Chpt 14
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Hong Kong provides ab example of a country that has maintained a currency board. The purpose of the currency board is to…
maintain an especially strong commitment to a fixed exchange rate
Under a system of fixed exchange rates, the purpose of a currency devaluation is to cause the exchange value of a currency to ______, thus counteracting a balance of payments ______.
depreciate, deficit
For Ecuador, an advantage of adopting the dollar as its official currency is that
Ecuador escapes the likelihood of a speculative attack
Assume that interest rates in London increase relative to those in Switzerland. Other things being equal, under a floating exchange-rate system one would expect the pound (relative to swiss franc) to…
appreciate due to the increased demand for pounds.
Developing nations with more than one major trading partner tend to peg the value of their currencies to
a basket of currencies
Under a system of floating exchange rates, other things being equal, a U.S trade deficit with Japan will cause…
an increase in the dollar price of yen
To defend a pegged exchange rate that overvalues its currency, a country could
purchase its own currency in international markets
Given a two-country world, assume Canada and Sweden devalue their currencies by 20 percent. other things being equal, this would result in…
an appreciation in neither currency
To offset an appreciation of the dollar against the yen, other things being equal, the federal Reserve would
sell dollars on the foreign exchange market and lower domestic interest rates
In recent years, the United States has accused China of manipulating the yuan so as to gain an unfair competitive advantage in global trade. Thus, proposals have been made that the United States should offset China’s currency manipulation by…
buying yuan and selling dollars, thus appreciating the yuan against the dollar
T/F: Sources of a currency crisis include weak financial systems and budget deficits financed by inflation
True
T/F: If Uganda sets its par value at 400 shillings per SDR and Burundi sets its par value at 200 francs per SDR, the offical exchange rate is 1 franc = 0.5 shillings
False
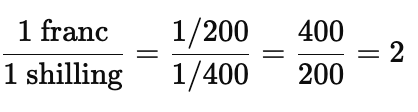
1 franc = 2 shillings
Suppose that the United States increases its imports from Switzerland, resulting in a rise in the demand for francs from D0 to D1. Other things being equal, under a floating exchange-rate system, the new equilibrium exchange rate would be…
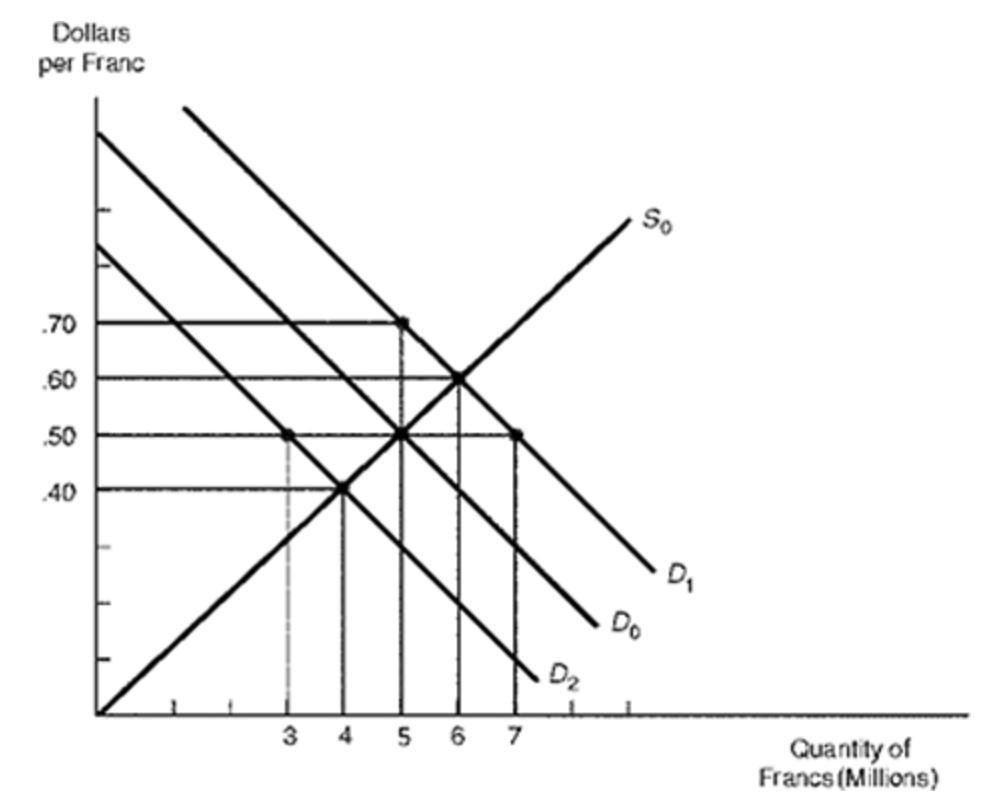
$0.60 per franc
The excess demand for francs leads to an increase in the exchange rate from $0.50 to $0.60 per franc
Demand and supply of British pounds is initially D0 and S0. Suppose the United States decreases financial investment in England. Other things being equal, under a floating exchange-rate system the new equilibrium exchange rate would be…
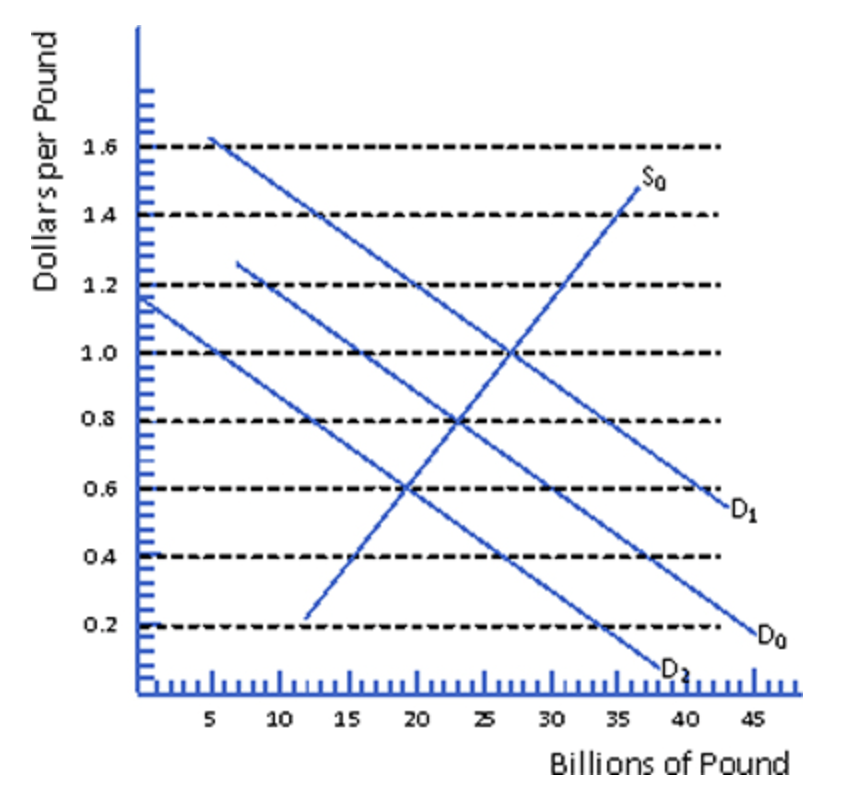
$0.60 per pound
Suppose the demand for pounds increases from D0 to D1. Other things being equal, under a fixed exchange-rate system the U.S. exchange stabilization fund could maintain a fixed exchange rate of $0.80 per pound by…

selling pounds for dollars on the foreign exchange market
If the demand for pounds increases, the pound would appreciate (dollar would depreciate). To defend the official exchange rate of $0.80 per pound, the exchange stabilization fund must purchase the excess supply of dollars with an equivalent amount of pounds
T/F: Fixed exchange rates tend to be used primarily by small developing nations whose currencies are anchored to a key currency such as the U.S dollar
True
T/F: Large Countries with large and diversified economies often prefer floating rates
True
T/F: Small nations whose financial and trade relationships are mainly with a single trading partner, often choose to adopt pegged rates
True
T/F: Large nations with many trading partners tend to choose floating rates
True
What factors underlie a nations decision to adopt floating exchange rates or fixed rates?
Size of nation
Degree of labor mobility
Openness of the economy
Availability of fiscal policy to cushion downturns
T/F: Managed floating exchange rates combine market-determined exchange rates with foreign exchange market intervention to take advantage of the best features of floating exchange rates and fixed exchange rates
True
What characterizes the operation of a managed floating exchange rate?
A nation can alter the degree that it intervenes in the foreign exchange market
T/F: A currency board is a monetary authority that issues notes and coins convertible into a foreign anchor currency at a fixed exchange rate.
True
T/F: Usually the fixed exchange rate is set by law, making changes to the exchange rate costly for governments
True
T/F: Currency boards offer the strongest form of a fixed exchange rate that is possible short of full currency union
True
T/F: The term crawling peg implies that par value changes are implemented in a large number of small steps. The crawling peg mechanism has been used primarily by nations having high inflation rates.
True
Why do nations use a crawling peg exchange rate system?
To make small but frequent exchange rate adjustments promoting payments balance
T/F: Capital controls are government-imposed barriers to foreign savers investing in domestic assets or to domestic savers investing in foreign assets. A government that has a virtual monopoly over foreign exchange dealings may require that all foreign exchange earnings be turned over to authorized dealers. The government then allocates foreign exchange among domestic traders and investors at government-set prices.
True
T/F: Exchange controls, including the rationing of foreign exchange among domestic importers, are sometimes used to help a nation gain control over its balance-of-payments position.
True
What factors contribute to currency crises?
Weak Financial Systems
Changes in interest rates on world markets
Budget deficits financed by inflation
politcal uncertainty
T/F: Developing nations with more than one major trading partner anchor their currencies to a basket of currencies to reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on the domestic economy.
True
T/F: The SDR is a currency basket composed of the currencies of the four IMF countries that have the largest shares of world exports. The basket valuation technique allows the SDR's value to be more stable than the value of any single national currency.
True
What techniques can a central bank use to offset a depreciation of its currency?
Use international reserves to sell that currency on the foreign exchange market
Use international reserves to purchase that currency on the foreign exchange market
Anchoring to a Special Drawing Right (SDR)
Basket of 4 currencies by IMF
Loss of independent monetary policy
Central bank intervention to offset appreciation/depreciation of currency
Impossible Trinity
Free Capital Flows
Independent Monetary Policy
Fixed Exchange Rates
Can only have 2 of the 3
Speculative attacks
Uncertainty/loss of confidence in currency
Sluggish economy, political/economic shocks, large CA deficit
Currency Crisis
Currency depreciates with large and sudden capital outflow
Central bank runs out of reserves keeping the exchange rate fixed
Sudden depreciation of currency as central bank abandons fixed exchange rate
Creates recession and large losses of GDP growth
How to fix currency crisis…
Devalue currency
Increase interest rate to attract capital inflow
Capital controls
Currency Board
Dollarization
Dollarization