mechanics and materials ^0^
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is the difference between mass and weight?
mass is the amount of matter in an object, weight is the measure of the pull of gravity on an object
what is the principle of moments?
For an object in rotational equilibrium the sum of the clockwise moments about any point is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments about that point.
what does it mean if an object is in equilibrium?
It is at rest or moving with constant velocity
what is a moment?
The turning effect of a force
what is meant by a couple?
A pair of equal and opposite coplanar forces that have equal magnitude and opposite direction, applied to a body parallel to each other but not along the same line.
what is meant by centre of mass?
The point through which all the mass of an object acts, for a uniform object the centre of mass is the centre of the object
How do the SUVAT equations reflect that all objects fall at the same rate?
mass is not included showing that mass of an object does not effect its speed or acceleration
in projectile motion what is the vertical acceleration?
gravitational field strength
what is meant by terminal velocity?
When the forces acting on the falling object become balanced, the acceleration becomes zero and the object is moving at maximum velocity.
what is meant by friction?
A resistance to motion between an object and a surface or an object moving through a fluid. Friction is a force that acts in the opposite direction to the movement.
what is newtons 3rd law?
for every force there is an equal and opposite force
What is Newton's second law?
Force = mass x acceleration
What is Newton's first law?
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
what is the difference between elastic and inelastic collisions?
in elastic the kinetic energy is equal to the kinetic energy afterwards. in inelastic it isnt.
calculation for momentum?
momentum = mass x velocity
what is impulse?
Impulse is the change in momentum
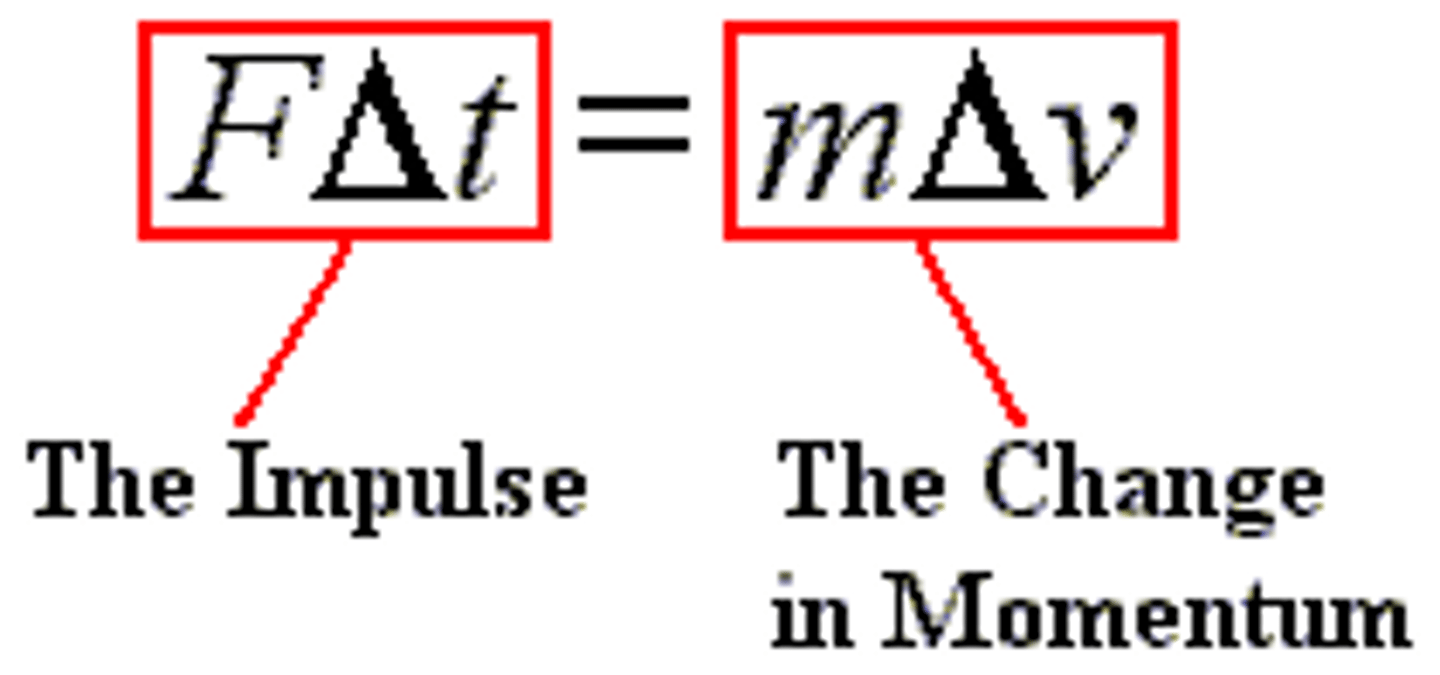
What is the conservation of energy?
a principle stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be altered from one form to another.
what is lift?
force acting on a body in a fluid in a direction perpendicular to the fluid flow
What is Hooke's Law?
When a spring stretches, the extension of the spring is proportional to the force stretching it, provided the elastic limit of the spring is not exceeded.
what is tensile stress?
The force applied per unit cross sectional area.
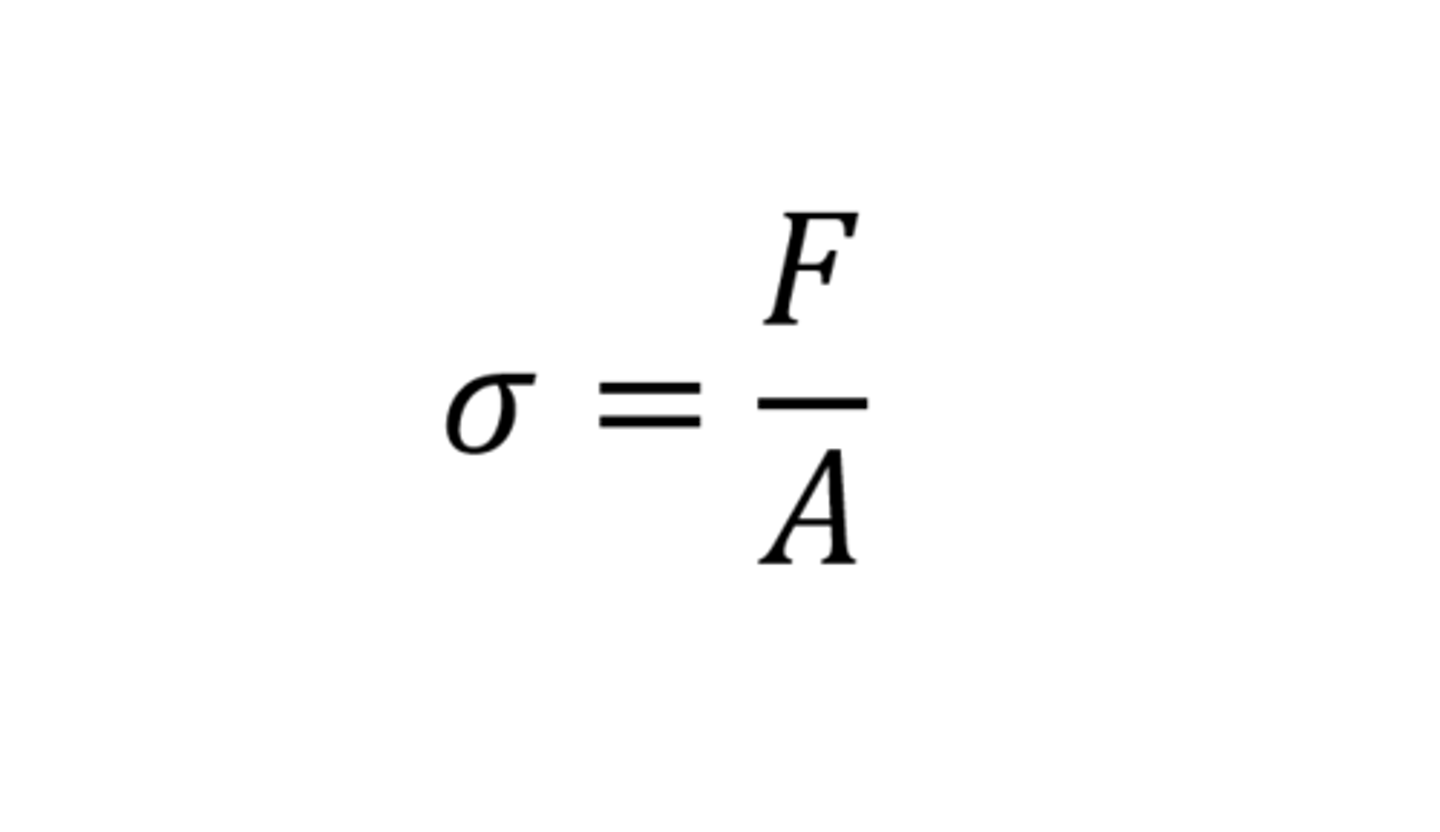
what is tensile strain?
A measure of how the material stretches: the extension divided by the original length. This value is a ratio, so it has no units.
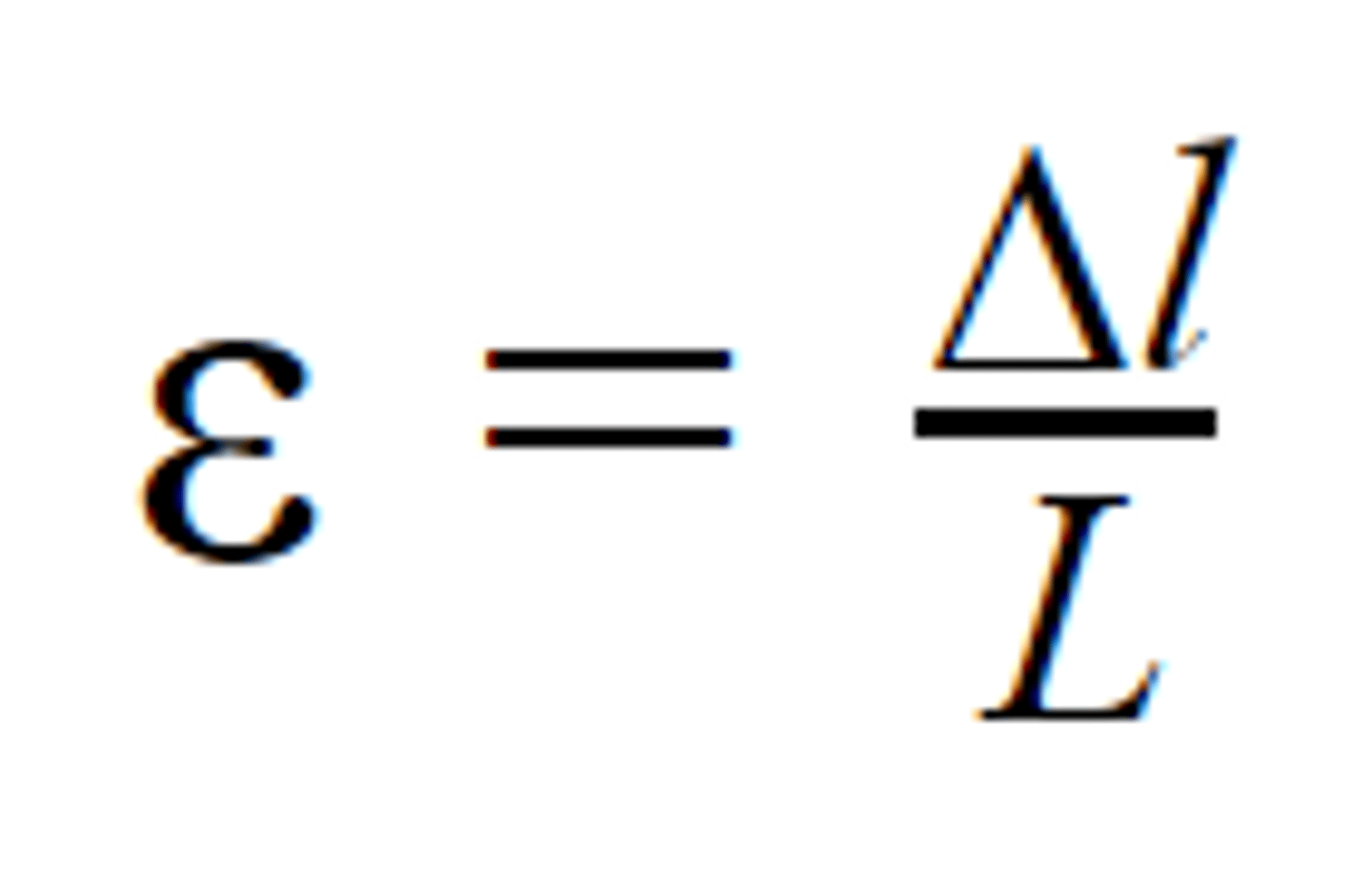
what is the difference between elastic and plastic deformation?
elastic - when the object returns to its original form after the load is removed.
plastic - object doesnt return to its original shape.
What is breaking stress?
The minimum stress needed to break a material.
what is meant by brittle?
it doesnt deform plastically but breaks when it reaches a certain point.
what is the elastic limit?
The point where an object stops distorting elastically and begins to distort inelastically
What is Young's modulus?
A measure of stiffness/ how difficult it is to change the shape of a material
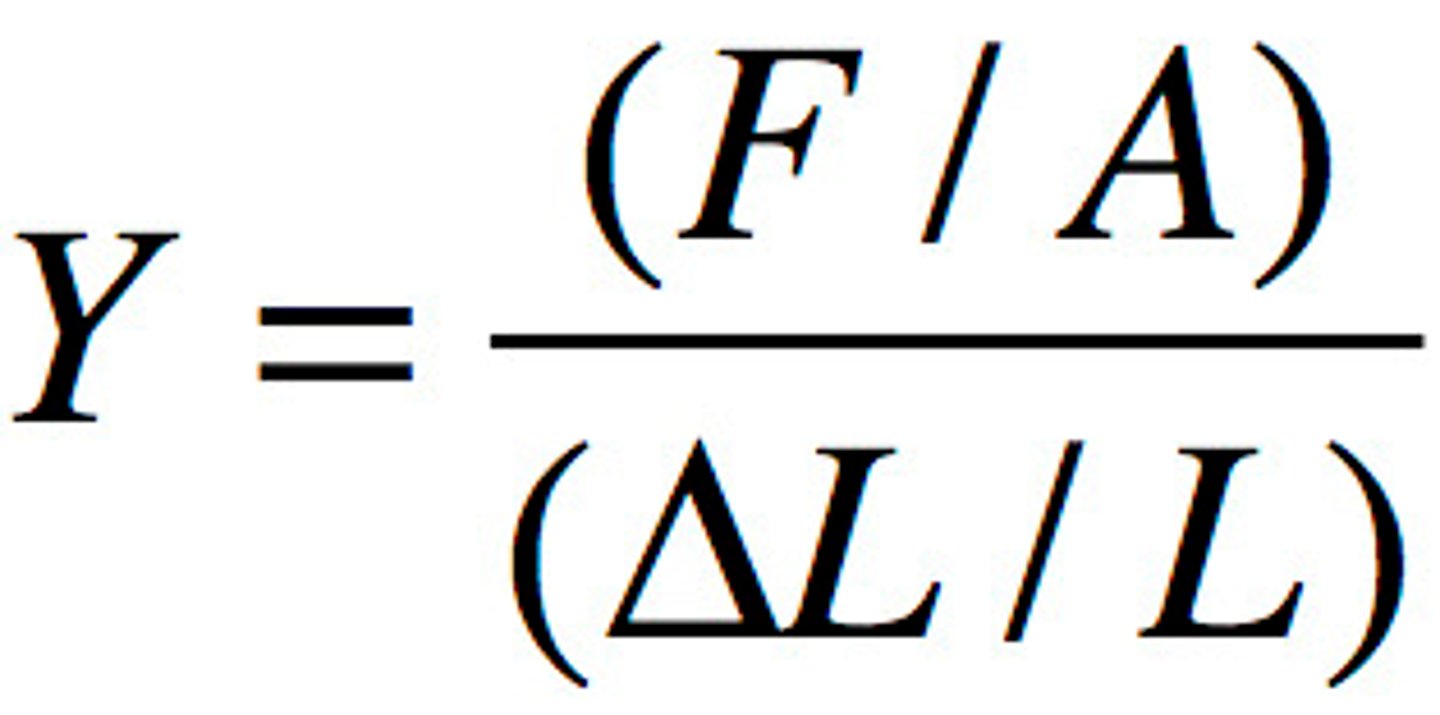
Why are the loading and unloading lines parallel on a force-extension graph for a plastically deformed material?
the stiffness constant hasnt changed. the forces between the atoms are the same when loading and unloading
why isnt work done stored as plastic strain energy when stretch is plastic?
work done to move atoms apart so energy is not stored as elastic strain energy but dissipated as heat.
How is the dissipation of energy in plastic deformation used to design safer vehicles?
crumple zones deform plastically in a crash so less energy and force is transferred to the passenger
seat belts to decrease to force acting on the passenger.