genomics - functional assays II computation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
MAVE
multiplexed assay of variant effect
i think this is the same as deep mutational scans
needs sophisticated models to predict effect of variants in proteins that havent yet been assayed, to account for noise and epistasis
problems with mpra measurements
ratio of counts (RNA/DNA) can be unstable
multiple barcodes might be tagging the same element
transfection of complex libraries across biological replicates can introduce significant variation
problems w barcode rna/dna ratios
ratio of 2 noisy measurements
when read counts are low, small differences in reads lead to very large changes in ratio
errors across measurements of multiple barcodes can be propagated to estimate variance, but common approaches dont do that
RNA = a x DNA
a = transcription rate
assuming linear relationship between dna and rna molecules
plug a into dna and rna linear regression model → produces lower variance in the estimate of transcriptional activity. increases power to detect functional impacts of alternative alleles
what can a genotype - phenotype map look like?
additive (all positions in a sequence contribute independently)
neighbor (interaction terms between neighboring positions)
pairwise (each position interacts w every other position)
black box (roll your own relationship function lol)
biophysical (model ∆∆Gs) w neural network
sort seq expression values
discrete data - limited by num of sorted bins
barcode rna-seq
continuous data
global epistasis
mutations may act non-additively on phenotype, but this may be due to additive effects on some underlying trait
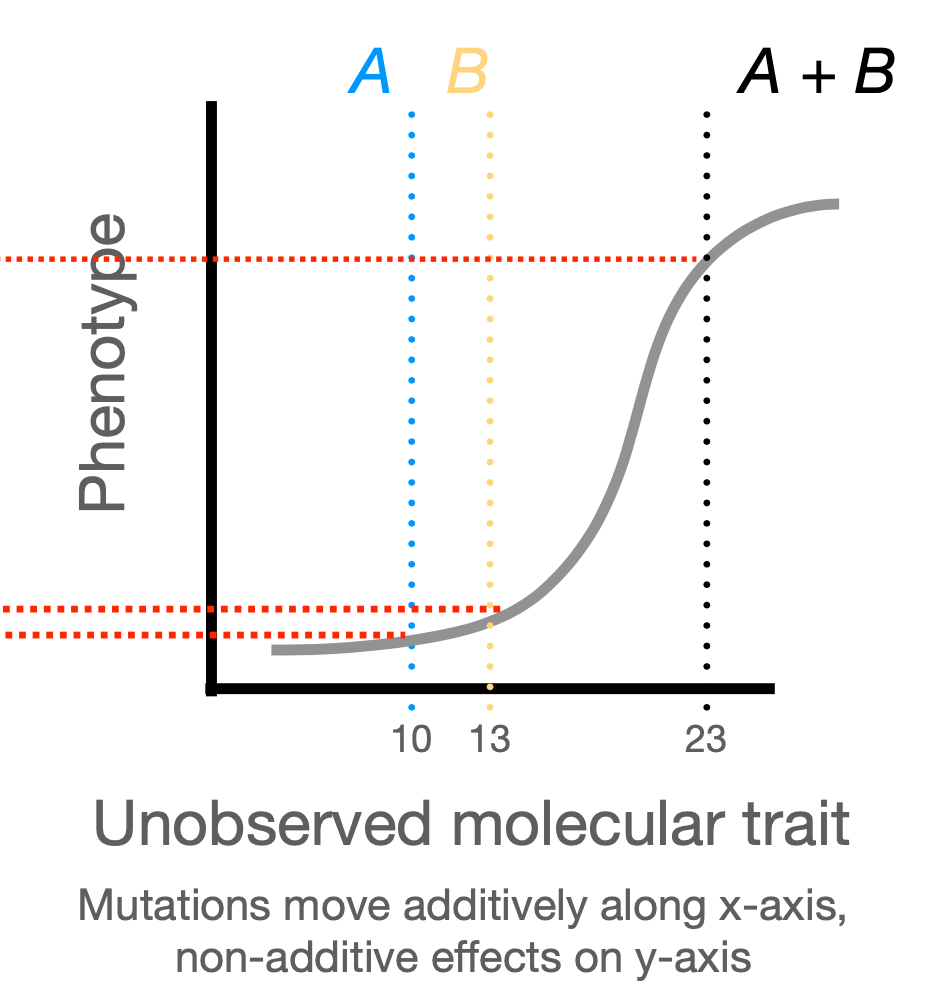
local epistasis
specific pairwise interactions between residues
modeling takeways
mave output is sequencing data, not a direct measure of the property of interest
modeling translates your sequencing data into a measure of the function of interest
a quantitative sequence to function model enables you to predict the effects of unmeasured variants and to learn epistasis
DeepSTARR
deep learning + starr seq
can be used to predict enhancer activity based on dna sequence, and then design synthetic cres
biophysical models of variant effect
capturing biophysical effects underlying the phenotype will lead to better predictions of combinations of variants
big mutant library, include single mutations and many double mutants → assay variant effect in 2 ways (protein binding and protein stability/abundance) → train a neural network model w biophysical ∆G values → ∆G values produce biophysically-based, interpretable
predictions → determine free energy changes → quantify how mutations tune binding affinity
protein fragment complementation (PCA)
bindingPCA: binding = yeast survives
abundancePCA: reporter for how much of the protein is in the cell
recommendations for using MAVEs for variant interpretation
assay should have sufficient dynamic range to robustly separate damaging variants from benign variants
choose an assay that captures effects that are relevant (what variants might not be detected in the assay?)
deposit data in repositories, disclose all experimental and statistical methods, make code available
provide measures of reproducibility and error estimates
validate results w some single variant tests and include known variants as controls