Heart sound 2 new
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Changes of P2 as per respiration
On expiration - Early closure of P2
On inspiration - late closure of P2
Causes of valvular aortic stenosis
Bicuspid aortic valve (infants)
Rheumatic fever
Valve calcification (>65 years)
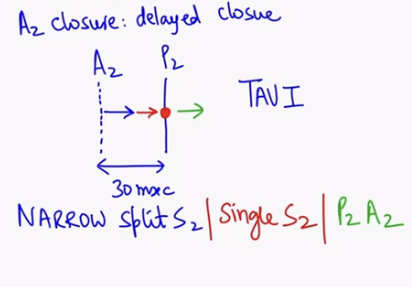
Why narrow splitting in aortic stenosis?
S2 = A2P2
first A2 close and the P2 closes
In aortic stenosis, A2 is delaying as per condition
This will cause narrowing of s2 / narrow splitting S2
In severe cases, single S2 is heard and sometimes P2A2 (reverse splitting) can also heard
Severity depend on time ( early - narrow splitting, late - single s2, severe - reverse splitting )
Cause of angina in AS?
Aortic stenosis →LV hypertrophy → increased O₂ demand
Characteristic pulse in aortic stenosis?
Pulsus parvus et tardus/ anacrotic pulse ( slow rising with low amplitude pulse)
Type of apex beat in AS?
Heaving apex beat ( due to left side hypertrophy )
What is heaving beat?
forceful beat that can lift your finger
What special apical impulse is seen in AS?
Double apical impulse ( due to both LVH and LAH )
Apex beat position in AS?
6th intercostal space (normally in 5th intercostal space )
Apex beat finding in aortic stenosis
heving beat
Double apical impulse
Displacement of apex beat to 6th space
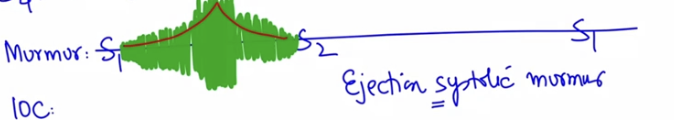
Type of murmur in AS?
Ejection systolic (crescendo–decrescendo) murmer
Murmer in aortic stenosis present in
systole
Which word in question directly find aortic stenosis?
carotid thrill
Why balloning is contraindicated AS manageent?
it will break valve because of calcification
Which test is contraindicated in severe AS
tredmill test ( because low output → syncope)
What is Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
Persistent connection between pulmonary artery and aorta
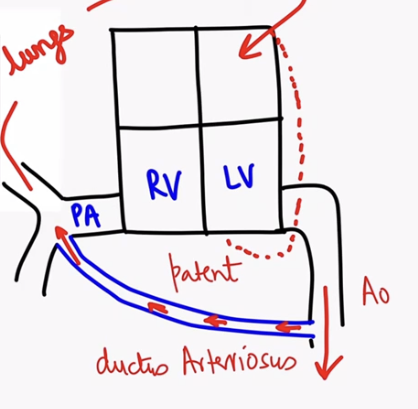
Why left ventricle is failing in PDA?
Most blood is bypassing RV. Due o connection, blood is going to pulmonary artery and then to LA→LV
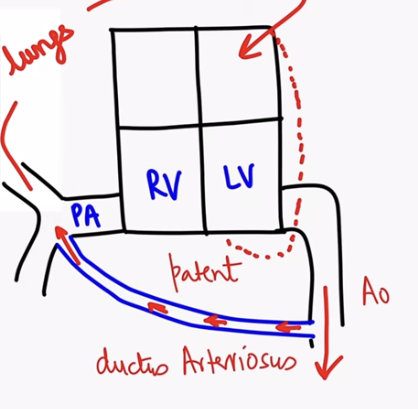
S2 finding in PDA?
Narrow split S2 (because delay in aortic valve closure)
Characteristic murmur of PDA?
Machinery / continuous murmur
Mechanism of PDA in preterm infants
Hyaline membrane disease→Hypoxia → ↑ PGE₂ → PDA
Difference in continuous /machinery and cresendo-decresendo murmer?
Continuous murmer peak at S2 and present in both systole and diastole
Cresendo decresendo presnet only in systole
Clinical features of PDA in babies
Poor feeding |
Irritability |
Dyspnea during breastfeeding
Diagnostic test for PDA?
TTE (tranbsthoracic echo)
Complications of PDA
Pulmonary hypertension |
NEC |
CHF |
AKI
Severe Complication of PDA
eisenmenger syndrome
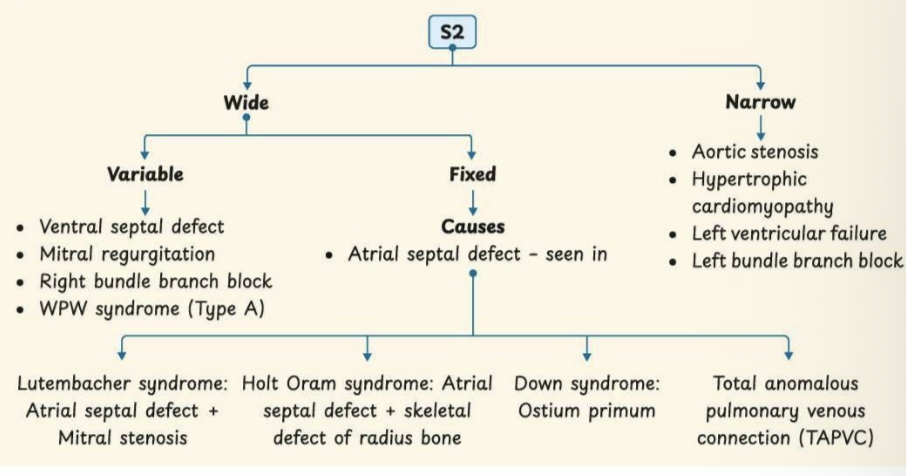
Causes of narrow split s2
Aortic stenosis
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy ( subvalvular AS)
Left ventricle failure →
Anterior wall MI
Myocarditis
Wet beri beri ( with pulmonary edema )
PDA
Severe anemia
Causes of mitral valve regurgitation
mitral valve prolapse
Infectiveendocarditis
Myocardial ischemia
Pathophysiology of MR
blood leak in left atria → less blood pumped to aorta
Examination finding of MR
S2 wide split
Pansystolic murmer
Why wide spllit murmer in MR?
less blood come in ventricle → less time to exit blood →early A2 closure
S2 finding in VSD?
Wide split S2 ( less blood - less time )
Types of VSD
Perimembranous VSD
Muscular VSD
Supracristal VSD
VSD with spontaneous closure?
Muscular VSD ( close till 3rd birthday)
Pressure difference between left and right atrium
4 mmhg
Which ventricle fails in ASD?
Right ventricle (due to volume overloading)
S2 finding in ASD?
Wide fixed split S2 ( delayed pulmonary closure and early A2 closure)
ASD diffrenece in inspiration and expiration
Feature | Normal – Inspiration | Normal – Expiration | ASD – Inspiration | ASD – Expiration |
Venous return to right heart | ↑↑ Increased | ↓↓ Decreased | ↑↑ Increased | ↓↓ Decreased |
Inter-atrial pressure difference | - | - | No pressure difference | Pressure difference develops |
Inter-atrial shunting | - | - | ⌠No shunt | ✅ LA → RA shunt |
Right ventricular filling | Increased | Decreased | Same | Same |
Right ventricular ejection time | Prolonged | Shortened | Constant | Constant |
Pulmonic valve closure (P2) | Delayed | Earlier | Delayed | Delayed |
Effect on S2 | Physiological split | Split narrows / single | Wide fixed split | Wide fixed spli |
1st column - normal inspiration
2nd column - normal expiration
3rd column - ASD inspiration
4th column - ASD - expiration
Wide fixed split 2nd heart sound is characteristic of
ASD
ASD seen in
Lutenbacher syndrome
Holt oram syndrome
down syndrome
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Chart of s2 splitting