Chemistry of Carbon and Life
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Why is carbon essential to life?
All life is built on carbon, making up about 25% of cell composition.
What are the four major classes of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is organic chemistry?
The study of carbon compounds.
What are hydrocarbons?
Combinations of carbon and hydrogen that are non-polar and hydrophobic.
What are isomers?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties.
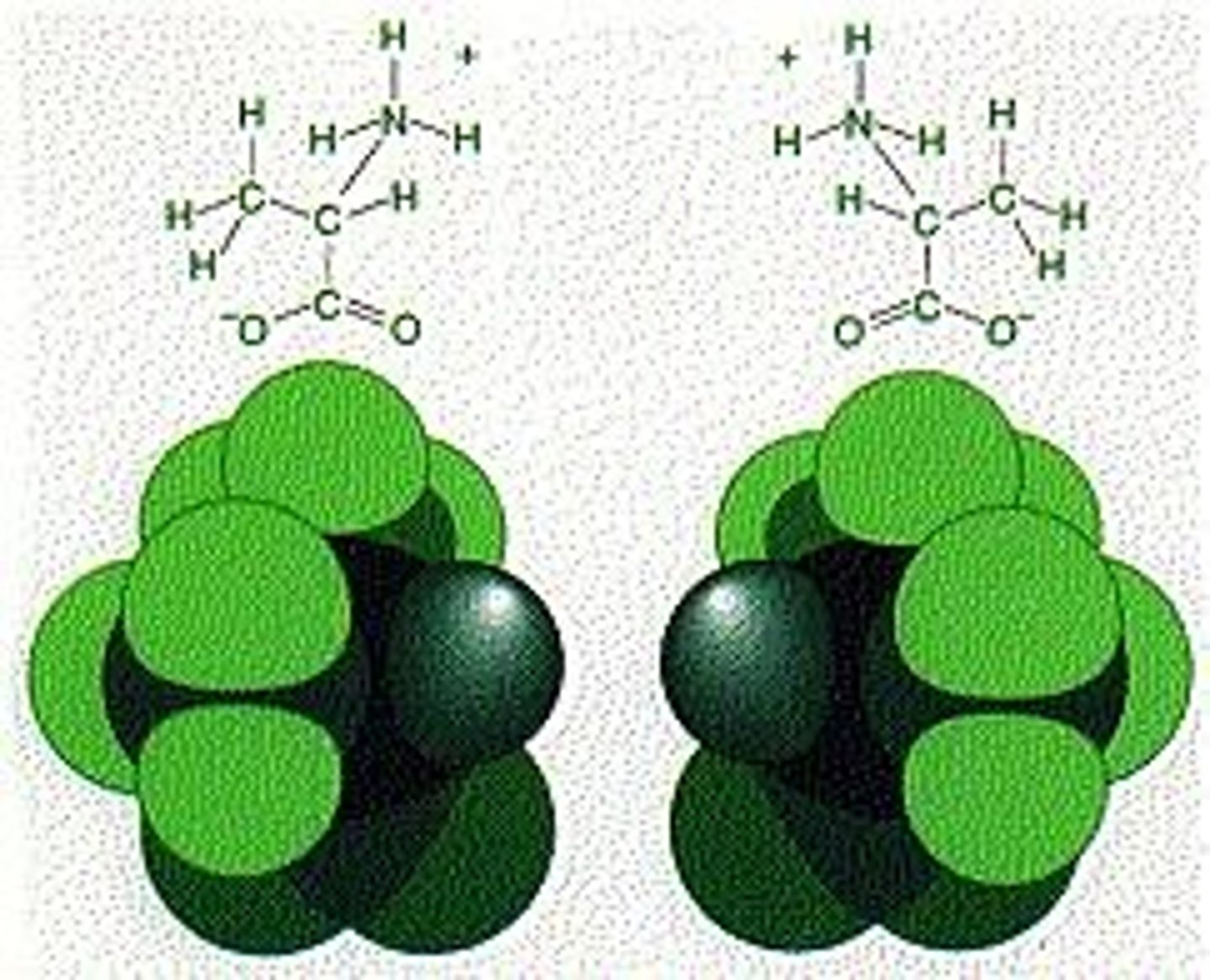
How do structural differences in isomers affect their function?
Structural differences create significant functional significance, as seen in amino acids.
What is the role of functional groups in organic molecules?
Functional groups are involved in chemical reactions and give distinctive properties to organic molecules.
What is dehydration synthesis?
A process that joins monomers by removing water to form polymers.
What is hydrolysis?
The process of breaking down polymers by adding water.
What is the significance of ATP in biological systems?
ATP is an energy carrier that transfers energy between organic molecules.
What are the properties of water that make it essential for life?
Cohesion, adhesion, being a good solvent, lower density as a solid, high specific heat, and high heat of vaporization.
What is cohesion in the context of water?
The attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding, leading to surface tension.
What is adhesion in the context of water?
The attraction between water molecules and other substances, facilitating capillary action.
What is the pH scale?
A scale that measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 1 (acidic) to 14 (basic).
What role do buffers play in biological systems?
Buffers help maintain pH levels by absorbing or donating H+ ions as needed.
What are the characteristics of polar covalent bonds?
Electrons are shared unequally between atoms, resulting in partial positive and negative charges.
What distinguishes nonpolar covalent bonds?
Electrons are shared equally between two atoms, resulting in a balanced charge.
What is the effect of ice floating on water?
Ice insulates water below, allowing aquatic life to survive in winter.
What is the difference between hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances?
Hydrophilic substances attract water, while hydrophobic substances do not.
What is the structure and function of amino acids?
Amino acids are building blocks of proteins, with specific structures affecting their role in biological functions.
What is the significance of L- and D- amino acids?
Only L-amino acids are used in proteins, while D-amino acids can have different biological effects.
What is the role of the hydroxyl functional group?
Hydroxyl (-OH) groups make compounds polar and can act as alcohols.

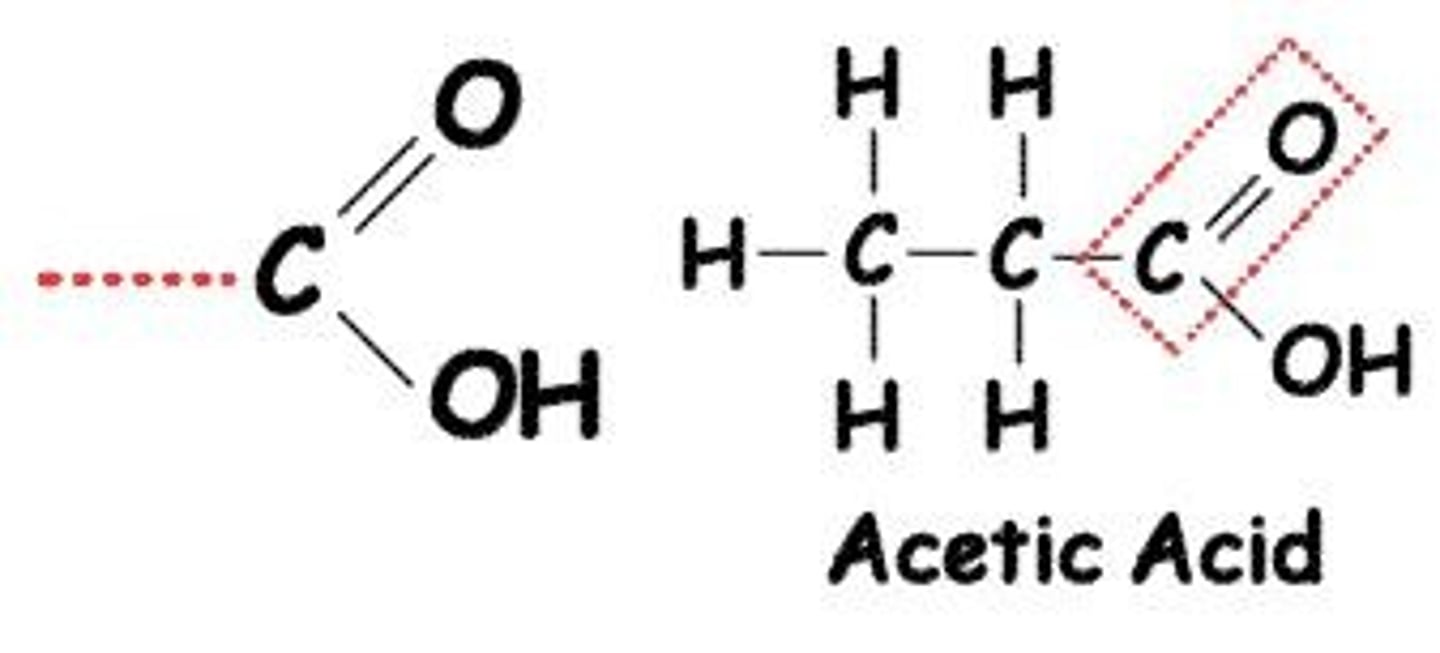
What is the carboxyl functional group?
Carboxyl (-COOH) groups are found in acids, including fatty acids and amino acids.
What is the carbonyl functional group?
Carbonyl (C=O) groups can be found in aldehydes (at the end of a molecule) or ketones (in the middle).
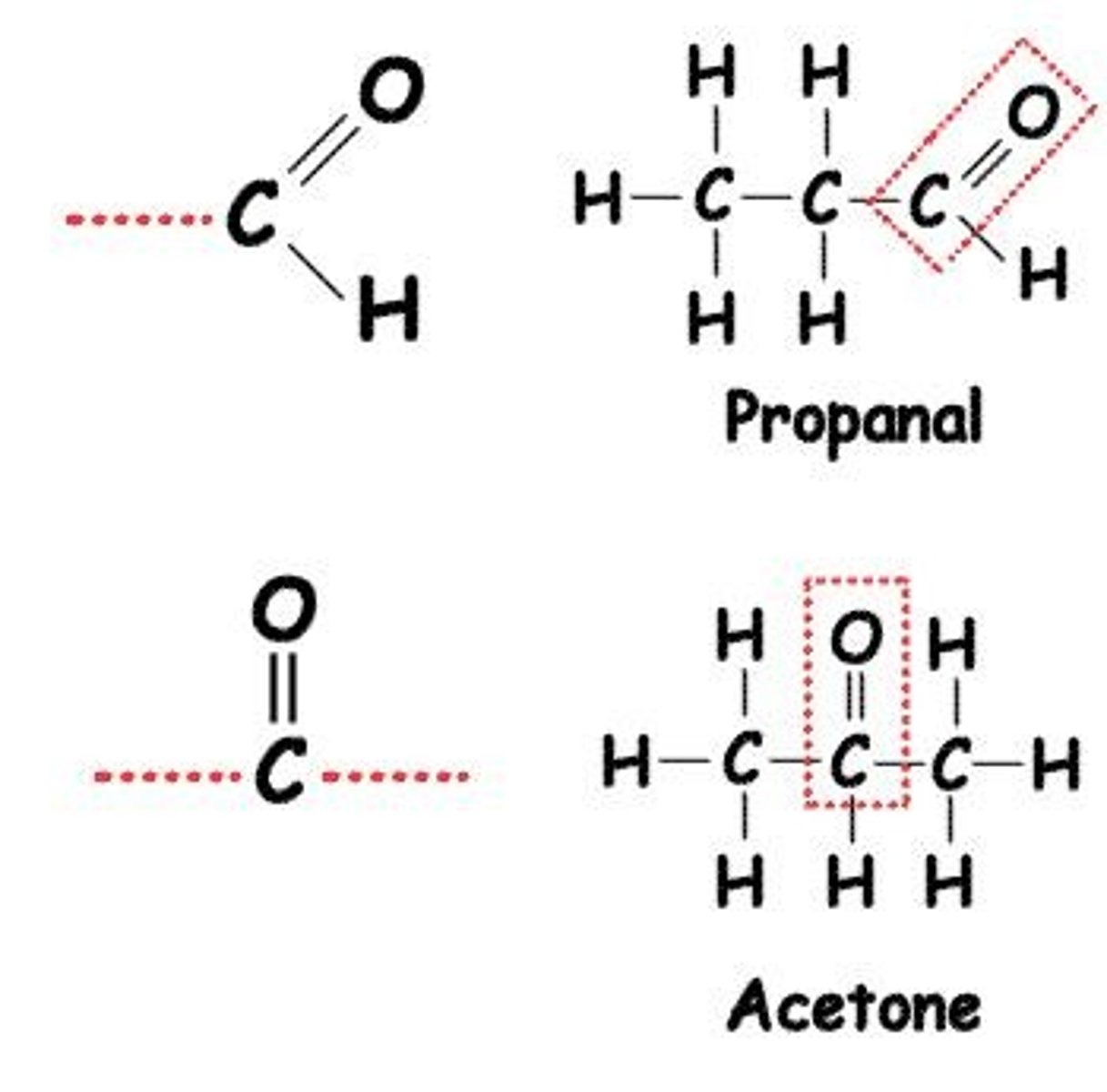
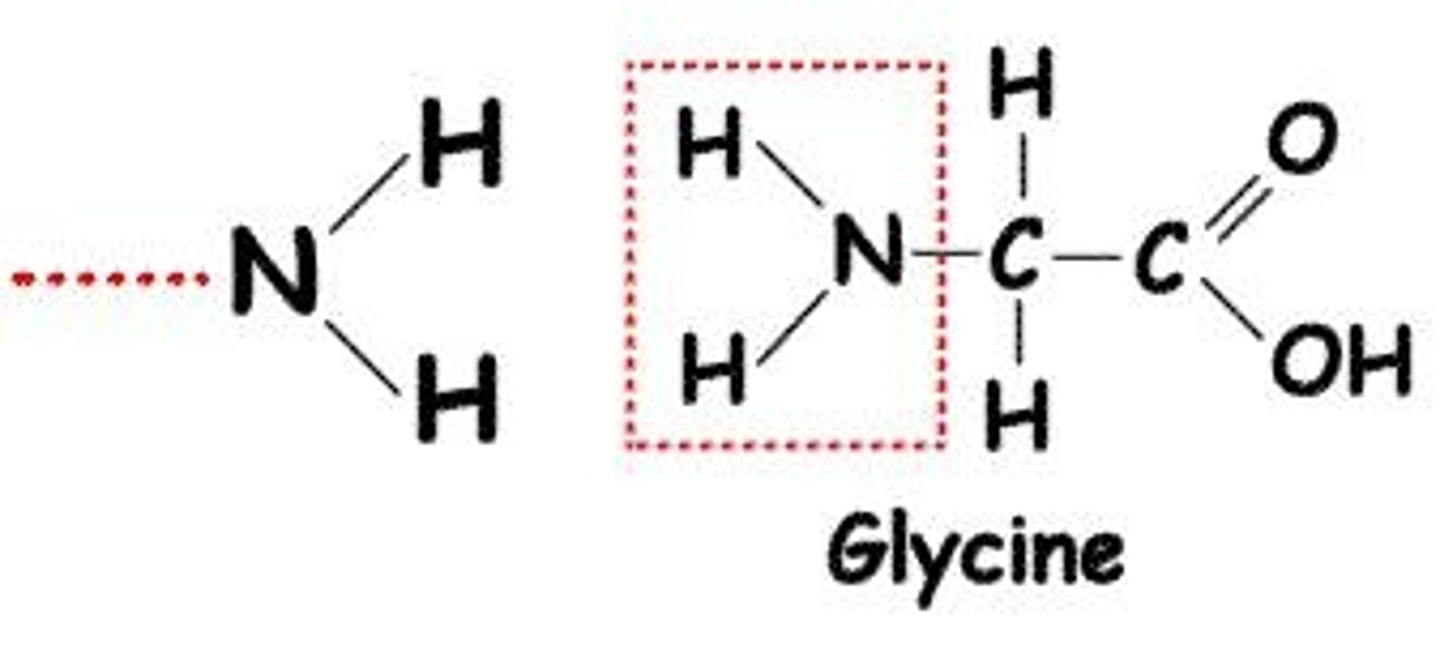
What is the amino functional group?
Amino (-NH2) groups act as bases and are found in amino acids.
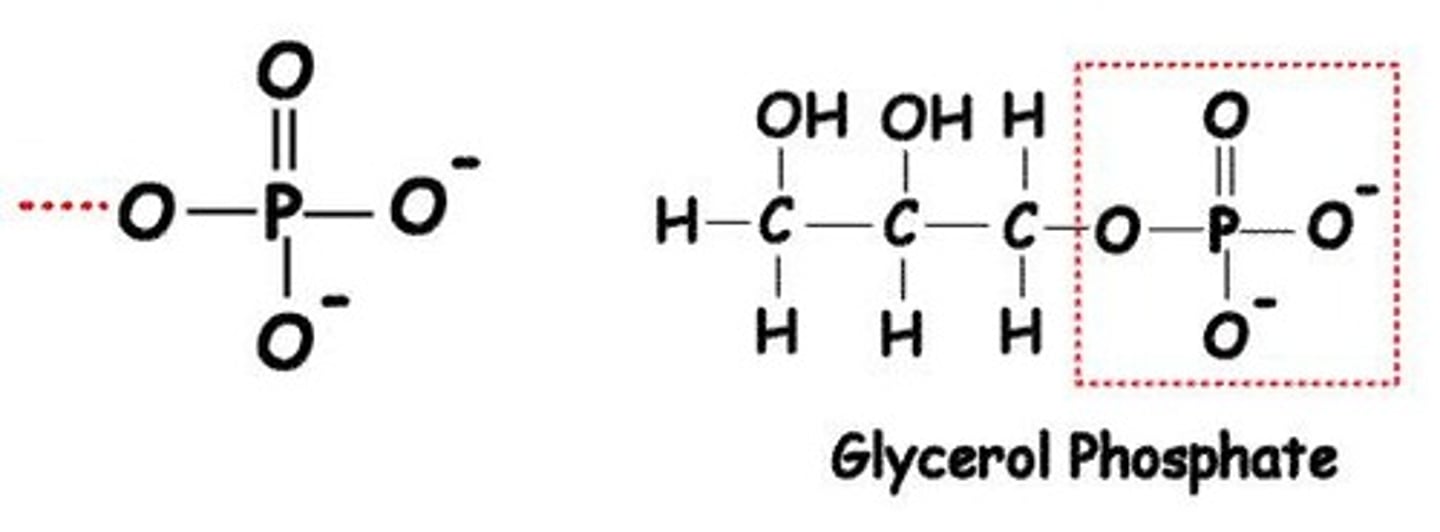
What is the phosphate functional group?
Phosphate (-PO4) groups are highly reactive and play a key role in energy transfer.