mastering biology chapters 6 & 7
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Last updated 5:12 PM on 2/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
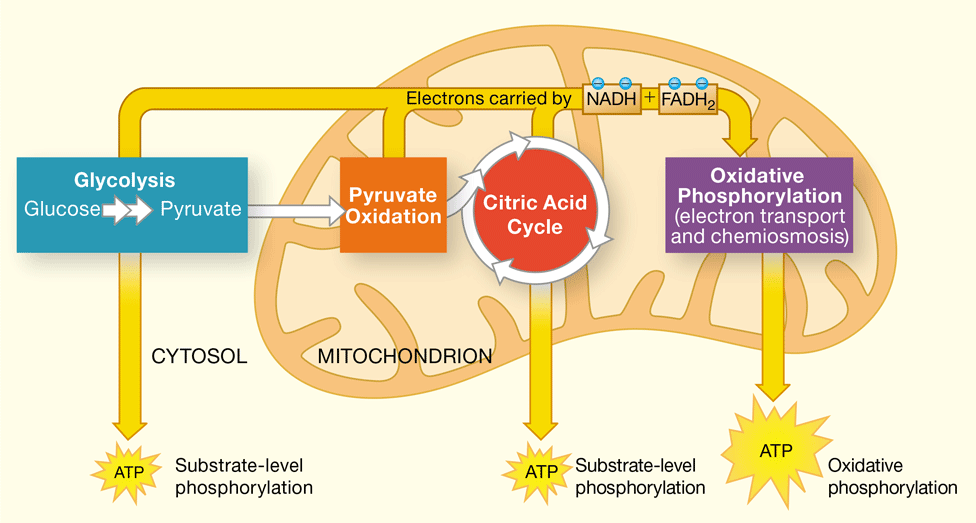
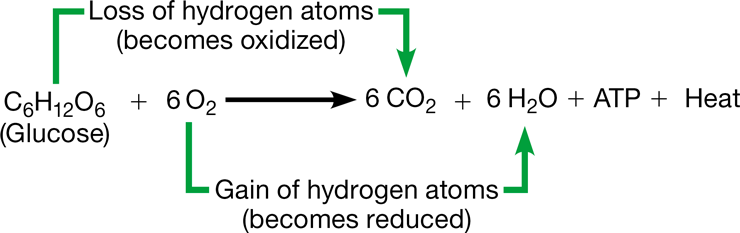
cellular respiration
* C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP
* Exergonic process in which 34% of the energy in glucose is captured in ATP
* Glucose oxidizes to CO2 by losing H+
* Oxygen reduces to H2O by gaining H+
* O2 is consumed as organic molecules are broken down to CO2 & H2O
* Exergonic process in which 34% of the energy in glucose is captured in ATP
* Glucose oxidizes to CO2 by losing H+
* Oxygen reduces to H2O by gaining H+
* O2 is consumed as organic molecules are broken down to CO2 & H2O
2
New cards
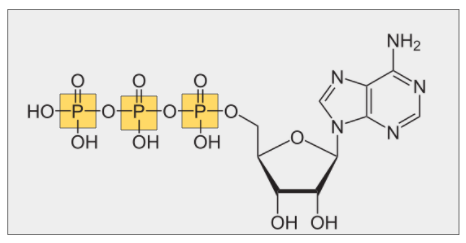
ATP
* Main energy source for cells
* Releases energy when its phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed
* Contains 2 phosphoanhydride (high-energy) bonds
* Releases energy when its phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed
* Contains 2 phosphoanhydride (high-energy) bonds
3
New cards
respiration
* Exchange of gases
4
New cards
redox reaction (oxidation-reduction reaction)
* Transfer of electrons from one molecule to another
* In cellular respiration, electrons are transferred from organic fuels (glucose) to oxygen, releasing energy
* In cellular respiration, electrons are transferred from organic fuels (glucose) to oxygen, releasing energy
5
New cards
oxidation
* Loss of electrons from a substance
* In cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to CO2 as it loses H+
* In cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to CO2 as it loses H+
6
New cards
reduction
* Gain of electrons by a substance
* In cellular respiration, O2 is reduced to H2O as it gains H+
* In cellular respiration, O2 is reduced to H2O as it gains H+
7
New cards
NAD+
* Organic molecule used to shuttle electrons in redox reactions
* Reduced to NADH after it accepts 2 electrons
* Reduced to NADH after it accepts 2 electrons
8
New cards
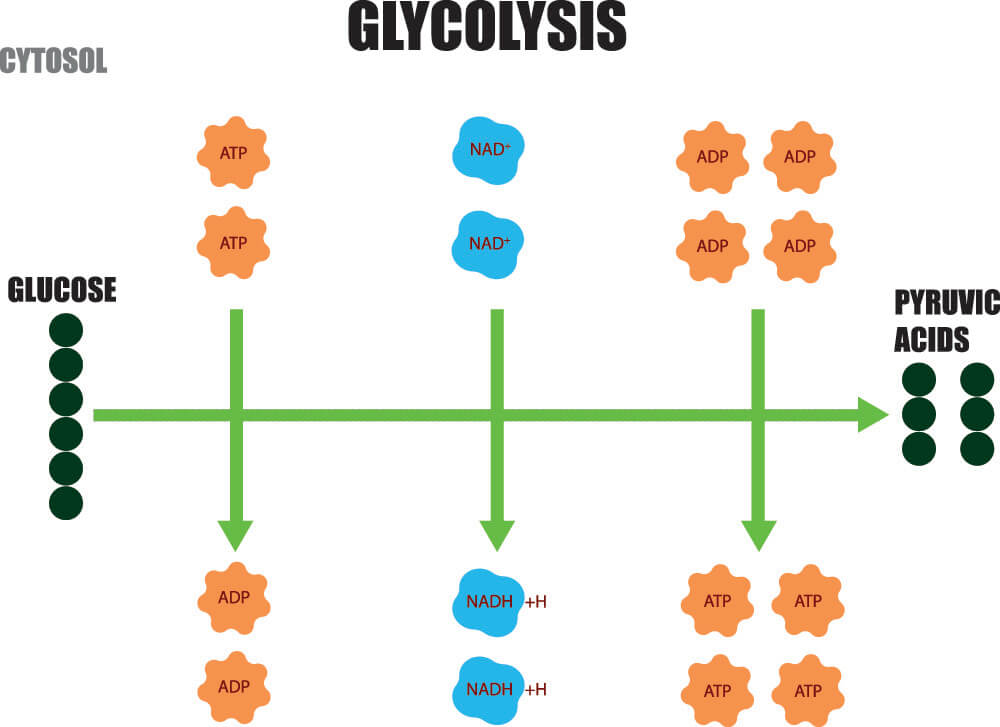
glycolysis
\
* Glucose is oxidized into 2 molecules of pyruvate, using 2 ATP
* 2 molecules of NAD+ are reduced to 2 NADH, producing 4 ATP (net gain of 2 ATP)
* Occurs in the cytoplasm, not requiring any oxygen
* Glucose is oxidized into 2 molecules of pyruvate, using 2 ATP
* 2 molecules of NAD+ are reduced to 2 NADH, producing 4 ATP (net gain of 2 ATP)
* Occurs in the cytoplasm, not requiring any oxygen
9
New cards
substrate-level phosphorylation
Formation of ATP by an enzyme directly transferring a phosphate group from a substrate (organic molecule) to ADP
\
\
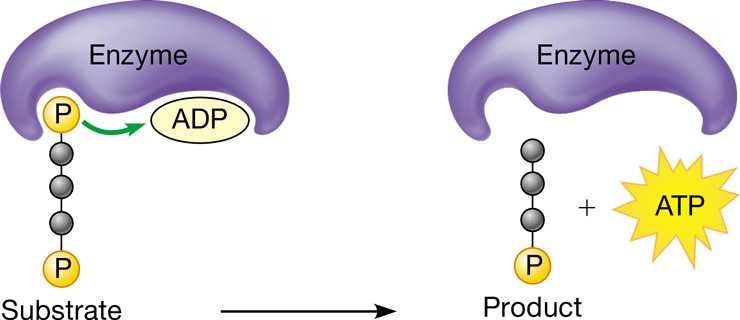
10
New cards
intermediate
* Compound that forms between the initial reactant & the final product in a metabolic pathway
11
New cards
pyruvate oxidation
* Carboxyl group is removed from pyruvate, releasing CO2
* Remaining 2C molecule is oxidized, reducing NAD+ to NADH
* Oxidized 2C molecule (acetyl group) is attached to CoA, forming acetyl CoA
* Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
* Remaining 2C molecule is oxidized, reducing NAD+ to NADH
* Oxidized 2C molecule (acetyl group) is attached to CoA, forming acetyl CoA
* Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
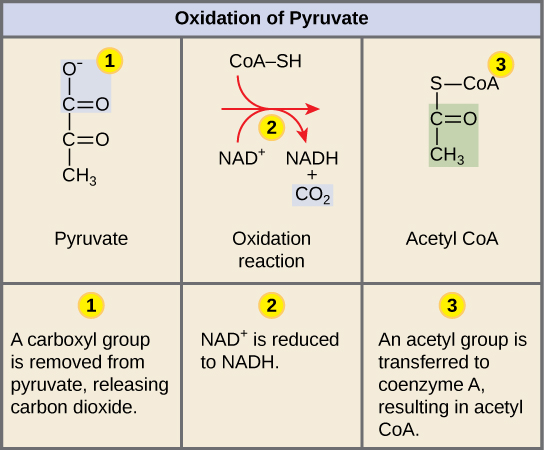
12
New cards
acetyl CoA
* Entry compound for the citric acid cycle
* Formed from a 2C fragment of pyruvate attached to a coenzyme
* Formed from a 2C fragment of pyruvate attached to a coenzyme
13
New cards
citric acid cycle
* Acetyl CoA is attached to a 4C oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate, releasing the CoA group
* Oxidation of isocitrate & a-ketoglutarate __releases CO2 & reduces NAD+ to NADH__
* __3 ATP__ are formed after 3P are transferred to 3 ADP
* Oxidation of succinate __reduces FAD to FADH2__
* Oxaloacetate is regenerated by the oxidation of malate, __reducing NAD+ to NADH__
* Oxidation of isocitrate & a-ketoglutarate __releases CO2 & reduces NAD+ to NADH__
* __3 ATP__ are formed after 3P are transferred to 3 ADP
* Oxidation of succinate __reduces FAD to FADH2__
* Oxaloacetate is regenerated by the oxidation of malate, __reducing NAD+ to NADH__
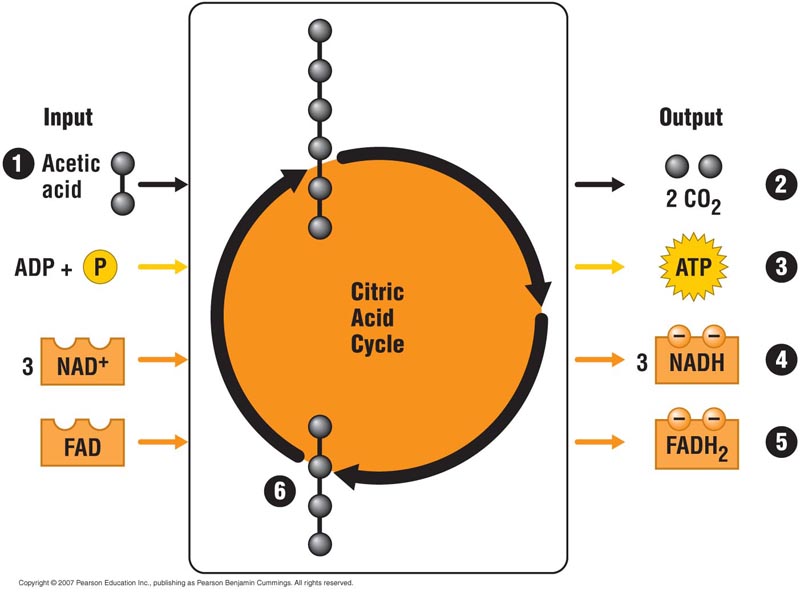
14
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
* Involves the electron transport chain (ETC) & chemiosmosis
* Nearly 90% of the ATP generated is made in this stage
* Nearly 90% of the ATP generated is made in this stage
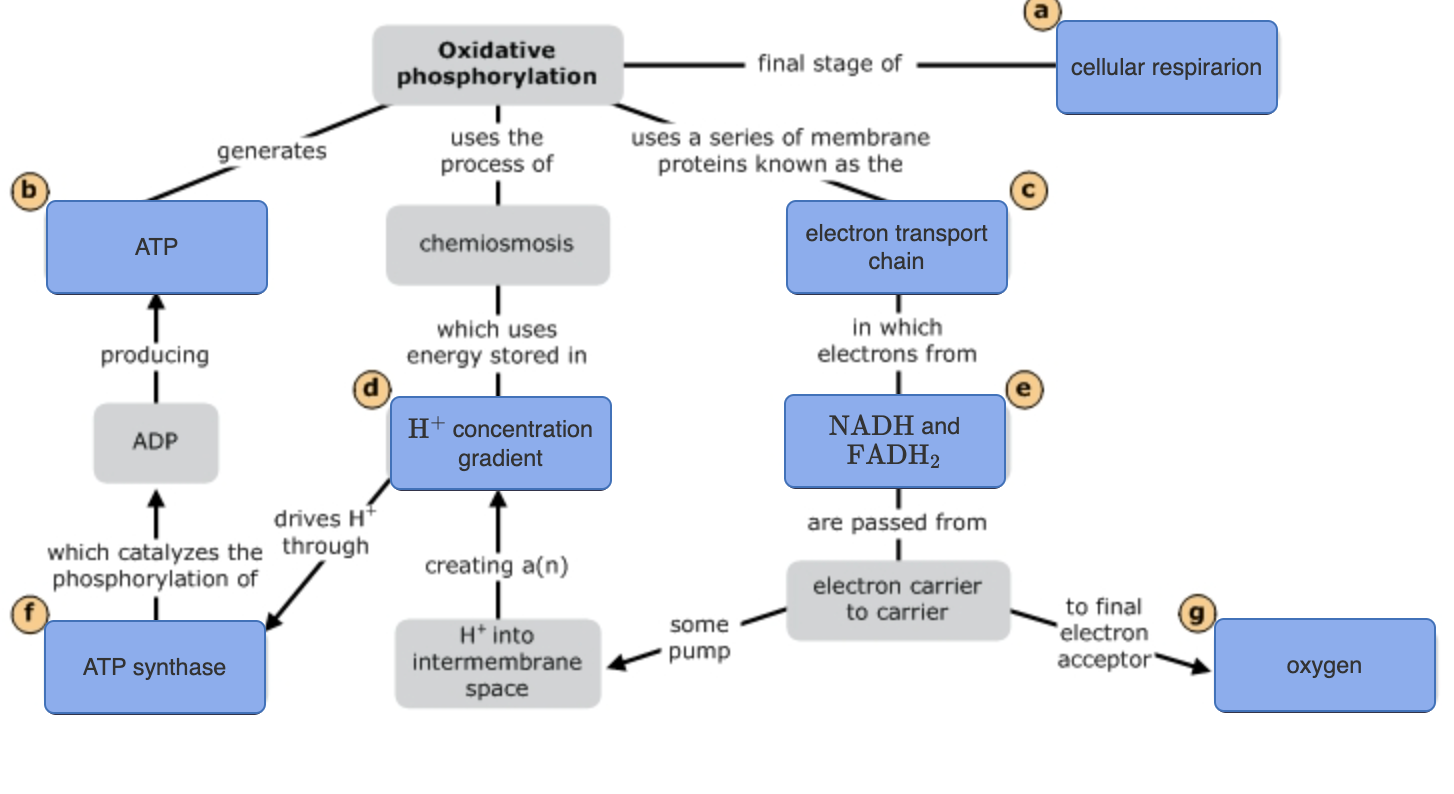
15
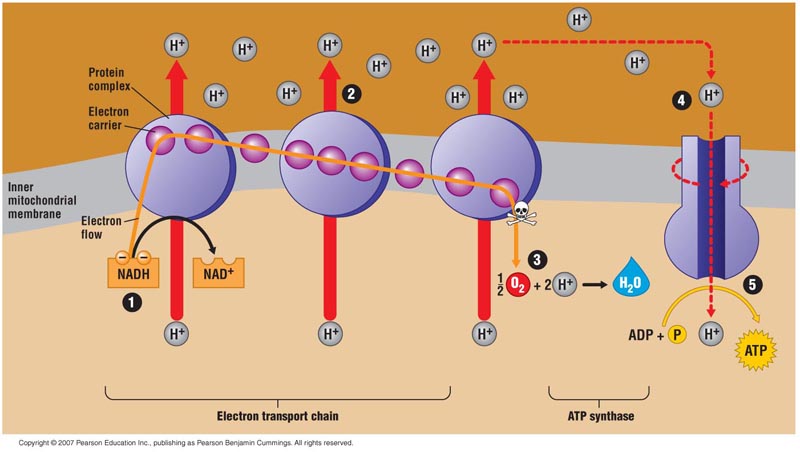
New cards
electron transport chain (ETC)
* Series of electron carrier molecules that shuttle electrons during redox reactions, releasing energy used to make an electrochemical gradient
* NADH & FADH2 shuttle electrons to the ETC, regenerating into NAD+ & FAD+
* Electron carriers pass electrons down the staircase to O, the final electron acceptor, forming H2O as it takes up H+
* Most of the ATP produced by cellular respiration is generated by this process
* Located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria
* NADH & FADH2 shuttle electrons to the ETC, regenerating into NAD+ & FAD+
* Electron carriers pass electrons down the staircase to O, the final electron acceptor, forming H2O as it takes up H+
* Most of the ATP produced by cellular respiration is generated by this process
* Located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria
16
New cards
chemiosmosis
* Uses the energy released from the ETC to pump H+ into the intermembrane space
* H+ flows through ATP synthase back into the matrix, harnessing the flow to synthesize ATP
* Powers most ATP synthesis in cells
* Energy of the H+ concentration gradient is used to make roughly 28 ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
* H+ flows through ATP synthase back into the matrix, harnessing the flow to synthesize ATP
* Powers most ATP synthesis in cells
* Energy of the H+ concentration gradient is used to make roughly 28 ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
17
New cards
ATP synthase
* Enzyme that functions in chemiosmosis with adjacent ETC’s
* Uses the energy of the H+ concentration gradient to synthesize ATP
* Uses the energy of the H+ concentration gradient to synthesize ATP
18
New cards
fermentation
* Anaerobic harvesting of energy from glucose
* Nets 2 ATP by taking advantage of glycolysis
* Provides an anaerobic path for oxidizing NADH to NAD+
* Nets 2 ATP by taking advantage of glycolysis
* Provides an anaerobic path for oxidizing NADH to NAD+
19
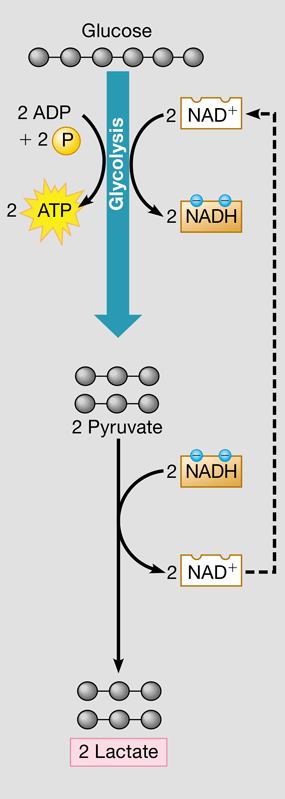
New cards
lactic acid fermentation
* Glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate into lactate
* Regenerates NAD+ for glycolysis
* Muscle cells can switch to lactic acid fermentation when the need for ATP exceeds the delivery of O2
* Used to make cheese & yogurt by bacteria
* Regenerates NAD+ for glycolysis
* Muscle cells can switch to lactic acid fermentation when the need for ATP exceeds the delivery of O2
* Used to make cheese & yogurt by bacteria
20
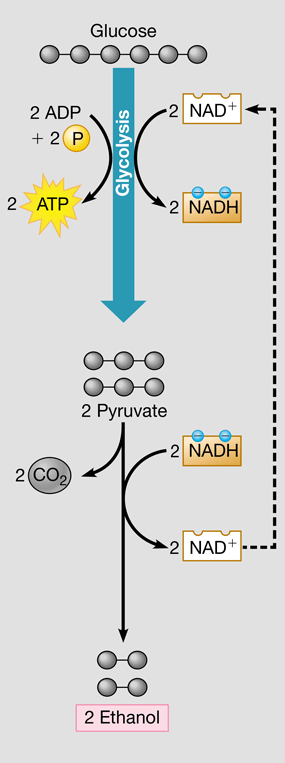
New cards
alcohol fermentation
* Glycolysis followed by the reduction of a derivative of pyruvate into ethanol
* Regenerates NAD+ & releases CO2
* Used by yeast cells to produce ethanol in alcoholic drinks
* Regenerates NAD+ & releases CO2
* Used by yeast cells to produce ethanol in alcoholic drinks
21
New cards
obligate anaerobe
* Organisms that are poisoned by oxygen, requiring anaerobic conditions
* I.e. stagnant ponds, deep soils
* I.e. stagnant ponds, deep soils
22
New cards
facultative anaerobe
* Organisms not poisoned by oxygen
* I.e. yeast & bacteria
* Can switch between aerobic respiration & anaerobic pathways
* I.e. yeast & bacteria
* Can switch between aerobic respiration & anaerobic pathways
23
New cards
biosynthesis
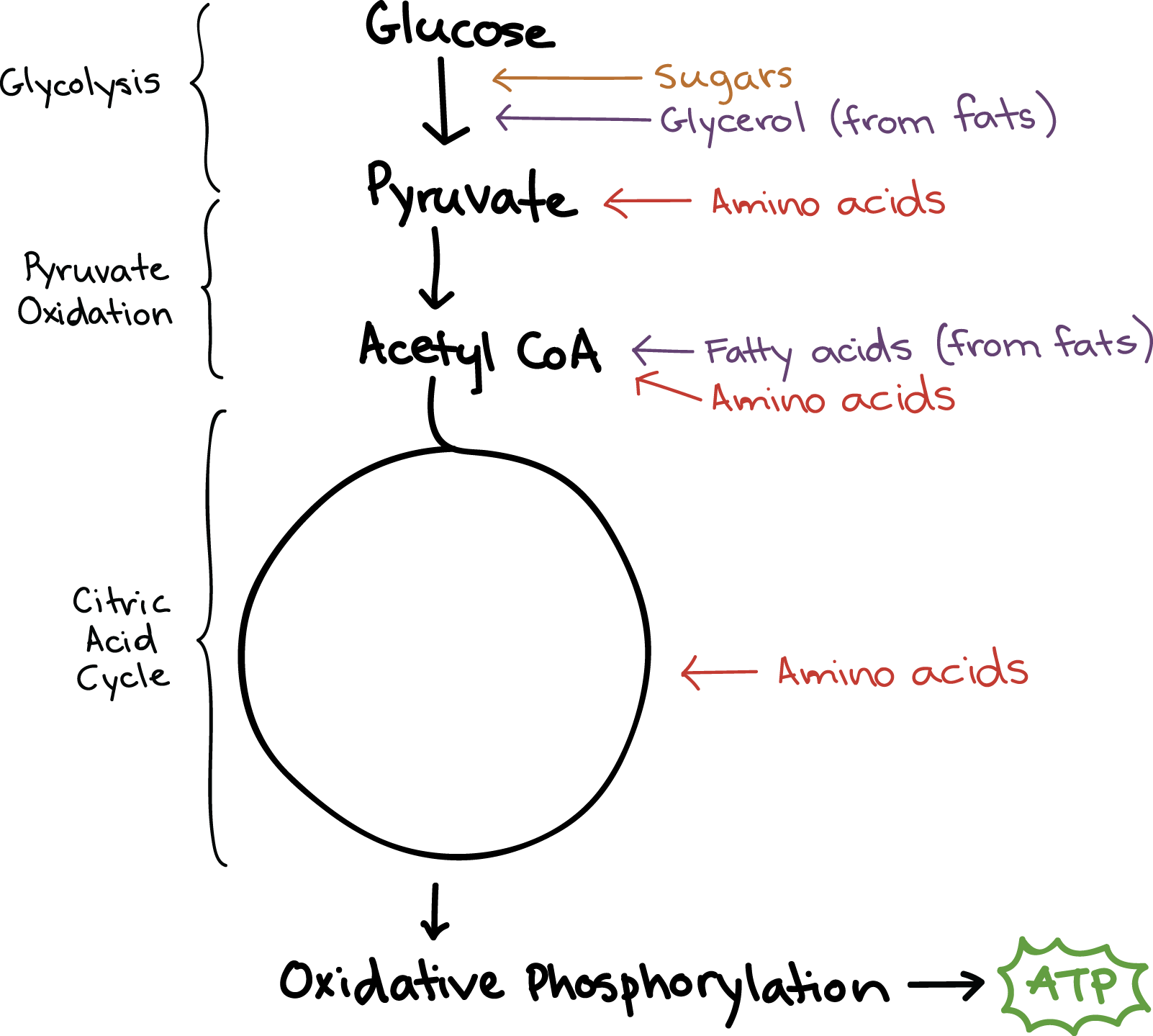
* Production of organic molecules using energy-requiring metabolic pathways
* Amino acids, lipids, & other carbohydrates can be converted into intermediates of glycolysis & citric acid cycle
* Amino acids, lipids, & other carbohydrates can be converted into intermediates of glycolysis & citric acid cycle
24
New cards
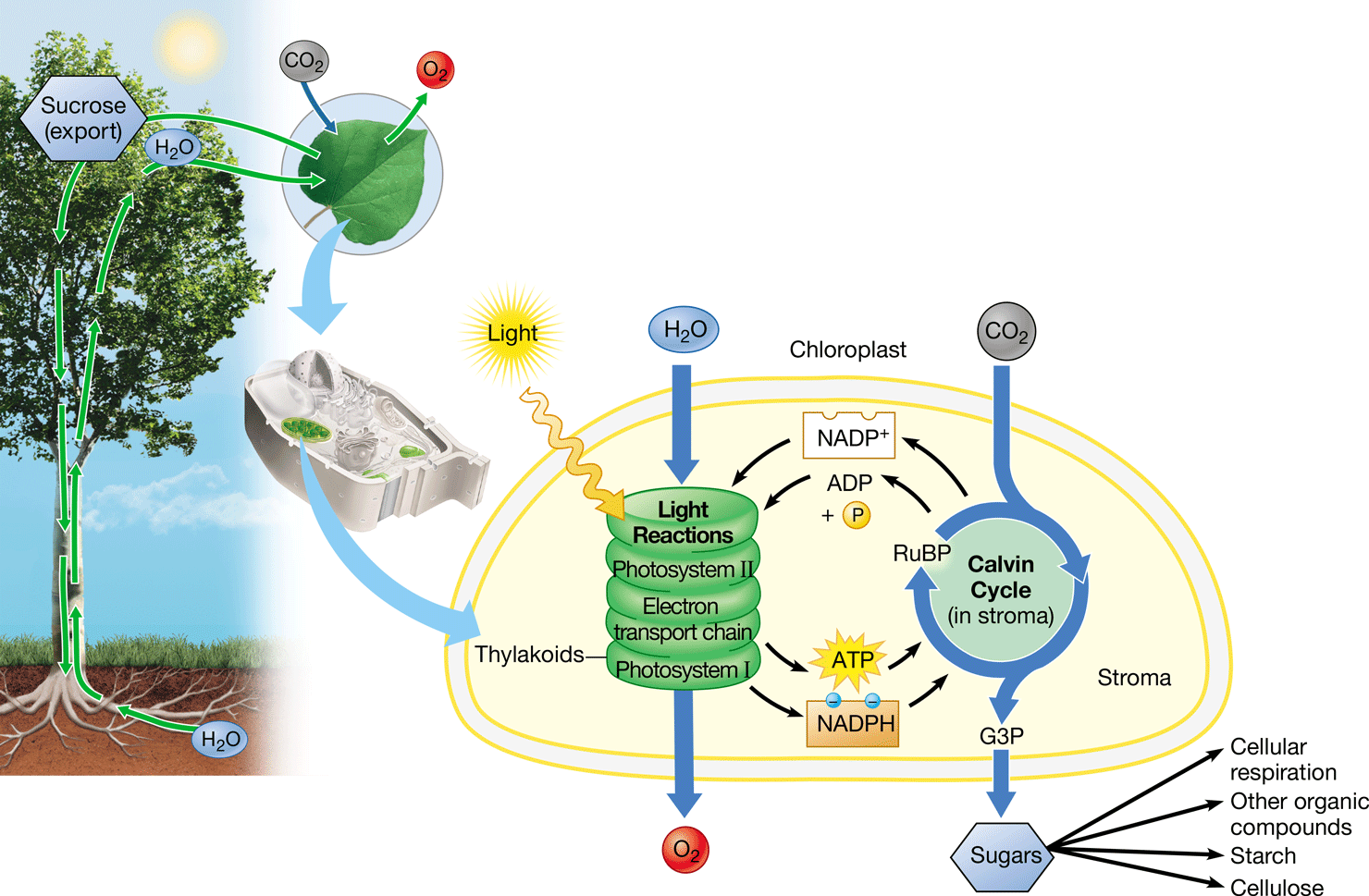
photosynthesis
* 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
* Process in which solar energy is used to convert CO2 & H2O into glucose & O2
* Occurs in the chloroplast of plants & algae & some protists & prokaryotes
* CO2 becomes reduced to glucose after H2O is oxidized
* Electrons are transferred along with H+
* Process in which solar energy is used to convert CO2 & H2O into glucose & O2
* Occurs in the chloroplast of plants & algae & some protists & prokaryotes
* CO2 becomes reduced to glucose after H2O is oxidized
* Electrons are transferred along with H+
25
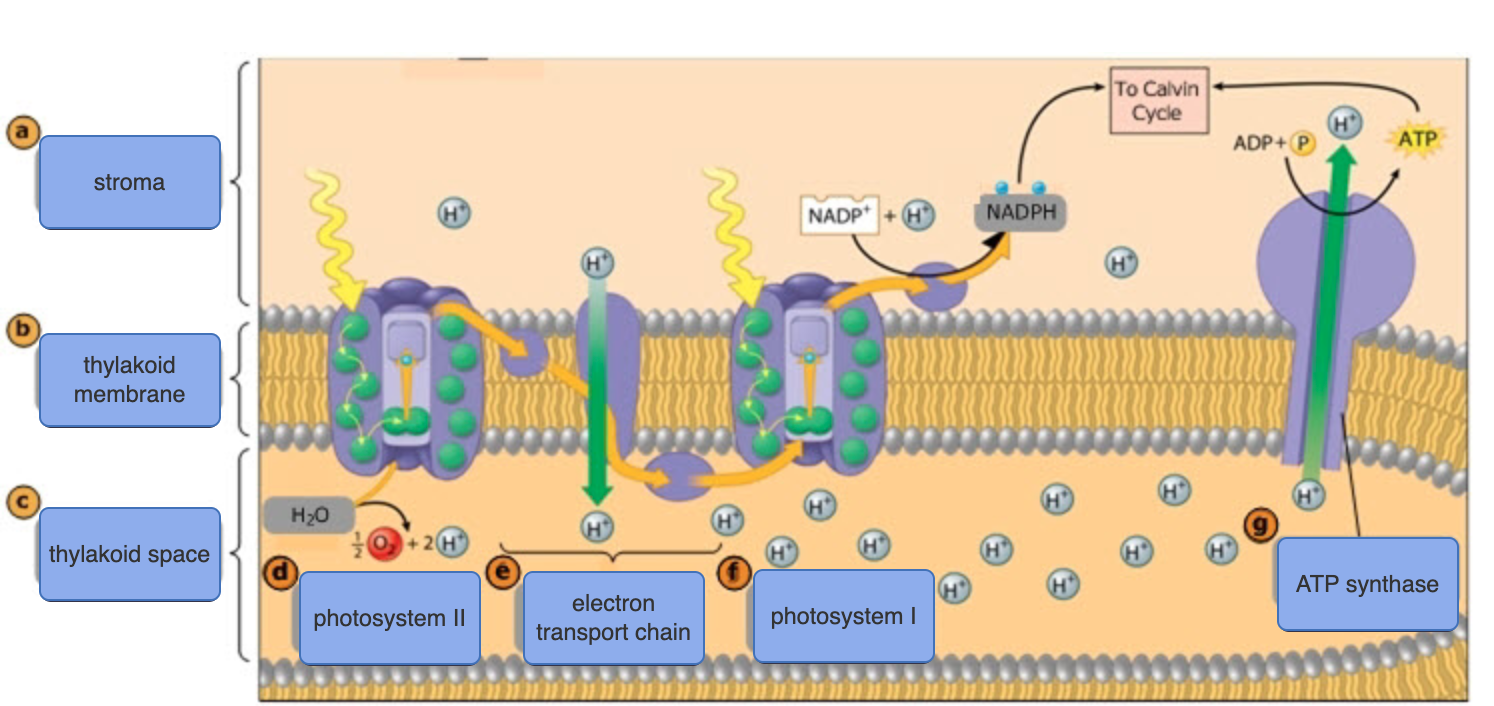
New cards
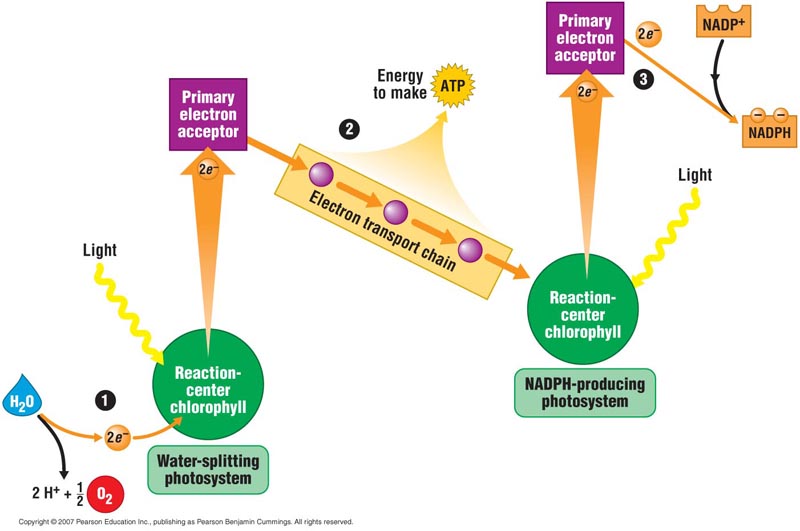
light reactions
* Process by which solar energy is absorbed & converted into the chemical energy of ATP & NADPH
* H2O is converted into O2
* Forms an electrochemical gradient to synthesize ATP
* Occurs in the thylakoids
* H2O is converted into O2
* Forms an electrochemical gradient to synthesize ATP
* Occurs in the thylakoids
26
New cards
NADP+
* Electron acceptor that, as NADPH, temporarily stores energized electrons produced during the light reactions
* Provides electrons for reducing C compounds in the Calvin cycle
* Provides electrons for reducing C compounds in the Calvin cycle
27
New cards
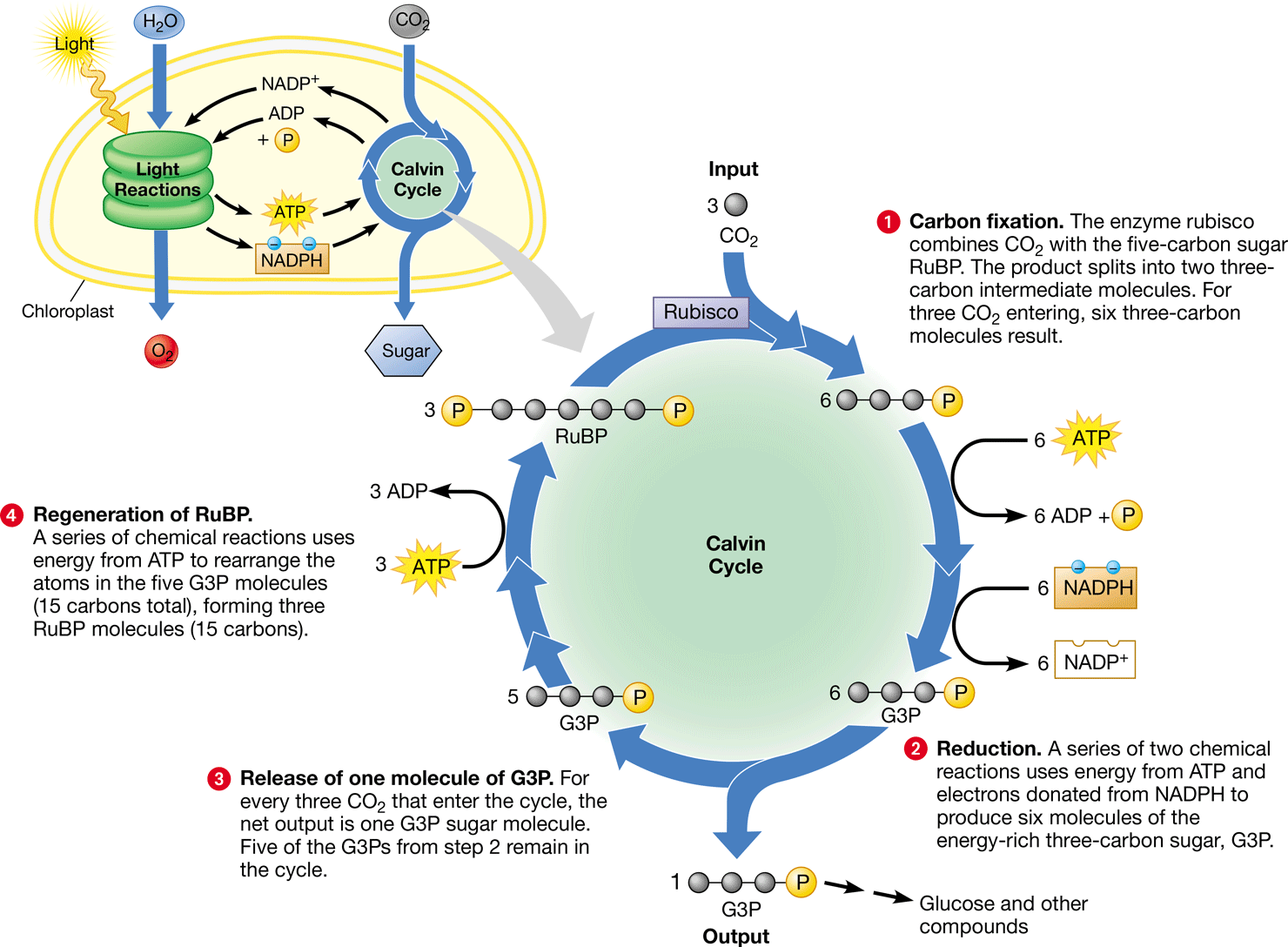
Calvin cycle
* In __carbon fixation__, rubisco combines 3CO2 with 3RuBP to form 6 3-PGA
* P from 6 ATP & electrons from 6 NADPH __reduce__ the 6 3-PGA into 6 G3P
* 1 G3P exits the cycle & can be used to make glucose for a net gain of 1 G3P for every 3 CO2
* During __regeneration__, 3 ATP are used to rearrange the remaining 5 G3P (15 C’s) into 3 RuBP (15 C’s)
* Occurs in the stroma
* P from 6 ATP & electrons from 6 NADPH __reduce__ the 6 3-PGA into 6 G3P
* 1 G3P exits the cycle & can be used to make glucose for a net gain of 1 G3P for every 3 CO2
* During __regeneration__, 3 ATP are used to rearrange the remaining 5 G3P (15 C’s) into 3 RuBP (15 C’s)
* Occurs in the stroma
28
New cards
carbon fixation
* Incorporation of C from atmospheric CO2 into an organic compound
* C that is fixed into sugar during photosynthesis can be used to build other organic molecules
* C is fixed into a 3C sugar as it enters the Calvin cycle in C3 plants
* C is fixed into a 4C sugar as it enters the Calvin cycle in C4 & CAM plants
* C that is fixed into sugar during photosynthesis can be used to build other organic molecules
* C is fixed into a 3C sugar as it enters the Calvin cycle in C3 plants
* C is fixed into a 4C sugar as it enters the Calvin cycle in C4 & CAM plants
29
New cards
C3 plant
Plant that uses the Calvin cycle to fix CO2 into an organic 3C compound as the first stable intermediate (3-PGA)
30
New cards
C4 plant
Plant that uses reactions to fix CO2 into a 4C compound (oxaloacetate), providing CO2 for the Calvin cycle
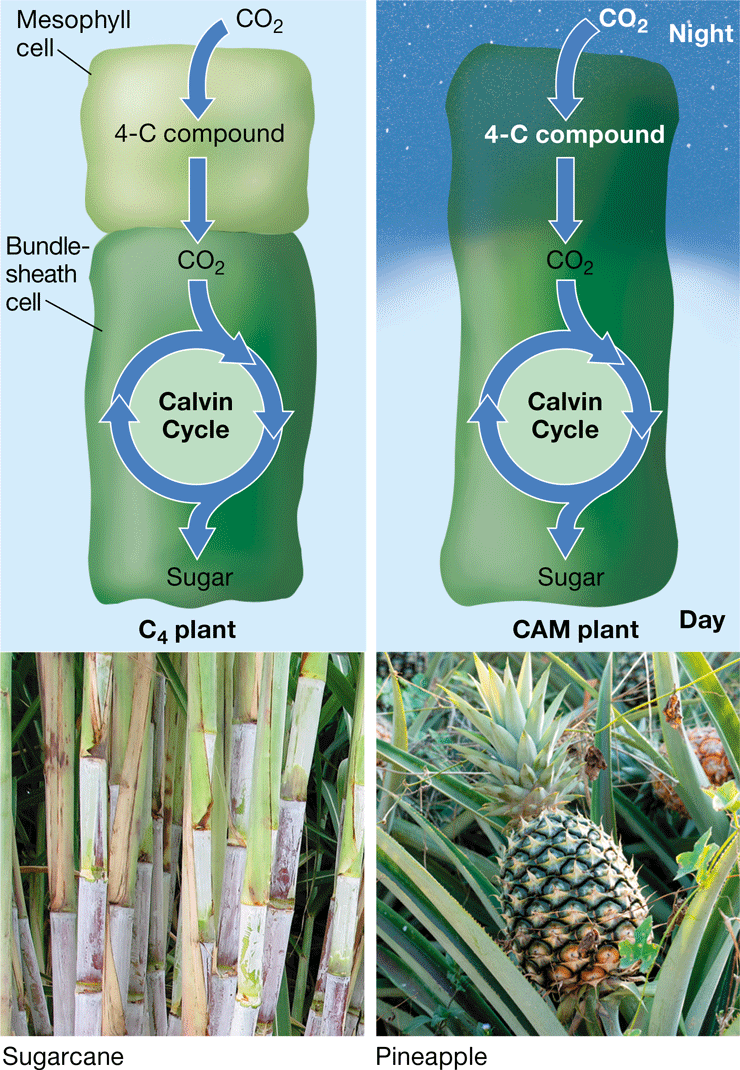
31
New cards
CAM plant
* Plant that uses a photosynthetic adaptation in arid conditions
* CO2 enters open stomata in the night, converting it into oxaloacetate
* Releases CO2 for the Calvin Cycle during the day, where the stomata are closed
* CO2 enters open stomata in the night, converting it into oxaloacetate
* Releases CO2 for the Calvin Cycle during the day, where the stomata are closed
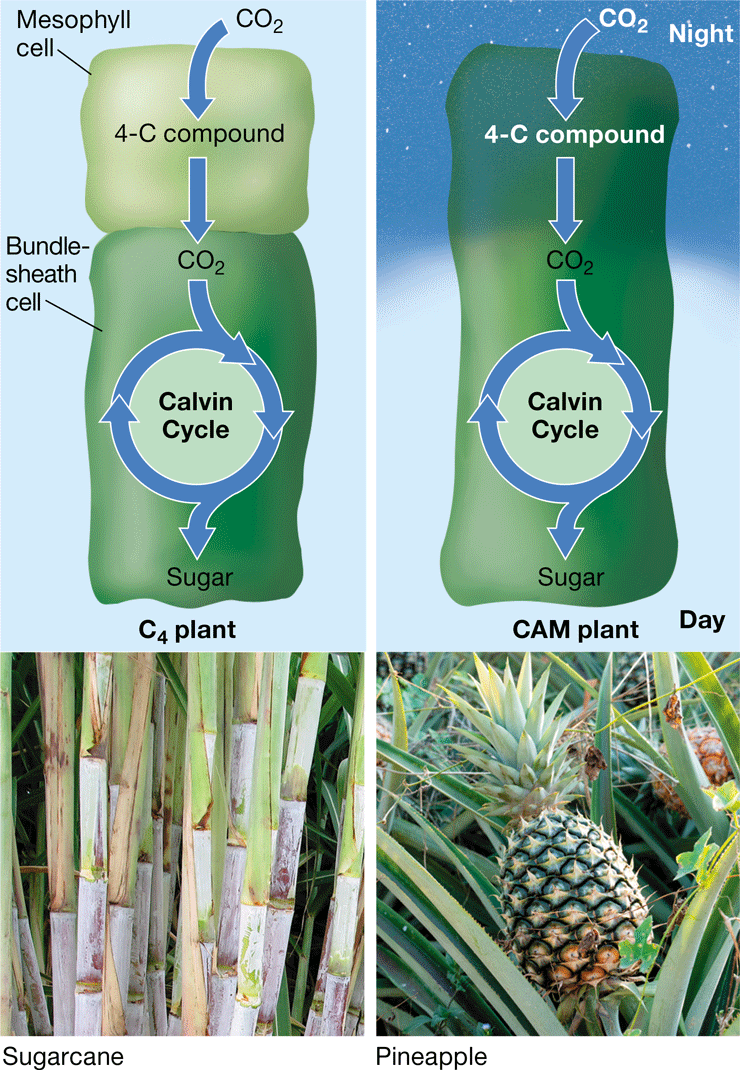
32
New cards
chloroplast
* Uses solar energy to convert CO2 & H2O into glucose & O2
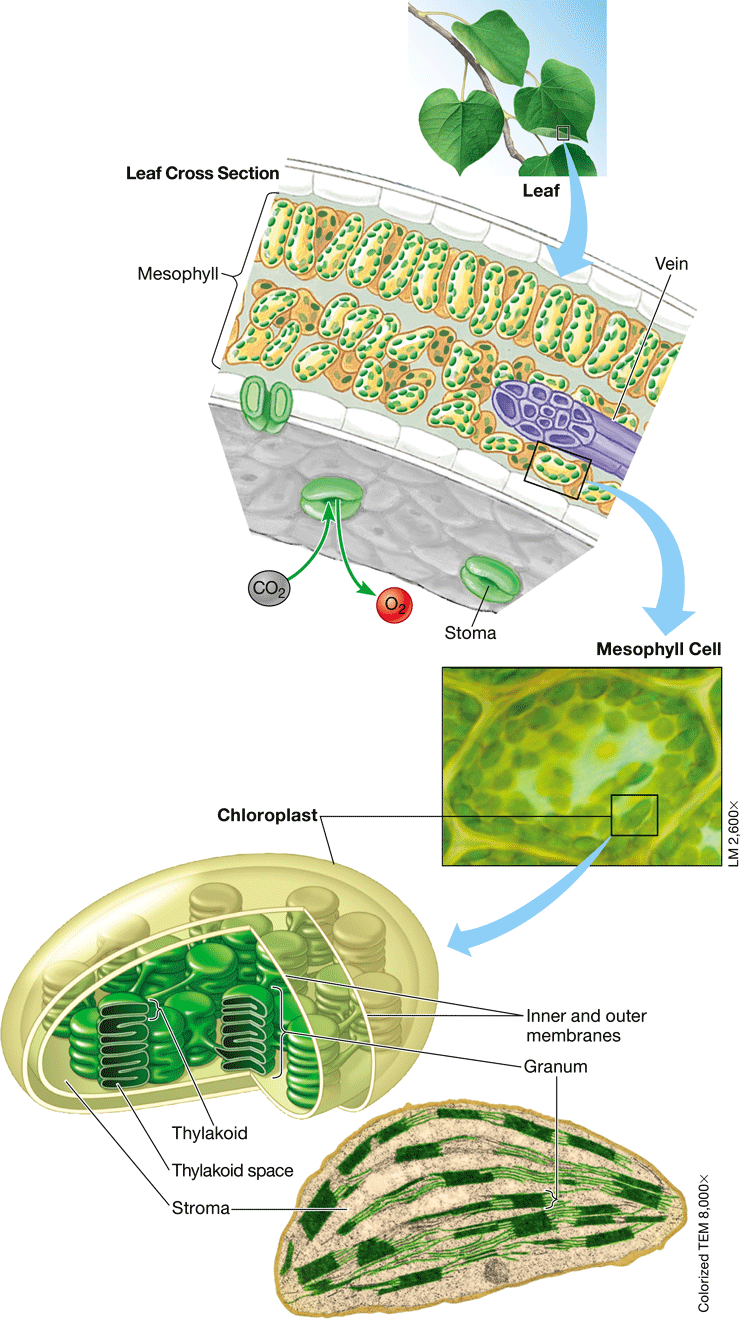
33
New cards
carotenoid
* Yellow & orange pigments located in the chloroplast
* Shows through once the green chlorophyll breaks down
* Can absorb & dissipate light energy, preventing damage to chlorophyll & the interaction with O to form damaging oxidative molecules
* Shows through once the green chlorophyll breaks down
* Can absorb & dissipate light energy, preventing damage to chlorophyll & the interaction with O to form damaging oxidative molecules
34
New cards
photosystem
* Light-capturing protein & pigment complex of a thylakoid membrane
* Consists of a reaction-center complex surrounded by light-harvesting complexes
* Consists of a reaction-center complex surrounded by light-harvesting complexes
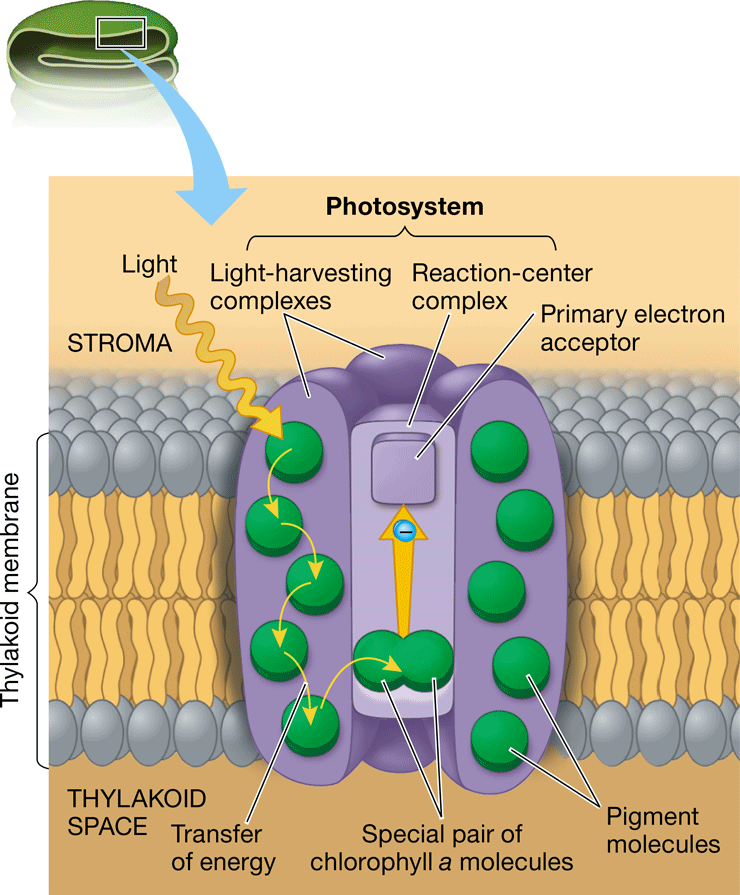
35
New cards
photosystem II
* Pigment molecules absorb light energy, passing it to the reaction center complex
* Primary electron acceptor captures electrons from chlorophyll *a* when boosted to a higher energy state
* H2O is split to replace the captured electron
* Electrons are donated to photosystem II, with the remaining O & H ions released into the thylakoid
* Released energy pumps H+ into the thylakoid space, driving chemiosmosis
* Primary electron acceptor captures electrons from chlorophyll *a* when boosted to a higher energy state
* H2O is split to replace the captured electron
* Electrons are donated to photosystem II, with the remaining O & H ions released into the thylakoid
* Released energy pumps H+ into the thylakoid space, driving chemiosmosis
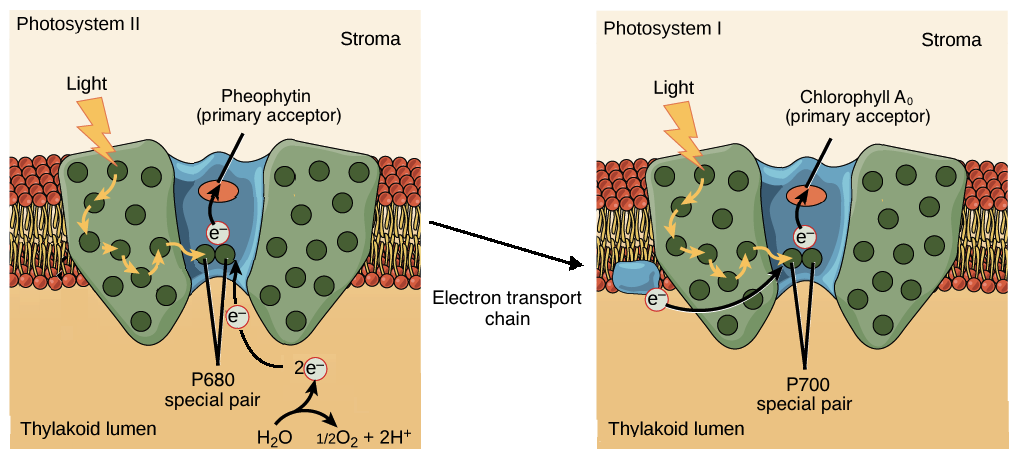
36
New cards
photosystem I
* Pigment molecules absorb light energy, passing it to the reaction center complex
* Primary electron acceptor captures electrons from chlorophyll *a* when boosted to a higher energy state
* Electrons that flow down the ETC from PSII replace the captured electron
* Captured electron is passed through a short ETC, reducing NADP+ to NADPH at the end of the chain
* NADPH provides some energy to fuel the Calvin cycle
* Primary electron acceptor captures electrons from chlorophyll *a* when boosted to a higher energy state
* Electrons that flow down the ETC from PSII replace the captured electron
* Captured electron is passed through a short ETC, reducing NADP+ to NADPH at the end of the chain
* NADPH provides some energy to fuel the Calvin cycle
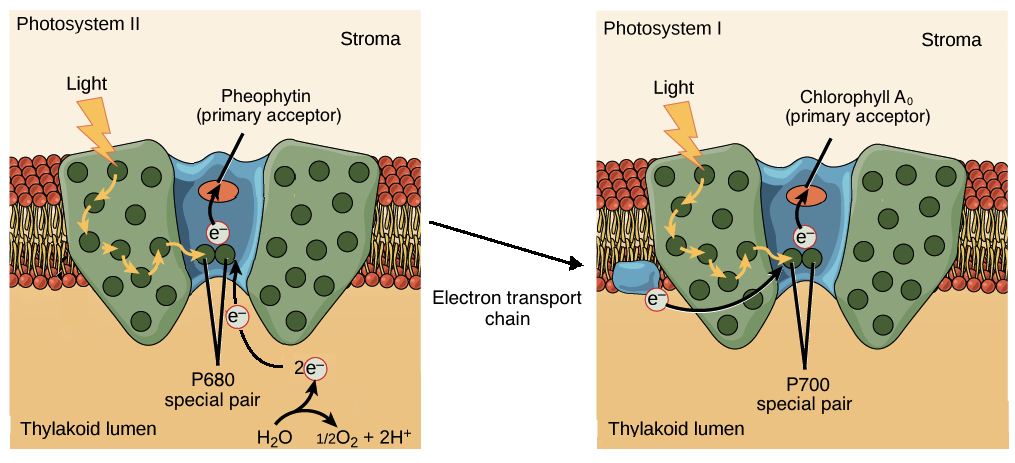
37
New cards
chlorophyll
Green pigment located within the chloroplasts or in the membranes of certain organisms
\
\
38
New cards
chlorophyll *a*
* Participates directly in light reactions, converting solar energy into chemical energy
* Absorbs mainly blue-violet & red light
* Absorbs mainly blue-violet & red light
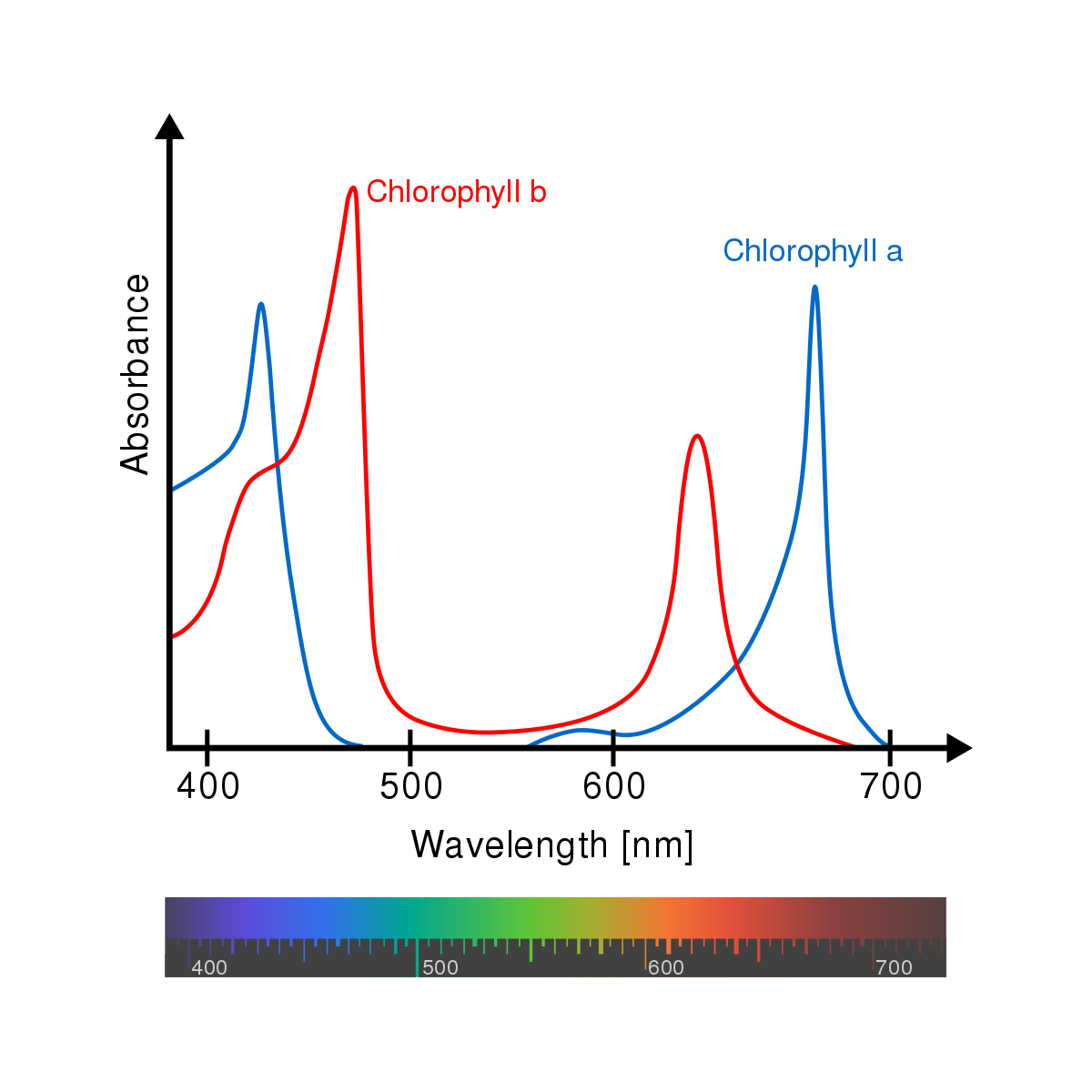
39
New cards
chlorophyll *b*
* Absorbs blue & orange light
* Broadens the range of light a plant can use by conveying absorbed energy to chlorophyll *a*, which uses it in the light reactions
* Broadens the range of light a plant can use by conveying absorbed energy to chlorophyll *a*, which uses it in the light reactions
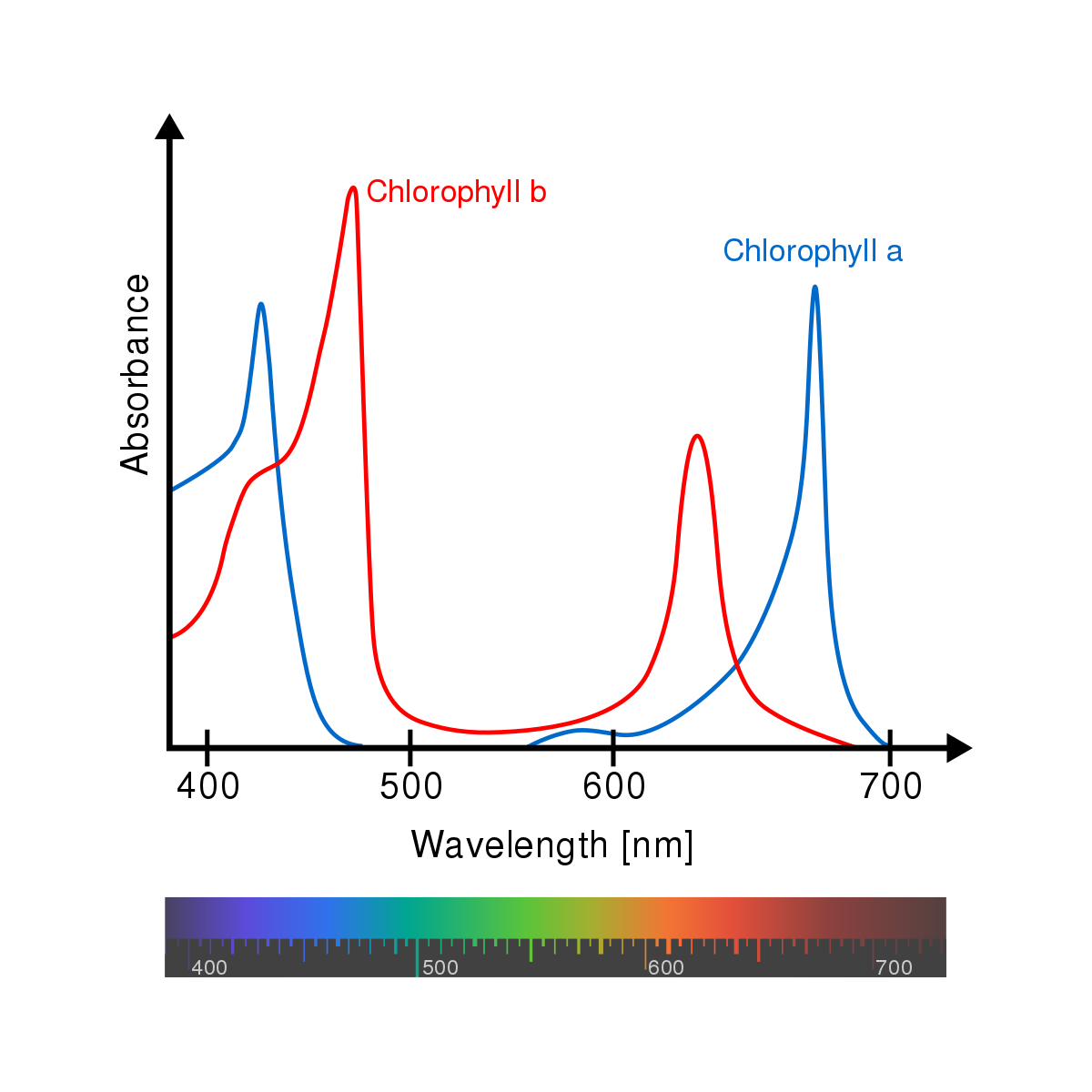
40
New cards
mesophyll
* Leaf cells specialized for photosynthesis
* A leaf’s ground tissue system
* A leaf’s ground tissue system
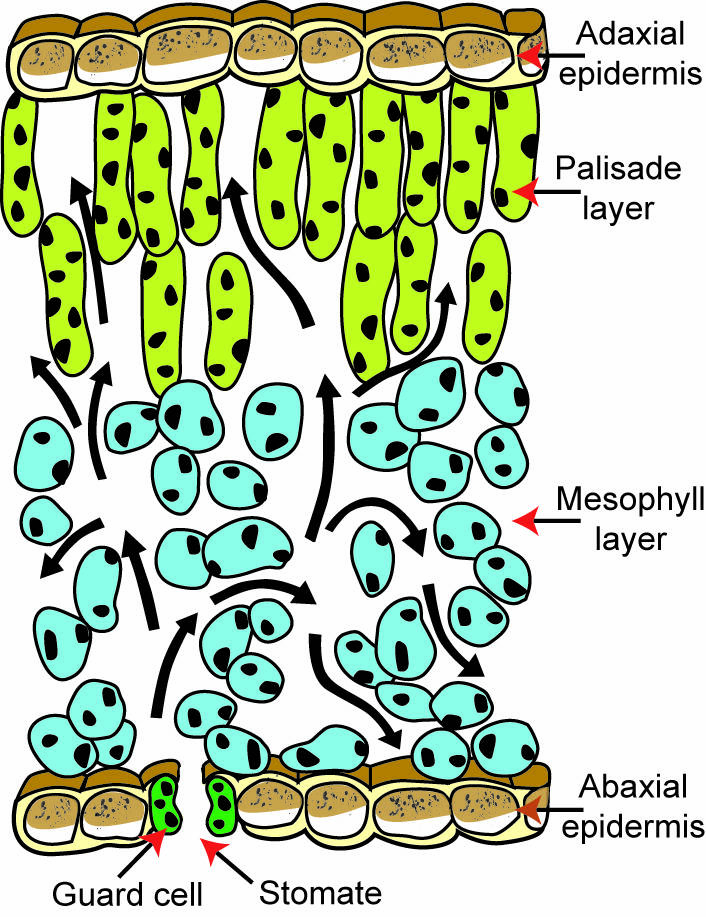
41
New cards
stomata
* Pores surrounded by guard cells in the lower epidermis of a leaf
* When open, CO2 enters a leaf, H2O & O2 exit into the mesophyll layer
* Plants conserve H2O when its stomata are closed
* When open, CO2 enters a leaf, H2O & O2 exit into the mesophyll layer
* Plants conserve H2O when its stomata are closed
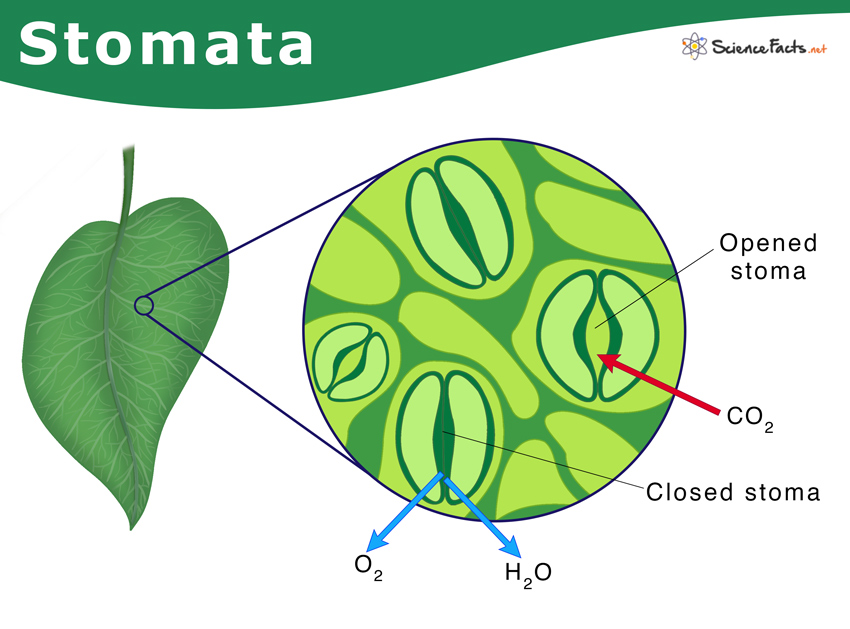
42
New cards
stroma
* Fluid in the chloroplast that surrounds the thylakoid membrane
* Sugars are made here by the enzymes of the Calvin cycle
* Sugars are made here by the enzymes of the Calvin cycle
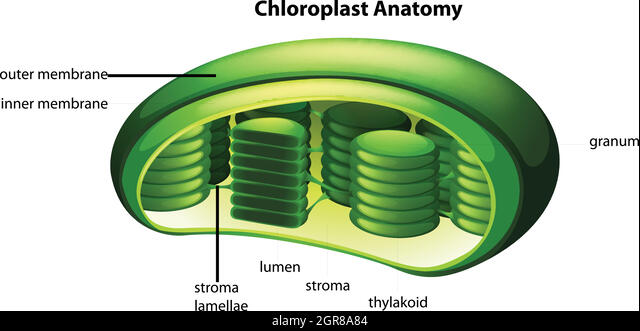
43
New cards
thylakoid
* Flattened membranous sac inside a chloroplast
* Membranes contain chlorophyll & the light reaction complexes
* Membranes contain chlorophyll & the light reaction complexes
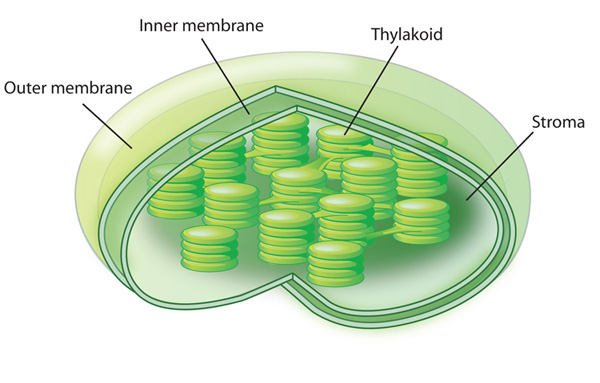
44
New cards
pigment
* Light-absorbing molecules built into the thylakoid membranes that absorb or reflect certain wavelengths of light
45
New cards
granum
* Stack of thylakoids
46
New cards
photophosphorylation
Production of ATP by chemiosmosis during the light reactions of photosynthesis
47
New cards
photorespiration
* Metabolic pathway that consumes O2, releases CO2, & decreases photosynthetic output
* Usually occurs on hot, dry days
* Stomata close, O2 accumulates, rubisco fixes O2 instead of CO2
* Produces no sugar molecules or ATP
* Usually occurs on hot, dry days
* Stomata close, O2 accumulates, rubisco fixes O2 instead of CO2
* Produces no sugar molecules or ATP
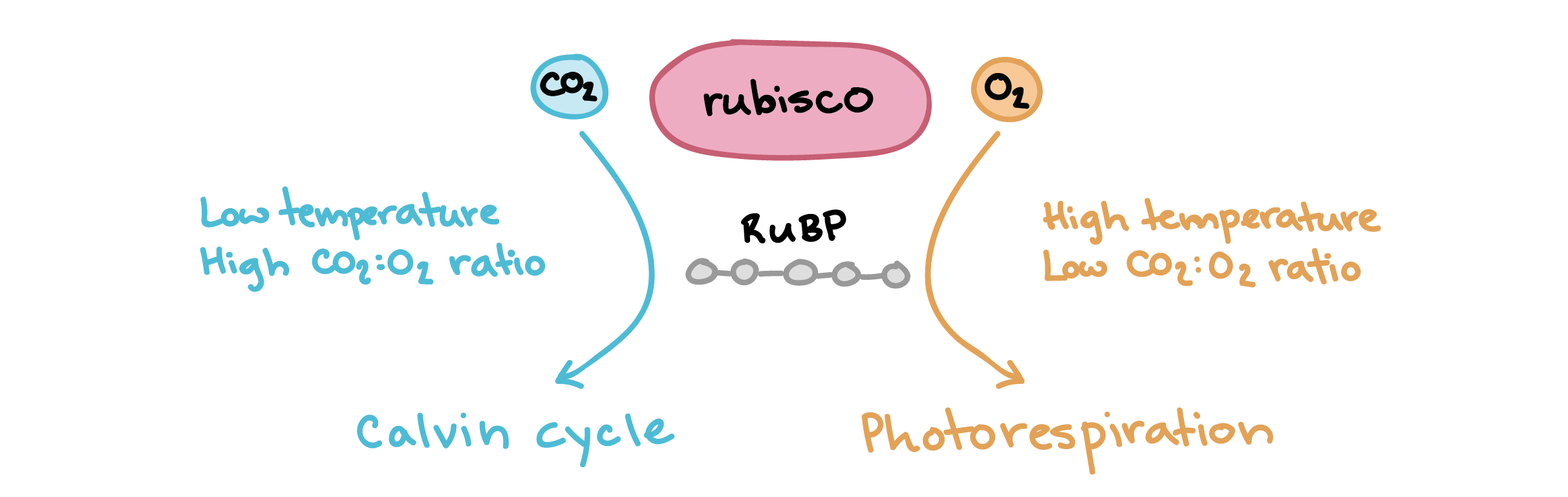
48
New cards
wavelength
Distance between crests of adjacent waves
49
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum
Entire spectrum of electromagnetic radiation ranging in wavelength
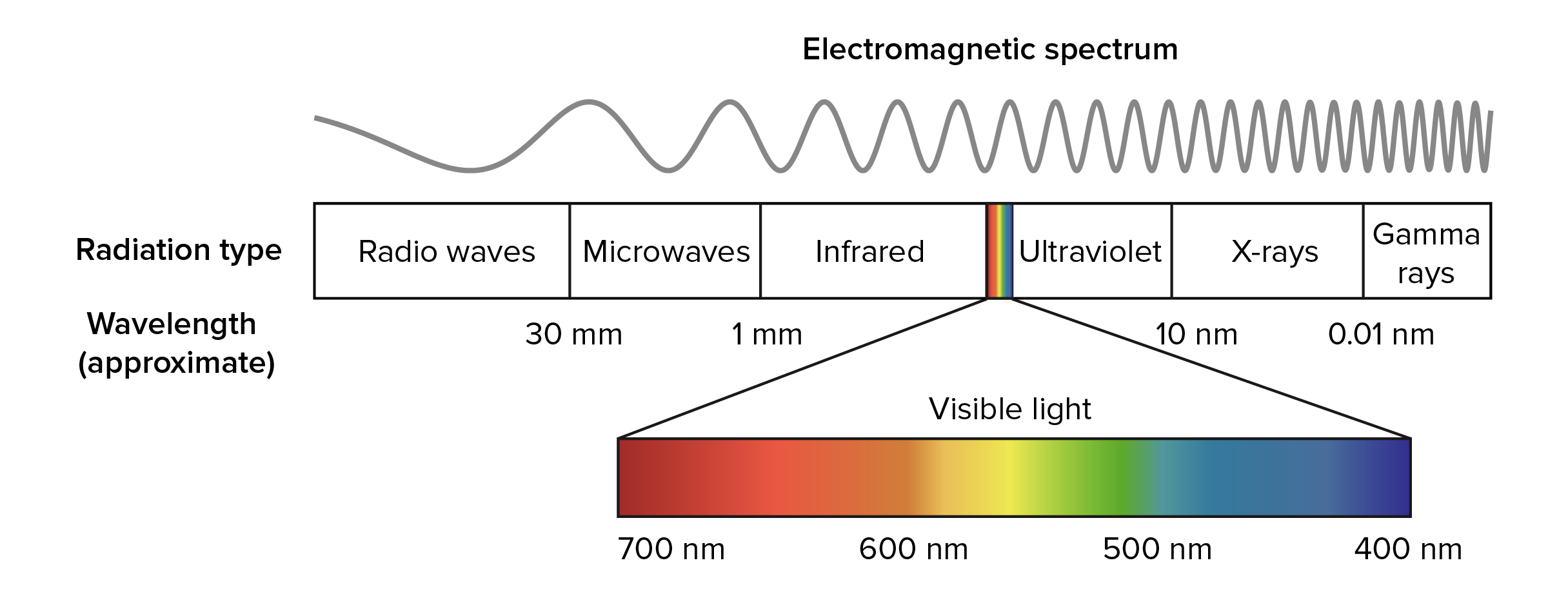
50
New cards
photon
* Fixed quantity of light energy
* The shorter the wavelength of light, the greater the energy of a photon
* The shorter the wavelength of light, the greater the energy of a photon
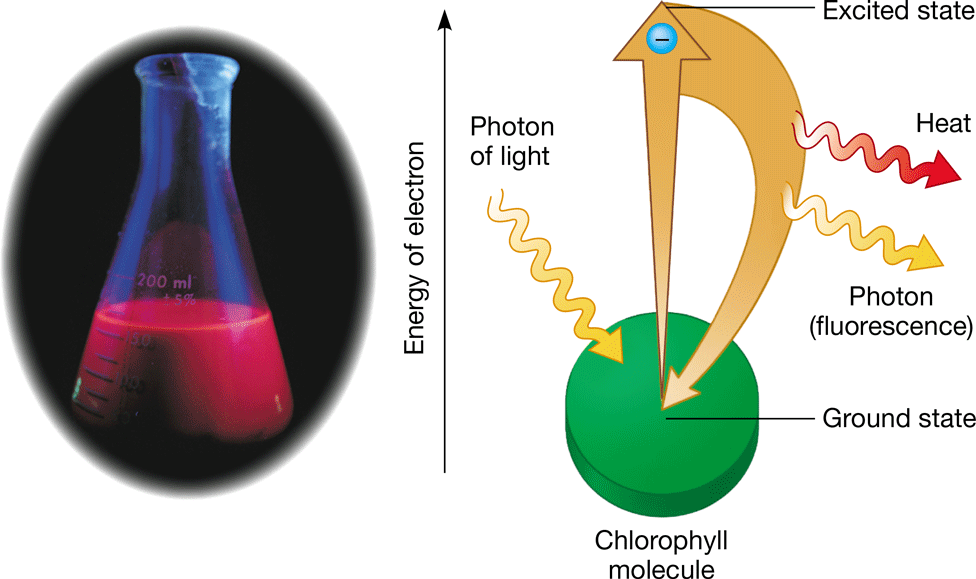
51
New cards
autotroph
* Organism that makes its own food
52
New cards
photoautotroph
* Organism that obtains energy from sunlight to convert CO2 into organic molecules
53
New cards
heterotroph
* Organism that obtains organic food molecules by consuming other organisms
* Consumer or decomposer in a food chain
* Consumer or decomposer in a food chain
54
New cards
kilocalorie (kcal)
* Quantity of heat equal to 1,000 calories
* Called a “calorie” when measuring the energy content of food
* Called a “calorie” when measuring the energy content of food
55
New cards
greenhouse effect
Warming of Earth due to the atmospheric accumulation of CO2 & other gases, absorbing infrared radiation & reradiating some it back towards Earth
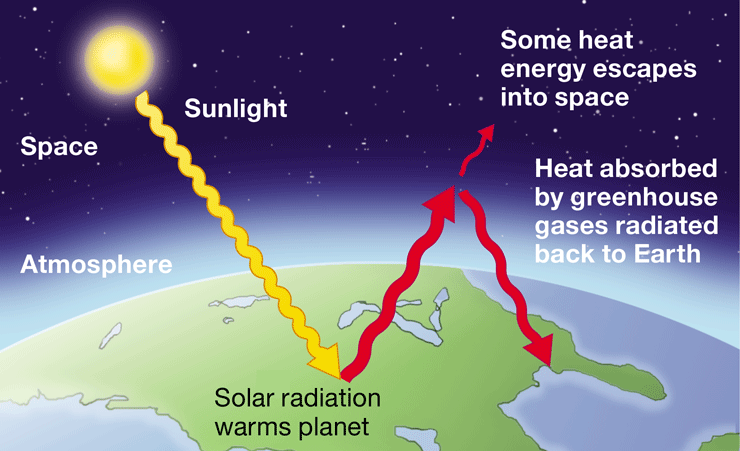
56
New cards
climate change
Increase in temperature & change in weather patterns around the planet due to the burning of fossil fuels