APP Lecture 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Thoracic Cavity
Cavity between neck and abdomen
Contents of the thoracic cavity
Pulmonary anatomy
Cardiac anatomy
More
Mediastinum
Space between the pleura in the thoracic cavity
2 main parts of the mediastinum
Superior and inferior
3 parts of the inferior mediastinum
Anterior
Middle
Posterior
Superior border of the mediastinum
Superior thoracic aperture
Inferior border of the mediastinum
Diaphragm
Vertebral levels of the superior mediastinum
T1-T4
Vertebral levels of the inferior mediastinum
T5-T9
Separated into anterior, middle, and posterior
Vessels in the superior mediastinum
Superior vena cava
Brachiocephalic veins
Arch of the aorta (Brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery)
Thoracic duct
Nerves in the superior mediastinum
Phrenic
Vagus
Left recurrent laryngeal
Cardiac and Pulmonary Plexus
Viscera of the superior mediastinum
Esophagus
Trachea
Thymus
Inferior anterior mediastinum contents
Thymus remnant (sometimes)
Lymph nodes
Inferior middle mediastinum contents
Pericardium
Heart
Ascending aorta
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary trunk
Pericardiacophrenic vessels
Inferior posterior mediastinum contents
Esophagus
Thoracic duct
Thoracic aorta
Azygos and Hemiazygos veins
Vagus nerve
Esophageal plexus
Thoracic Splanchnic nerves
Sympathetic trunk
Fibrous Pericardium
Surrounds the heart and great vessels
Inelastic
Roots heart in thorax
Protects heart
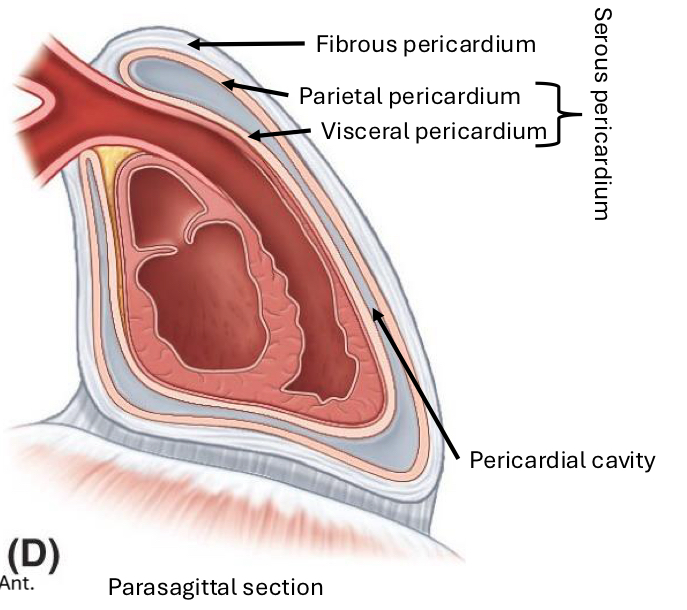
Serous Pericardium: 2 sections
Parietal and Visceral
Creates lubricated surface between both layers, reducing friction of the heart
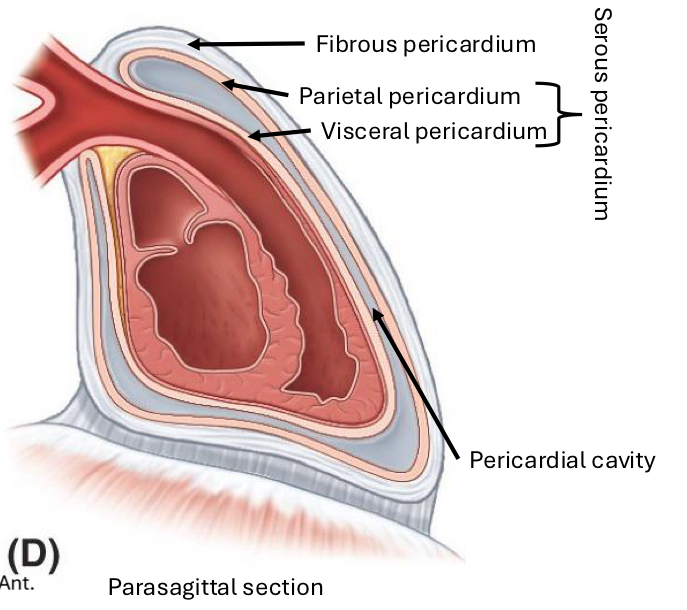
Parietal Serous Pericardium
Against the fibrous layer
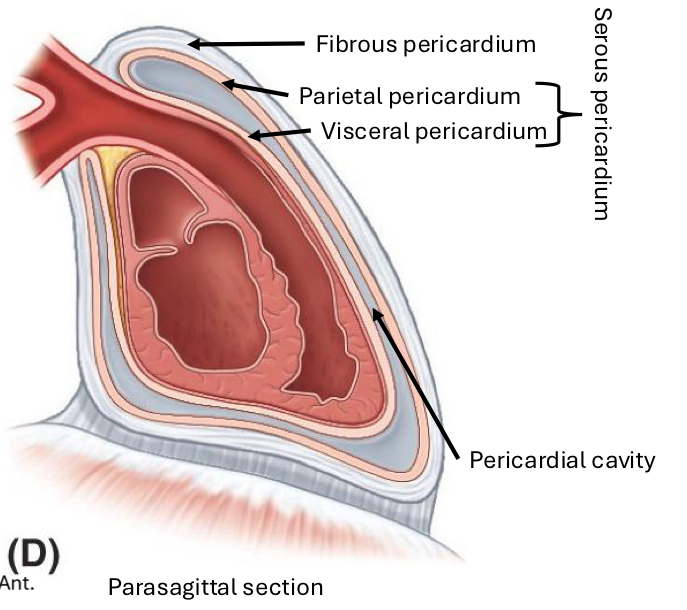
Visceral Serous Pericardium
Against heart and great vessels
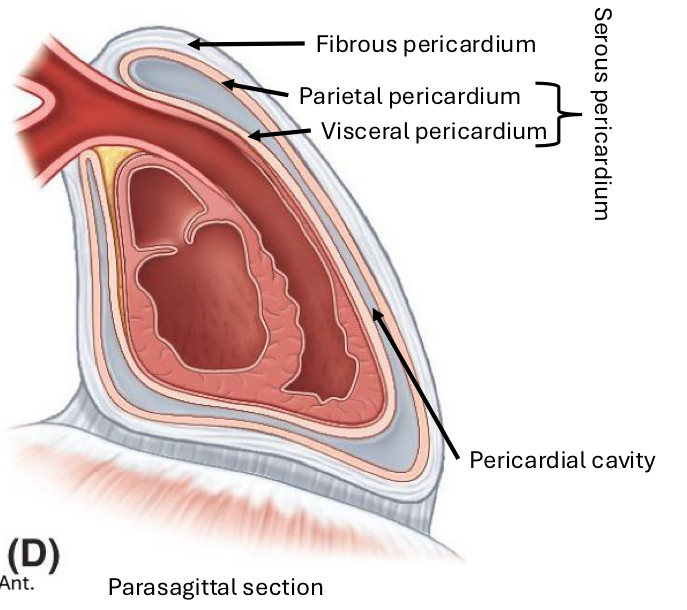
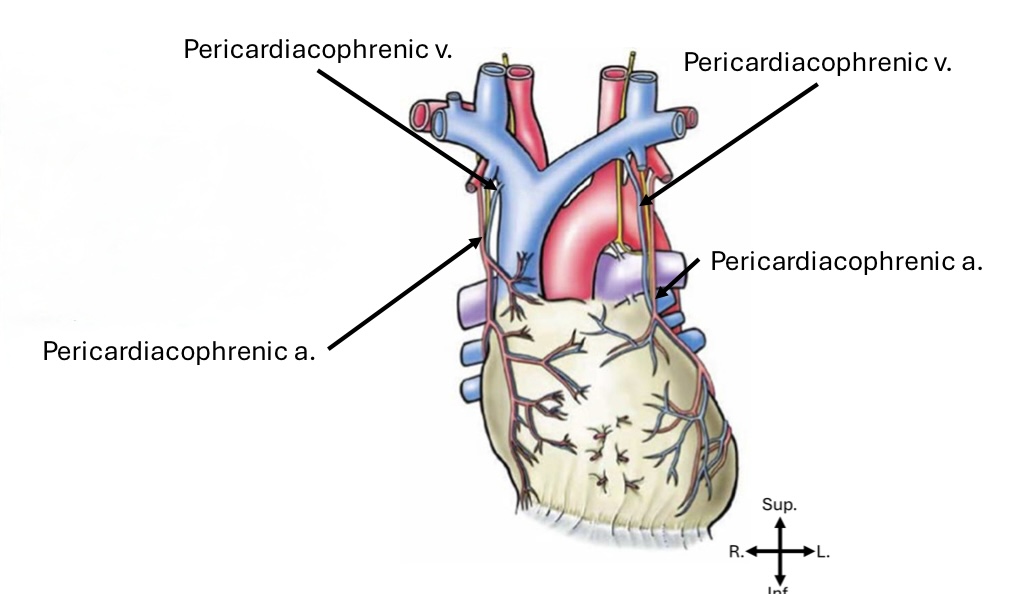
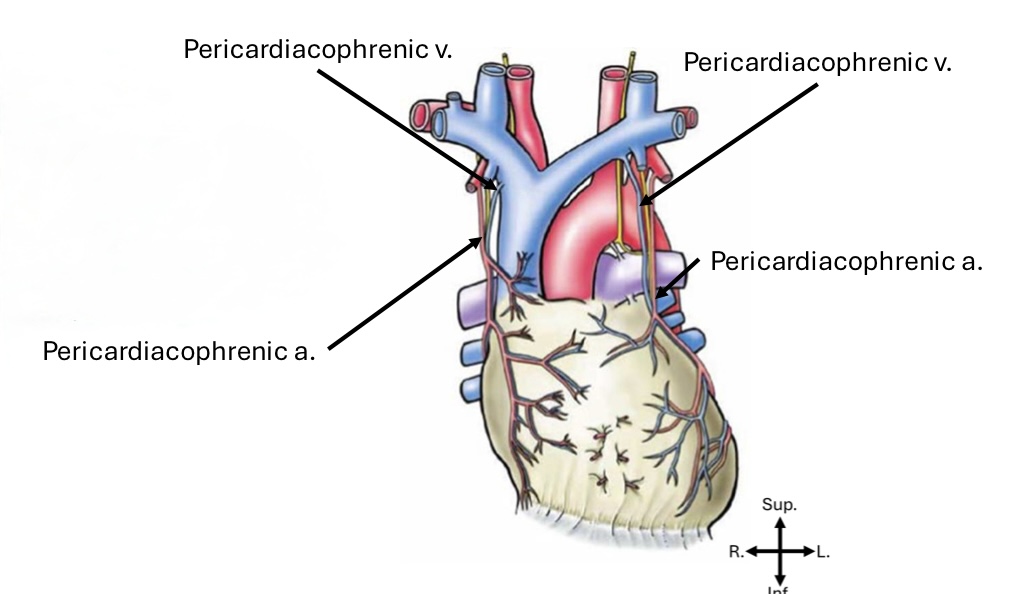
Pericardium primary arterial blood supply
Pericardiacophrenic artery
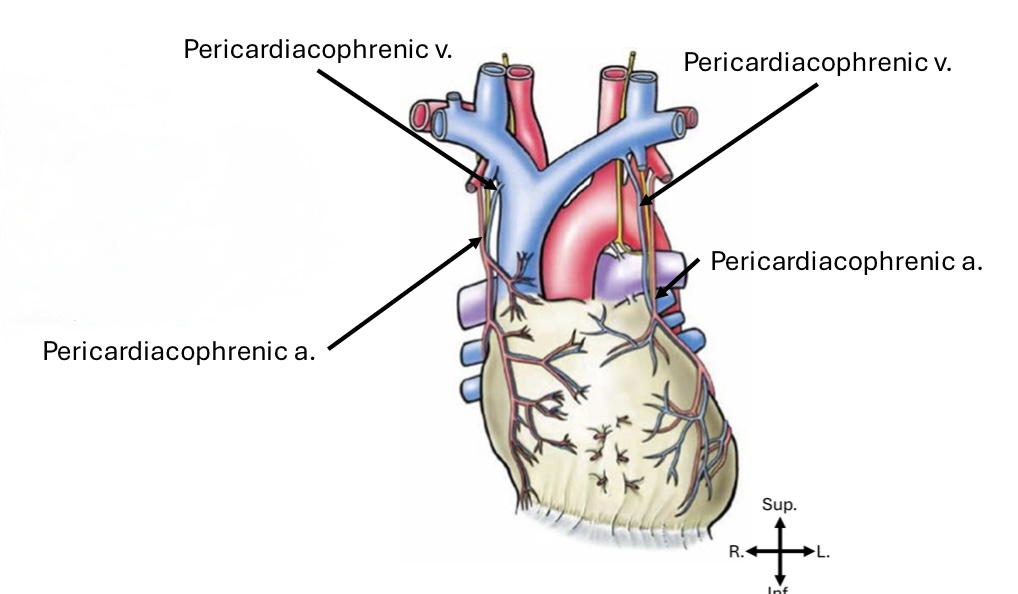
Pericardium primary venous blood return
Pericardiacophrenic vein
What provides blood supply for the visceral pericardium?
The coronary system
What provides general somatic afferent innervation to the pericardium?
Phrenic nerve
Where does phrenic nerve pain refer to?
Shoulder/neck/arm
C3-C5 dermatomes
What provides vasomotor innervation to the pericardium?
Sympathetic Trunk
Where is the heart located?
Inferior middle mediastinum
What shape is the heart?
Trapezoidal, roughly
What are the 4 chambers of the heart?
Right atrium
Left atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Which 2 heart chambers are receiving chambers
The right and left atrium
Which 2 heart chambers are discharge chambers?
The right and left ventricles
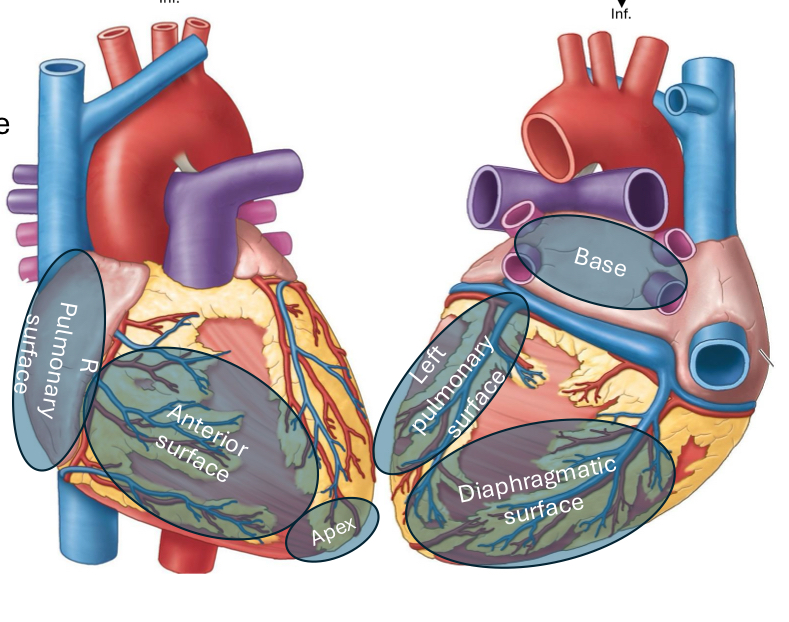
What is the anterior (sternocostal) heart surface formed by?
Mainly the right ventricle
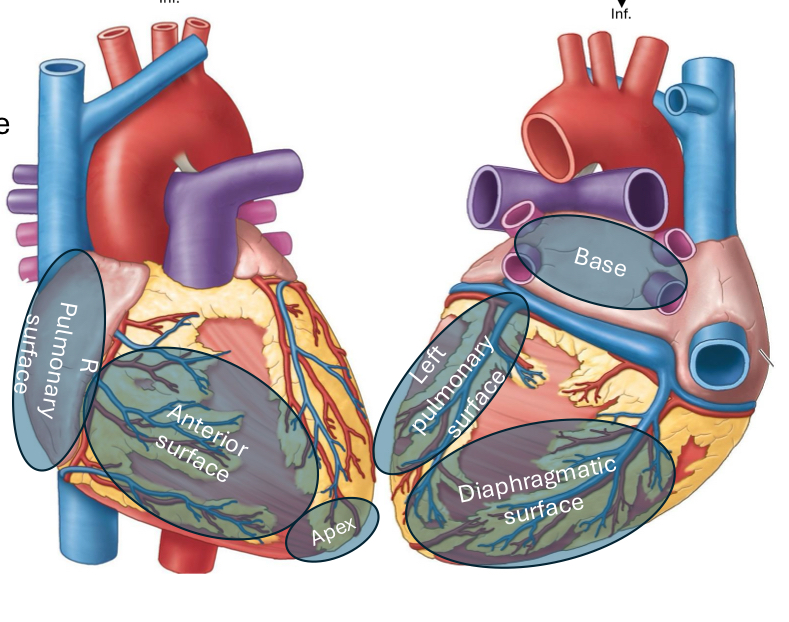
What is the diaphragmatic (inferior) heart surface formed by?
Mainly the left ventricle, partly the right ventricle
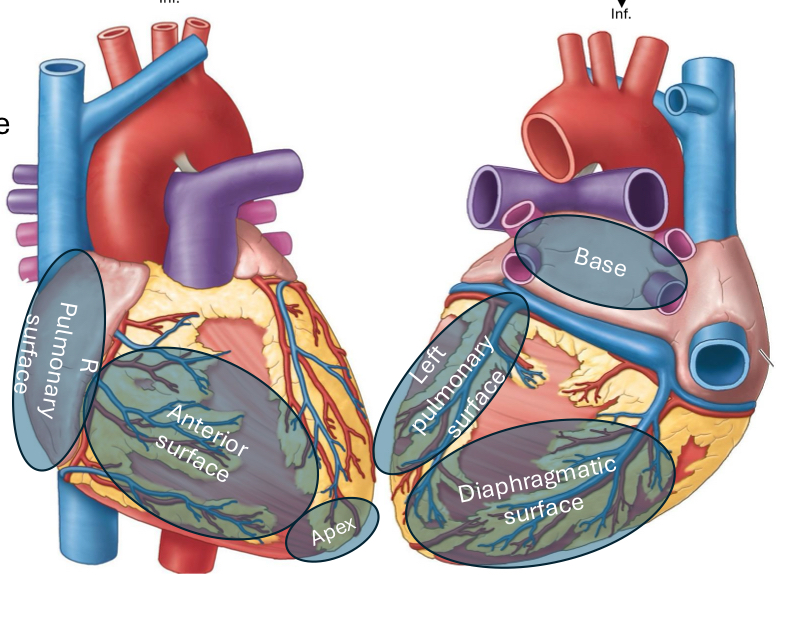
What is the right pulmonary heart surface formed by?
Mainly the right atrium
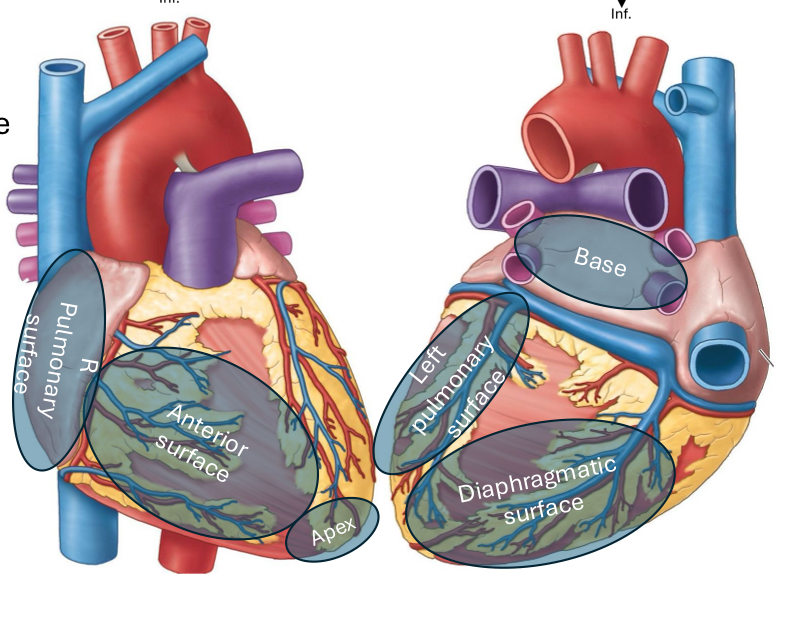
What is the left pulmonary heart surface formed by?
Mainly the left ventricle
What makes up the superior border of the heart?
Right and Left atria and auricles
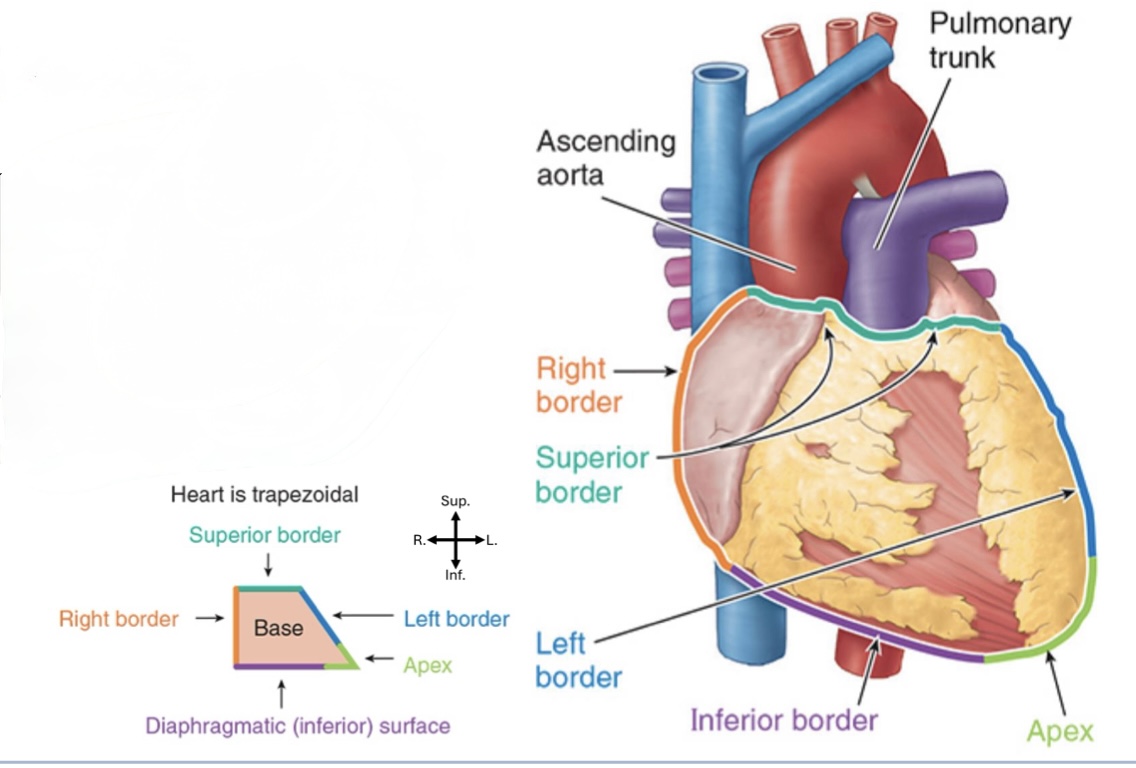
What makes up the inferior border of the heart?
Mostly the Right ventricle, some Left ventricle
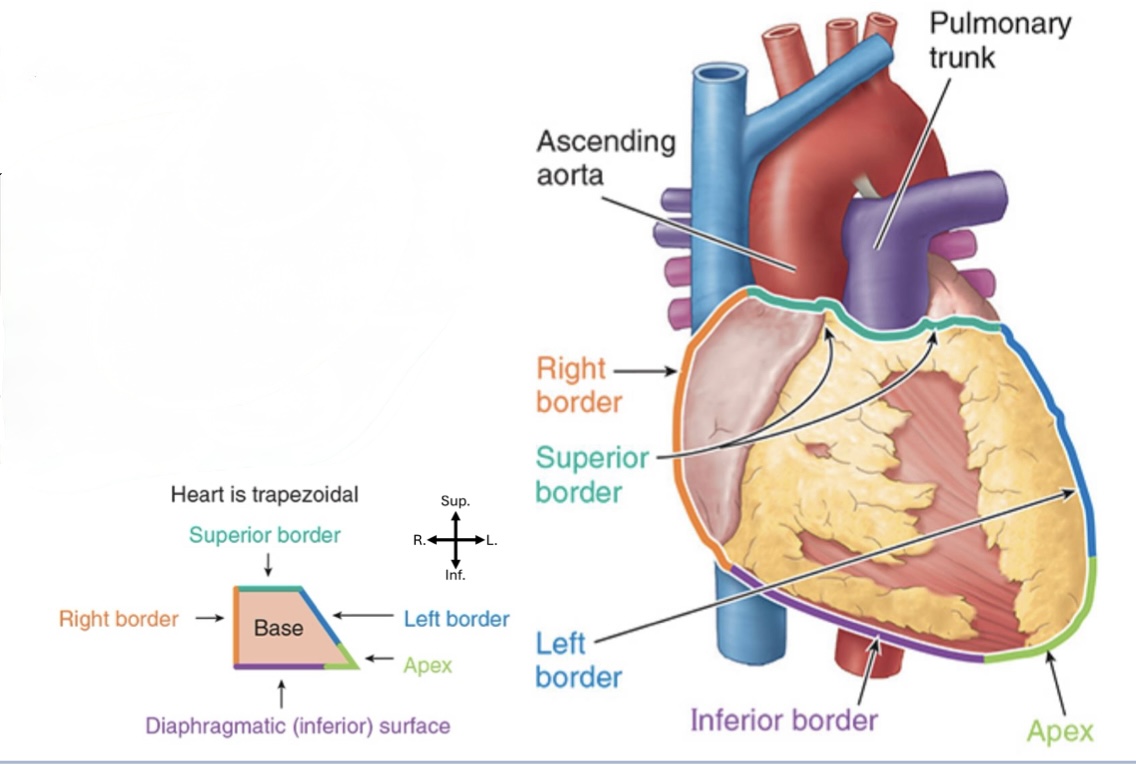
What makes up the right border of the heart?
Mostly right atrium
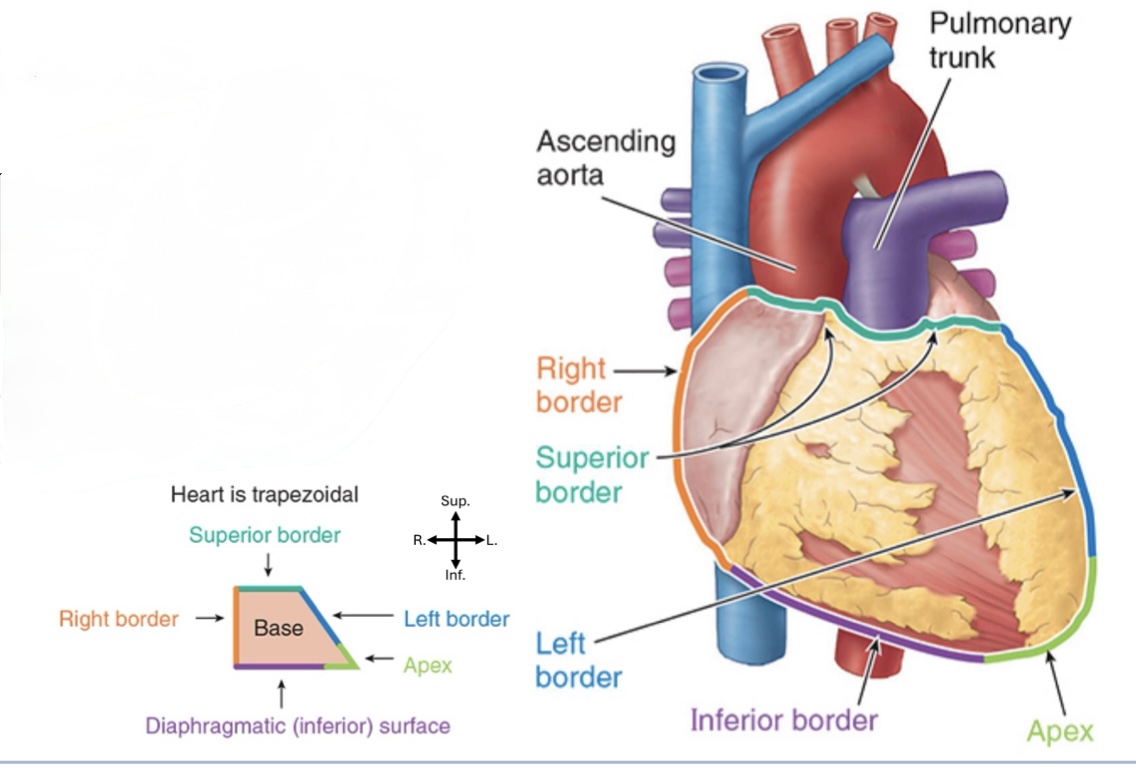
What makes up the left border of the heart?
Mostly left ventricle
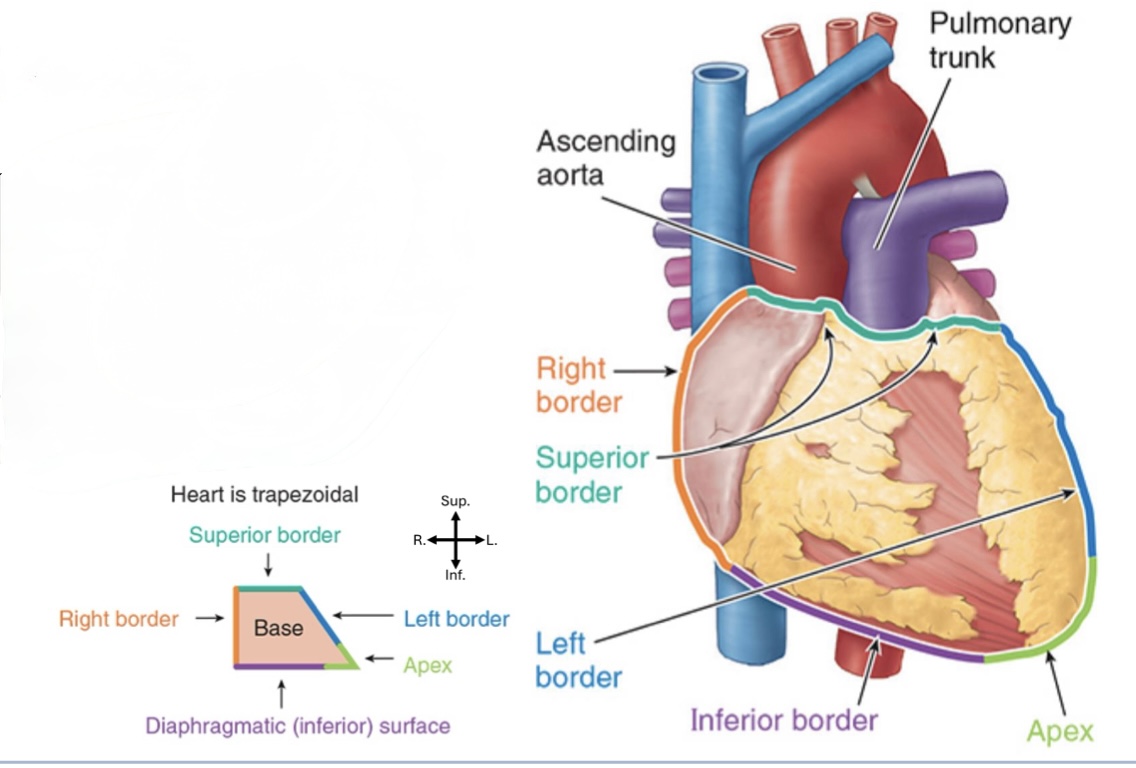
What makes up the apex of the heart?
Mostly left ventricle
How many layers of the heart wall?
3
What are the 3 layers of the heart wall?
Endocardium
Myocardium
Epicardium
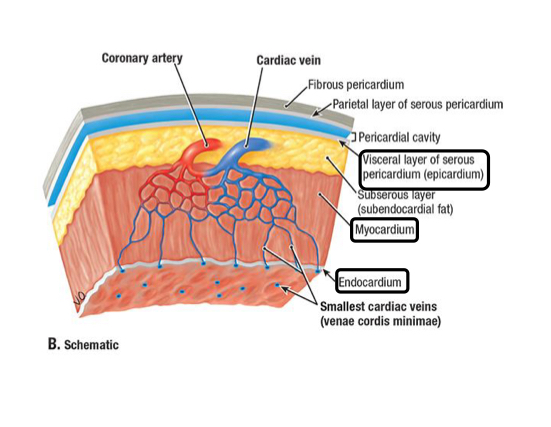
Endocardium
Inner layer of the heart wall made of epithelium and supporting connective tissue
Lubricates inner heart surface
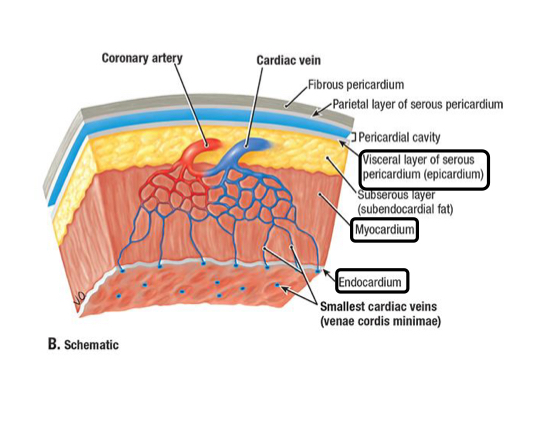
Myocardium
Muscled layer of the heart wall made of cardiac muscle
Provides the pumping force
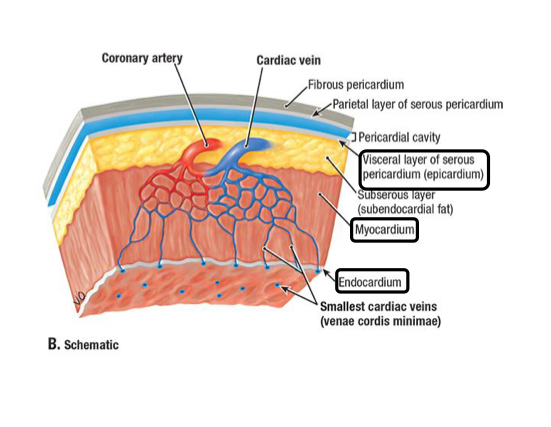
Epicardium
Outer layer of the heart wall made of visceral pericardium
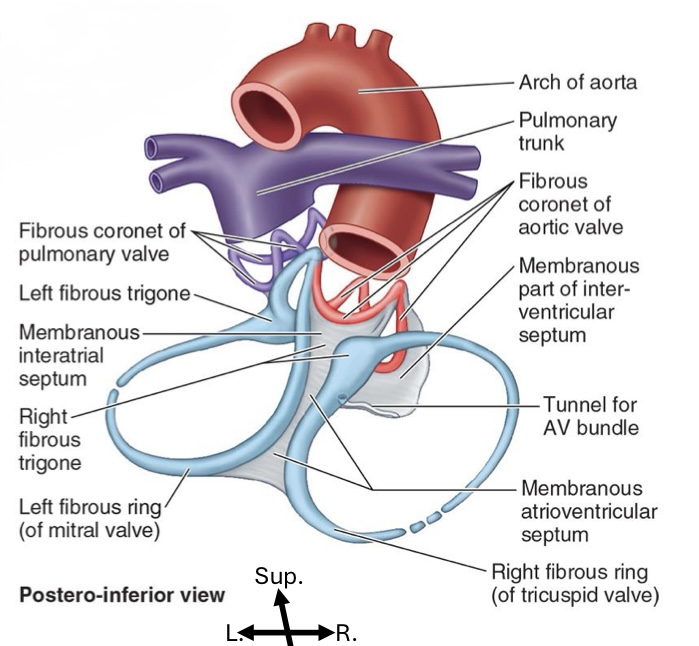
Heart “skeleton”
Fibrous support structure
Keeps valve openings patent
Valve leaflet attachment site
Anchors myocardium, allowing for its twisted loop form
Forms electrical insulator
Right atrium receives what type of blood from where?
The sinus venorum of the right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the superior and inferior vena cava and coronary sinus
Where does the right atrium pump blood to?
Right ventricle via atrioventricular orifice
What muscles form the anterior walls of the right atrium?
Pectinate muscles
What is the oval indentation in the right atrium?
Fossa ovalis
Where is Trabeculae carnae located?
In the right ventricle
What do the papillary muscles in the right ventricle do?
Contract to pull chrodae tendinae taught
What are the chordae tendinae in the right ventricle?
Connective tissue connecting papillary muscles to atrioventricular valves
Prevents valve buckle during systole
Where is conus arteriosus located?
Right ventricle
What kind of blood does the left atrium receive and from where?
Oxygen-rich blood from the 4 pulmonary veins
What does the left atrium do?
Pumps blood into the left ventricle
What kind of muscles are in the left atrium?
Pectinate muscles
What does the left ventricle do?
Pumps blood to the body through the aorta
What structures are in the left ventricle?
Papillary muscles
Chordae tendinae
Trabeculae carnae
Thick myocardium
Atrioventricular valves
Prevent backflow from ventricles into atria
Semilunar valves
Prevent backflow back into ventricles
Right Atrioventricular valve
Tricuspid
Prevent backflow into left atrium
Left Atrioventricular valve
Bicuspid
Prevent backflow into right atrium
Pulmonary Valve
Prevents backflow into right ventricle
Aortic valve
Prevents backflow into left ventricle
Opens into the right and left coronary arteries in respective sinuses
3 divisions of the cardiac plexus
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Afferent (visceral)
2 ways the heart is innervated
Via the cardiac plexus
Via the conduction system
Cardiac plexus
Convoluted nerves from Vagus nerve branches and sympathetic trunk (via splanchnic nerves)
Parasympathetic innervation
Derive from CN X branches
Synapse in local ganglia located on the cardiac structures
Stimulation results in reduced heart rate, output, contractile force
Visceral afferent associated with parasympathetics
Provide general visceral afferent innervation
Run from heart to medulla via vagal cardiac nerves
Sympathetic innervation
Presynaptic fibers in thoracic spinal nerves, run into sympathetic chain
Postsynaptic fibers exit trunk through cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves, go to targets in heart
Stimulation results in increased heart rate, increased blood pressure and pulse
Visceral Afferent innervation
Provide general visceral afferent innervation
Run from heart to medulla via splanchnic nerves into the spinal cord at T1
Conduction system
Anterolateral wall of right atrium near SVC
Initiates impulse conducted to muscles, causing contraction in atria
Impulse spreads rapidly
Conduction system signaling pattern
Signals arrive at AV node
SA node impulse disturbed from AV node through AV bundles and their branches
Left and right bundles give off Purkinjie fibers that stimulate papillary muscles and the walls of the ventricles