1 - Coagulation Disorders
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
thrombosis definition
formation of blood clots (partial or complete) within the blood vessels which limits natural blood flow
hemostasis definition
tightly regulated process where the body attempts to maintain normal blood flow in vessels despite damage/trauma
hemostasis process (steps)
constriction of the blood vessel
primary hemostasis: formation of a temporary platelet plug
secondary hemostasis: activation of the coagulation cascade
formation of a fibrin plug
primary hemostasis
initiated due to damage to the endothelium of the blood vessel
smaller vessel allows for less blood loss
several biomarkers are released to promote vasoconstriction
promotion of platelet adhesion and activation at the injured site
formation of temporary platelet plug
biomarkers that support vasoconstriction
endothelin-1
collagen
ATP
von Willebrand factor (vWF)
platelet plug steps
part of primary hemostasis
activation: platelet plug stabilizes to the vessel wall via vWF
granules of serotonin, ADP, and Ca2+ are released
glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors are activated
aggregation
platelet plug
aggregation definition
attracts other platelets to the site
platelet plug definition
a weak, temporary seal in primary hemostasis
secondary hemostasis
AKA coagulation cascade
clotting factors are activated
prothrombin is converted to thrombin
fibrinogen is converted to fibrin
a strong plug is formed
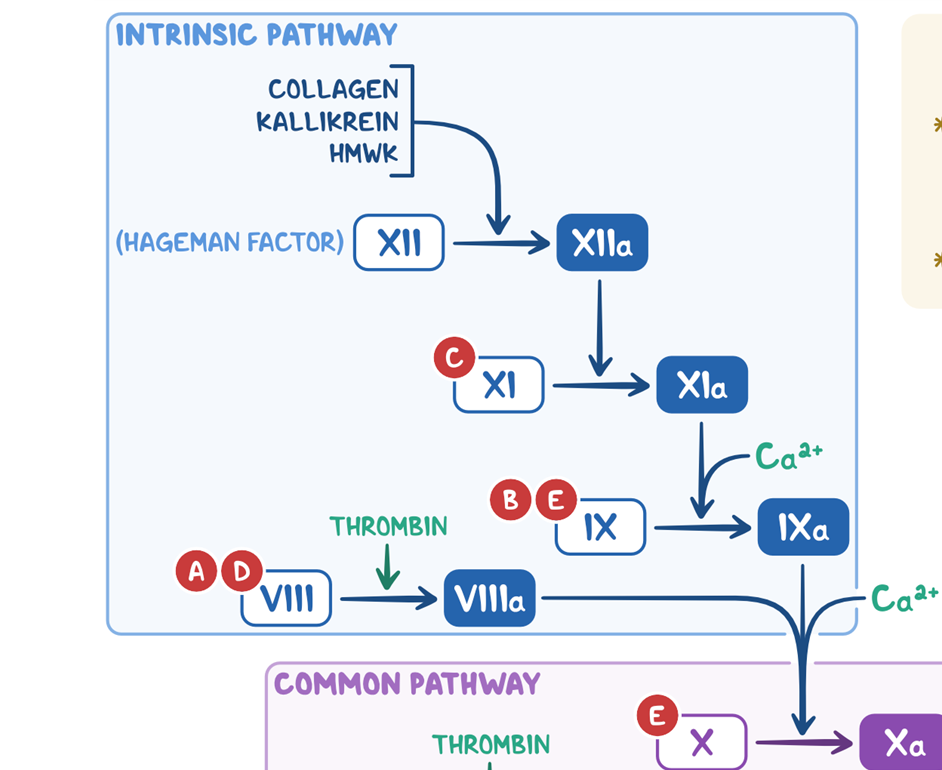
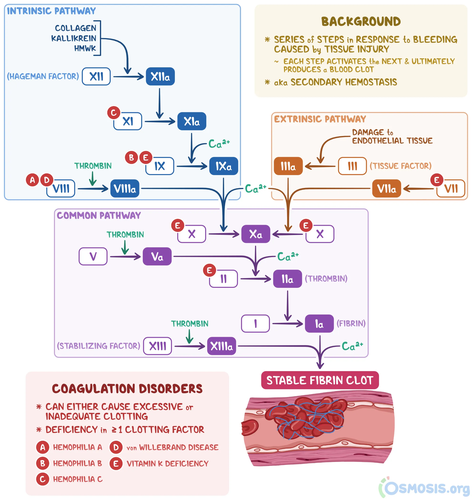
intrinsic pathway AKA contact activation pathway - speed
slower than extrinsic pathway (takes minutes)
intrinsic pathway AKA contact activation pathway - activation & beginning
begins when Factor XII comes into contact with foreign material from injury to vessel wall
activated by calcium
vessel wall examples
endothelial cells
collage
extravascular material
intrinsic pathway AKA contact activation pathway steps
Hageman Factor (XII) → XIIa via collagen, kallikrein, HMWK
XI → Xla via XIIa
IX → IXa via Xla and calcium
VIII → VIIIa via thrombin
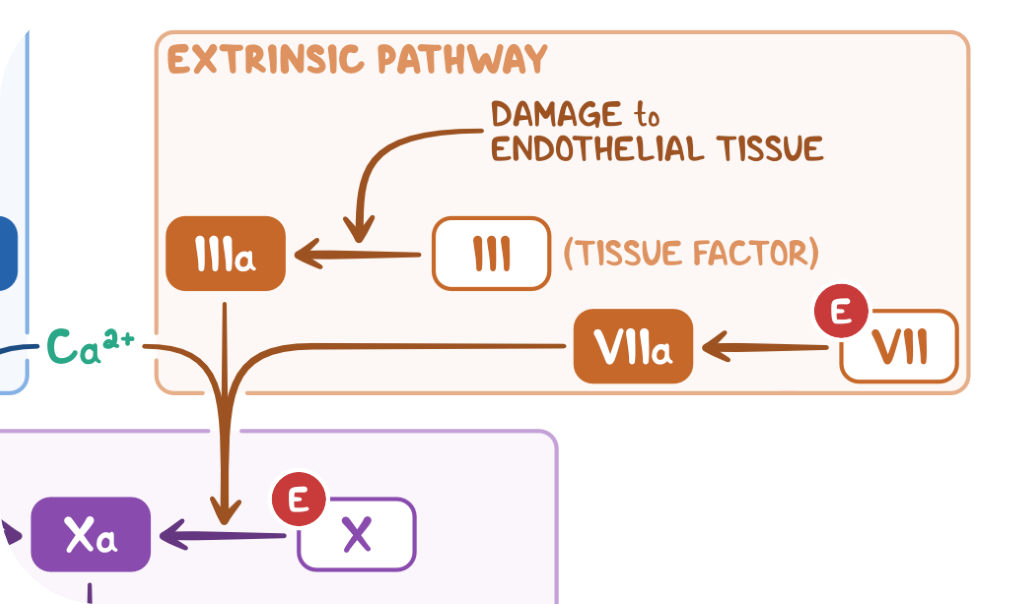
extrinsic pathway AKA tissue factor pathway - speed
very fast pathway (seconds)
extrinsic pathway AKA tissue factor pathway - what activates it?
TF (Factor III)
what forms activated complex in extrinsic pathway AKA tissue factor pathway?
TF and Factor VII form activated complex
extrinsic pathway AKA tissue factor pathway - steps
tissue factor (III) → IIIa via damage to endothelial tissue
VII → VIIa
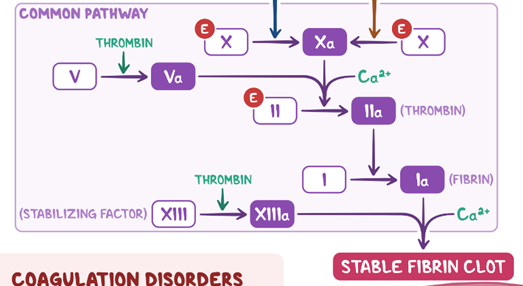
common pathway - steps
X → Xa via:
calcium, VIIa, IIIa
or
IXa, calcium, VIIIa
V → Va via thrombin
II → IIa (thrombin) via Xa, Va, and calcium
I → Ia (fibrin) via IIa (thrombin)
XIII (stabilizing factor) → XIIIa via thrombin
stable fibrin clot via Ia (fibrin), calcium, and XIIIa
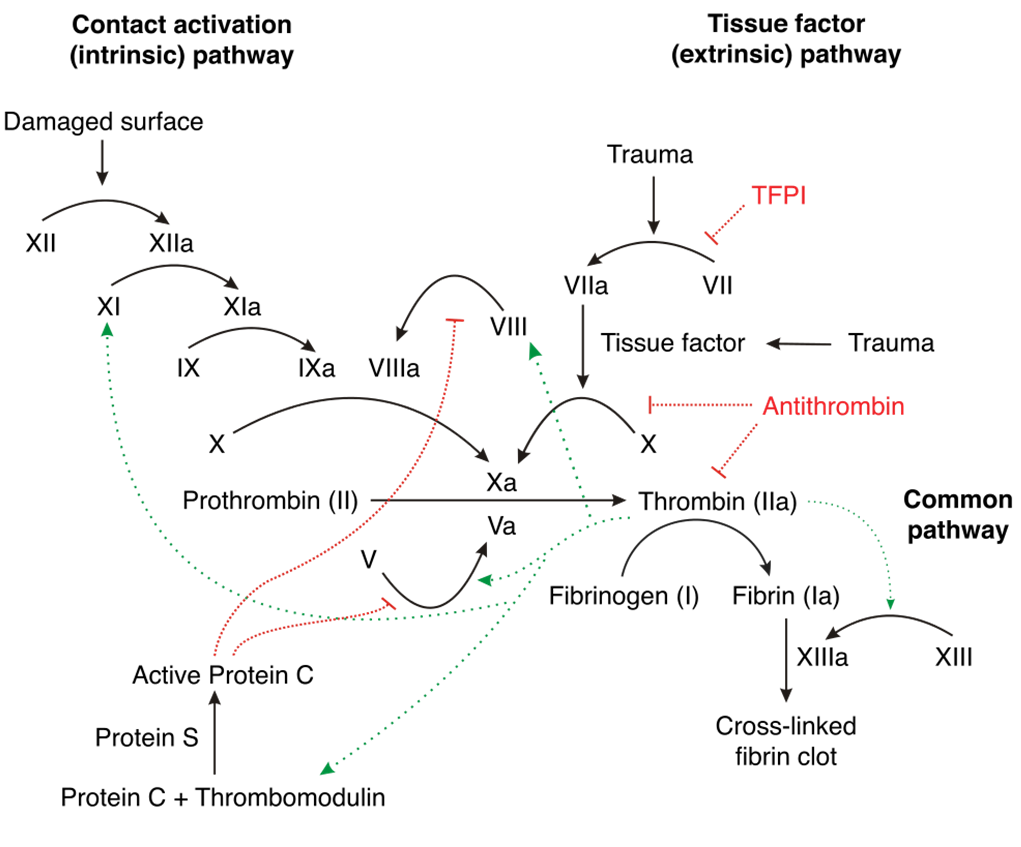
natural anticoagulants in the clotting cascade
Protein C
Protein S
Antithrombin (ATIII)
TFPI: Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (FVIIa)
Protein C
a natural anticoagulant
part of the clotting cascade
inhibits FVIIIa and FVa (vitamin K dependent)
factors VIIIa and Va are ______ dependent
vitamin K dependent
Protein S
a natural anticoagulant
part of the clotting cascade
cofactor for protein C
antithrombin (ATIII)
a natural anticoagulant
part of the clotting cascade
inhibits factors Xa and IIa primarily
clotting cascade steps
another name for II and IIa
II = prothrombin
IIa = thrombin
another name for I and Ia
I = fibrinogen
Ia = fibrin
in the clotting cascade, what can inhibit the formation of VII → VIIa?
TFPI
in the clotting cascade, what can inhibit X → Xa?
antithrombin
in the clotting cascade, what can inhibit thrombin (IIa)?
antithrombin
in the clotting cascade, what can inhibit V → Va?
active protein C
in the clotting cascade, what inhibits VIII → VIIIa?
active protein C
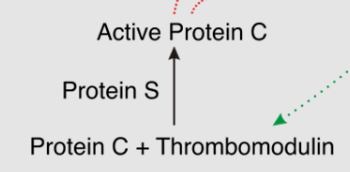
how is protein C created in the clotting cascade?
protein C + thrombomodulin → active protein C
catalyzed by Protein S
Protein C half life
medium-long
Protein S half life
medium-long
Factor II half life
long
factor VII half life
short
Factor IX half life
long
Factor X half life
very long
fibrinolysis
blood clot = temporary patch
once the vessel has healed, fibrin is lysed (fibrinolysis)
what activates the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin
Factor XII
what breaks down fibrin in the fibrinolytic cascade
activated plasmin
practice question: Daisy is in the kitchen chopping veggies. She cuts herself with a knife. She applies pressure and the bleeding stops.
What is the process called where the bleeding is stopped?
What pathway is triggered?
hemostasis
extrinsic pathway
rationale: something external is causing blood loss
practice question: If a pt has a deficiency in Factor VIII, would they clot or bleed?
bleed
practice question: If a pt has a deficiency in Protein C, would they clot or bleed?
clot
practice question: If a pt has a deficiency in antithrombin, would they clot or bleed?
clot
arterial thrombosis - activation
platelets
injury to vessel wall
arterial thrombosis - common causes
inflammation
high LDL level
infection
HTN
composition of arterial thrombosis
antiplatelet
examples of arterial thrombosis
ischemic stroke due to atherosclerosis
acute coronary syndrome
venous thrombosis - activation
clotting cascade
venous thrombosis - common cause/s
stasis
state of hypercoagulability
venous thrombosis - composition
fibrin rich
venous thrombosis - tx
anticoagulant
venous thrombosis - example/s
DVT
PE
cardioembolic stroke due to AFib
Virchow’s Triad
3 components that can contribute to the development of a thrombus
hypercoagulability
(circulatory) stasis
vascular damage AKA endothelial injury
hypercoagulability
part of Virchow’s triad
blood
increased blood coagulation/hyperviscosity due to genetic defects, certain disease states, medications
examples:
major surgery/trauma
malignancy
pregnancy
infection
thrombophilias
medications
estrogen
tamoxifen
raloxifene
cancer drugs
heparin products
autoimmune disease
dehydration
factor deficiencies/mutations
nephrotic syndrome
VTE etiology
(circulatory) stasis
part of Virchow’s Triad
flow
interrupted blood flow
examples:
immobility
obesity
tumors
pregnancy
surgery
acute illness
paralysis
older age
etiology of VTE
vascular damage AKA endothelial injury
part of Virchow’s triad
vessel
irritation and inflammation of vessel wall leading to injury/trauma
examples:
cellulitis
thrombophlebitis
atherosclerosis
heart valve
physical trauma or injury
etiology of VTE
due to surgery, trauma, indwelling catheters, damage to valves leads to venous stasis
What component of triad is… cancer?
hypercoagulability
What component of triad is… mechanical heart valve?
vascular damage AKA endothelial injury
What component of triad is… obesity?
(circulatory) stasis
practice case:
What risk factors does this pt have for a clot?
67 yo F with PMH of depression, osteoarthritis, and post menopausal vasomotor sx.
Medication List: estradiol 0.5mg once daily, sertraline 50mg once daily, acetaminophen PRN
Social sx: 1 PPD smoker x 30 yrs, occasional alcohol use (1-2 drinks per day)
Pt is s/p TKA (Total Knee Arthroplasty) this morning. She has just been moved to a room from the PACU (Post-Anesthesia Care Unit)
estradiol
osteoarthritis (decreased movement)
TKA (decreased movement)
age (decreased age could possibly mean decreased movement/mobility)
smoking (vascular damage/endothelial injury)
alcohol use (vascular damage/endothelial injury)
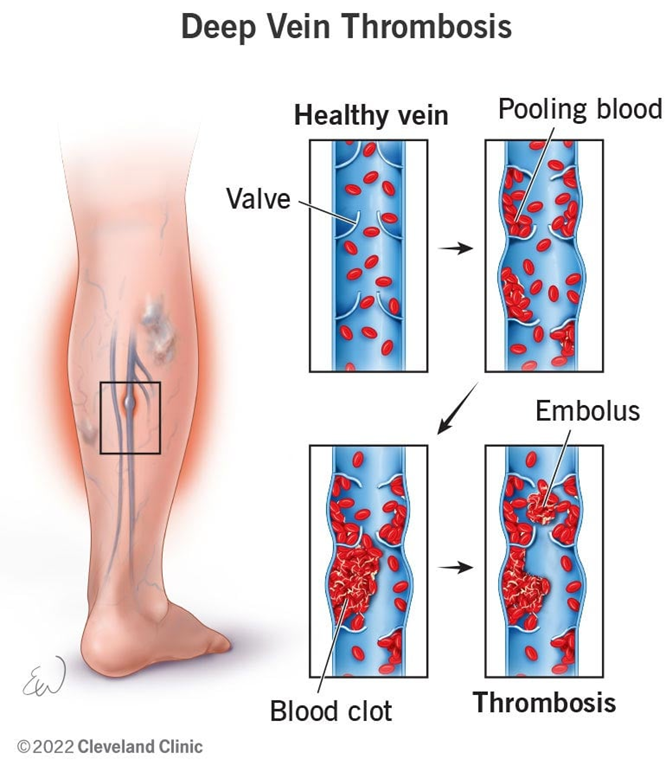
VTE pathophysiology (steps)
healthy vein in valve
blood pools in vein
blood clot forms in vein
embolus forms, causing thrombosis
DVT presentation
unilateral leg pain and swelling
Homan’s sign
tenderness
skin discoloration
ulceration
warmth
asymptomatic
Homan’s sign
pain in back of knee when dorsiflexing the foot
PE clinical presentation
chest pain/tightness
shortness of breath
tachypnea
tachycardia
syncope, dizziness, light-headedness
cardiogenic shock
hemoptysis
signs of DVT first (occasionally)
ischemic stroke etiology
stasis in the atria
ischemic stroke pathophysiology
emboli from heart circulates to brain causing blood vessel occlusion
ischemic stroke presentation
numbness/weakness in face, arm, or leg
confusion
trouble speaking
vision changes
trouble walking
severe headache
Factor V Leiden (FVL) - etiology
point mutation in the F5 gene
Factor V Leiden (FVL) - pathophysiology
insensitive to activated protein C, 20-fold slower degradation of FVL
Factor V Leiden (FVL) - clinical presentation
VTE
asymptomatic
prothrombin 20210 - etiology
point mutation of the G20210A gene
prothrombin 20210 - pathophysiology
increased concentration of prothrombin in circulation
prothrombin 20210 - clinical presentation
VTE
asymptomatic
Protein C&S deficiency - etiology
Protein C: genetic mutation of PROC gene
Protein S: genetic mutation of PROS1 gene
Protein C&S deficiency - pathophysiology
increased factors V & VIII → increased thrombotic production → prothrombotic state
Protein C&S deficiency - clinical presentation
VTE
stroke
miscarriage
warfarin induced skin necrosis
antithrombin III deficiency - etiology
hereditary
autosomal dominant trait → heterozygous for variant SERPINC1 gene
acquired
disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
liver disease
trauma
critical illness (sepsis)
medications
heparin
estrogen products
antithrombin III deficiency - pathophysiology
reduced levels of AT lead to uncontrolled thrombin generation and fibrin deposition
antithrombin III deficiency - clinical presentation
VTE
heparin resistance
stroke
antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) - etiology
autoimmune disorder creating antiphospholipid antibodies (APLA)
triple positive has highest risk of thrombosis
antiphospholipid antibodies (APLA)
anticardiolipin antibodies
anti-beta-2-glyocprotein-I antibodies
lupus anticoagulants
antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) - pathophysiology
upregulation of tissue factor
decreased nitric oxide
increased endothelial injury
antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) - clinical presentation
DVT (more common)/PE
stroke
catastrophic APS
miscarriage
hyperhomocysteinemia - etiology
variation in the methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene
hyperhomocysteinemia - pathophysiology
exact mechanism unknown
thought to cause endothelial injury and inflammation
hyperhomocysteinemia - clinical presentation
VTE
cardiovascular disease
Which of the following clotting disorders leads to upregulation of FV and FVIII?
a. FVL
b. Protein C deficiency
c. 20210 mutation
d. antiphospholipid syndrome
Which of the following clotting disorders leads to upregulation of FV and FVIII?
a. FVL
b. Protein C deficiency
c. 20210 mutation
d. antiphospholipid syndrome
In a patient with hyperhomocysteinemia, which of the following are they at an increased risk for? Select ALL that apply.
a. PE
b. hypotension
c. bleeding
d. MI
e. DVT
In a patient with hyperhomocysteinemia, which of the following are they at an increased risk for? Select ALL that apply.
a. PE
b. hypotension
c. bleeding
d. MI
e. DVT