Exam 3 Review: Cognitive Learning and Memory
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Sensory Memory
Brief retention of sensory information, lasting milliseconds.
Encoding
Transforming information into a memory trace.
Explicit Memory
Conscious recall of facts and events.
Nodes
Units of information in a semantic network.
State Dependent Learning
Memory retrieval influenced by internal state during learning.
Maintenance Rehearsal
Repetition of information to keep it in memory.
Method of Loci
Memory technique using spatial relationships for recall.
Shaping
Gradually reinforcing behaviors toward a desired goal.
Modeling
Learning through observation and imitation of others.
Self-Instruction
Guided self-talk to facilitate learning and task completion.
Bloom's Taxonomy
Framework categorizing educational goals into levels.
Objectivist View
Learning as a process of acquiring knowledge objectively.
Stage Model of Memory
Framework outlining sensory, working, and long-term memory stages.
Salience
Prominence or importance of a stimulus in context.
Selective Attention
Focusing on specific information, influenced by top-down processing.
Auditory Loop
Component of working memory for verbal information.
Visio-Spatial Scratchpad
Component for visual and spatial information processing.
Retrieval
Accessing stored information from memory.
Episodic Memory
Memory of personal experiences and specific events.
Semantic Memory
Memory of facts and general knowledge.
Links
Connections between nodes in a semantic network.
Proactive Interference
Old information disrupts recall of new information.
Mnemonic Strategies
Techniques to enhance memory retention and recall.
Acronym
Word formed from initial letters of phrases.
Peg Method
Associating items with pre-memorized cues for recall.
Constructivist View
Learning as an active process of constructing knowledge.
Attention
Focus on specific stimuli while ignoring others.
Flashlight Model
Attention is focused like a beam of light.
Funnel Model
Attention filters information, allowing some through.
Top-Down Processing
Perception influenced by prior knowledge and expectations.
Bottom-Up Processing
Perception driven by sensory input and data.
Working Memory
Active processing and manipulation of information.
Implicit Memory
Unconscious memory, such as skills and habits.
Procedural Memory
Memory for skills and actions, like riding a bike.
Dispositional Memory
Memory related to personal traits or dispositions.
Network Model of Semantic Memory
Conceptual framework linking related information.
Retroactive Interference
New information disrupts recall of old information.
Levels of Processing
Deeper processing leads to better memory retention.
Elaborative Rehearsal
Connecting new information to existing knowledge.
Sensory memory
What is this
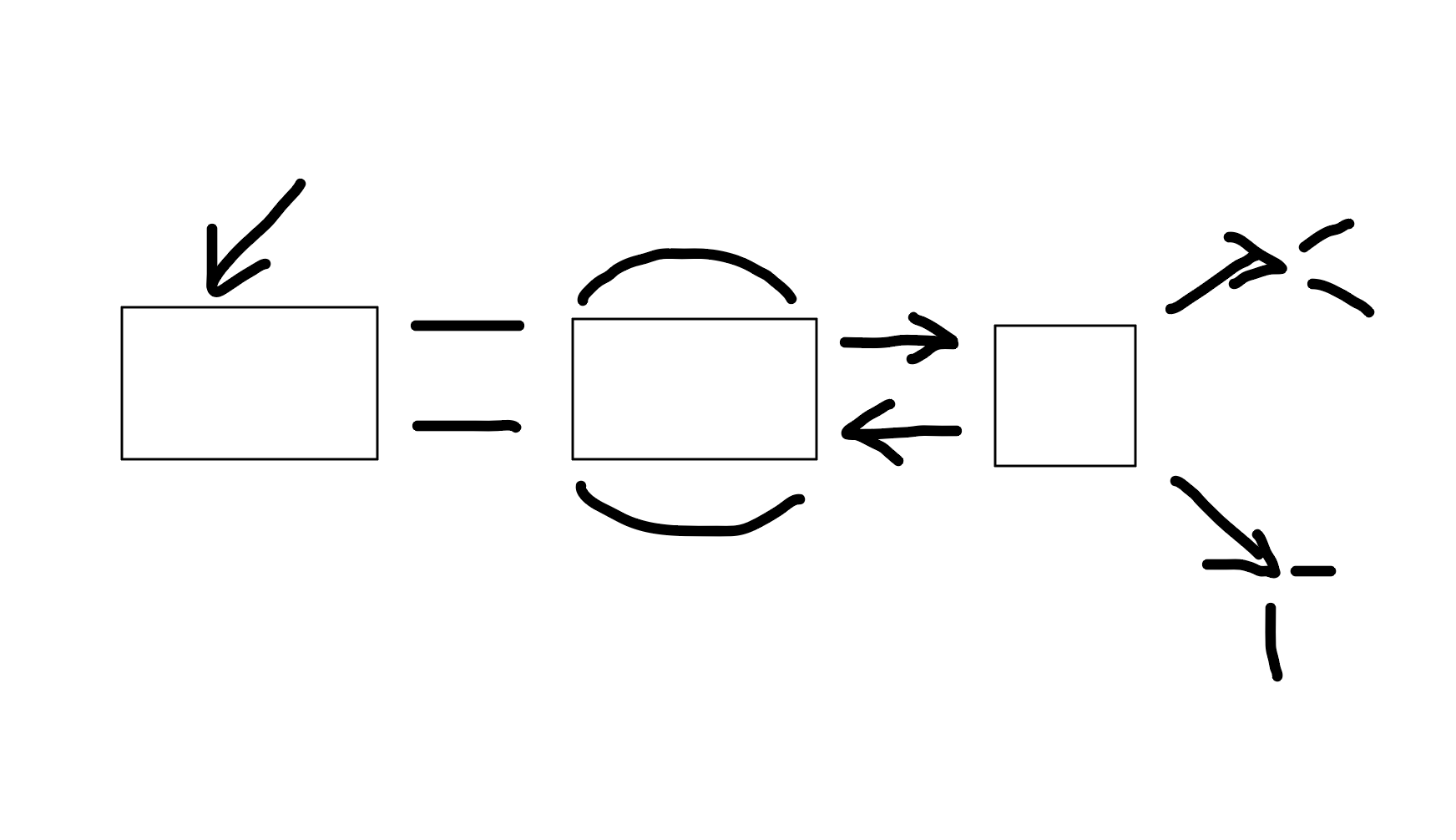
attention
What is this
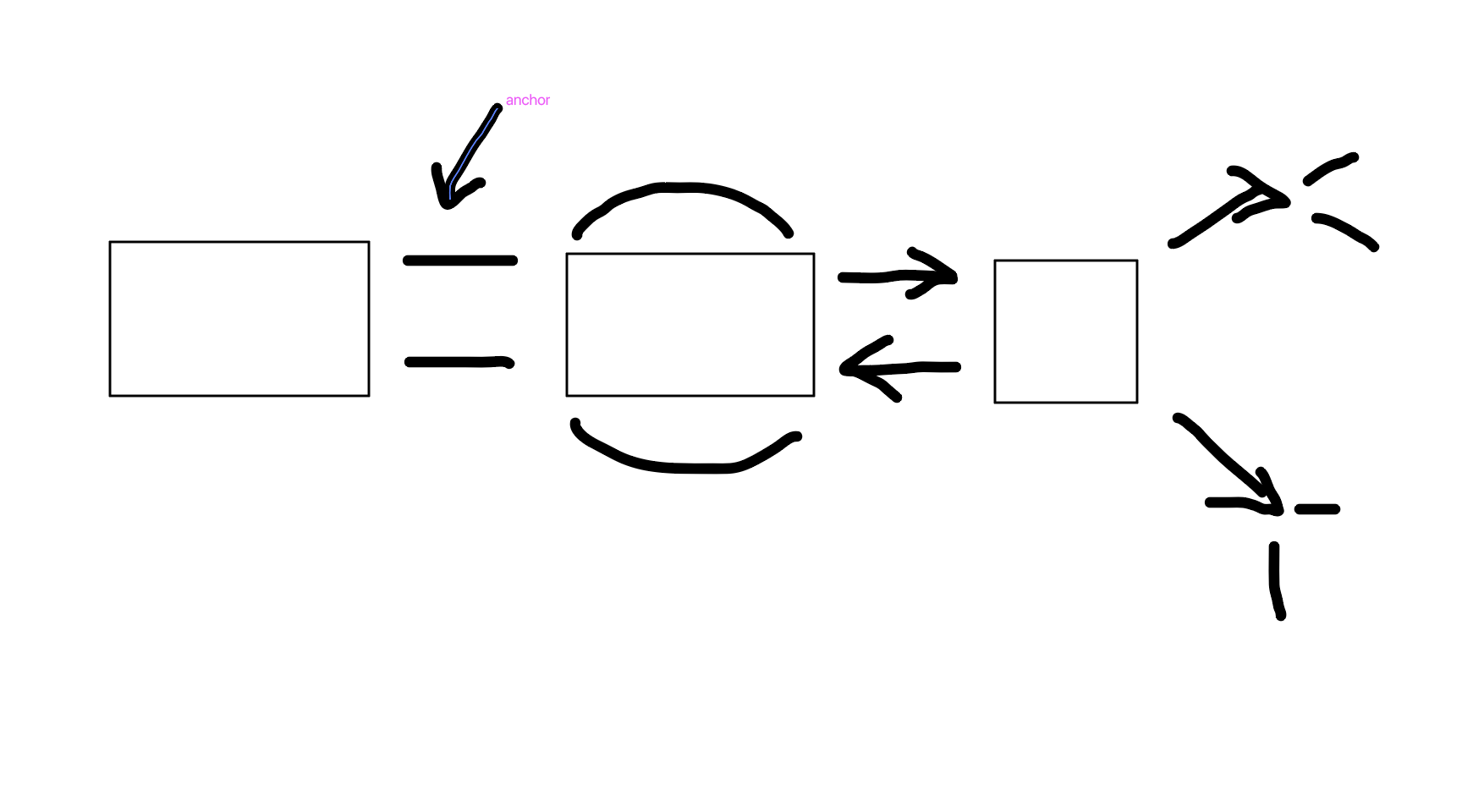
Auiditory loop
What is this
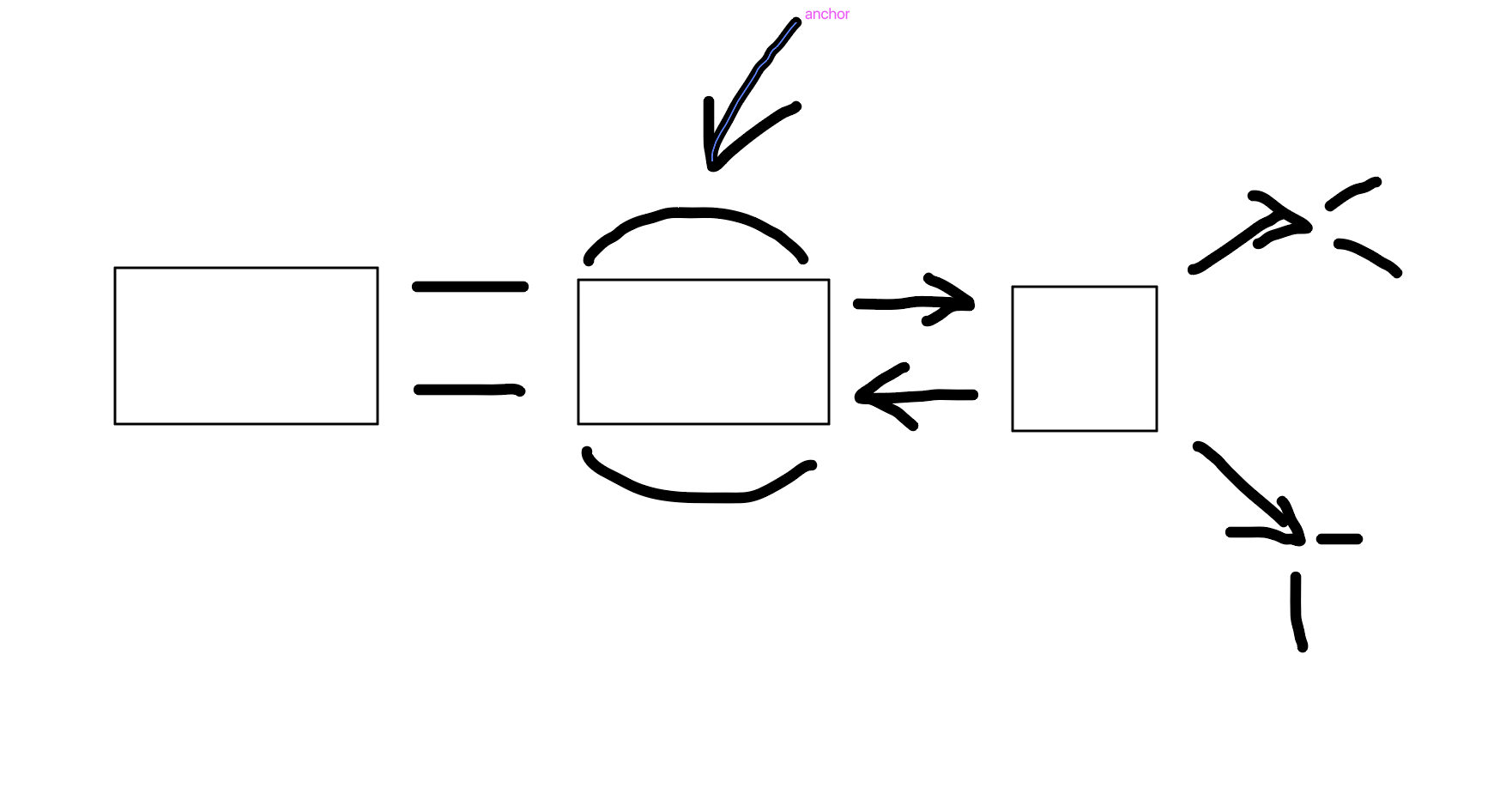
Visio spatial scratch pad
What is this
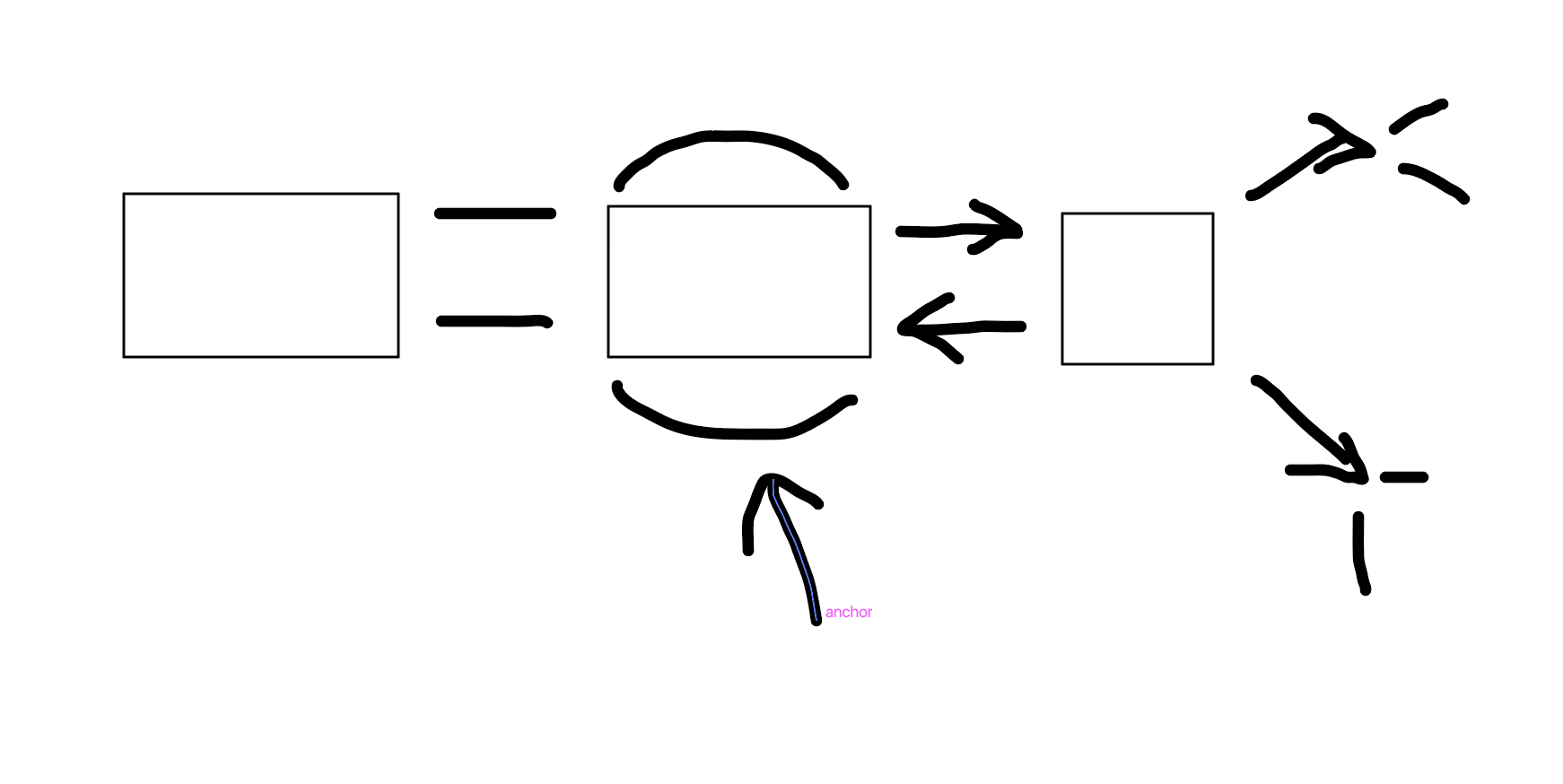
Working memory
What is this
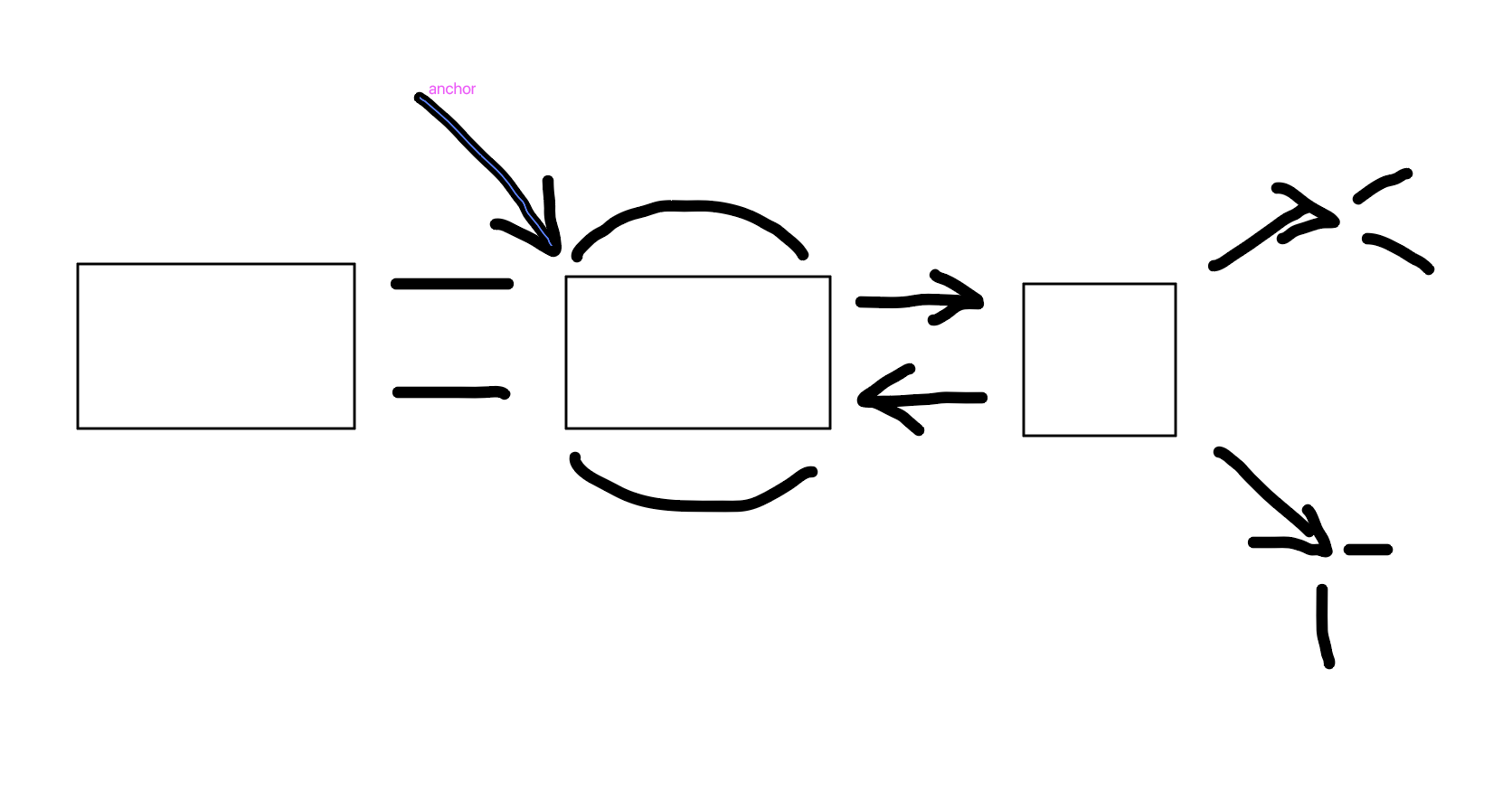
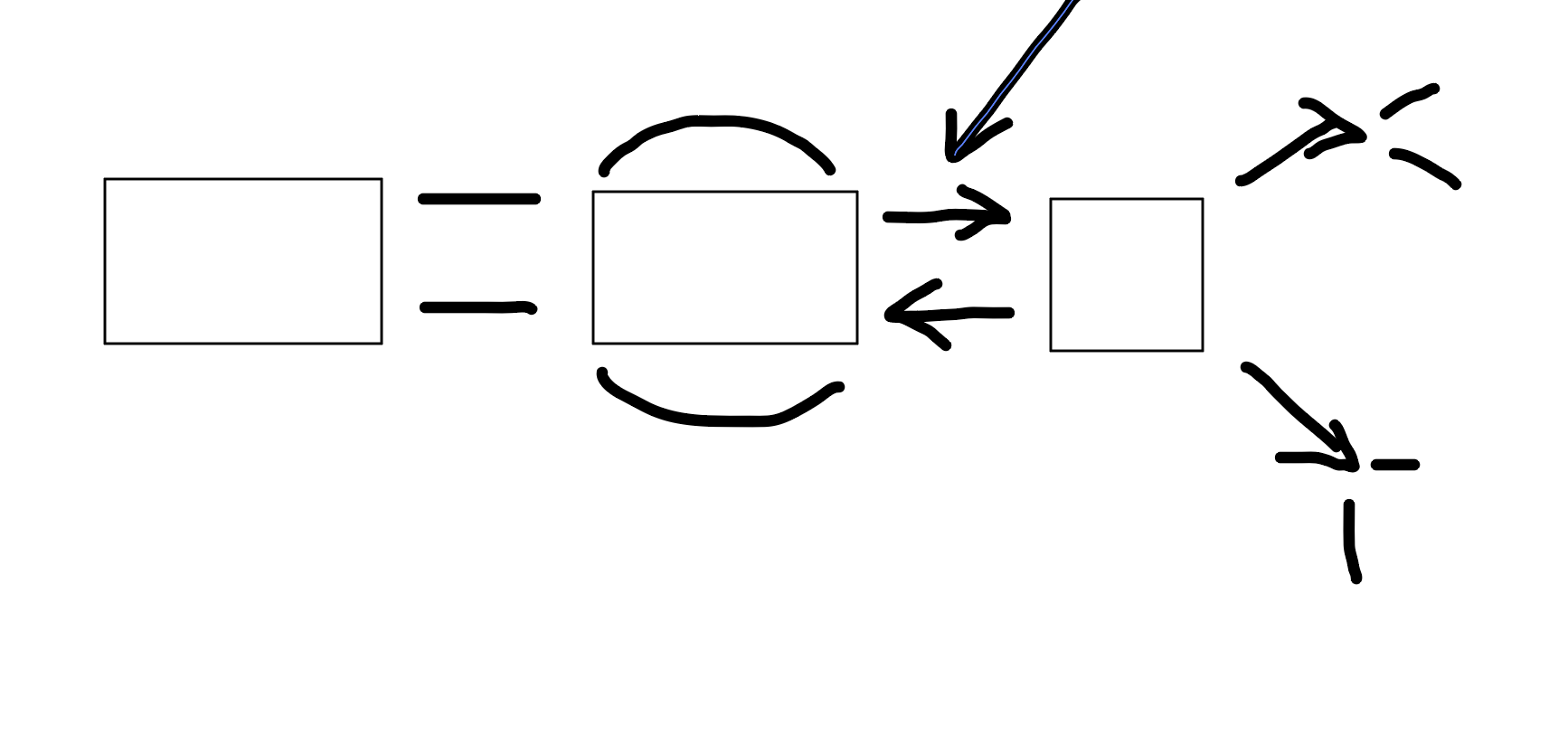
Encoding
What is this
Retreval
What is this
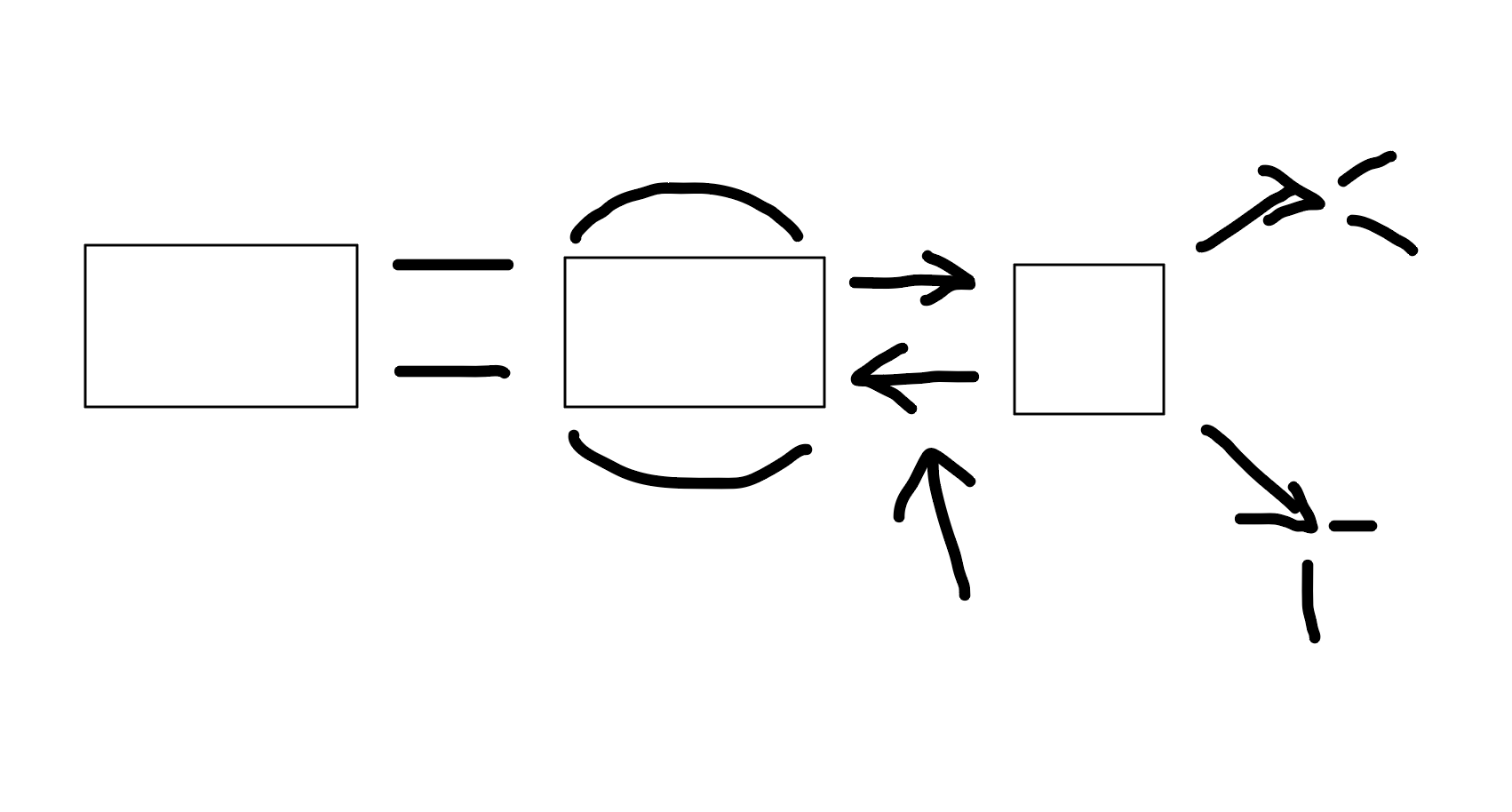
Long-term memory (LTM)
What is this
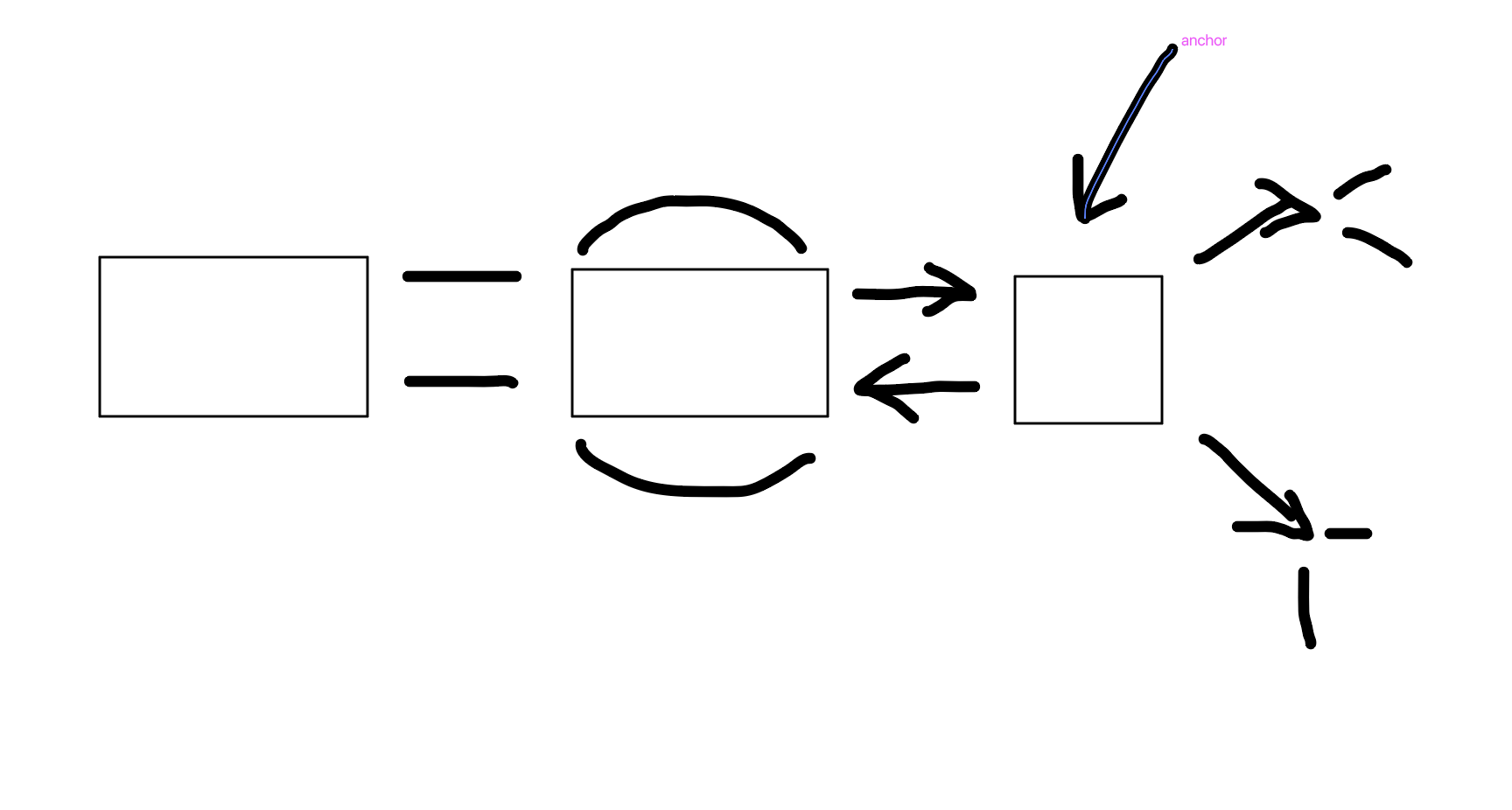
Implicit
What is this
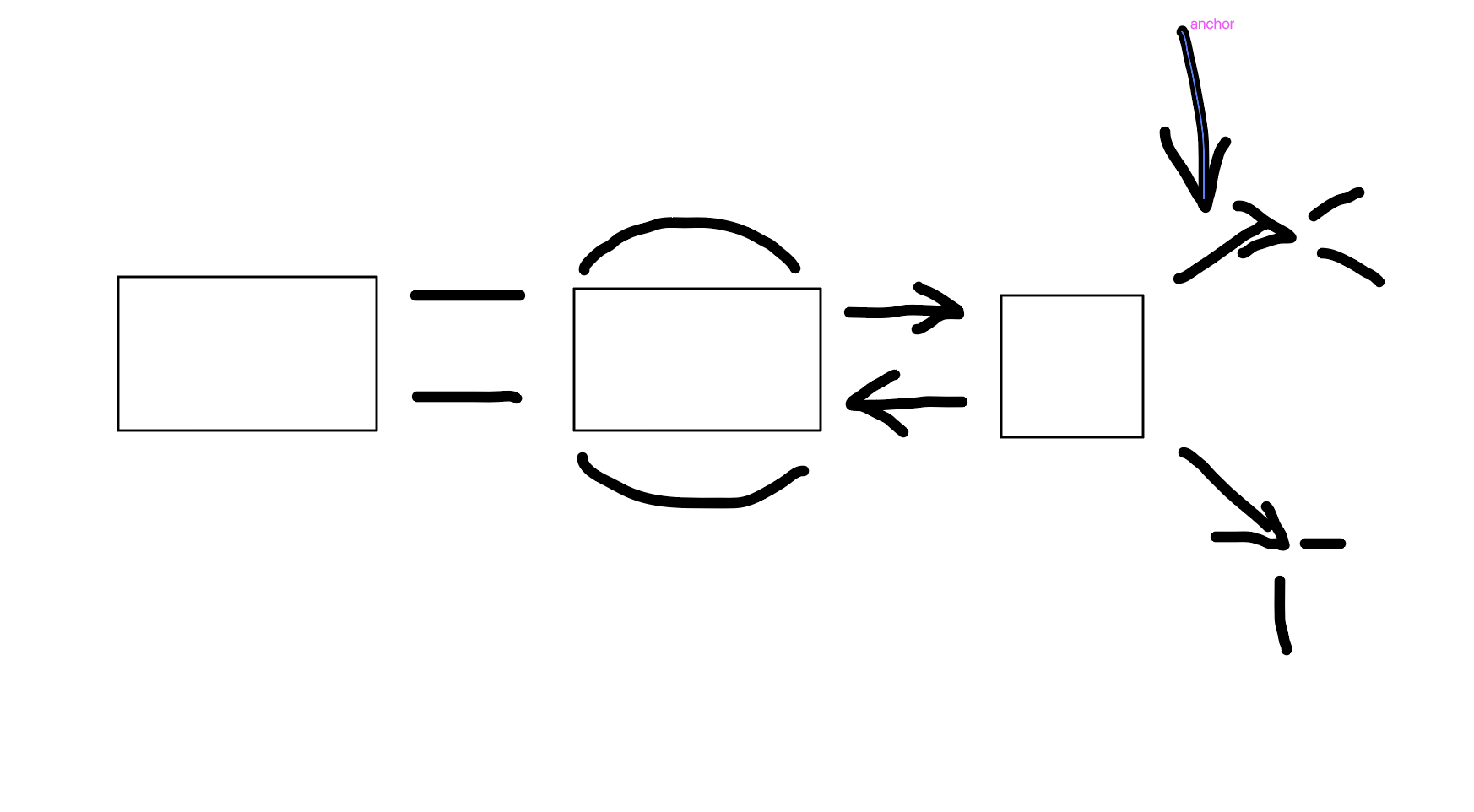
Explicit
What is this
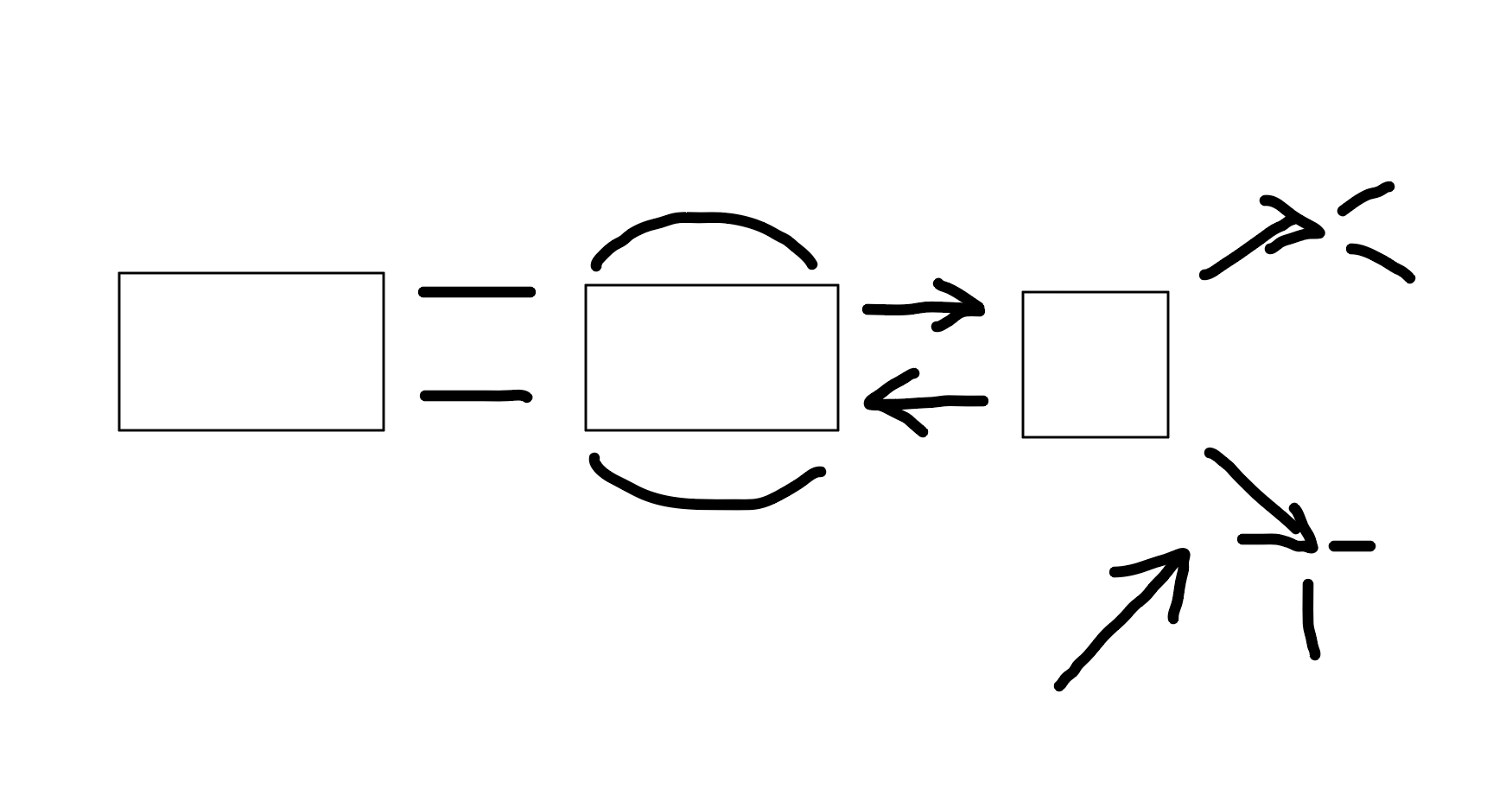
Procedural
What is this
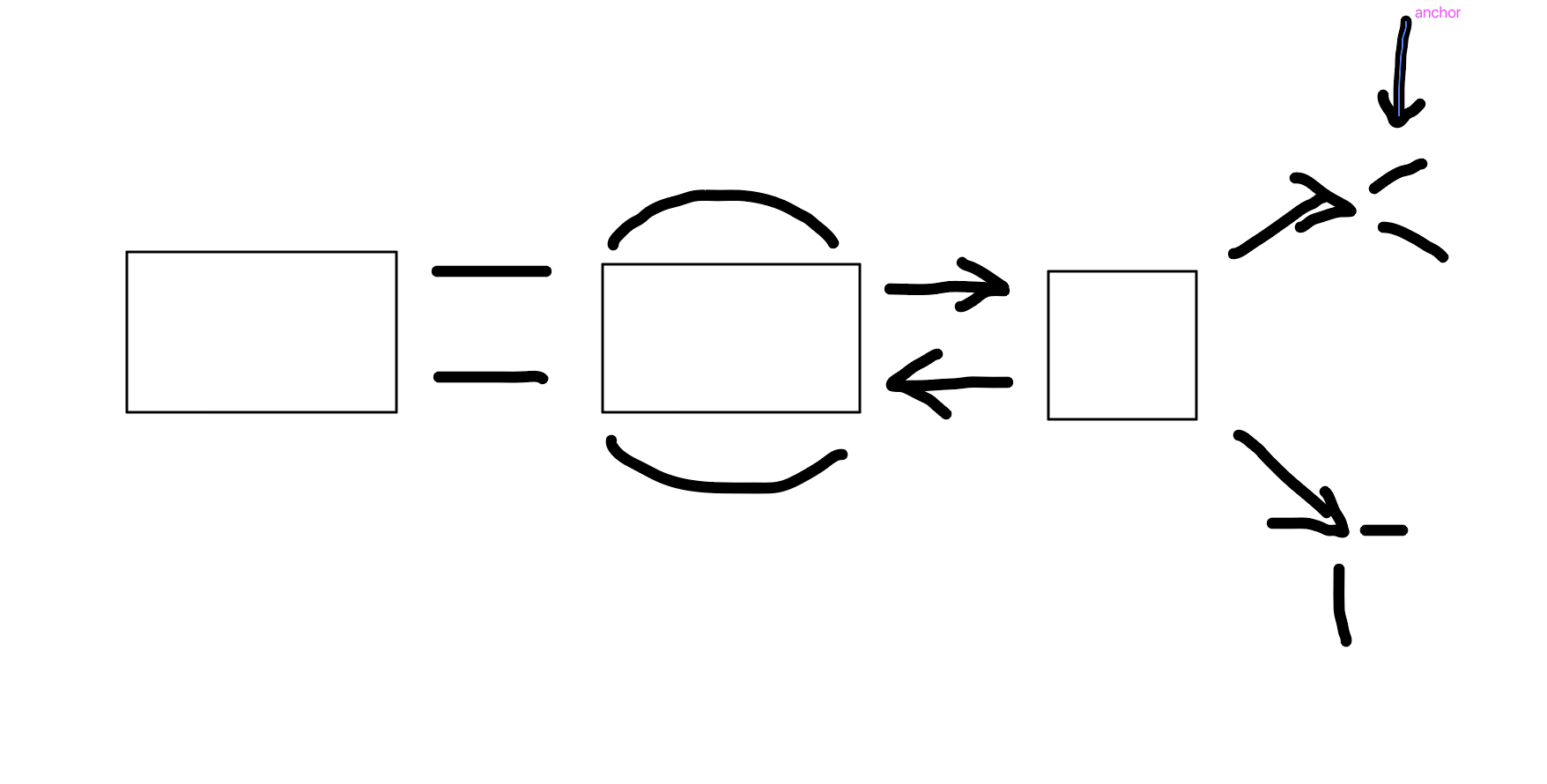
Aispositional
What is this
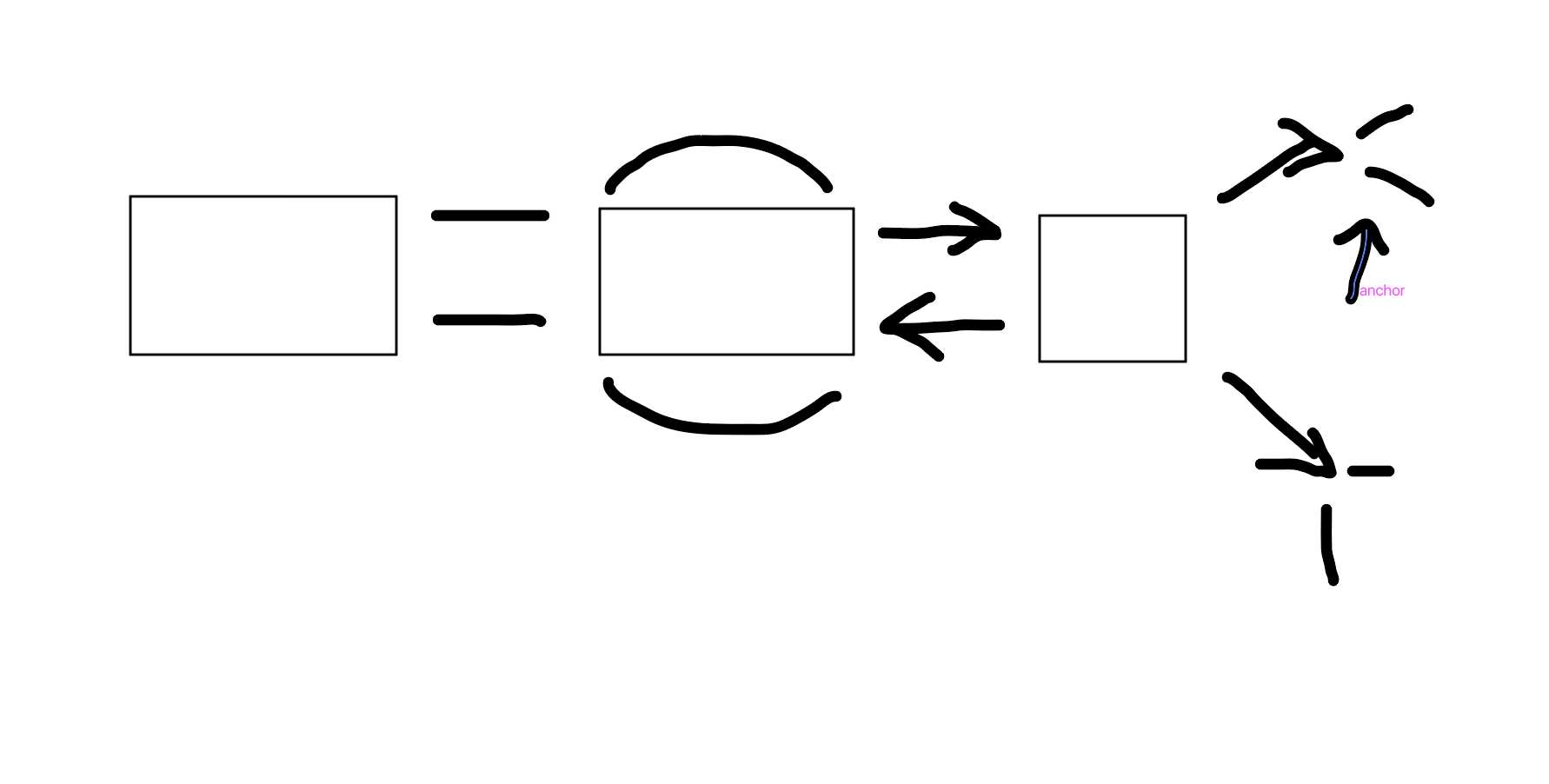
Sematic
What is this
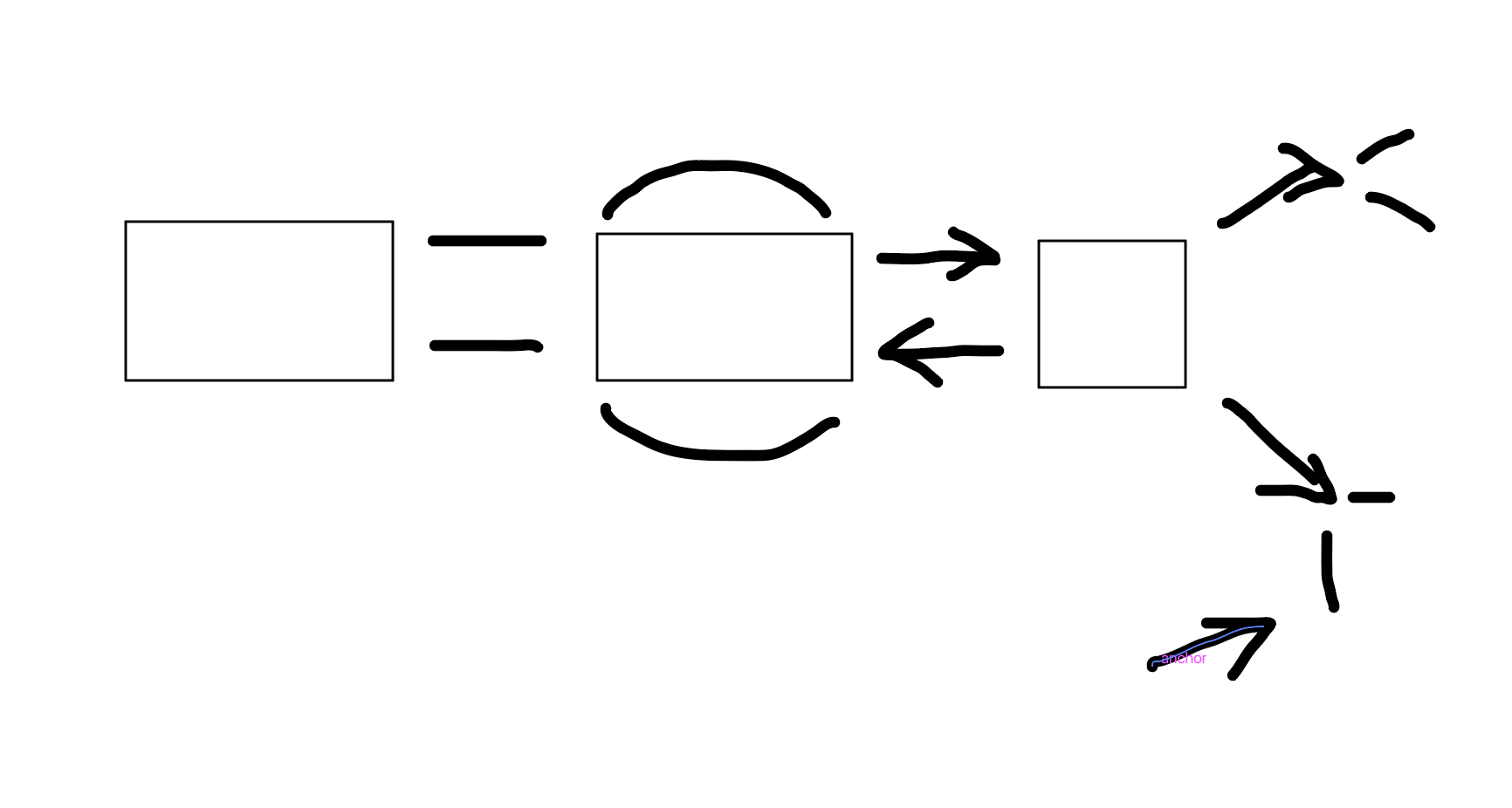
Episodic
What is this
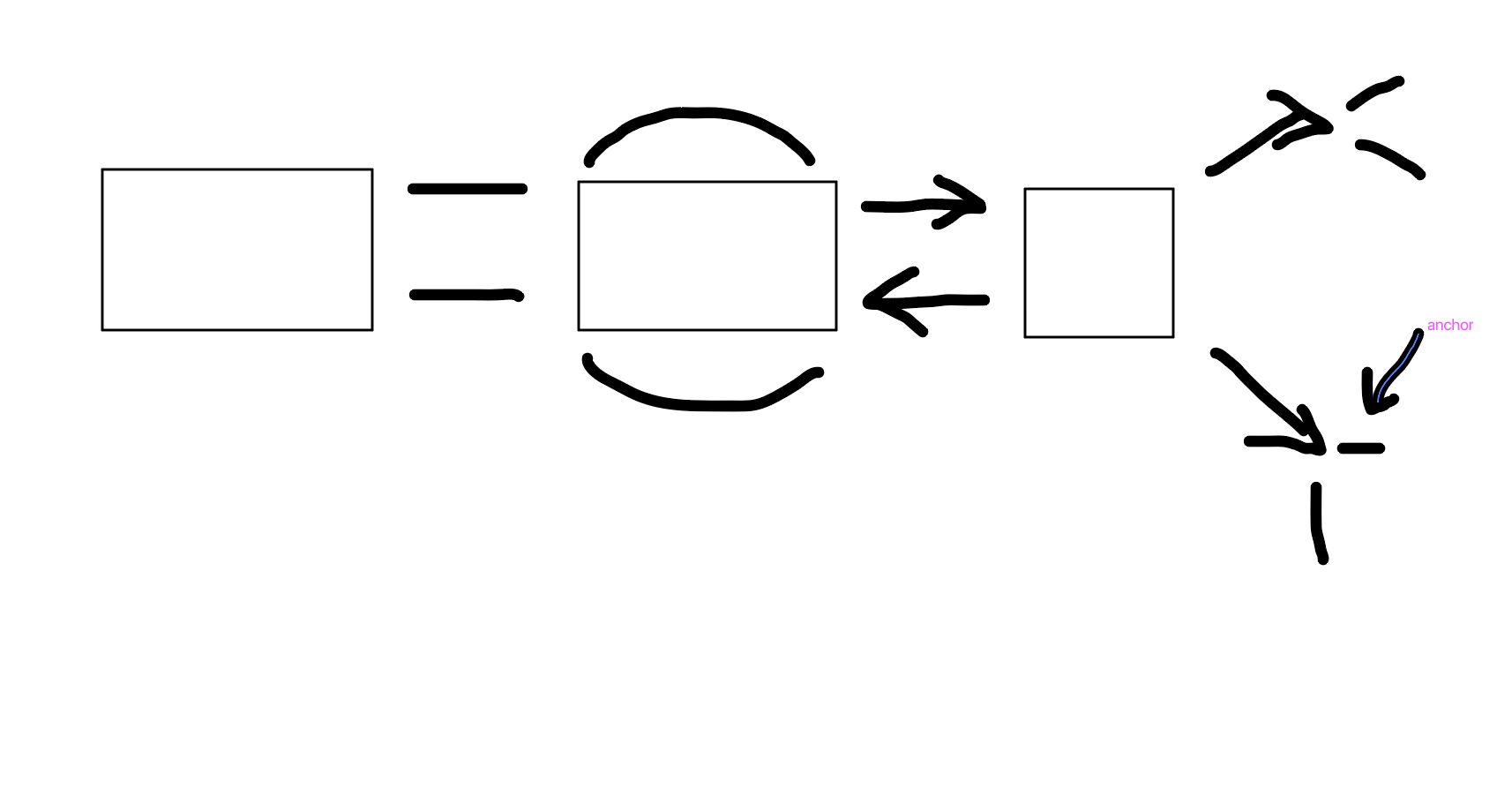
Long-term Memory (LTM)
The part of the memory system for storing information over extended periods, potentially indefinitely.
Implicit Memory
Unconscious memory, such as skills and habits.
Explicit Memory
Conscious recall of facts and events.
Procedural Memory
Memory for skills and actions, such as riding a bike.
Dispositional Memory
Memory related to personal traits or dispositions.
Episodic Memory
Memory of personal experiences and specific events.
Semantic Memory
Memory of facts and general knowledge.