A&P Lab Exam #2 Review (Lymphatic System)
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lymphatic System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Is the flow of lymph fluid to the heart unidirectional or bidirectional?
The flow of lymph fluid to the heart is unidirectional, moving only toward the heart through lymphatic vessels and preventing back flow through valves. It’s a one-way system using valves and skeletal muscle contractions to push lymph upward.
How are dietary fats absorbed from the small intestine? Explain the function of lacteals.
In the small intestine, lacteals (special lymphatic capillaries) absorb fat molecules called chylomicrons, transporting them into lymph and then into the bloodstream.
How is interstitial fluid taken into the lymphatic system?
Fluid enters lymphatic capillaries through overlapping endothelial cells that act as mini valves. These allow fluid in but prevent it from leaking back out.
What regions of the body do the thoracic and right lymphatic ducts?
Be able to identify them on an image of a full body
Point out the cisterna chyli
Right lymphatic duct: drains right arm, right side of head and thorax → right subclavian vein.
Thoracic duct: drains the rest of the body → left subclavian vein.
It begins in a sac-like chamber called the cisterna chyli.
Where do B-Cells mature? Where do T-Cells mature?
B-cells: mature in bone marrow.
T-cells: mature in the thymus.
What structure in the lymphatic system filters lymph fluid?
Lymph nodes filter lymph to remove bacteria, viruses, and debris before the lymph reenters circulation.
Define humoral and cell-mediated immunity.
Humoral immunity: B-cells produce antibodies that target pathogens in body fluids.
Cell-mediated immunity: T-cells attack infected or abnormal cells directly.
What are the roles of the spleen?
What area in the spleen are WBCs found?
Removes old red blood cells and platelets.
Stores iron and platelets.
Houses white blood cells (especially lymphocytes and macrophages) in its white pulp.
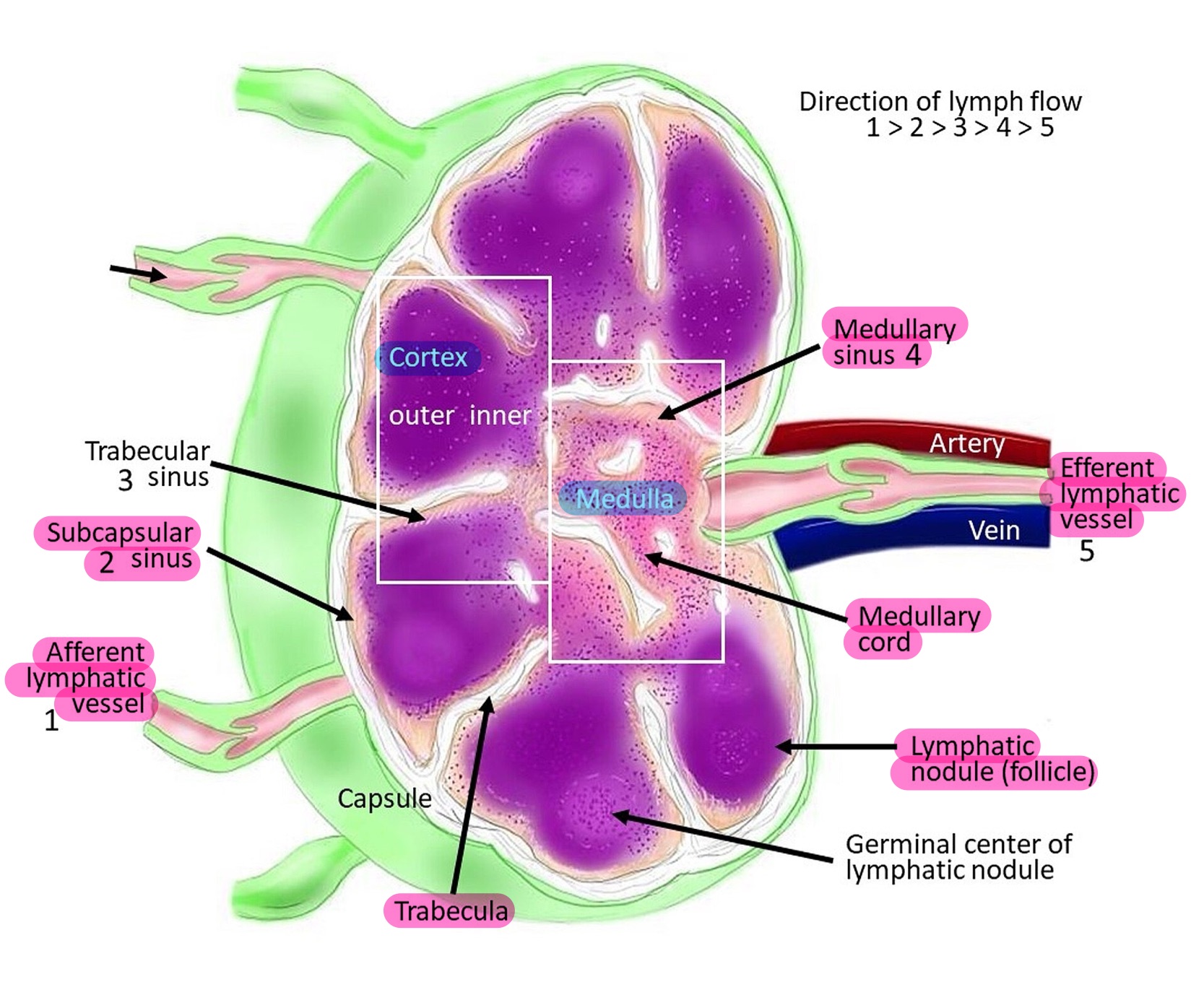
Identify the basic anatomy of a lymph node
a. Subcapsular sinus
b. Medullary Sinus
c. Medullary Cords
d. Trabeculae
e. Efferent/Afferent Vessels
f. Cortex
g. Medulla
h. Lymphatic nodules
What is the term used to describe an infection of the tonsils?
What are the names of the 3 types of tonsils?
Tonsillitis: inflammation of the tonsils.
Types of tonsils:
Pharyngeal (adenoids)
Palatine
Lingual
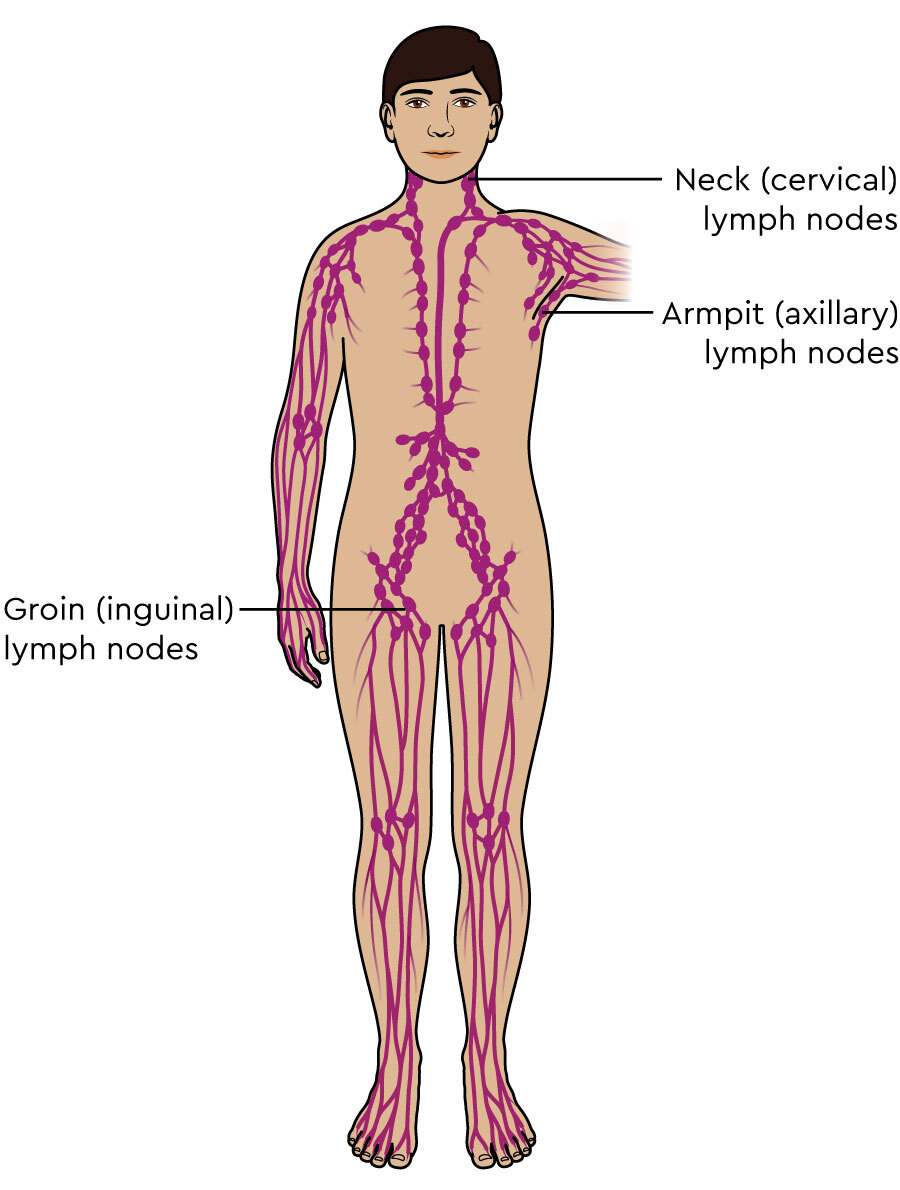
Identify the following collections of lymph nodes:
a. Cervical nodes
b. Axillary nodes
c. Inguinal nodes
Cervical: neck
Axillary: armpits
Inguinal: groin
Trace the path of lymph flow from a lymph capillary to where they empty in the subclavian veins
Lymph capillaries → collecting vessels → lymph nodes → lymph trunks → lymph ducts → subclavian veins.
State the functions of the lymphatic system
Hint: first figure out what structures are actually IN the lymphatic system, and which are not.
Returns excess interstitial fluid to the bloodstream.
Absorbs dietary fats.
Provides immune defense (houses lymphocytes).
Where do you find lymphoid (lymphatic) nodules in the body?
Found in:
Tonsils
Small intestine (Peyer’s patches)
Appendix
Mucosa of various organs (MALT: mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue)