Economics - National accounts aggregates
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
National account
an accounting record of the total value of production, income and expenditure in a country … & is used to measure economic activities of a country i.e. GDP
2
New cards
Final goods
goods that are ready for consumption by the participants in the economy
3
New cards
Intermediate goods
goods that are used as inputs to produce other goods and services
Goods: wood to make tables, plastic to make aircons, flour to bake a cake, water to grow plants
Services: transportation, electricity, internet for communication
Can be intermediate and final at the same time
Goods: wood to make tables, plastic to make aircons, flour to bake a cake, water to grow plants
Services: transportation, electricity, internet for communication
Can be intermediate and final at the same time
4
New cards
Double-counting
occurs when intermediate products are added to final products and will cause national accounts to reflect an incorrect higher total
5
New cards
Residual item
balancing item due to errors and omissions
6
New cards
Taxes on production
taxes not linked to a specific good or service (e.g. tax on land and buildings, business licensees, payroll taxes)
7
New cards
Taxes on products
taxes payable per unit of some good and service e.g. VAT - paid by consumers
8
New cards
Subsidies on production
subsidies that are not linked to specific goods or services, e.g. subsidy on employment.
9
New cards
Subsidies on production
financial incentives to help struggling industries produce, as well as direct subsidies payable per unit exported to encourage exports (e.g. government subsidy on bread).
10
New cards
Gross domestic expenditure (GDE)
the value of total spending within the borders of a country in a specific period
11
New cards
Gross national income (GNI)
total remuneration for the factors of production
12
New cards
Real GDP (GDP at constant prices)
adjusted for price changes
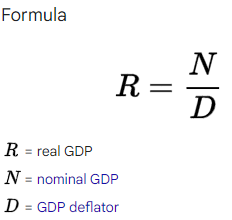
13
New cards
Nominal GDP (GDP at current prices)
gives the current value of the price, not adjusted for price changes
14
New cards
GDP Deflator
ratio of GDP at current prices to the GDP at constant price for a particular period
Formula for GDP Deflator: Nominal GDP ÷ Real GDP x 100
Reasons for calculating GDP deflator: to eliminate the effect of price changes to get the actual GDP not distorted by inflation
Formula for GDP Deflator: Nominal GDP ÷ Real GDP x 100
Reasons for calculating GDP deflator: to eliminate the effect of price changes to get the actual GDP not distorted by inflation
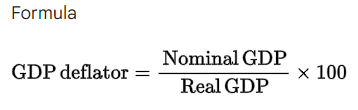
15
New cards
GDP @ basic price
total value of all final goods and services produced within the borders of a country in a specific period
16
New cards
GDP @ market price
total value of all final goods and services sold within the borders of a country in a specific period plus taxes on products minus subsidies on products
17
New cards
GVA (Gross Value Added)
the value of goods and services produced by an industry, sector, manufacturer, area or region in an economy
(same thing as GDP at basic price - sometimes refered to as “GVA at basic price”)
(same thing as GDP at basic price - sometimes refered to as “GVA at basic price”)