Peripheral Vascular System Overview and Examination Techniques
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Palpable arterial pulses of the Upper Limb
a. Brachial pulse
b. Radial pulse
c. Ulnar pulse
Palpable arterial pulses of the Lower Limb
a. Femoral
b. Popliteal
c. Posterior tibial
d. Dorsalis pedis
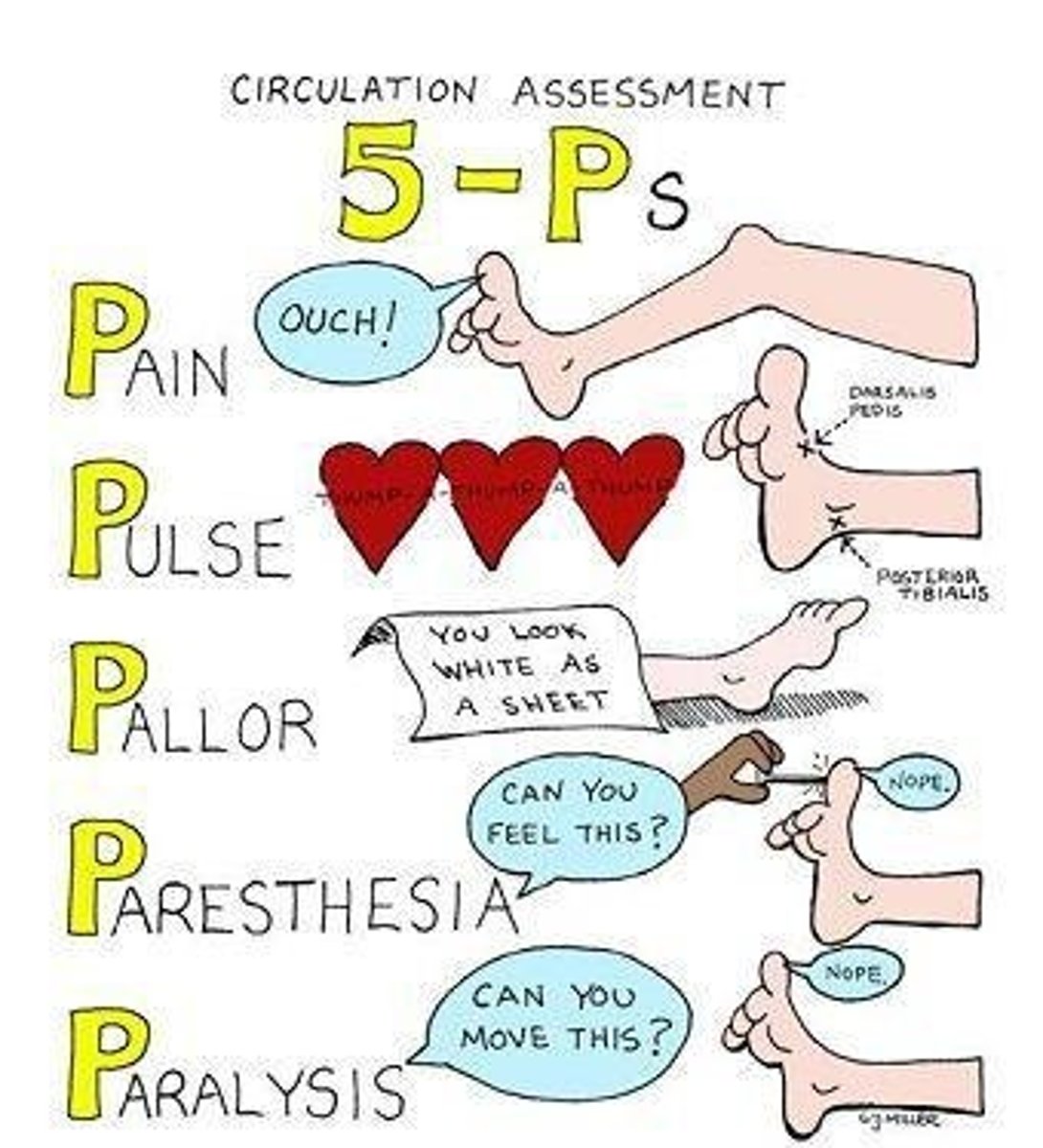
6 P's of arterial pathologies
1. Pallor (Pale; dt arterial occlusion)
2. Polar (Cold; dt arterial occlusion)
3. Pulselessness (Diminished; dt arterial occlusion)
4. Paraesthesia ('Pins & Needles'; dt arterial occlusion)
5. Pain (Works with paraesthesia)
6. Paralysis (dt necrosis of tissue or gangrene)
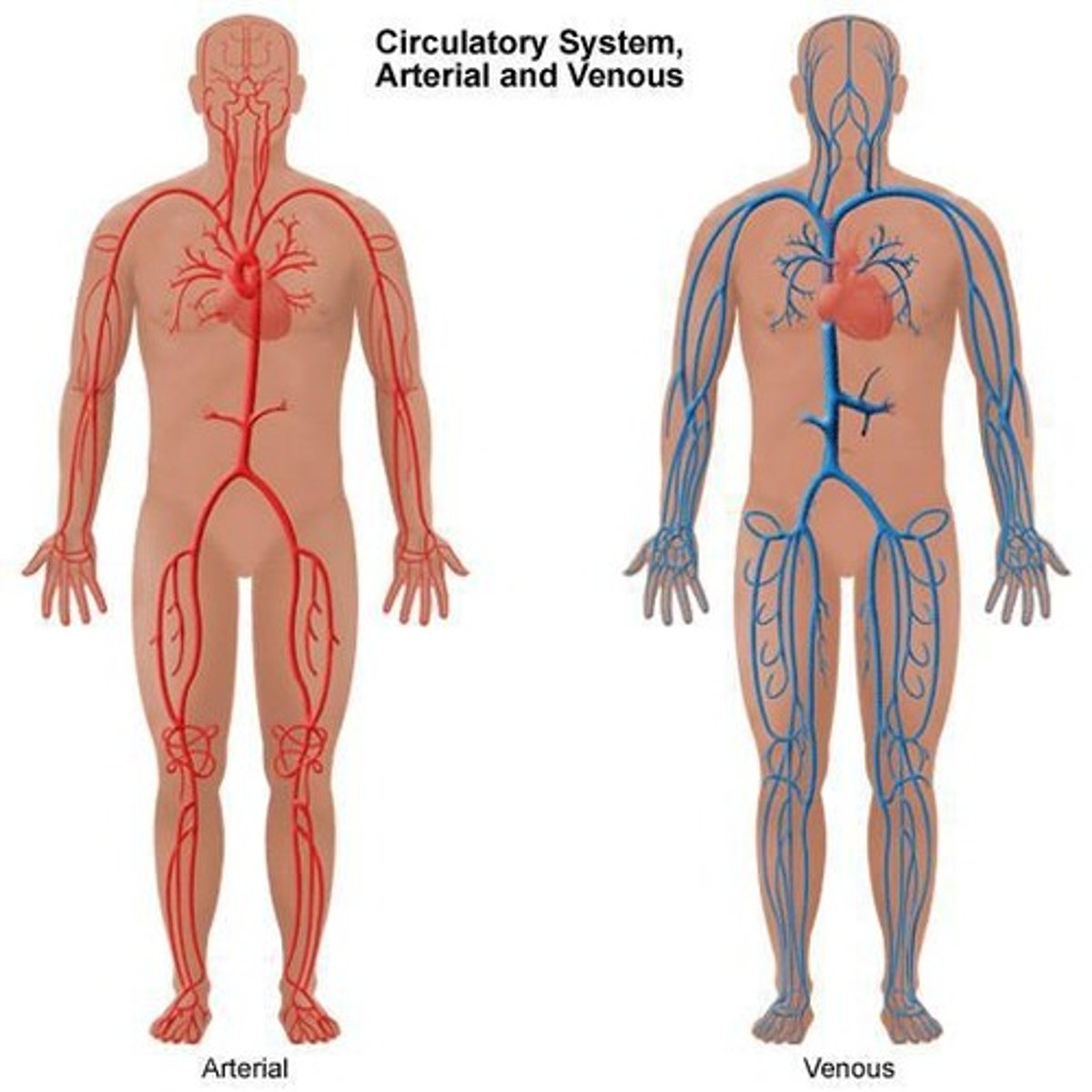
Venous system made up of:
1. Deep veins (90% of venous return)
2. Superficial veins (Great and small saphenous)
3. Anastomotic veins (connect the saphenous veins)
4. Perforating/ communicating veins (connect deep to superficial veins)
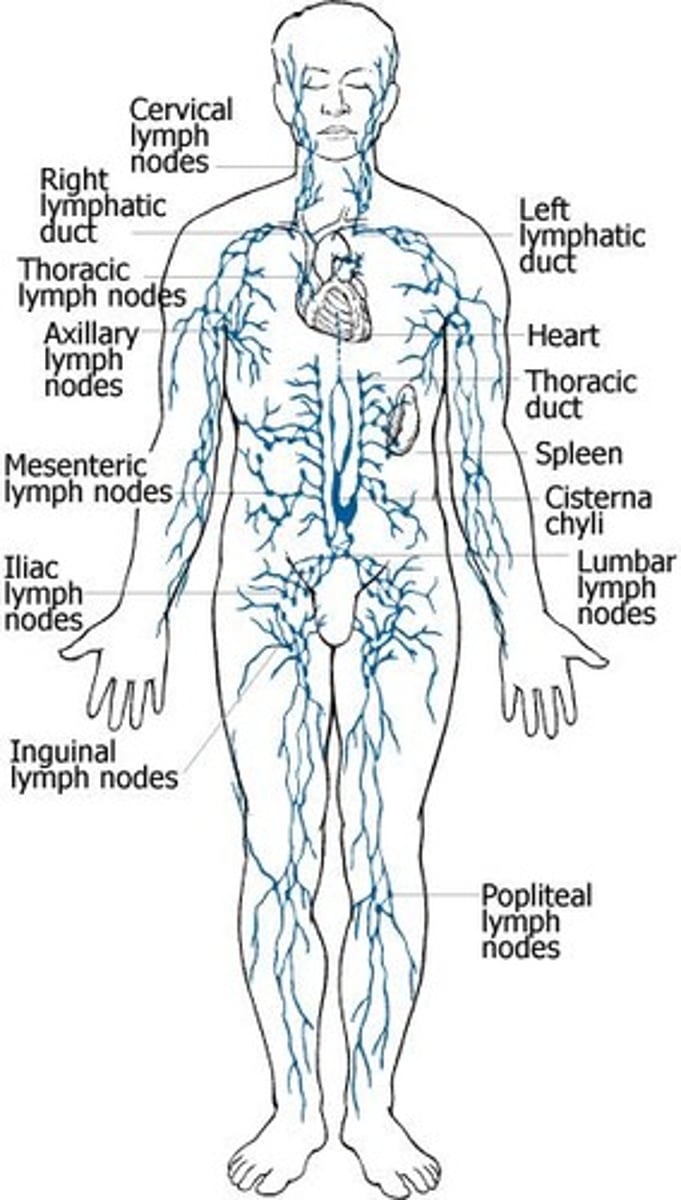
Lymphatic system
Vascular network that drains lymph fluid from the body tissues and returns it to venous circulation
Upper limb palpable nodes
Epitrochlear
Axillary
Lower limb palpable nodes
Inguinal nodes - vertical and horizontal
Pitting oedema
• Soft and usually bilateral
• Pitting after 2 seconds over bony
prominences
• Skin thickening, ulceration and
pigmentation depends on cause
• Causes include: Dependency,
immobilisation, heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, liver cirrhosis, chronic venous insufficiency, hypoalbuminemia, medications.
Non-pitting oedema
• Most common is lymphoedema
• Soft in early stages
• Thickening of skin
• Ulceration is rare
• No pigmentation
• Unilateral or bilateral
• Due to obstructed lymph channels by tumours, fibrosis, inflammation and surgical intervention
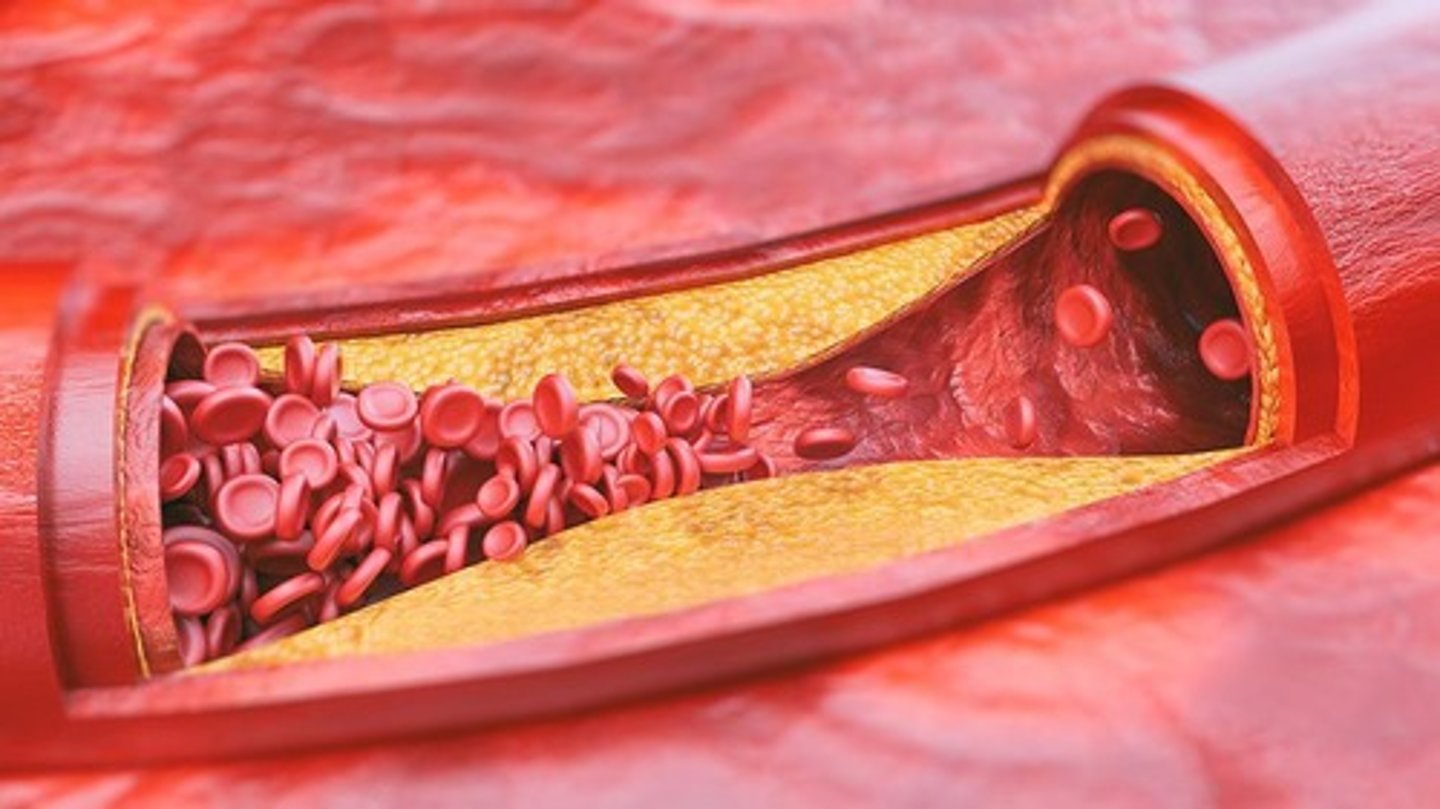
Atherosclerosis
Hardening of arteries due to plaque causing decreased blood flow
Clot = Atheroma
Predominantly in the legs - intermittent claudication
Buergers disease
When an atheroma breaks off and results in thrombus (i.e. decreased blood flow and necrosis)
Form of vasculitis
A.K.A Thromboangitis obliterans
Sxs:
Pain (IC)
Numbness
Paraesthesia
Predisposition to stroke or MI
Risk factors:
Smoking
Rx:
Amputation
Deep vein thrombosis
Blood clot in a deep vein
Sxs:
Pain
Swelling
Warmth + Redness (dt inflammation)
Occurs mostly in leg (calf)
Cx's:
Surgery
Pregnancy
Trauma
Hormones
Refer to doppler ultrasound
Rx:
Anticoagulant
Thrombophlebitis
Formation of a clot in a vein resulting in inflammation
Sxs - Same as DVT
Risk factors - Same as DVT
Difference from DVT = Different vein; saphenous veins
Self limiting
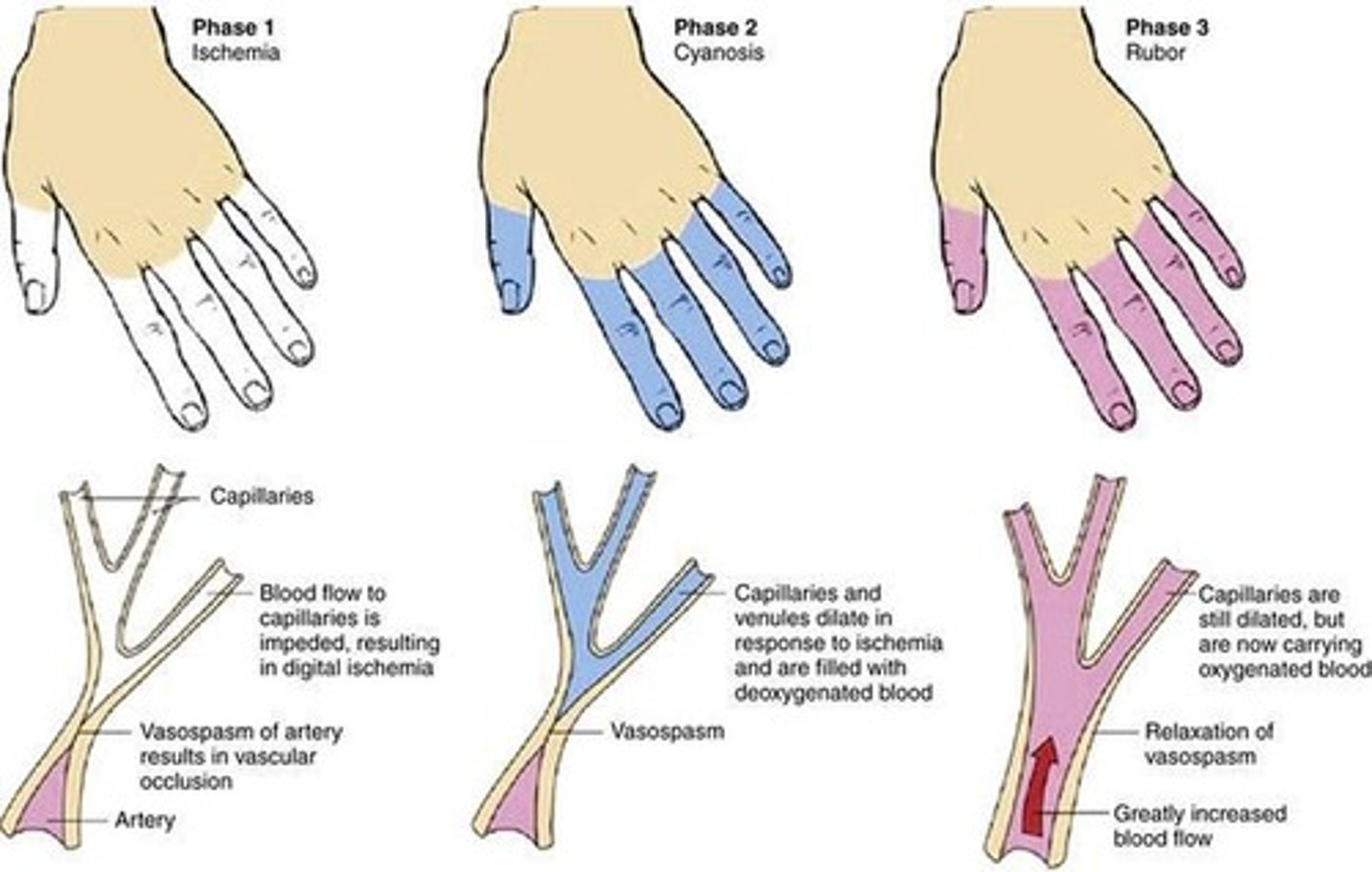
Raynaud's disease
Vasospasm of blood vessels which will prevent blood flow leading to colour changes in the extremities, nose, and ears
3 phases:
1. Whiteness - pallor dt ischaemia
2. Blueness - P.cyanosis dt vasodilation
3. Rubor - Normal flow
Primary Raynaud's disease:
Dt cold exposure and emotional stress
Secondary Raynaud's disease:
Dt pre-existing condition (RA)
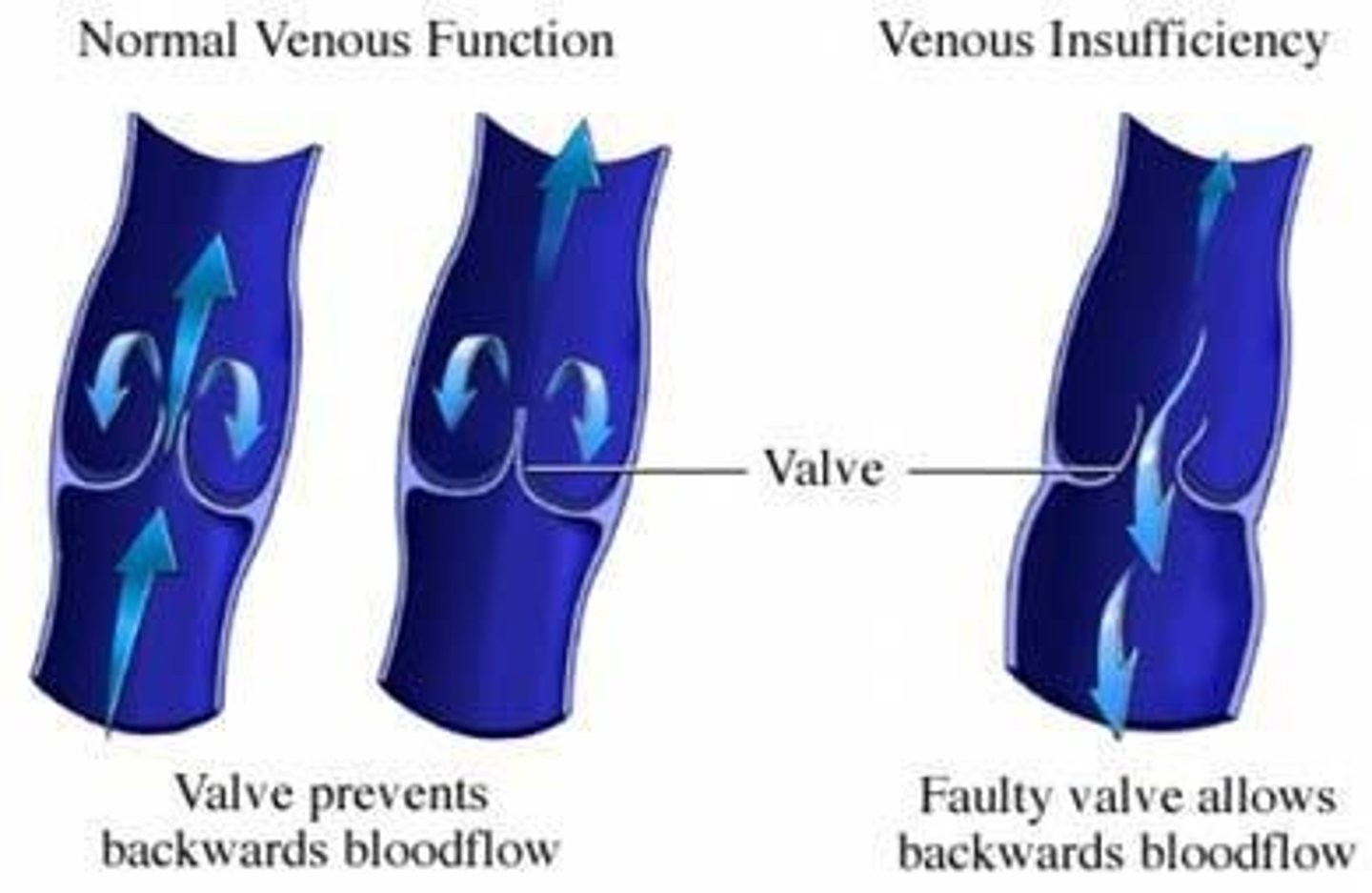
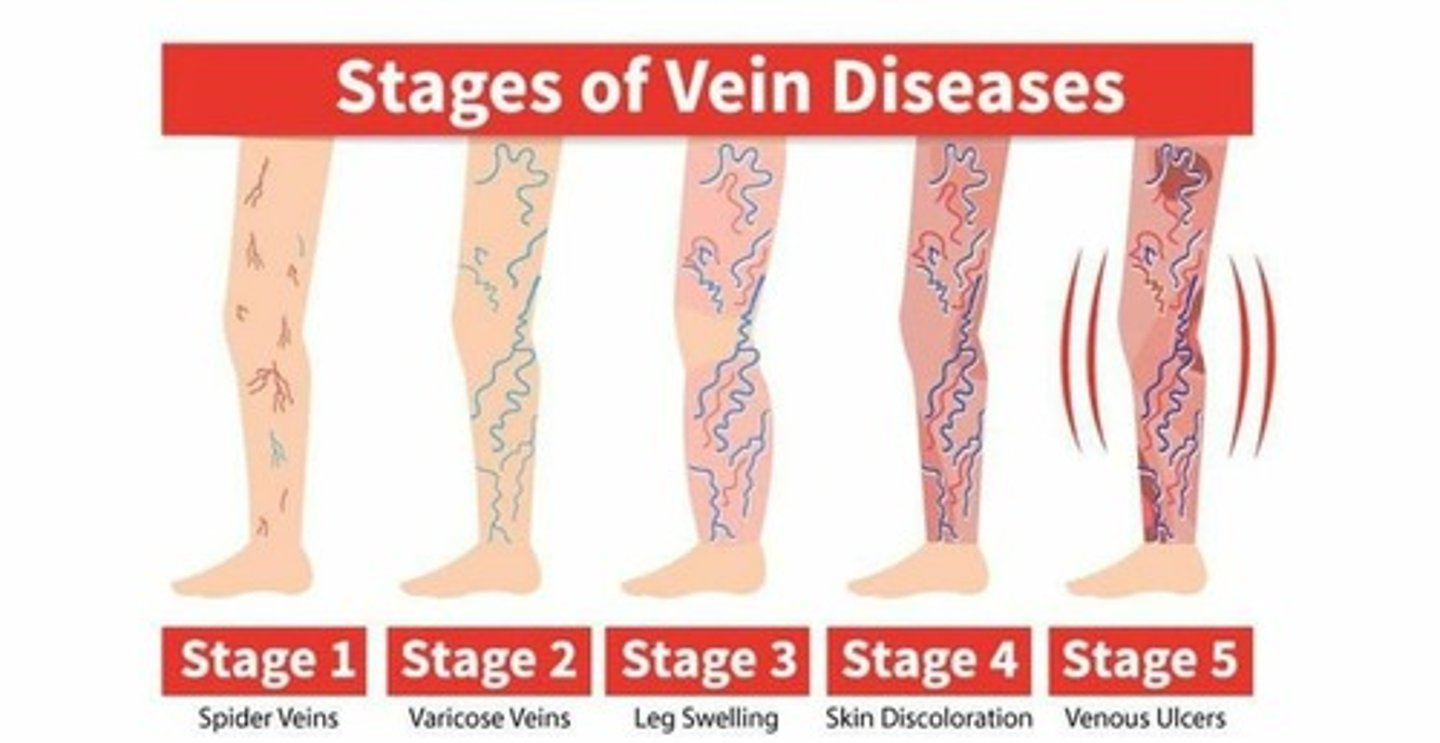
Varicose veins
Tortuous appearance of superficial veins
Occurs in lower limbs dt gravity - i.e. valves work harder
Valves damaged ->swelling ->discoloration (blue/purple) ->surrounding skin becomes darker dt venous insufficiency
Cx's:
Pregnancy
Medication
Long standing periods
Spider veins - same process but smaller vessels walls are affected bcoz they have no valves
Compartment syndrome
Increased pressure within fascial compartments of extremities.
Dt:
Muscular damage
Trauma
Surgery
Mechanism:
Muscles get inflammed, swell, enlarge, and compress N's and V's (i.e. poor circulation)
Fascia can no longer expand & becomes red, warm, and painful
Rx:
Surgical fascial decompression
Lymphangitis
Inflammation of lymphatic vessels
Red appearance (red streaks)
Sxs (local):
Pain
Redness
Warmth
Swelling
Sxs (systemic):
Fever
L. node enlargement
Cx:
Bac/Fungal infection (streptococcus)
Staphylococcus
Dermatological, not vascular
Bacterial infection of the skin
Types of ulcers
1. Pressure ulcer
2. Arterial insufficiency ulcer
3. Venous insufficiency ulcer
4. Neuropathic ulcer
Chronic Arterial Insufficiency
Arterial occlusion; tissue ischaemia
Combination of:
Atherosclerosis & Beurgers disease
chronic venous insufficiency
Venous hypertension
Combination of:
DVT & Varicose veins
Venous stasis:
Pitting oedema
Pruritis
Brown pigmentation of skin
Lipodermatosclerosis
Ulceration
Where do ulcerations most commonly occur and what are their characteristics
Dorsum of the foot - smaller, painful, deeper, dry, well delineated
Risk factors:
Obesity
T2DM
Htn
Genetics
Pulse grading
0 = Absent
+1 = Diminished
+2 = Normal
+3 = Increased
+4 = Bounding
Capillary refill
Time for color to return after pressure.
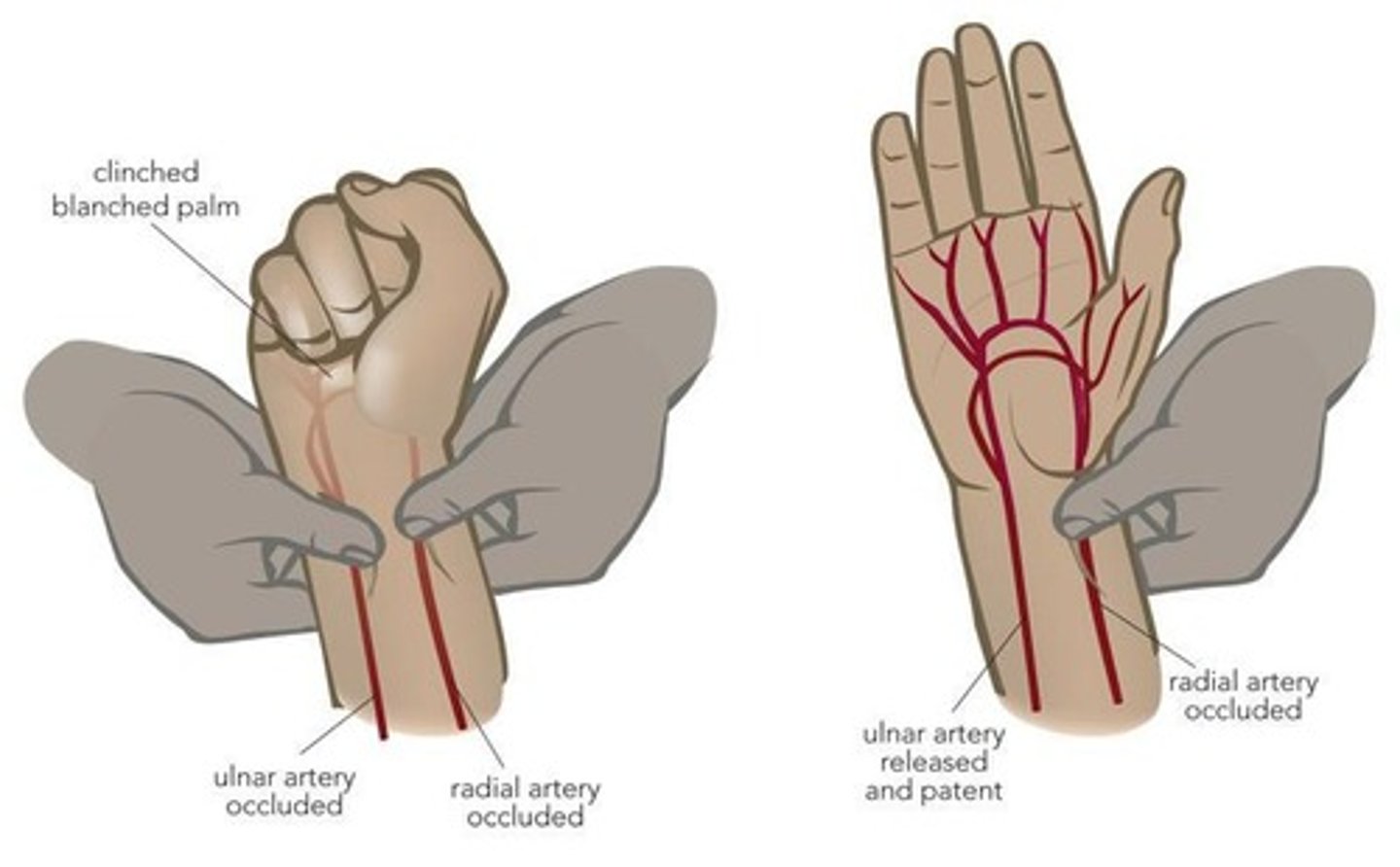
Allens Test
Assesses arterial supply to the hand.
Special tests for lower extremities
1. Beurgers test
2. Trendelenburg's test
3. Varicose vein mapping
Special investigations
1. Dopper ultrasound
2. Angiogram
3. Venogram
4. D-dimer (blood test)
5. Biopsy
Refferals
1. Vascular surgeon
2. Phlebologist
3. Endocrinologist