OTM Refraction
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Refraction purpose
Determine refractive status of the pt. using pt’s input
Manifest refraction is objective or subjective?
Subjective
Succesful refractions require a high level of clinician subjectivity
-How the doctor judges the pt’s responses
Goal of subjective refraction
Improve patient’s vision to BEST CORRECTED
Vast majority of patients, goal is 20/20 acuity in each eye
However, many patients are unable to see 20/20 due to
Retinal disease
Media opacity
Ambylopia (refractive/strabismic)
Neurological issues
If you can’t get your patient to see 20/20
Secondary cause of decreased VA MUST be explained
Name some objective and subjective findings needed to create the final prescription
Patient visual complaints
Patient daily visual demands
Habitual RX- What are they wearing/ how are they wearing it
Visual acuity measurements (uncorrected or through habitual Rx)
Some pts. are unable to provide accurate responses, and should not perform manifest refraction on them
Name the type of pts
Very young children
Non-verbal patients
Intellectual disabilities
Malingering patients - use other tests to help determine if a pt. is malingering
Refractive analysis begins with
History
Refractive analysis
Myopic symptoms
Blurred distance vision, esp. in dim illumination
Report holding objects closer or moving closer to see
Report needing to squint to see
Push glasses back toward face
Refractive analysis
Hyperopic symptoms
Vary greatly by age and magnitude of error
Adults = trouble reading
Large magnitude or older adults = blurred distance vision
Young adults = intermittent blur, esp when fatigued or in poor lighting
-Headaches with near work (esp. prolonged) frequent
-worsens as day progresses
-Diplopia at near possible
Children/teens = no visual complaints, but may avoid near work
Pull glasses down nose
Refractive analysis
Astigmatism symptoms
Vision complaints present at BOTH distance and near
-May be worse at one or the other
Head-tilting with oblique axis possible
Squinting common
Ghosting or doubling of images
Low astigmatic errors usually have good vision, but not tired eyes when doing detail oriented work
Higher astigmatism = poorer acuity
Refractive analysis
Reduced vision at either distance or near
Refractive error likely the culprit
Refractive analysis
Reduced vision at BOTH distance AND near
Refractive error possibly the culprit
Refractive analysis
Pinhole testing gives an idea if
Pt’s vision will improve with refraction
Refractive analysis visual acuity
Myopia
Simple myopia each line of decreased acuity =
0.25 D minus sphere power
Refractive analysis visual acuity
Myopia
Compound myopia each line of decreased acuity =
0.25 D minus spherical equivalent power
Spherical equivalent = sphere power + ½ (cylinder power)
Refractive analysis
Example:
VA 20/50
Find the total error
20/20 → 20/25 → 20/30 → 20/40 → 20/50
-0.25 -0.25 -0.25 -0.25
Total error = -1.00 D
Refractive analysis visual acuity
Hyperopia:
Very challenging to estimate based on VA
Refractive analysis visual acuity
Hyperopia:
Young patients with active accomodation may have
Good distance acuity with large refractive errors
Presbyopes experience decreased ____ and ____ vision
Can estimate ___D to ___D increased power per line of decreased vision
Not as ____ as a change in myopes
Presbyopes experience decreased distance and near vision
Can estimate +0.25 D to +0.50 D increased power per line of decreased vision
Not as linear a change as myopes
Refractive Analysis: Visual acuity
Astigmatism
Low amounts have ___ impact on acuity
Uncorrected ATR astigmatism has ____ impact on acuity than WTR of the same amount
Oblique has _____ impact on acuity
Estimation includes both ____ and ____ of astigmatism
Astigmatism
Low amounts have little impact on acuity
Uncorrected ATR astigmatism has greater impact on acuity than WTR of the same amount
Oblique has highest impact on acuity
Estimation includes both amount and orientation of astigmatism
What questions about Lensometry should you ask in Refractive analysis
What prescription is the patient currently wearing?
Is the patient wearing their glasses correctly?
Refractive analysis
Lens effectivity
Change in ____ of light occuring at different points along the path
Effective lens power depends on the _____ in ___ of the eye
Change in vergence of light occurring at different points along the path
Effective lens power depends on the location in front of the eye
Refractive analysis
Lens effectivity
Pushing a lens closer to the eye = _____ power
Pushing a lens closer to the eye = Minus power
Minus lens = more ____ power
Plus lens = less _____ power
Minus lens = more MINUS power
Plus lens = less PLUS power
Moving a lens away from the eye =
Minus lens = less ____ power
Plus lens = more ____ power
Moving a lens away from the eye = More PLUS power
Minus lens = less minus power
Plus lens = more plus power
You finished refractive analysis and have results of history, acuity, and lensometry
What 3 questions should you ask before doing refraction
Does the patient’s acuity correspond to the patient’s symptoms?
What type of refractive error might account for the pt’s complaint?
If acuity is decreased with current Rx, what type of change should improve vision?
Having hypothesis on what you expect the end results helps evaluate the
Reliability of the patient’s responses
- Prevents the patient from controlling the exam
Pt. complaint
“I feel like I can’t see well when I drive home at night”
What are the possibilities?
Myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism
Pt. complaint
“I feel like I can’t see well when I drive home at night”
Visual acuity: 20/30 distance, 20/20 near
What are the possibilities?
Myopia
Pt. complaint
“I feel like I can’t see well when I drive home at night”
Visual acuity: 20/30 distance, 20/30 near
What are the possibilities?
Hyperopia, astigmatism
Young patients have a ____ amount of hyperopoia
Old patients have a ______ amount of hyperopia
Moderate amount of hyperopia
Small amount of hyperopia
Pt. complaint
“My eyes feel tired after working on the computer all day”
What are the possibilities?
Hyperopia, astigmatism
Pt. complaint
“My eyes feel tired after working on the computer all day”
Visual acuity: 20/20 Distance, 20/30 Near
What are the possibilities?
Hyperopia
Pt. complaint
“My eyes feel tired after working on the computer all day”
Visual acuity: 20/30 Distance, 20/25 Near
What are the possibilities?
Astigmatism
Just noticeable difference (JND) - aka which is clearer 1 or 2?
JND is the amount of _____ change at which a difference in ____ or ____ should be appreciated
JND is the amount of optical change at which a difference in clarity or blur should be appreciated
To estimate the JND the denominator of ___ ___ is divided by ___
The denominator of Snellen acuity is divided by 100
20/200
How many D of JND is needed?
What do you show a patient a difference with cross cylinder lens?
20/200 → 200/100 = 2.00 D JND is needed
In order to show a patient a difference of 2.00 D a cross cylinder lens with +/- 1.00 D is needed
20/50
How many D of JND is needed?
What do you show a patient a difference with cross cylinder lens?
20/50 → 50/100 = 0.50 D JND is needed
In order to show a patient a difference of 0.50 D a cross cylinder lens with +/- 0.25 D is needed
What does the phoropter having a set JCC lens usually 0.25 or 0.50D correlate with the patient’s VA?
Patient needs to have a minimum VA to proceed with standard phoropter refraction techniques
What if the patient does not have the minimum VA necessary?
Need to move on to a Trial frame refraction
Setup Target Lighting
Both eyes are OPEN, pt. not wearing habitual rx, head straight
Target: Distance Visual acuity chart
Lighting: Dim room illumination
If hard to see, turn on stand lamp after completing retinoscopy (behind patient)
——allows you to see what you’re doing, allows for more natural pupil size
Refractive determination steps
Gross sphere power determination
Cylinder axis refinement
Cylinder power refinement
—-Cylinder power search if no cylinder was found during retinoscopy
Sphere power refinement
Gross sphere power determination
Always start with right eye unless
For a specific reason (monocular patient, large macular scar, etc.)
Gross sphere power determination
Fog the patient to at least 20/___ for a 20/20 patient or at least ___ lines above the starting VA
Fog the patient to at least 20/40 for a 20/20 patient or at least 2 lines above the starting VA
Gross sphere power determination
Patients perceive more minus power as clearer vision because it makes the image darker
Smaller/darker = stimulating ______
Leads to trouble with ____ vision or headaches
Ask the patient if the vision is ____ with every increment
Smaller/darker = Stimulating accomodation
Leads to trouble with near vision or headaches
Ask the patient if the vision is CLEARER with every increment
Use terminology; CLEARER
Never say better
Goal of gross sphere power determination
What VA is needed from patient to complete step 1?
If patient cannot see 20/50 questions you should ask yourself?
Most plus (least minus) power to best visual acuity
Patient needs a VA of 20/50 or better
What were the pinhole results? Is the patient capable of seeing 20/40?
Repeat retinoscopy
Look at pts. habitual Rx- was there astigmatism? Where?
JCC theory:
Consists of? Two _____ cylinders of ____ power but _____ signs 90 degrees apart
Oriented?
- Red dots represent ____ cylinder
- White dots represent ____ cylinder
Consists of two opposing cylinders of equal power but opposite signs
90 degrees apart
- Red dots represent minus cylinder
- White dots represent plus cylinder
JCC allows for refinement of patient’s
What is the spherical equivalent of lens?
JCC will produce a resultant ____ correction
Cylinder power and axis
ZERO
Resultant cylinder correction
Interval of sturm either expands or contracts depending on the orientation of the ___ lens and the patient’s ___ ____
Interval of sturm either expands or contracts depending on the orientation of the JCC lens and the patient’s refractive error
Starting lens that is not the patient’s cylinder correction - once choice will be perceived as _____
Starting lens that is the patient’s cylinder correction -
both choices will be equally ____ or equally _____
Starting lens that is not the patient’s cylinder correction - once choice will be perceived as clearer
Starting lens that is the patient’s cylinder correction -
both choices will be equally clear or equally blurred
If VA is 20/25 = isolate 20/
If VA is 20/20 = isolate 20/
Rotate the JCC lens in front of the right eye with the _____ coincident to the minus cylinder axis position
20/40
20/30
If pt. unable to see the line that is isolated, move to a larger line
Rotate the JCC lens in front of the right eye with the handle coincident to the minus cylinder axis position
In cylinder axis refinement we chase the
If pt. indicates the lens is clearer in the same direction, continue to move the lens in __ degree increments
If pt. indicates the lens is clearer in the opposite direction, move the axis in the opposite direction by _
chase the red
15 degree increments
5 degree increments in opposite direction
In cylinder power refinement align the P with the ____ ____
The JCC lens should ____ the pt’s view of the isolated line slightly. Confirm how?
axis arrows
(doesn’t matter if its a red or white dot)
The JCC lens should blur the pt’s view of the isolated line slightly. Confirm by asking the pt. if they can read the line
If the red dots line up with the arrow and provide clearer vision - add __D cylinder
If the white dots line up with the arrow and provide clearer vision - take away _ D cylinder
If the red dots line up with the arrow and provide clearer vision - add -0.25 D cylinder
If the white dots line up with the arrow and provide clearer vision - take away -0.25 D cylinder
Cylinder power refinement
Maintaining ______ equivalent
Spherical equivalent =
Every 0.50 D change in cylinder power corresponds to a 0.25 D change in ___ power in the opposite direction
- Add -0.50 D cyl, need to add ____D sphere
- Take away -0.50 D cyl, need to add ____D sphere
Cylinder power refinement
Maintaining spherical equivalent
Spherical equivalent = sphere power + ½ cylinder power
Every 0.50 D change in cylinder power corresponds to a 0.25 D change in sphere power in the opposite direction
- Add -0.50 D cyl, need to add +0.25 D sphere
- Take away -0.50 D cyl, need to add -0.25 D sphere
Maintaining spherical equivalent in Cylinder power refinement moves the CLC closer to?
If you just change cylinder power, you move the ____ of retina
Moves the CLC closer to the retina on either side
If you just change cylinder power, you move the CLC of retina
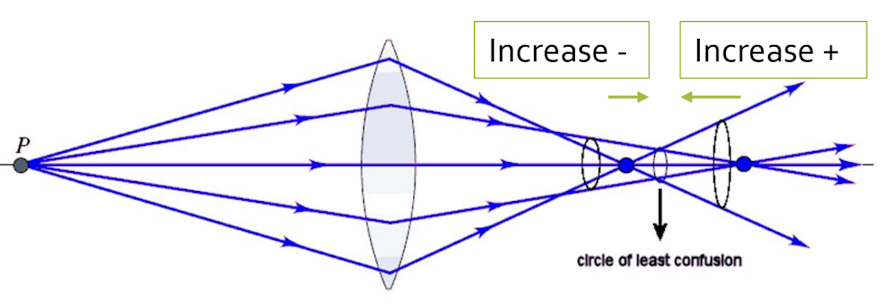
If pt. reports clearer with the RED dot at axis 180 degrees or SAME
Add -0.25 D cyl power and start with cylinder axis refinement and continue to cylinder power refinement
If pt. reports clearer with the white dot at axis 180 degrees move to the axis ____ and add ____ and go thorugh the 90, 135, etc. meridians to confirm pt. does not want cyl.
045 , add -0.25 D cyl power and go through 90, 135, meridians to confirm pt. does not want cyl
If cylinder power >2.00 D, axis refinement initial increments should be ___ degree and ___ degree
If you change axis location too far on high astigmatism Rx’s it will ___ the pt’s vision too much they will be unable to provide accurate results
High astigmatism powers rarely have
Axis refinement initial increments should be 5 degree and 1 degree not 15 degree and 5 degree
If you change axis location too far on high astigmatism Rx’s it will blur the pt’s vision too much they will be unable to provide accurate results
High astigmatism powers rarely have large axis changes
If there is a large increase in cyl power during cyl power refinement (-0.75 D or more) what should you do?
Go back and recheck cyl axis at higher power
Pt. should be discriminating more due to a more appropriate correction
If you start with a high cyl power and it decreases —- do not need to recheck axis
In sphere power refinement the end point for lab is
20/15