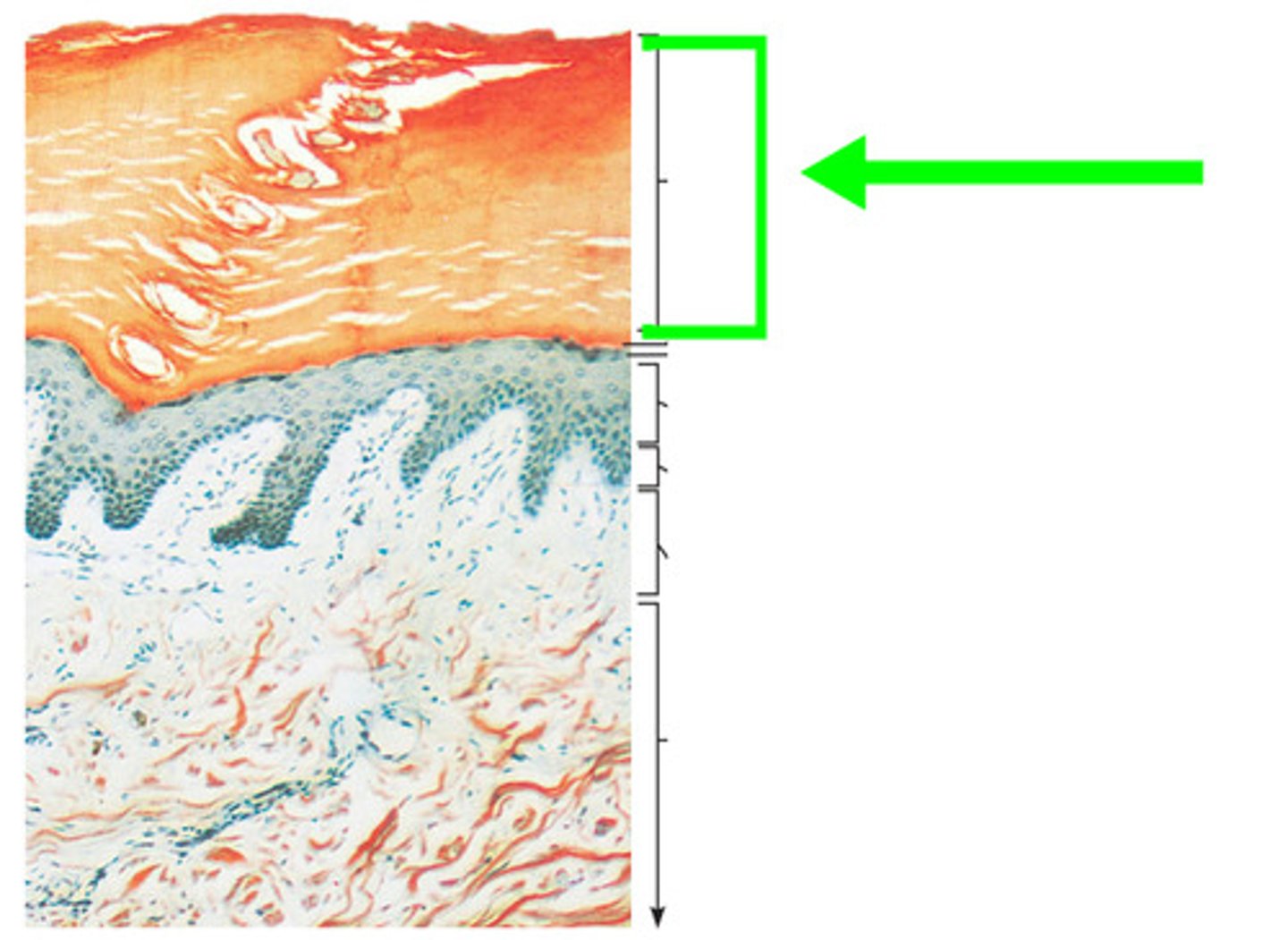
Stratum Corneum
The layer of skin that contains cells whose cytoplasm is filled with keratin, superficial layer of epidermis
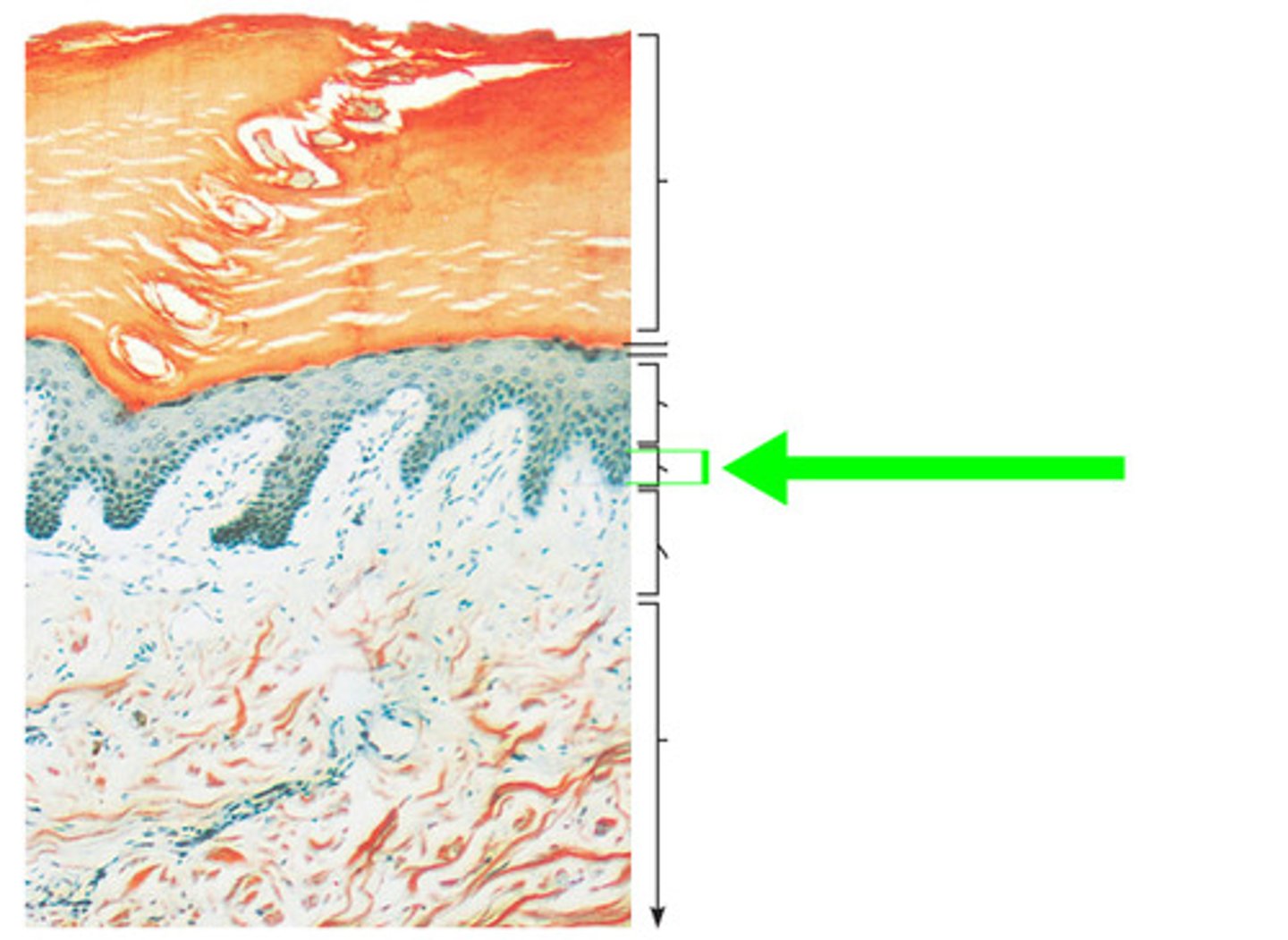
Stratum Lucidum
a thin, clear layer of dead skin cells in the epidermis named for its translucent appearance under a microscope found in thick skin
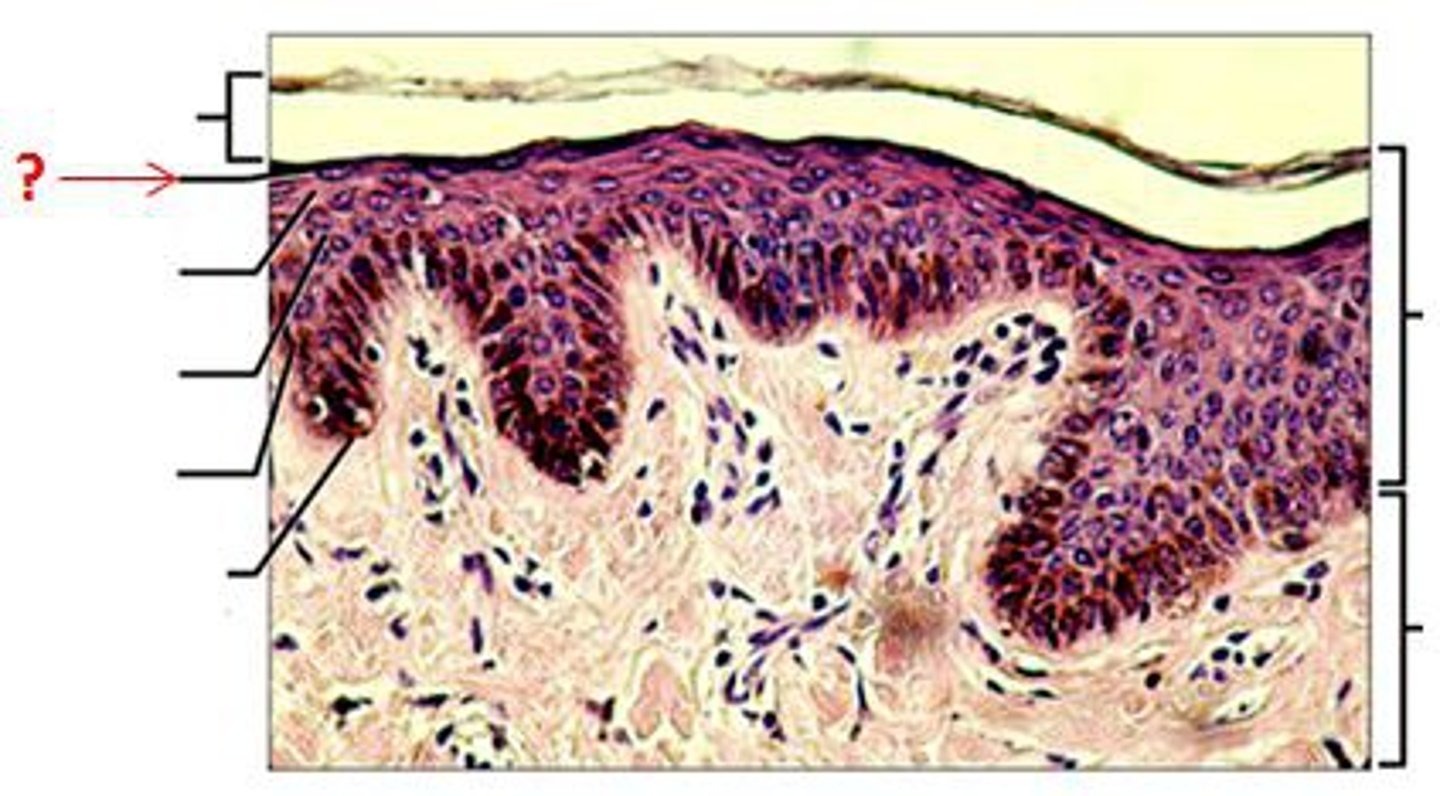
Stratum Granulosum
is a thin layer of cells in the epidermis. Keratinocytes migrating from the underlying stratum spinosum become known as granular cells in this layer.
Stratum Spinosum
is a layer of the epidermis found between the stratum granulosum and stratum basale. Held together by desmosomes
Mucous membranes are located in the
lining of cavities and tubes that have openings to the outside
Function of synovial membranes
to secrete a fluid that reduces friction
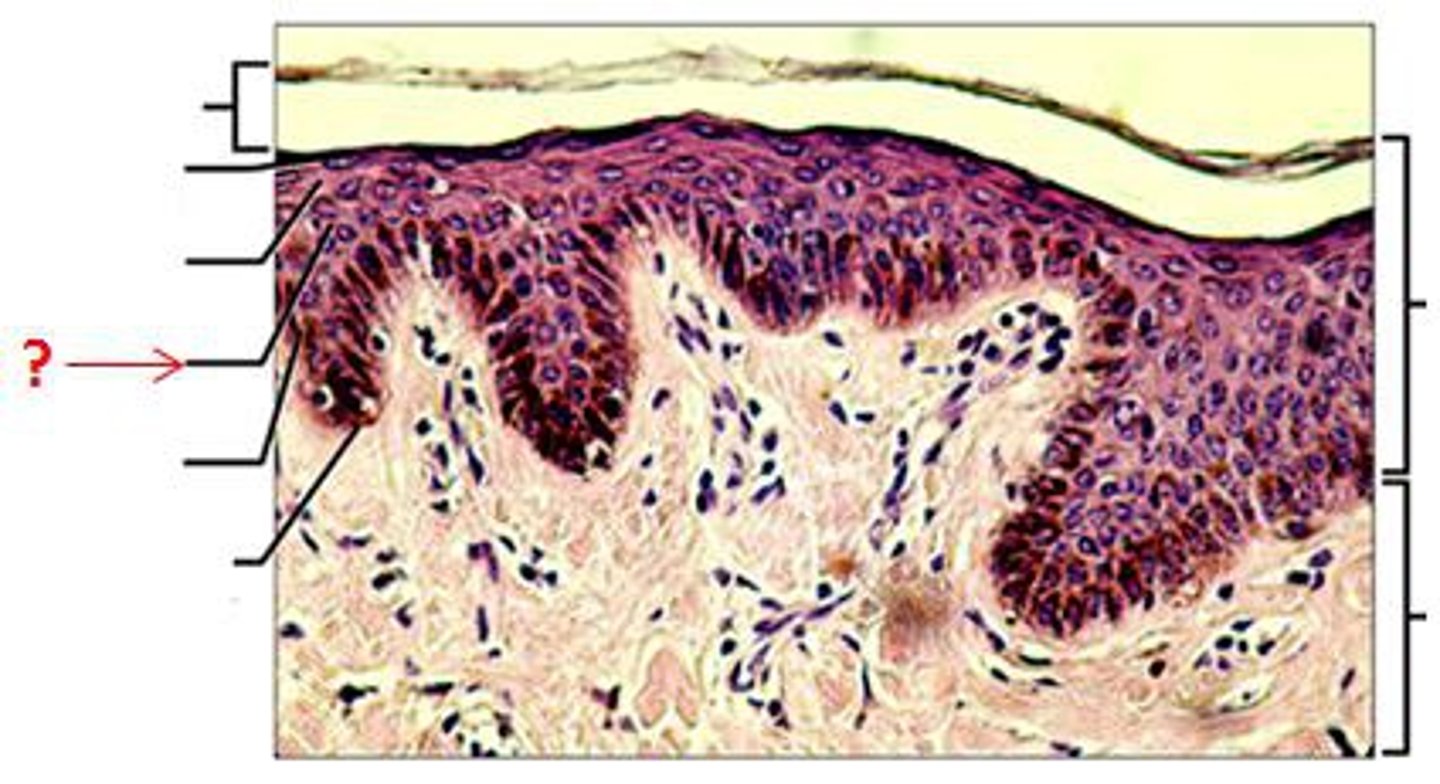
Stratum Basale
The cells of the skin reproduce here, basement of the epidermis
Functions of skin
regulate temperature, form a protective covering for underlying structures, sensory structure, ets
Melanocytes
The cell that produces melanin. Found in the deeper layer of skin
Melanin
The pigment that helps protect the deepest layers of the epidermis and the dermis
Vitamin D
The vitamin produced by the skin
Accessory organs of the skin
Sweat glands, finger and toe nails, and sebaceous glands
Pigments responsible for hair color
Trichosiderin, melanin, and carotene
What type of glands are sebaceous glands?
Glands that are associated with blackheads and may be connected to hair follicles
Lunula
The growing portion of the nail
Where are apocrine sweat glands most numerous?
The palm and soles
What sets occur in wound healing
inflammation, scab formation, scarring
Location of serous membrane
lining of internal areas like the intestines
Cutaneous Membrane
aka the skin
Location of basement membrane
Lies between the epidermis and the dermis
What determines skin color?
Genetic determination of melanin distribution
Why do goose bumps happen?
arrector pili muscles contract
Mucous Membrane
Secretes mucus
Describe a First Degree Burn
Burns in which the damaged areas are the epidermis only. Causes redness, swelling, and pain.
Describe a Second Degree Burn
Burns that damages the epidermis and the upper layer of the dermis. Causes blistering of skin and takes longer to heal
Describe a Third Degree Burn
The most severe of all, damages epidermis, dermis, and often the subcutaneous layer.
Hypothalamus
Main sensory receptor that detects temperature
Vasodialation
Pores that either shrink or enlarges depending on temperature (Heat=large, Cold=small)
Integumentary System Functions (x7)
Protection
Temperature control
Limit dehydration
House sensory organs
Excrete waste
Synthesize vitamin D
Blood reservoir
Eccrine sweat gland properties (x4)
Most numerous
Secretes water
Regulates temperature
Tactile sensitivity
Apocrine sweat gland properties (x3)
Body odor
Comes during stress or sexual stimulation
In the axillary, navel, genital and nipple areas
Mammary gland property
milk
Ceruminous gland property
earwax
1st Degree Burn (other name, layers, symptoms, first aid)
Other name: superficial
layers: epidermis
symptoms