Blueprint Reading, Measurement, and GD&T: Essential Skills for Engineering Students
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
What is the function of a blueprint?
To communicate the ideas and intentions of architects and engineers to those who will execute them.
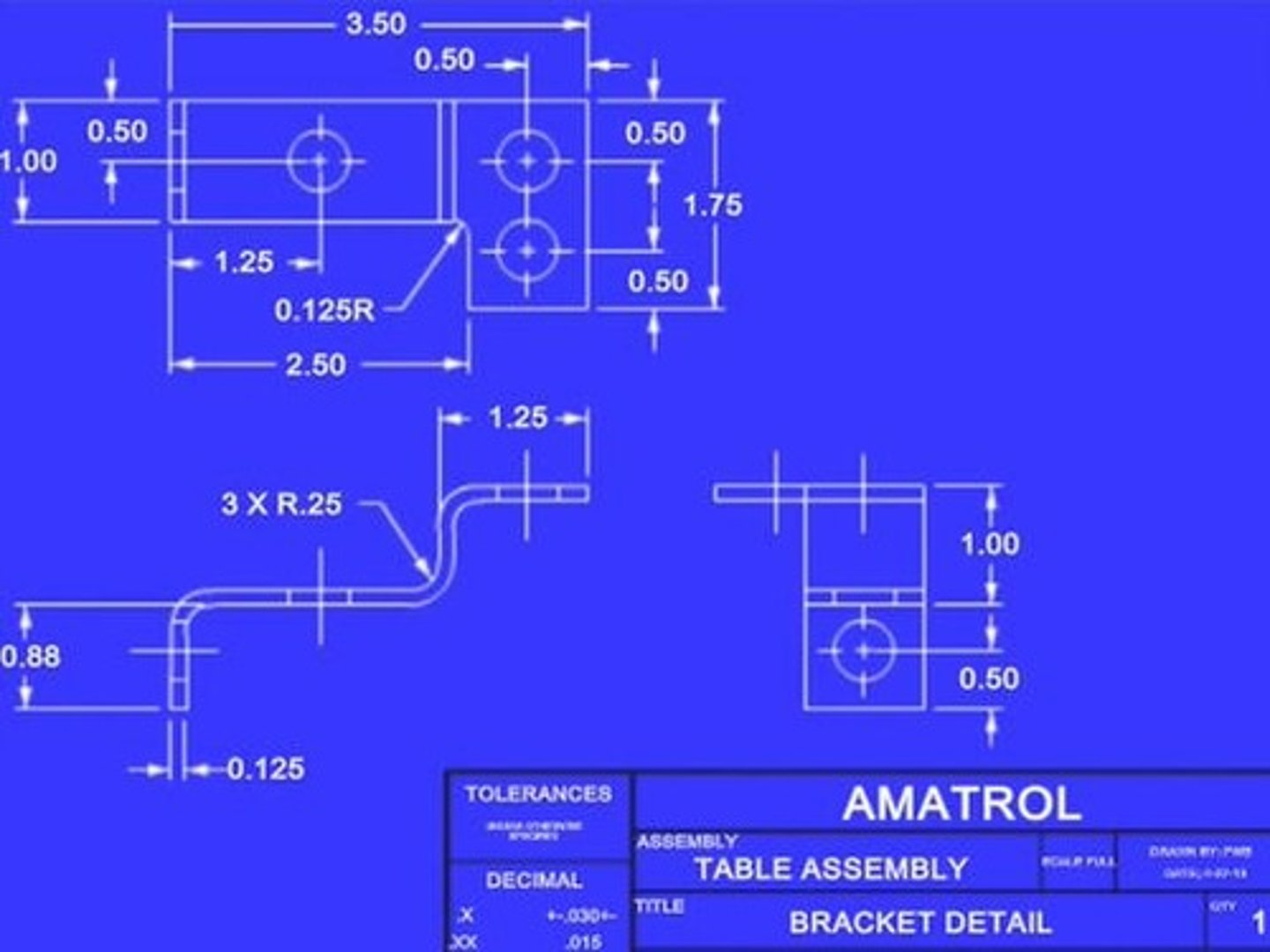
What are the three methods of creating a technical drawing?
Sketching, Instrument Drawing, and CAD (Computer Aided Drafting).
What is sketching in technical drawing?
Freehand drawing used to quickly relate an idea, with a lack of accuracy.
What is instrument drawing?
Accurate technical drawing created with tools like rulers and protractors.
What does CAD stand for?
Computer Aided Drafting (Design).
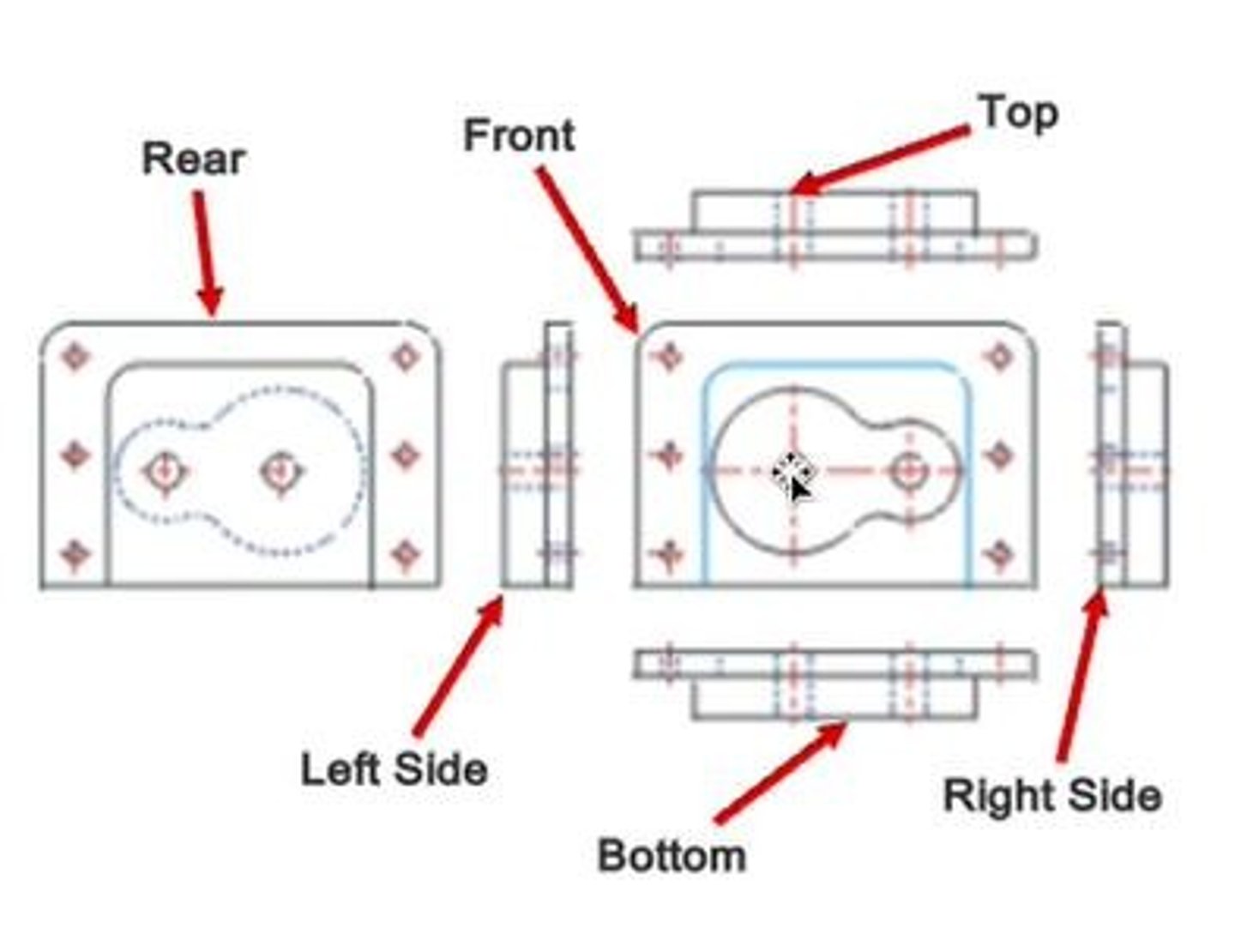
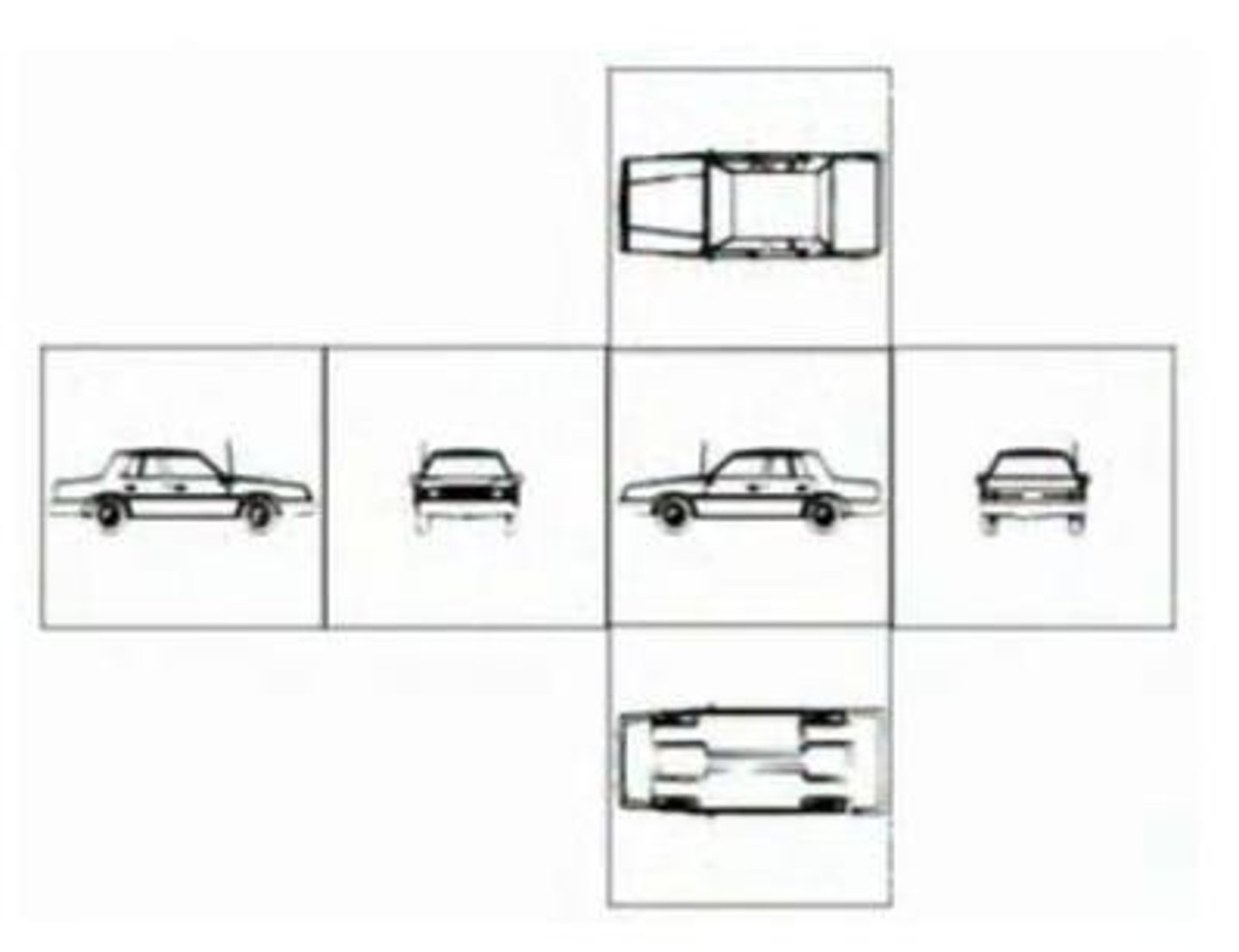
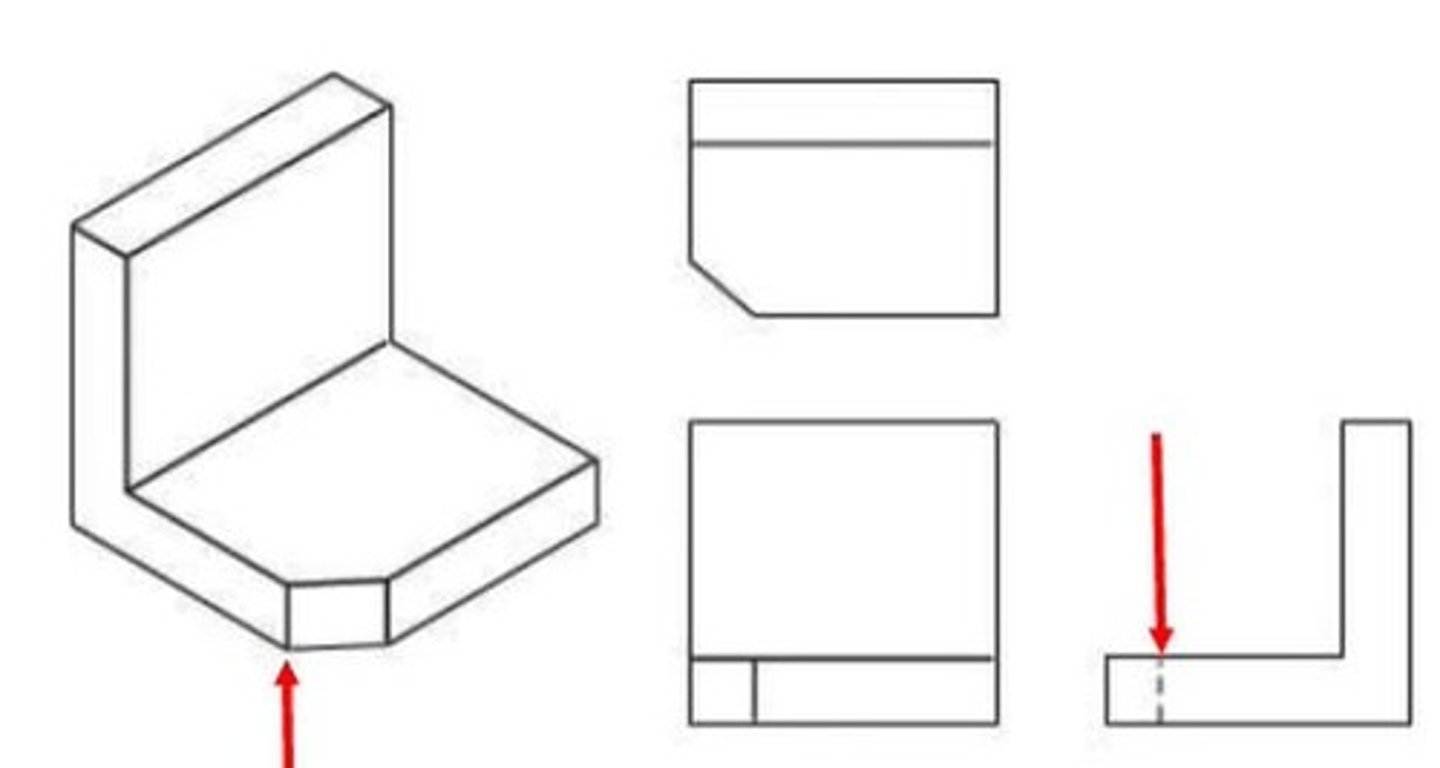
What is a multiview drawing?
A drawing that shows an object from different sides, typically up to six views.
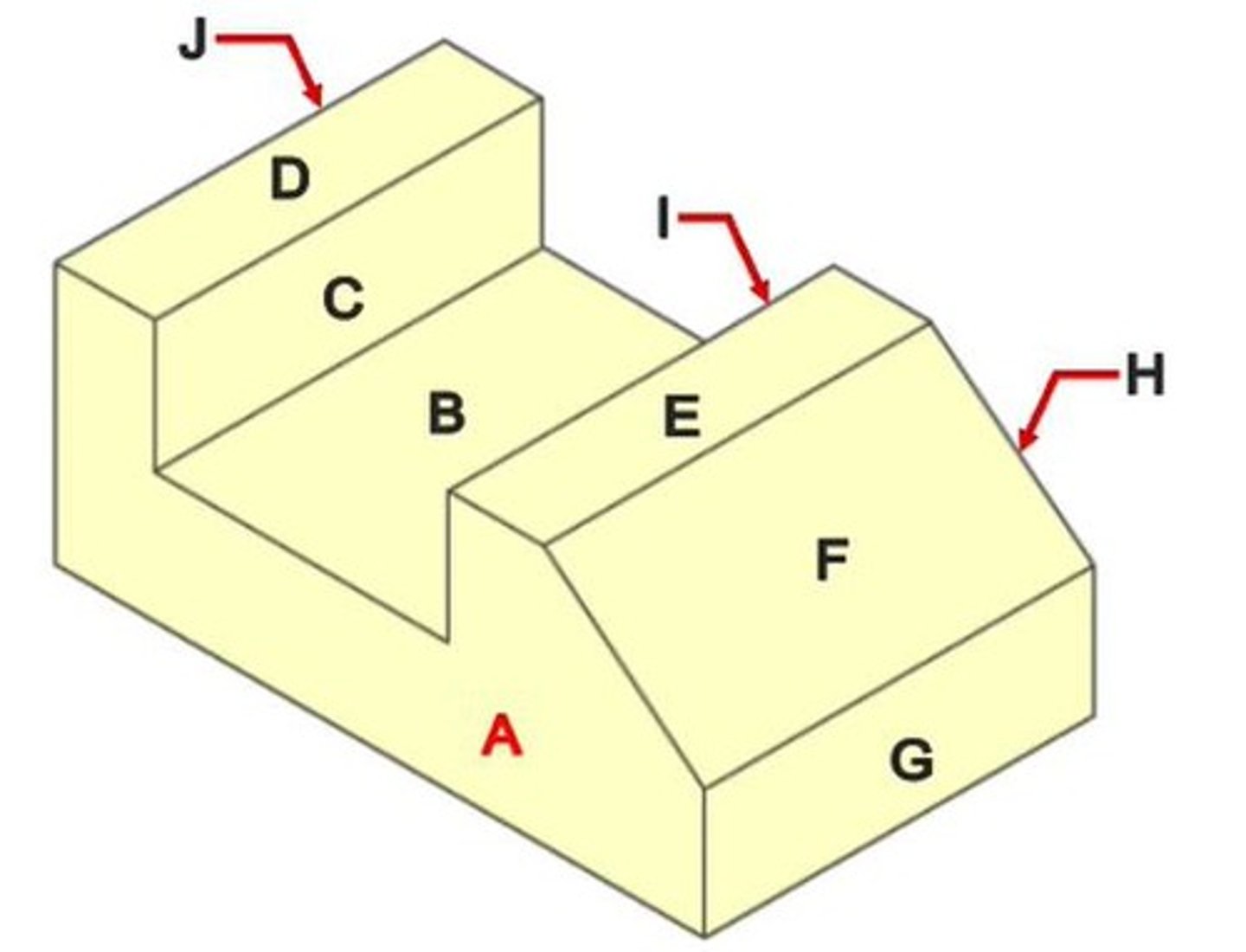
What is isometric/pictorial drawing?
A drawing that is easy to visualize but does not show all angles with true dimensions.
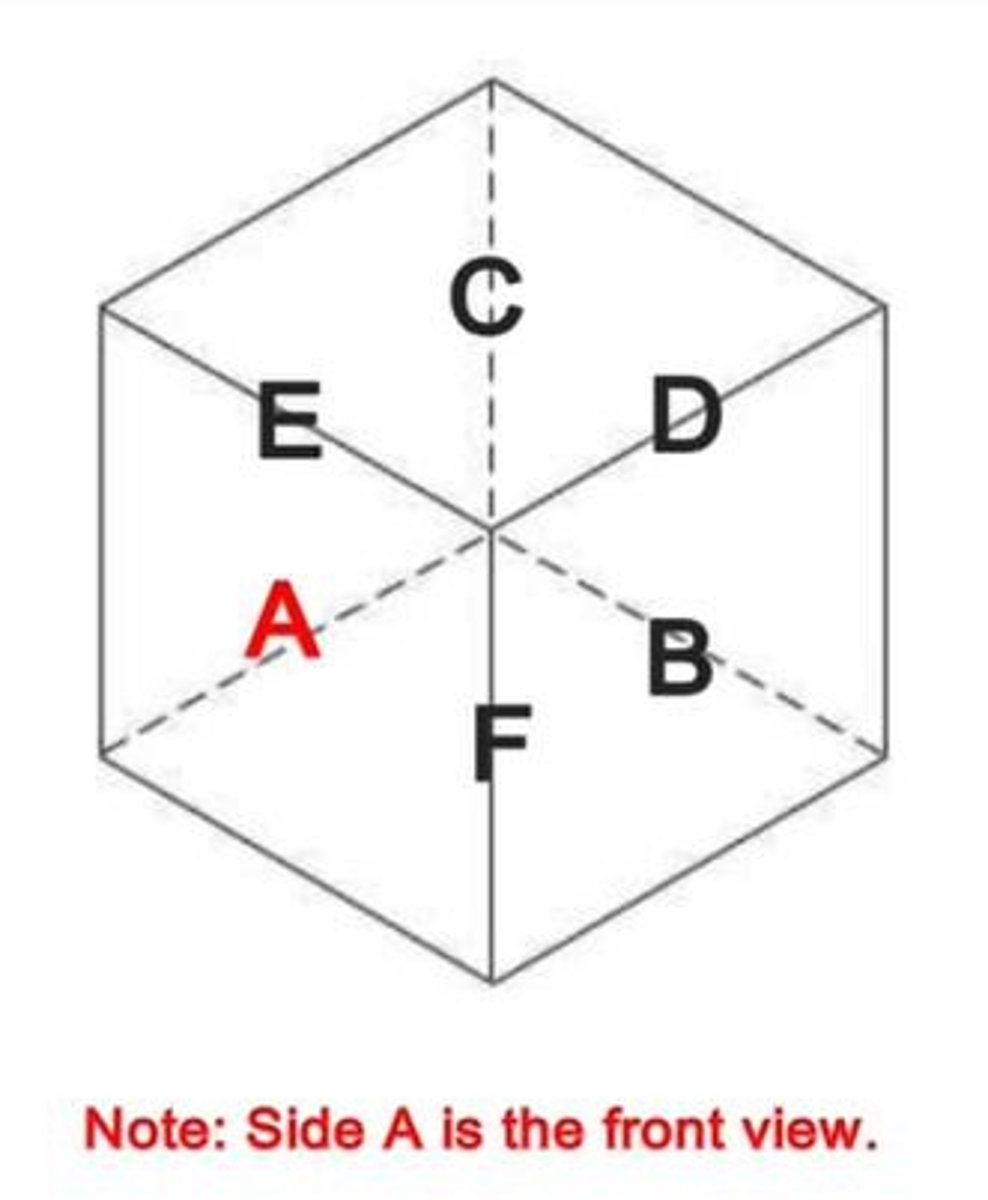
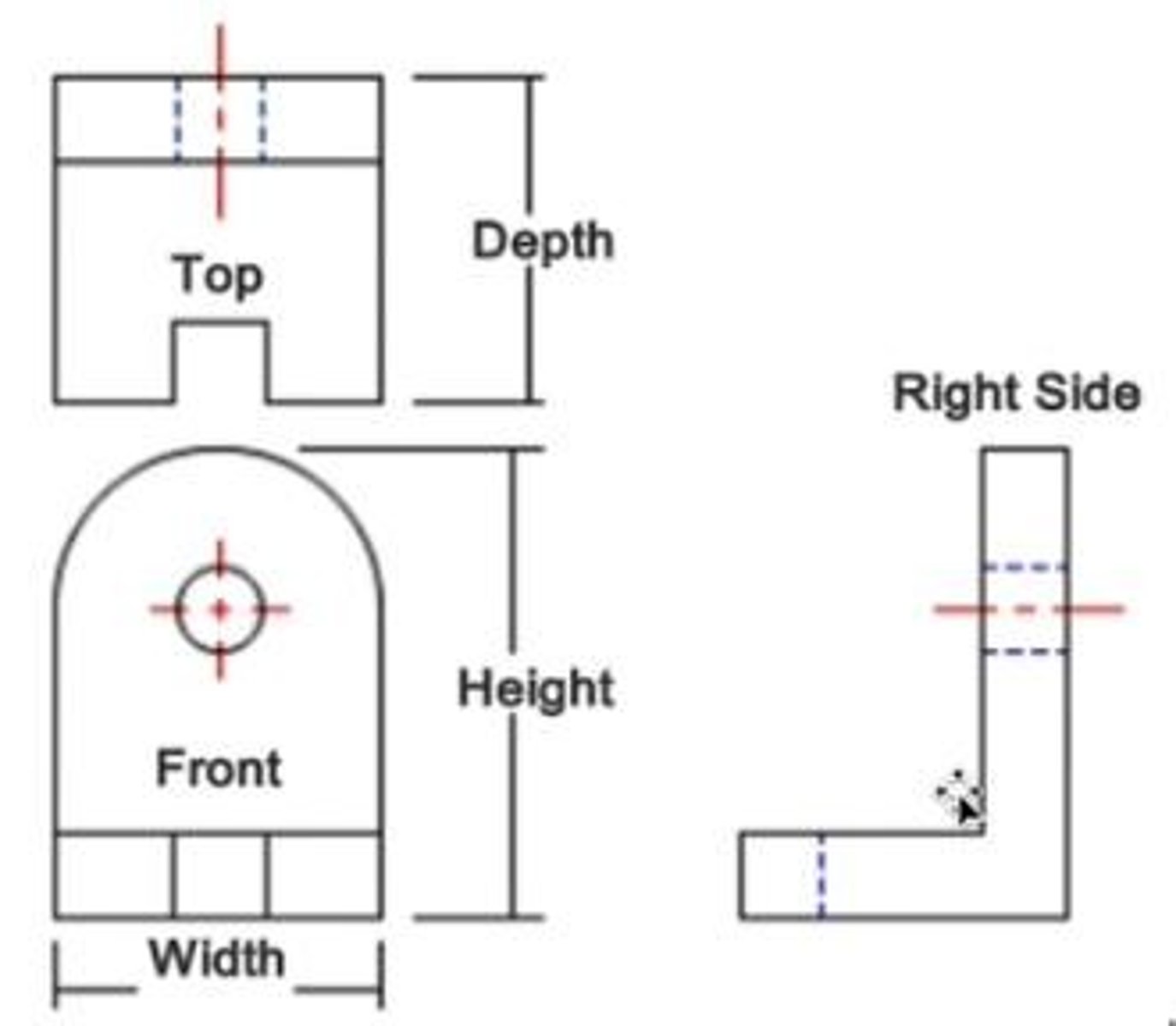
What are the principal dimensions of an object?
Width, Height, and Depth.
What is the glass box method in orthographic projection?
A method to arrange views by unwrapping a glass box around the object.
What are object lines in a multiview drawing?
Solid lines that show the size and shape of an object.
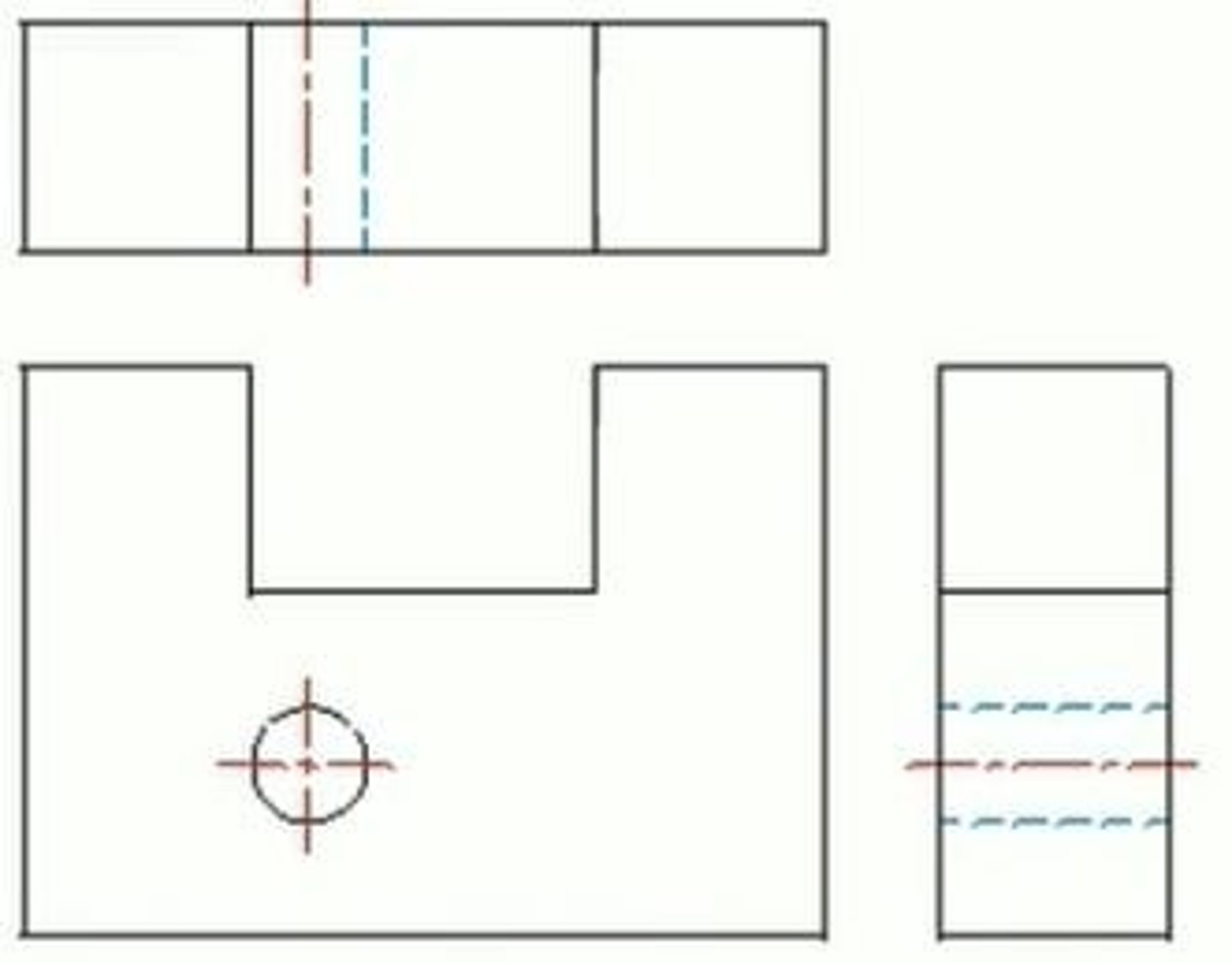
What do hidden lines represent?
Features that cannot be seen in a particular view, represented by dotted lines.
What do center lines indicate?
The center of a hole or a curve.
What is line precedence in technical drawing?
The order of priority for showing lines when more than one could occupy the same location.
What is the first view to choose in a multiview drawing?
The front view.
What is over-dimensioning?
Having too many dimensions that can lead to confusion in reading a part drawing.
What are extension lines used for in dimensioning?
To extend the edges of a feature to allow placement of a measurement.
What do dimension lines show?
Where the actual dimensions apply to, connecting two extension lines with arrows.
What does the diameter symbol look like?
An 'O' with a slash through it.
How are circles dimensioned?
Shown with a diameter measurement.
What are chamfers in technical drawing?
Transitional edges between two faces, often defined at a 45° angle.
What are tapers in technical drawing?
Displayed as a ratio to show how a diameter changes.
What should you consider when choosing views for a multiview drawing?
The side with the most information about the part.
What is the standard number of views in a multiview drawing?
Three views.
What is the purpose of dimensioning in a technical drawing?
To relate measurements to views and convey all needed information about a part.
What is the importance of using the fewest dimensions possible?
It reduces the number of mistakes in a drawing.
What is the purpose of leader lines?
To attach the dimension to the object.
What is the role of angular features in dimensioning?
To show angles, usually with measurements in degrees.
What is the significance of choosing the front view carefully?
It represents reality or the side with the most information about the part.
What are the rules for dimensioning a multiview projection?
Dimension an object completely, do not over dimension, dimension in a view that shows features clearly, do not dimension hidden lines, provide usable dimensions, and make dimensions readable.
What are complementary angles?
Two angles whose measures sum to 90 degrees.
What is a Thru hole?
A hole that passes completely through a part.
What is a Blind hole?
A hole that does not pass all the way through the workpiece.
What is a Counterbore?
A hole with a shelf at the top and an enlarged diameter at the top.
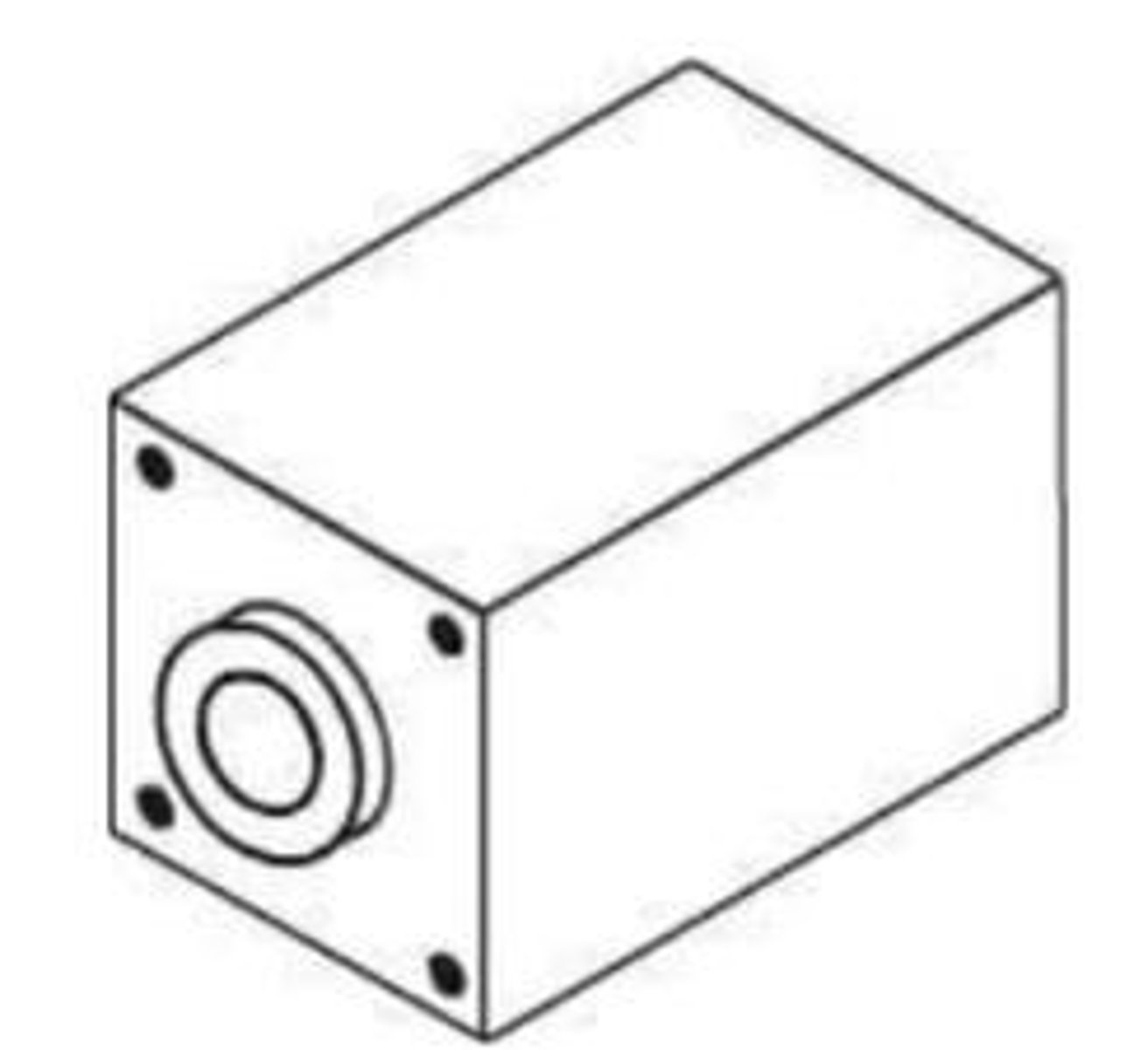
What is a Countersink?
A hole that has been enlarged with a taper, designed to allow a screw to seat flush.

What do drawing scales indicate?
They indicate when a drawing is larger or smaller than the actual object.
How can you convert measurements from a drawing scale to real size?
By dividing the measurement by the scale number.
What is a Title Block in a blueprint?
It contains all areas necessary to give context about the part, including assembly number, title, product, drawing number, revision number, scale, who drew it, material, and approval information.
What does a Cutting Plane Line represent?
It divides an object so that the sectional view can be shown.
What are Section lines used for?
They are drawn on a sectional view to show where there is solid material.

What is the function of threads in fasteners?
To hold objects together during assembly.
What is the difference between external and internal threads?
External threads are on the outside of an object (like a bolt), while internal threads are on the inside of an object (like a nut).
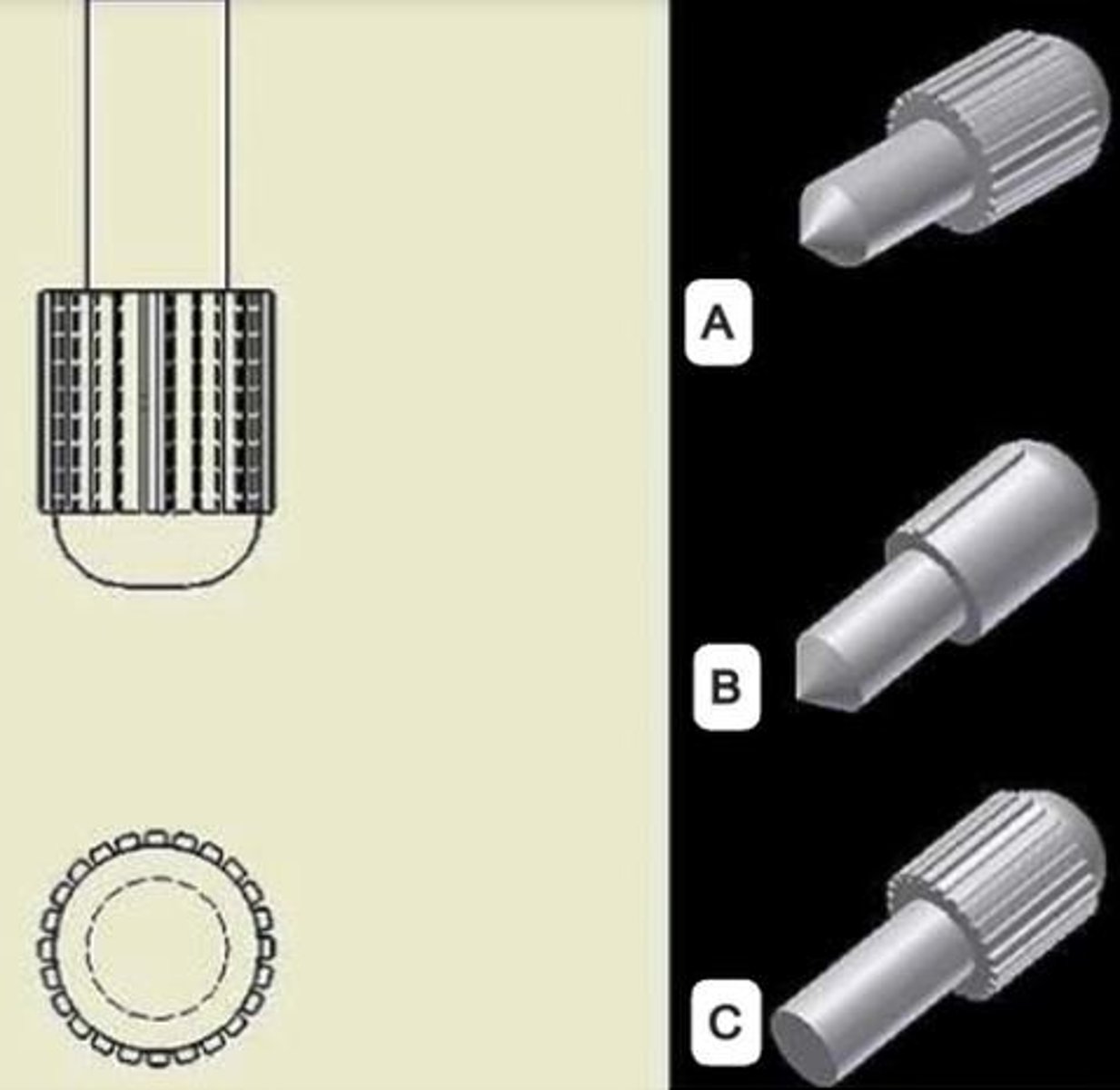
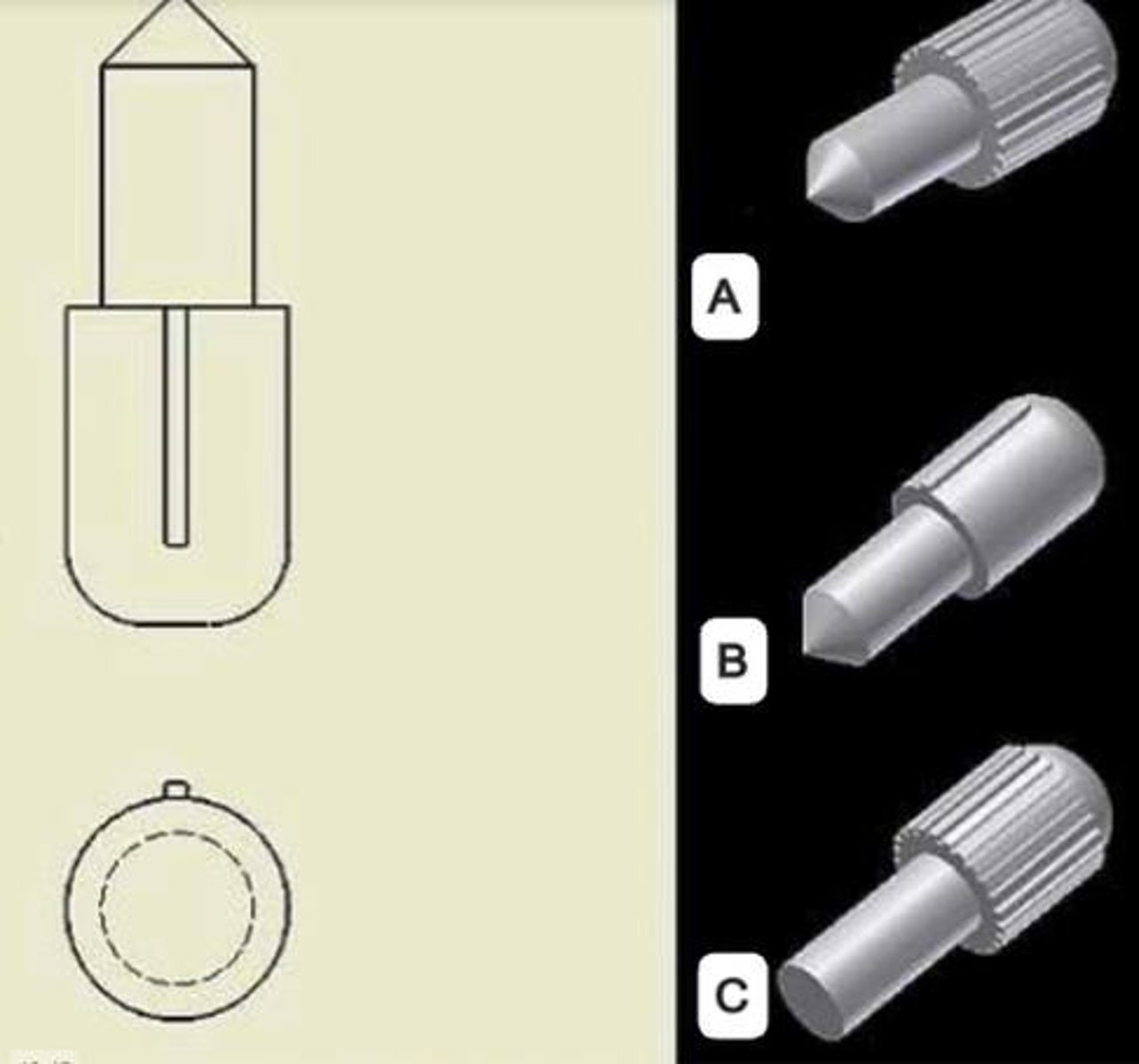
What is the SAE Grade for a bolt with 0 marks?
SAE Grade = 2.
What is the SAE Grade for a bolt with 3 marks?
SAE Grade = 5.
What is the purpose of a Washer in fastening?
To distribute the load for fastening and minimize damage to the workpiece.
What is the Major Diameter in threaded fasteners?
The diameter from the outer edges of the thread.
What does a sectional drawing represent?
The internal features of a part.
What is the purpose of a revision number in a Title Block?
To indicate how many times the drawing has been revised.
What is the significance of the scale in a Title Block?
It indicates the ratio of the drawing size to the actual size.

What does the term 'usable dimensions' refer to?
Dimensions that can be effectively used in manufacturing or assembly.
What is the purpose of dimensioning in a drawing?
To provide clear and accurate measurements for the features of a part.
What is the role of the Head in a threaded fastener?
It is the part the tool grips to turn the fastener.
What does the term 'taper' refer to in a Countersink?
The enlargement of a hole that creates a funnel shape.
What is the purpose of a Cutting Plane Line in a sectional drawing?
To indicate the direction from which the sectional view is taken.
What does a Counterbore require for dimensioning?
Two diameters and a depth.
What is the general tolerance in a drawing?
A default tolerance that applies to dimensions not explicitly specified.
What is the purpose of a nut in a fastening system?
To provide internal threads that engage with the external threads of a bolt.
What is the significance of the arrows on a Cutting Plane Line?
They indicate the direction of view for the sectional view.
What does the term 'grade' refer to in fasteners?
It indicates the strength of the fastener, calculated as 2 plus the number of marks on the head.
What is designed to be repeatedly fastened and unfastened?
Threaded fasteners
What is the major diameter of a thread?
Diameter from the outer edges of the thread
What is pitch in threaded fasteners?
Distance from the crest of one thread to the crest of the next thread
What is the pitch if there are 20 threads per inch?
1/20 of an inch apart
What are the two types of thread types?
Coarse (UNC) and fine (UNF)
What does UNC stand for?
Unified National Coarse
What does UNF stand for?
Unified National Fine
What is the class of fit in threaded fasteners?
Tolerance in the size of the thread

What does a higher class of fit number indicate?
Tighter fit
What is the external thread major diameter measured from?
Thread crest to thread crest
What is the internal thread major diameter measured from?
Thread root to thread root
What is the fastener length?
Bottom of the head to end of the fastener
What is the head type of a fastener?
Shape of the head
How are metric fasteners different from standard fasteners?
They have an M in front and use mm for major diameter and pitch
What is the major diameter of a metric fastener?
Outside diameter of the thread in mm
What is the thread pitch in the metric system?
Distance between thread peaks measured in millimeters
What is an exploded assembly drawing?
Isometric view showing how everything fits together
What do assembly drawings show?
How pieces fit together to perform one function
What is the purpose of detail drawings?
To give more information about a reference number
What is the first step in determining major diameter and thread type?
Measure the major diameter
What is the second step in determining major diameter and thread type?
Count the number of threads for 1 inch
What is a technical drawing also called?
Blueprint
What do dimensions specify in a drawing?
Size and location of the features of an object
What is the order of precedence of lines in a drawing?
Object, Center, Hidden
What type of hole is a countersink?
A hole with a conical shape at the top
What is the depth of a countersink typically measured in?
Inches
What does a dimension line indicate?
The measurement between two extension lines
What is the actual dimension if a feature is drawn 3 inches long at a scale of 1:4?
12 inches
What does 1/4 inch equal in a drawing scale?
1 inch
What material is indicated in the part drawing's title block?
Cast iron, Steel, Bronze, Brass
What part of a drawing indicates the most up-to-date information?
Drawing revision level
Where would you look in a title block to see if there have been changes?
Revision number
What does a sectional view represent?
Internal features of a part when hidden lines are not enough
What do section lines on a blueprint indicate?
A surface that has been cut
What is placed at the arrowheads of the cutting plane line?
Capital letter
What do section lines in a sectional view represent?
The portion of the object which has been cut
What protects the threads in a threaded fastener assembly?
Nut
What does a calibrated torque wrench measure?
The proper amount of torque
What is a torque wrench designed for?
To tighten fasteners to a specific level of torque
Which bolt is a grade 2?
B
What are the two types of threads?
Internal and external
What designation represents a screw with fine thread?
UNF