Proliferation, transformation, microenvironment, immunity
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
unlimited, stimuli, apoptosis
neoplastic cells have _______ proliferative potential that is independent of _______ or inhibitors.
These cells are also less susceptible to ___________
false; not technically, because irregular cycles and occasional death (cycle arrest)
true/false: growth of neoplastic cells is truly exponential
quiescence, G1/S checkpoint, G2/M checkpoint
unlimited proliferative cells will not enter the ________ phase of the cell cycle, and will bypass which two checkpoints?
mitotic count
_________: tell us the average mitotic figures per standardized field
malignant potential
Active division can increase the concern for _____________ even though some cells never complete the division process
senescence
_____________________: permenant arrest in G1 phase for neoplastic cells
DNA damage, oxidative stress, telomere shortening
telomerase
Cells get trapped in senescence (in G1) due to _________, ___________ or _________, but some neoplastic cells can reexpress __________ to lead to the expansion of telomeres and the escape of senescence
p53 inactivation
Some proliferative cells escape apoptosis by _______ inactivation
latency
_______: time before a tumor is clinically detectable
slow, fast
as a general rule, benign tumors are _____ moving and malignant are _______
cumulative
cell proliferation
DNA repair
angiogenesis
invasiveness
genetic and epigenetic changes in the neoplasm have a _________ effect overtime.
list a couple of the things that this can affect (4)
true
true/false: gradual change = stepwise motion = multistage carcinogenesis
This applies to many neoplasms but not all of them
(sorry, I didnt know how else to write this)
initiation, promotion, progression
what are the three general phases of a neoplastic timeline?
irreversible genetic damage
_______________________________ must occur for the development of a neoplasm to happen. (initiation)
mutagen
chemical, physical, or viral agents
Initiation stems from a genetic change that is introduced by an initiator/______________________ that can be _______, _______ or ________ agents that damage DNA
promoters, benign tumors
initiated cells can stay quiescent for years, but eventually they will encounter ________ that make the environment better for proliferation. They then begin outgrowth and give rise to ________________
false; they are NOT mutagenic (yes reversible)
true/false: the promotors that push initiated cells into the promotion phase are introducing mutagenic (irreversible) change
progression, malignant, subclones
When cells enter ________ the final stage, they have entered a _________ transformation and this is irreversible.
The increasing complexity and genetic instability means that growth is rapid and ________ can stem from heterogenous copies of tumor cells
BAD, they can help the tumor evolve and adapt
are subclones good or bad?
increase proliferation, immune system evasion, independent blood supply
what three things are necessary for neoplastic success in the progression phase?
neoplastic cells
the tumor parenchyma includes what?
extracellular matrix, blood vessels, fibroblasts, inflammatory/immune cells
what does the tumor stroma include?
growth factors, cytokines, hormones, inflammatory mediators
tumor-stromal interactions include the use of molecules like that? (4)
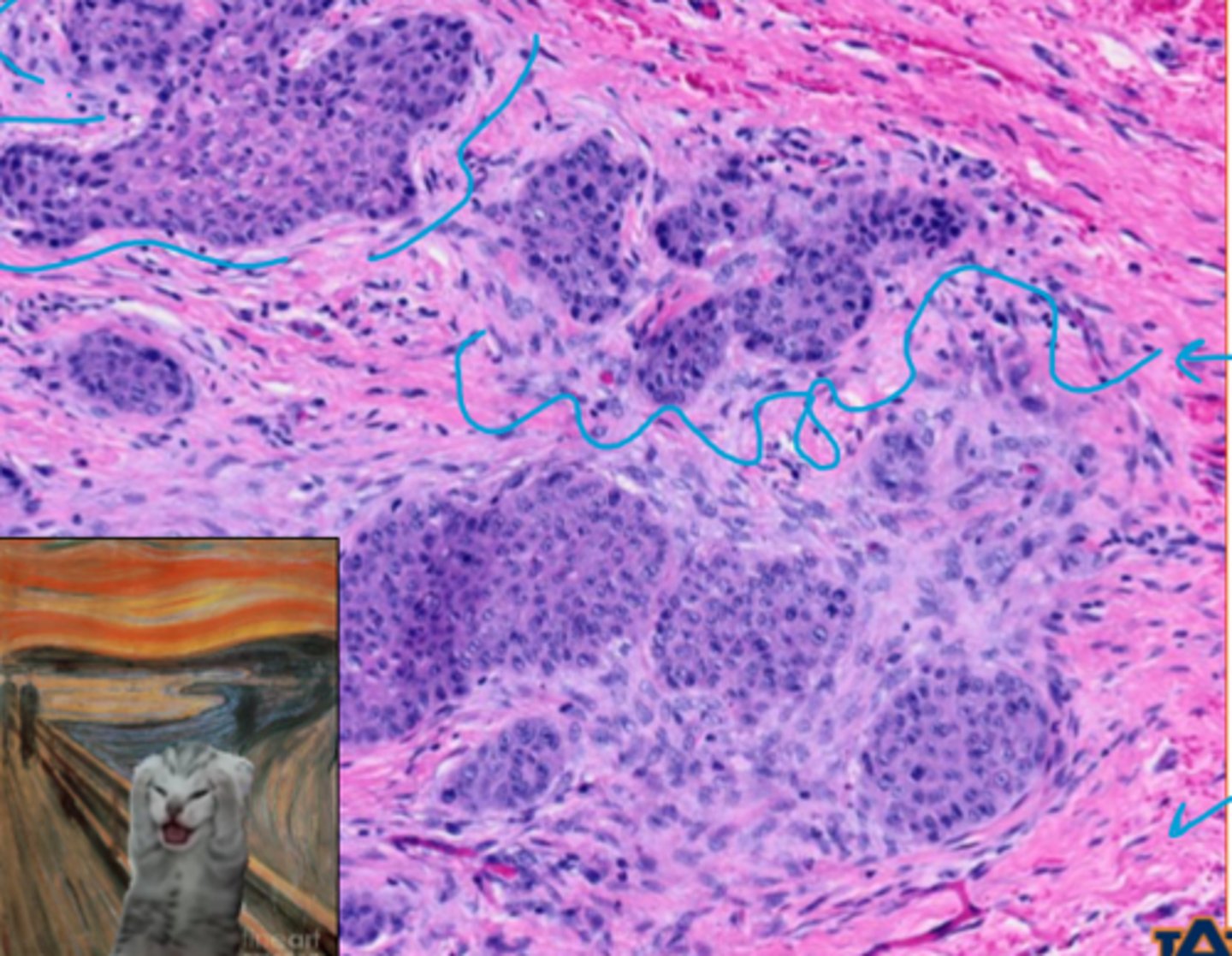
scirrhous
__________ = desmoplastic reaction with features of a carcinoma invasion; hyjacking the old host environment to degrade and rebuild new tissue
scirrhous reaction, pre-existing collagen, new collagen
What type of reaction is this?
What is the pink material around the outside?
What is the purple material surrounding the tumor islets??
angiogenesis
__________________: the formation of new blood vessels; pivotal for tumor growth and progression
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), Fibroblastic growth factor (FGFs)
______________________ stimulates endothelial cells to multiply and restore endothelial lining
_____________________ stimulates keratinocyte migration, angiogenesis, wound contraction
Both are necessary for angiogensis
lymphangiogenesis
_____________________: formation of new lymphatics; requires VEGF and is essential for lymph node metastasis
chemokines, cytokine
mixed
prostaglandins, leukotrienes, & ROS
inflammation around the tumor is attracted by ________ and _______ secreted by tumor cells
It is classified as ___________ and is a source of _______, ________ and ________
immunosurveilance
____________________: identification and targeting of infected or foreign cells
true
true/false: failure of antitumor response can allow neoplasms, so those who are immunosupressed can have increased tumor susceptibility
tumor antigens
_______________: proteins expressed on surface of neoplastic cells (includes neoantigens and tumor associated antigens)
tumor specific antigen, unique, unfamilliar
a tumor neoantigen is also called a _____________________________
These are ________ mutations in a transformed cell that lead to proteins that are ________ to T cells
Great therapy! for INDIVIDUALS. Can't really mass produce them
Because they are so unique to a specific tumor, these neoantigens should be really easy to target for therapy! SO! We cured cancer!!! Right?
tumor-associated antigen
_______________________ are expressed in both normal and neoplastic cells. but are way OVER produced or produced in the wrong location in tumor cells
study, identify, large scale therapies
tumor-associated antigen is easier to _______ and _______ than other markers and is far more convenient for _____________
NK cells, macrophages
what are the innate antitumor effector mechanisms?
dendritic cells presenting tumor antigens, cell mediated (CD8+, CD4+), humoral immunity
what are some of the adaptive antitumor effector mechanisms?
cell mediated
what is the most effective adaptive antitumor effector mechanism?
antigen masking, immunosuppression,
What are two ways that tumor cells evade the immune system?
antigen masking
___________: selection of clones lacking tumor antigen expression OR integration with glycocalyx molecules, fibrin and antibodies
PD-L1, TGF-a, Fas ligand
Neoplastic cells can express _________ which inhibits T cell killing; _________ which inhibits lymphocyte and macrophage function and secretion or _______ which binds to T cells and causes LYMPHOCYTE apoptosis
rapidly dividing cells
Chemotherapy targets _______ which means both host and tumor cells
antitumor effector, antitumor immune resposne
INSTEAD of chemo,
yuo can provide increased _____________ cells or antibodies which is a passive process, or you can stimulate _________ which is an active process
monoclonal antibodies, tumor antigens, fast, short-lived
passive immunotherapy includes giving the patient __________.
These target ____________ and provide a therapy that is [fast/slow], [long/short lived] and can also deliver therapeutic agents
vaccination, cytokine, proinflammatory
active immunotherapy includes __________ with tumor cells or antigens, ________ administration or ______________ compounds being stimulated or given to the patient
melanoma vaccine
___________: Tumor vaccine in dogs made from human DNA which aims to delay metastasis. The human DNA is seen as foreign and triggers the immune system
protein tyrosinase
melanoma vaccines target _________ which is overexpressed in melanomas