BSCI202: Circulatory System
1/174
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Justicia Opoku
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
The Circulatory System consists of 2 organ systems which fluid circulates:
Cardiovascular and Lymphatic system
Cardiovascular system
blood circulates in blood vessels
Lymphatic system
lymph circulates in lymphatic vessels
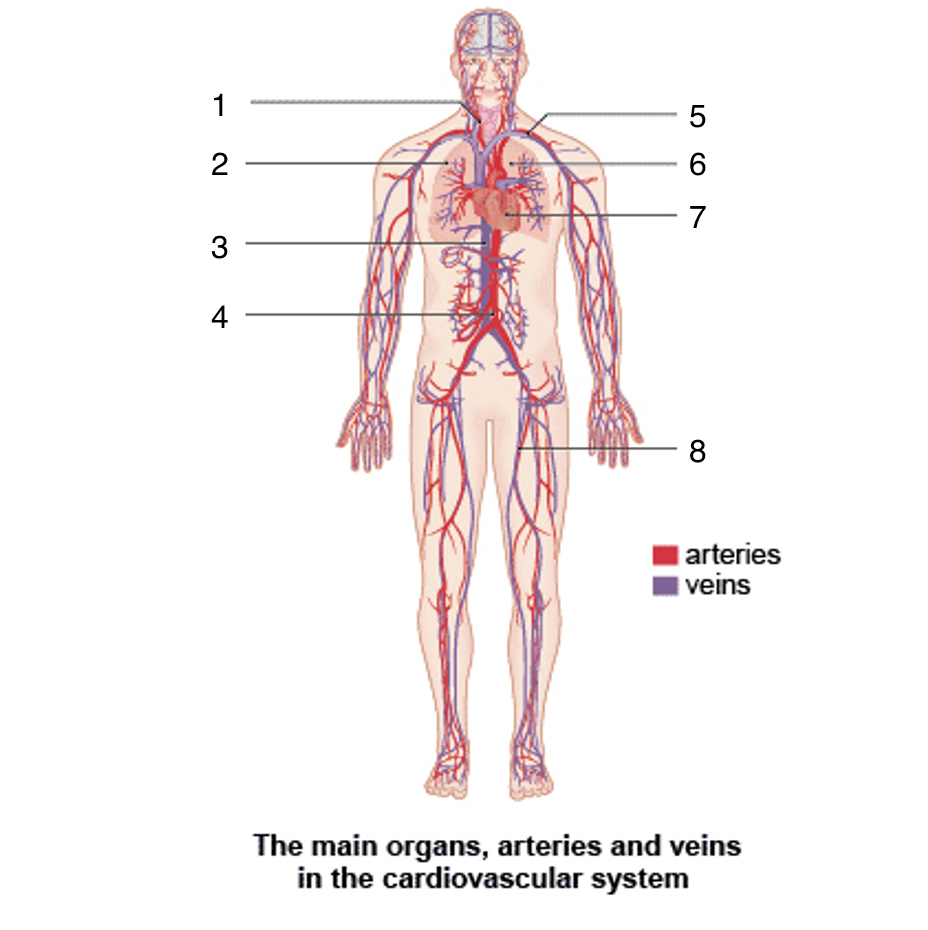
What is 1?
Carotid artery
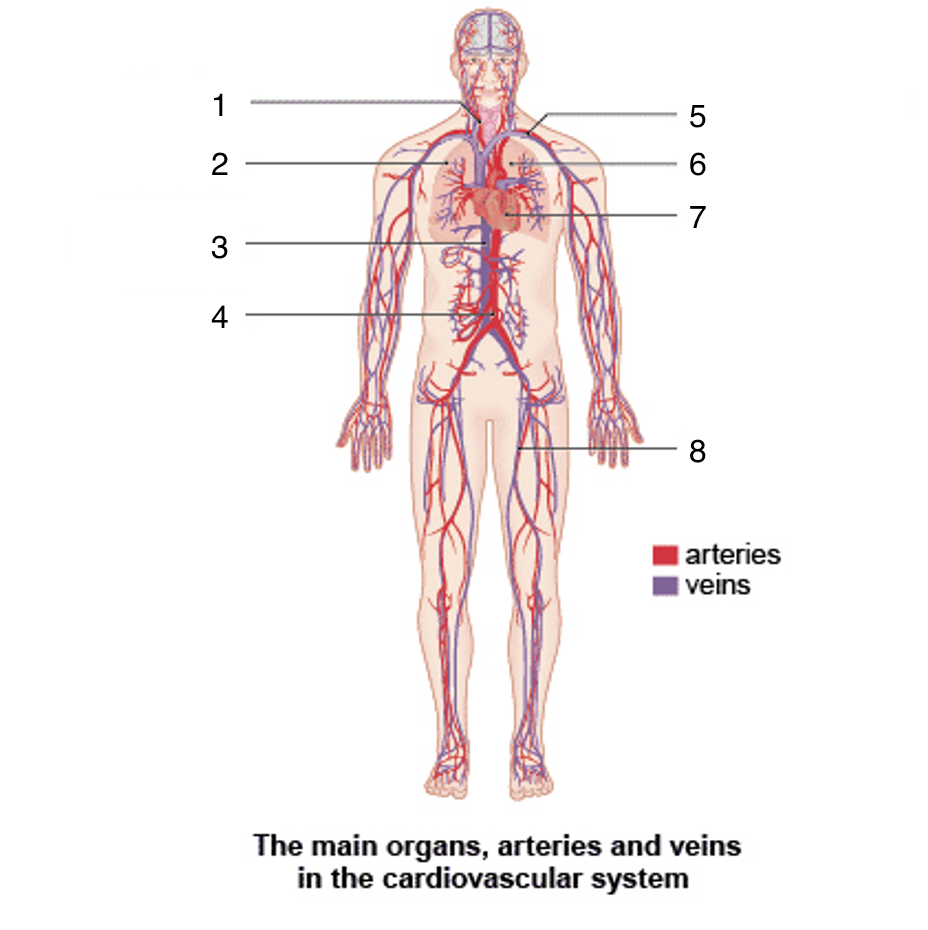
What is 2?
Right lung
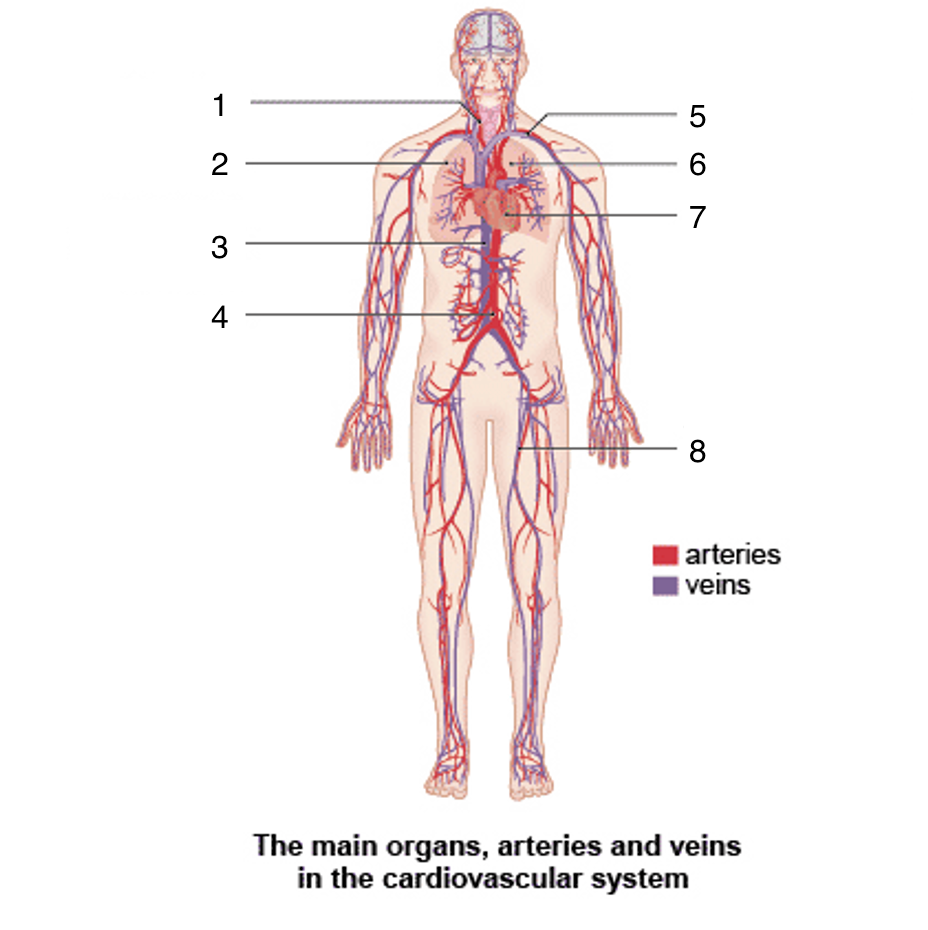
What is 3?
Vena cava
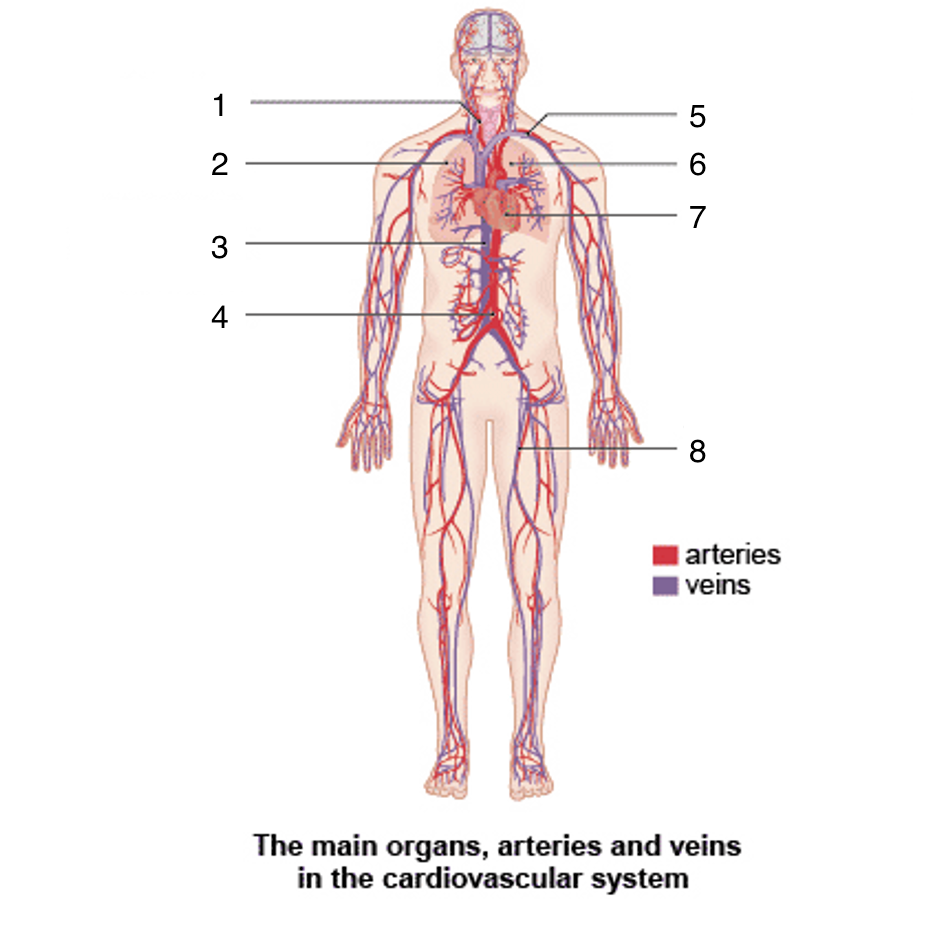
What is 4?
Aortic artery
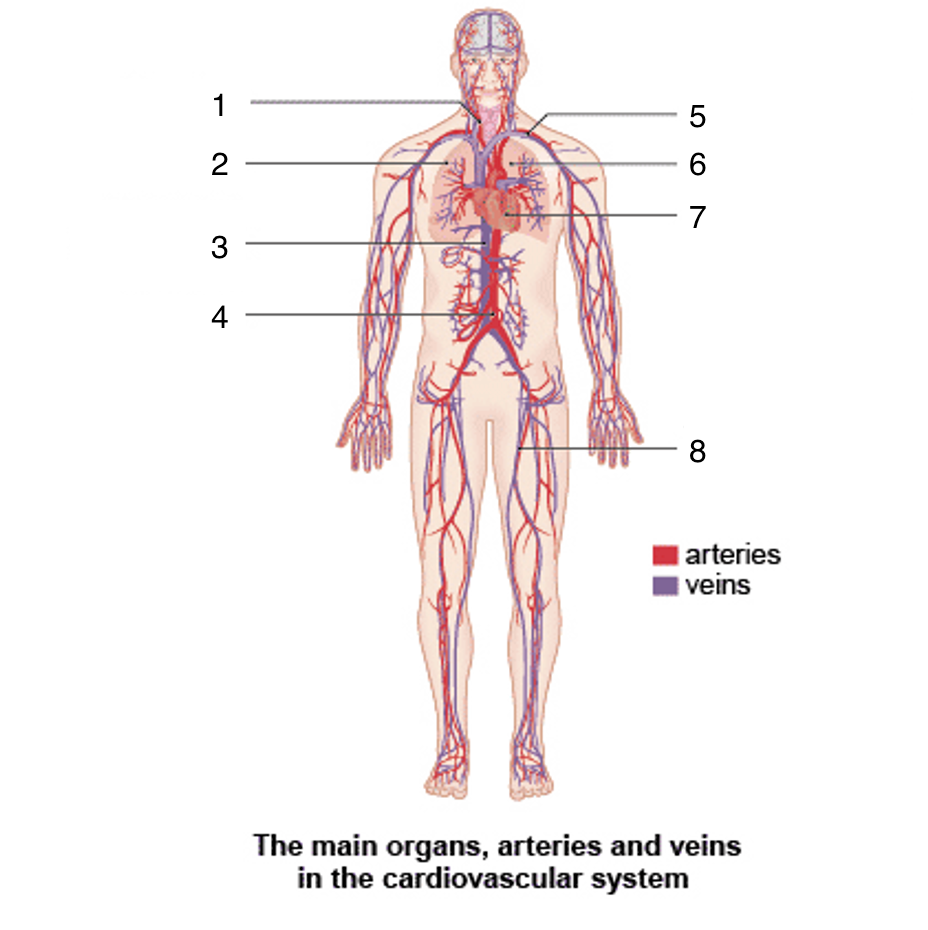
What is 5?
Subclavian artery and vein
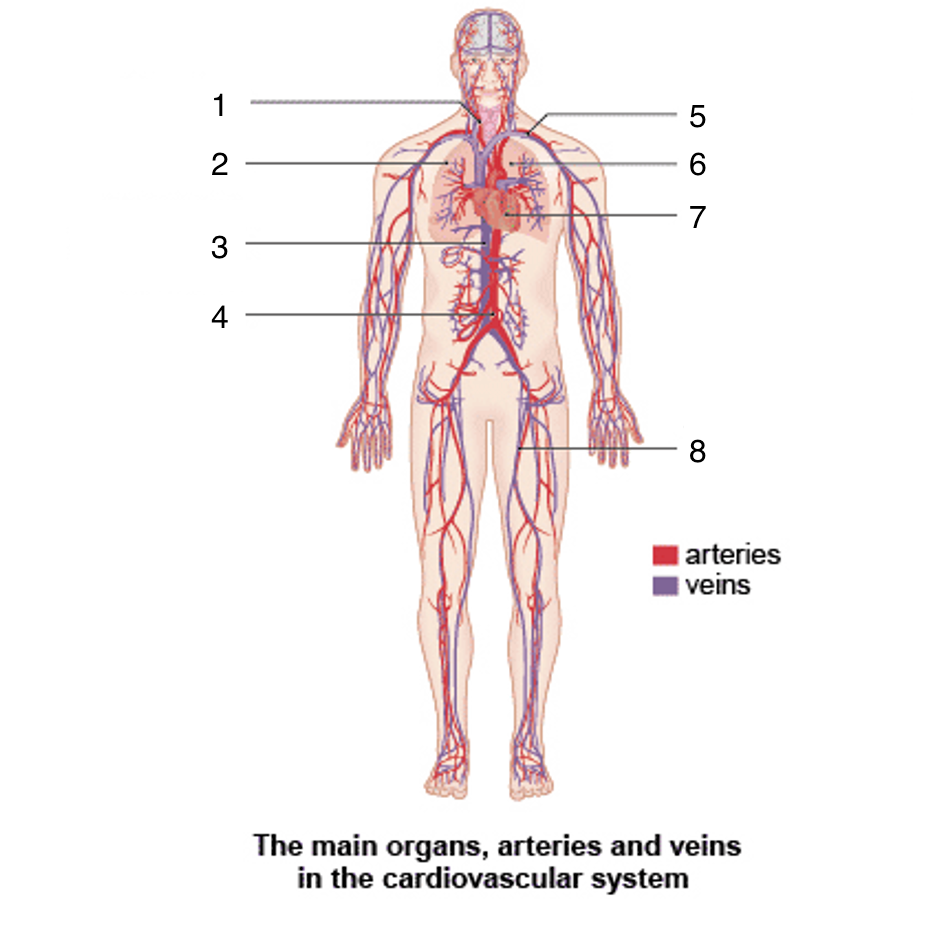
What is 6?
Left lung
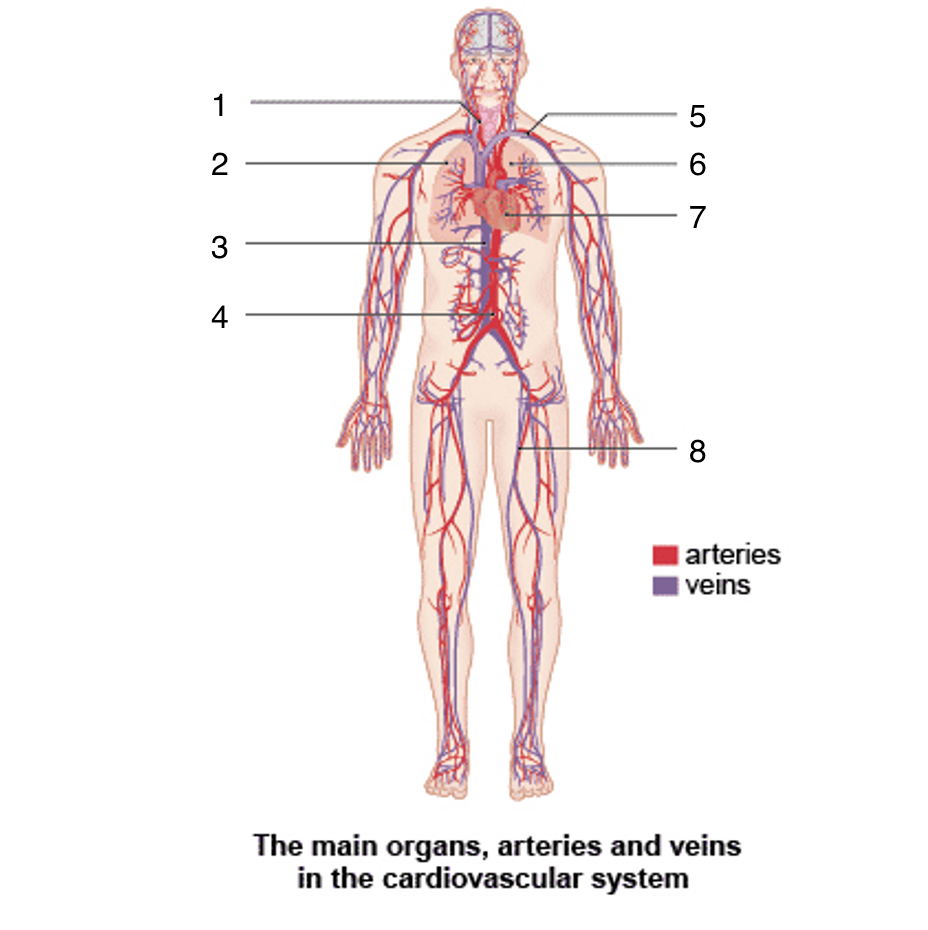
What is 7?
Heart
hypovolemic shock
caused from severe blood loss
Lymph
fluid contained within the lymphatic system
What is lymph similar to?
interstitial fluid
Where is diffuse lymphatic tissue found in the body?
Tonsils, mucosa associated lymph tissue, and red bone marrow
What are the lymph organs?
thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes
What is the main function of lymphocytes?
Immunity
What is the approximate blood volume as a percentage of body weight?
About 6-8% of body weight (in kg)
What is the typical total blood volume range for adults?
4.5-6.0 liters
What is the blood volume for adult males?
5-6 L
What is the blood volume for adult females?
4-5 L
Why do males generally have higher blood volume than females?
Due to larger body size, greater muscle mass, and hormonal differences (ie. testosterone increases red blood cell production)
What are two main factors that contribute to males having more blood volume than females?
Greater muscle mass and higher testosterone
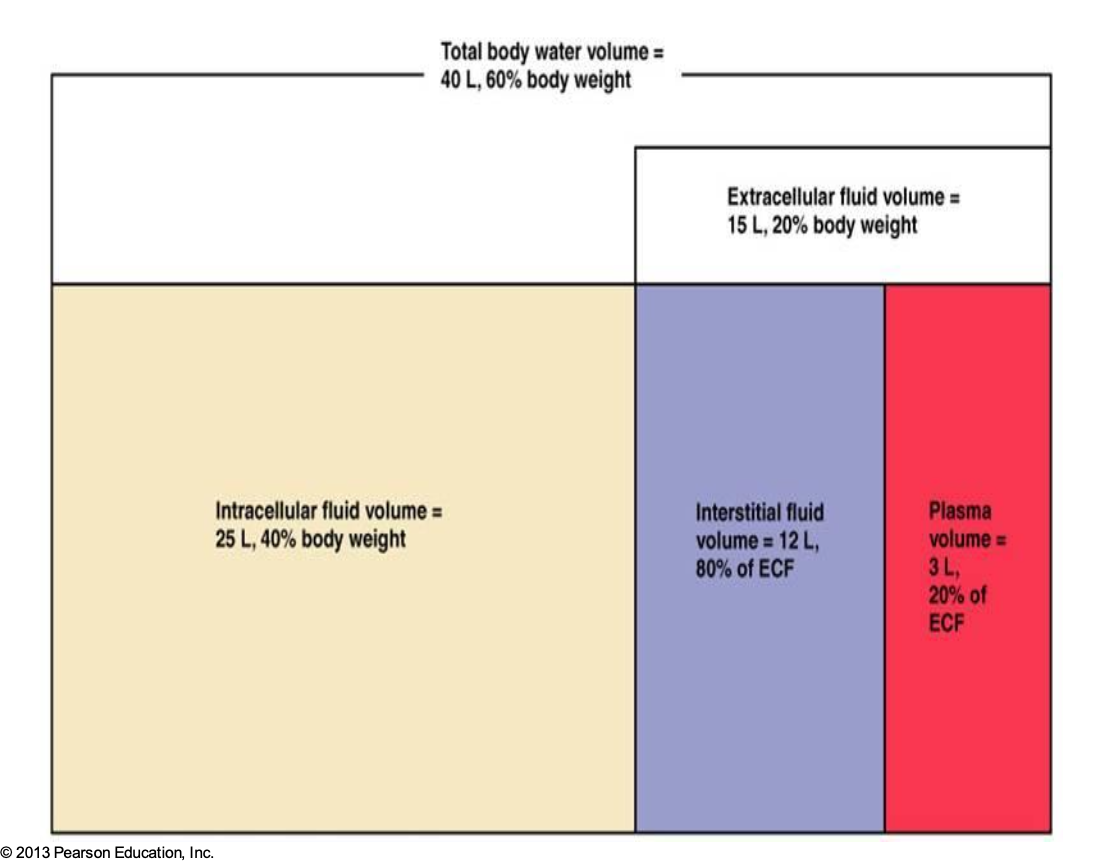
What is this?
Body Fluid Compartments
What is the first step in visualizing the composition of blood?
withdraw blood and place it in a tube, then centrifuge it
What are the three main layers formed when blood is centrifuged (top to bottom)?
Plasma, Buffy Coat, Erythrocytes
What percentage of whole blood is make up of plasma?
55%
What is found in the buffy coat, and what percentage of whole blood does it represent?
Leukocytes (white blood cells) and platelets; it makes up <1% of whole blood
What percentage of whole blood is made up of erythrocytes?
45%
What term describes the percentage of blood volume occupied by erythrocytes?
Hematocrit
What are the two main components of Plasma?
Water (90%) and dissolved substances (proteins, electrolytes, nutrients, gases, wastes)
What are the two main components of Blood?
Plasma and Formed Elements
What are the three major types of Formed Elements in blood?
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells), Leukocytes (White Blood Cells), and Platelets
What are the three major types of Plasma Proteins?
Albumin, Globulin, and Fibrinogen
What are the two main categories of Leukocytes?
Granulocytes and Agranulocytes
Which three leukocytes are classified as Granulocytes?
Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils
Which two leukocytes are classified as Agranulocytes?
Lymphocytes and Monocytes
What are the functions of plasma proteins?
Maintaining blood osmotic pressure
Transporting substances
Immune function
Blood clotting
Regulation of pH
Which plasma protein is most abundant and helps maintain osmotic pressure?
Albumin
What do Albumin and globulins help prevent?
fluid from leaking out of the blood vessels into the surrounding tissues
What do plasma proteins transport?
various substances such as hormones, nutrients, and waste products
How do plasma proteins help with immunity?
Immunoglobulins play a vital role in the immune system by fighting infections
What plasma protein helps with blood clotting?
Fibrinogen
What is the most commonly ordered blood test?
Complete Blood Count
What is the blood volume equation?



What is the key structural feature of an erythrocyte (RBC) and what is its functional advantage?
Biconcave disc shape; it provides a huge surface area-to-volume ratio, maximizing gas exchange efficiency
What major cellular components are absent in mature erythrocytes?
Nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles (including mitochondria)
What percentage of an RBC's content is hemoglobin?
More than 97%
Why is the absence of mitochondria in RBCs functionally beneficial?
It means RBCs use anaerobic respiration and do not consume the oxygen they carry, making them perfect oxygen transporters
What is the primary function of erythrocytes?
To transport oxygen in the blood
What are the two main structural components if a hemoglobin molecule?
Globin protein (4 polypeptide chains) and 4 Heme groups
What are the four polypeptide chains called?
Two alpha and two Beta polypeptide chains
How many hemoglobin molecules are in a single red blood cell (RBC)?
About 250 million hemoglobin molecules
How many oxygen molecules can one hemoglobin molecule carry at maximum?
Four oxygen molecules (one per heme group)
What is the total oxygen-carrying capacity of one RBC?
Up to 1 billion oxygen molecules
What is the main function of hemoglobin?
To transport oxygen from the lungs to peripheral tissues.
What percentage of oxygen in the blood is carried by hemoglobin?
More than 98%
What is hemoglobin called when it is bound to oxygen, and what is its color?
Oxyhemoglobin (HbO₂) – bright red.
What is hemoglobin called when it has released oxygen, and what is its color?
Deoxyhemoglobin (reduced hemoglobin) – dark red
What is hemoglobin called when it is bound to carbon dioxide?
Carbaminohemoglobin (HbCO₂).
Can hemoglobin bind both O₂ and CO₂ at the same time?
Yes, at different binding sites
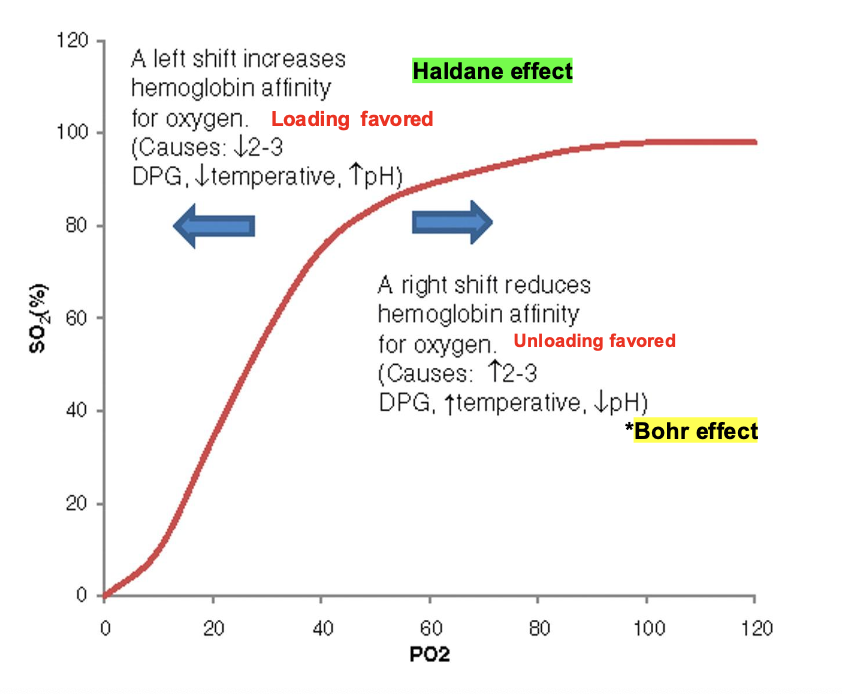
What is this?
Oxyhemoglobin (O2-Hb) Dissociation Curve
Bohr’s Effect
Presence of CO2 decreases the affinity of Hb for O2
Haldane Effect
Combination of O2 with Hb displaces CO2 from Hb
Bohr happens when what?
unloading
Haldane happens when what?
Loading
What is Erythropoiesis?
formation of red blood cells
What feedback loop is the hormonal regulation of erythropoiesis?
A negative feedback loop
What is the hormonal regulation of erythropoiesis based on?
Oxygen levels and Erythropoietin (EPO) levels in the blood
What is Erythropoietin (EPO) synthesized by?
peritubular cells of the kidney
What happens to EPO when in the presence of oxygen?
They are hydroxylated and digested by proteosomes
When do EPO always synthesize?
When EPO levels are decreased by sufficient levels of oxygen and when EPO levels are increased by hypoxemia/hypoxia
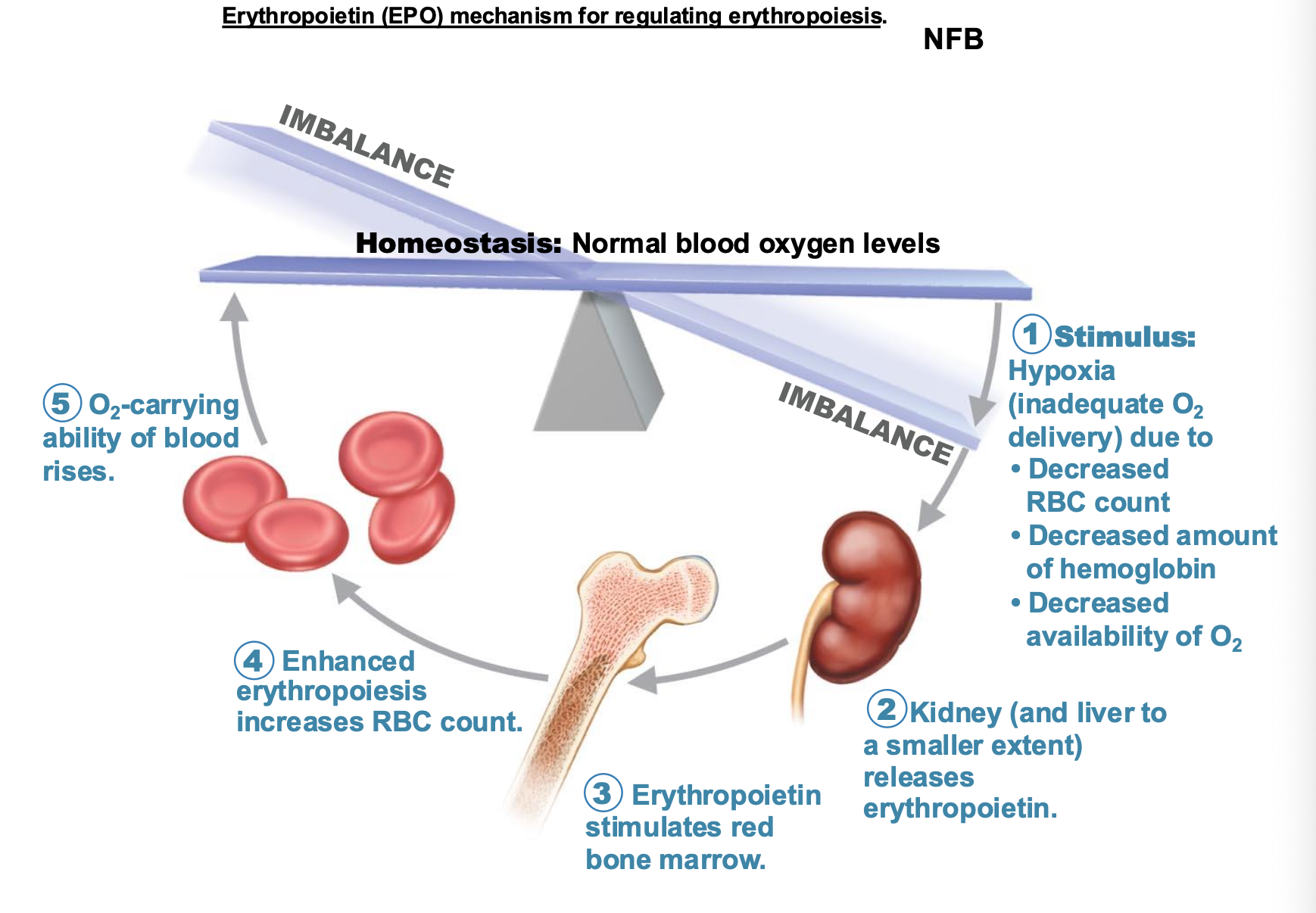
What are the steps in how Erythropoietin (EPO) mechanism for regulating erythropoiesis?
What is the life span of RBC?
Only 100-120 days, short
What stimulates the production of erythropoietin?
Low O2 levels in blood stimulate kidneys to produce erythropoietin
What promotes erythropoiesis in red bone marrow?
Erythropoietin and necessary raw materials in blood promotes erythropoiesis as new erythrocytes enter the bloodstream
What happens to older and damaged red blood cells? What happens to the hemoglobin?
engulfed by macrophages of spleen, liver, and bone marrow; the hemoglobin is broken down?
When the hemoglobin is broken down, what happens to the raw materials?
They are made available in blood for erythrocyte synthesis
Hemoglobin is broken into what two pathways?
Heme and Globin
What does globin provide back to the bloodstream?
Its amino acids are used for other protein synthesis
Heme splits into two different pathways, what are they?
Iron portion and non-iron portion
In the iron portion of Heme, what is iron stored as?
ferritin or hemosiderin
What is iron bound to? What happens after?
Transferrin; released to blood from liver as needed for erythropoiesis
What is the non-iron portion called? Where is it picked up?
Bilirubin; picked up by the liver
Where is Bilirubin released and secreted?
released in bile, secreted into blood
Bilirubin when in bile is metabolized to what by bacteria?
urobilinogen
Anemia
decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood
What are causes to Anemia?
Decrease in RBC number; Decreased hemoglobin content in RBC; Abnormal hemoglobin
What are three classifications of decrease in RBC number anemia?
Hemorrhagic anemia, Aplastic anemia, Hemolytic anemia
What are three types of anemia that has decreased hemoglobin content in RBC?
Sideroblastic anemia, Iron-deficiency anemia, Pernicious anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia
An adult requires 1 mg to 2 mg per day of iron. As the newly produced RBCs contain less amount of hemoglobin, they are relatively of small size when compared to normal RBCs, thus the name, microcytic
Pernicious anemia
Vitamin B12 deficiency causes a failure of DNA syntehsis and resultant impaired cell division
What are two types of abnormal hemoglobin?
Sickle-cell anemia and Thalassemia
What are severe symptoms of anemia?
Fainting, Chest pain, Angina, Heart attack
Hypoxemia
decreased blood O2 levels
Hypoxia
Inadequate oxygen supply to tissues/organs
What gene is prevalent in areas with high incidence of malaria?
Sickle-cell gene
Normal erythrocyte has normal hemoglobin amino acid sequence in the beta chain while sickled erythrocyte has how many amino acid changes in the beta chain of hemoglobin?
one
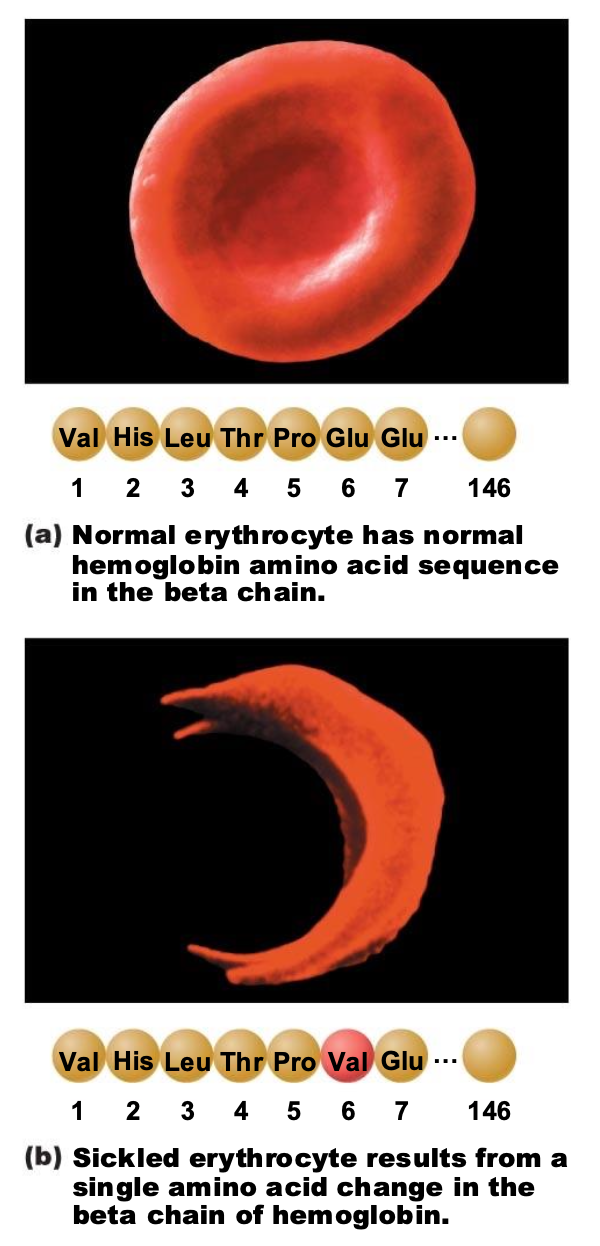
What treatment is there for sickle cell?
Hydroxyurea
What form of hemoglobin is present in fetus and small infants?
fetal hemoglobin (HbF), most disappear early in childhood but some persist