OTD: 5050 Health conditions final (not finished)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is health?
To reach a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing, an individual or group must be able to identify and to realize aspirations, to satisfy needs and to change or cope with the environment
What are health disparities?
They are systemic and not random, unfair and unjust, avoidable and unnecessary, not inevitable, and due to the vulnerabilities created by social structures and institutions
What is health inequality?
Systematic, avoidable, and unfair differences in health outcomes that can be observed between populations, between social groups within the same population or as a gradient across a population ranked by social position
Factors contributing to health disparities
Economic factors and poverty, education and literacy, access to healthcare services, physical environment and neighborhood conditions, and social and community support
Examples of health disparities
Racial and ethnic disparities, gender disparities, geographical disparities (urban vs. rural), and age-related disparities
Social determinants of health
They are found in the environment and examples are:
Economic policies & systems
Development agendas
Social norms
Social policies
Racism
Climate change
Political systems
Economic stability
Education Access and quality
Health Care access and quality
Neighborhood and built environment
Social and community context (HHS)
What are the 5 domains of SDOH?
Economic stability
Education access and quality
Health care access and quality
Neighborhood and built environment
Social and community context
T/F: Racial disparities are considered to be one of the 5 domains of SDOH
False
30 y/o M, recently diagnosed with MS, lives in a rural community with limited healthcare access. what SDOH is impacted?
neighborhood and built environment
T/F: the international classification of functioning, disability, and health (ICF) was developed by the AOTA
False, it was developed by WHO
What are core values of OT?
Altruism, Equality, Freedom, Justice, Dignity, Truth, and Prudence
Philosophical assumptions
Occupations are purposeful activity, occupations are fundamental, performance skills have an impact on function, body structures and functions are important
Person first language
Emphasizing the individual before their disability or condition
Example: A 5th grade child with autism
ICF
International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health is a framework that organizes information about health, disability, and how they affect a person’s ability to function
*It was endorsed by the WHO in 2001 as the international standard for measuring health and disability
Etiology of prenatal CP
Premature birth
Periventricular leukomalcia (PVL)
Intraventricular hemorrhage
Cerebral dysgenesis
Intrauterine
Maternal infections
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) fetal stroke, a disruption of blood supply to the developing brain
Mutations in genes that lead to abnormal brain development
Etiology of perinatal CP
Lack of oxygen to the brain related to difficulties during labor or delivery with:
umbilical cord
detachment of the placenta
uterine rupture
perinatal hypoxia
Etiology of postnatal CP
Infant infections that cause inflammation in or around the brain (e.g. encephalitis, meningitis)
Traumatic head injury to an infant from a motor vehicle accident, fall, child abuse
Developmental events
endocrine- hypoglycemia, hypothyroidism
respiratory distress syndrome
Data prevalence of CP
It is the most common motor disability in childhood
Globally: 1 to 4 per 1,000 live births
Prevalence is higher for: boys, non-hispanic black children, children born preterm or with low birthweight, and twins (higher among triplets)
Is CP more common in boys or girls?
Boys
Signs and symptoms of CP
poor coordination of movements, muscle stiffness, fatigue, seizures, balance issues, late developmental milestones, spasticity, muscle tremors, speech impairments, contractures and deformities
Is spastic pyramidal or extrapyramidal?
Pyramidal
Pyramidal vs extrapyramidal
Pyramidal tracts originate in the cerebral cortex and carry motor signals to the spinal cord and brain stem. They are responsible for voluntary control of muscles in face and body
Extrapyramidal tracts originate in the brain stem and carry motor signals to the spinal cord. They are responsible for involuntary and automatic control of muscles, such as balance, posture, and muscle tone
Is CP progressive or nonprogressive?
Non-progressive but permanent condition
Medical management of CP
Medications can decrease spasticity- diazepam, dantrolene, botox injections
Surgery- joint fusions, tendon lengthening, tendon transfers
Splinting and orthotics- AFO and TLSO
PT, OT, and SLP
Aging with CP
Weak muscles get even weaker over time
Abnormal muscle patterns often place joints in abnormal positions
This can lead to increased fall risks (greater injury with falls)
Health management tasks become more difficult
Severe arthritic changes
T/F: The OTPF is organized into 5 aspects: occupations, contexts, performance patterns, performance skills, and client factors
True
What is the most severe form of CP
spastic quadriplegic
T/F: CP can occur during any stage of brain development
True
What is spinal shock?
altered reflex activity immediately after a traumatic SCI
Dyskinesia or uncontrollable movements is associated to damage of the
basal ganglia
The Gross Motor Functional Classification System (GMFCS) is associated with
CP
T/F: Diagnosis of CP usually happens between ages 3-5 years old
False
Is macular degeneration loss of central or peripheral vision?
central
what type of macular degeneration is inherited from both parent recessive genes
juvenile MD
what is the leading cause of severe vision loss?
macular degeneration
T/F: fatigue is a common sign and symptom of all types of CP
False
Which type of low vision involves an increase in intraocular pressure?
Glaucoma
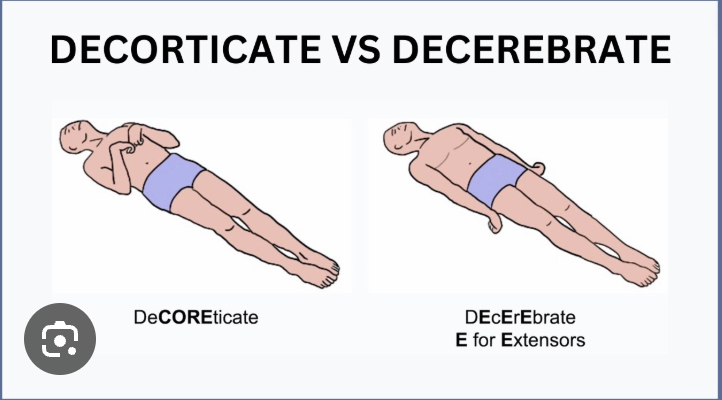
Decorticate posturing is extensor posture due to damage to brainstem
False, flexion of arms and damage to cerebral cortex
Swan neck deformity involves
dorsal migration of lateral bands
T/F: primary brain injury occurs at any time of injury
True
T/F: Falling is the most common and preventable cause of SCIs
False
T/F: Dyspnea, fatigue, and orthopnea are all associated with L sided HF
True
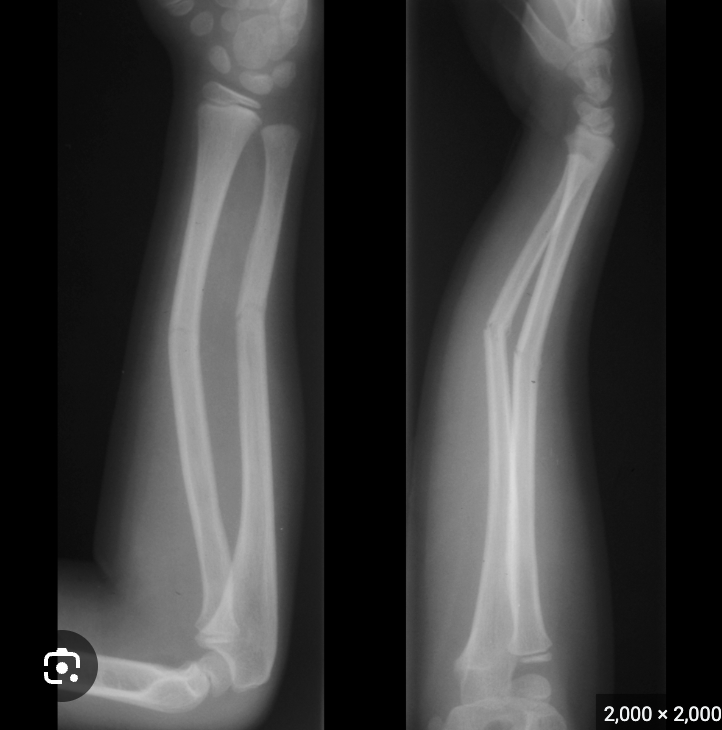
Which fracture has one side of the fracture a complete break and the other side bends rather than snaps?
greenstick
What are signs and symptoms of COPD
shortness of breath, hypertension, and persistent cough
T/F: fatigue is a sign and symptom of COPD
False
T/F: lupus is hereditary
True
T/F: cognitive domains are the most affected when it comes to NCDs
True
T/F: fatigue is the most debilitating factor of cancer
True
All are common sites for metastatic disease except:
Lungs
liver
ovaries
bone
ovaries
what is autonomic dysreflexia/hyperreflexia
exaggerated response of ANS
______ is a classic brainstem stroke
Wallenberg syndrome
what artery is the most affected in pediatric stroke?
MCA (middle cerebral artery)
“Plaques and tangles” is associated with which condition
Alzheimer’s
which area of the brain is responsible for coordination, balance, and fine motor movements?
cerebellum
what is the process of a reflex arc
producing a response without brain function
which is a common comorbidity for Autism
Fragile X
Left side of the brain is associated with:
difficulties with verbal memory and language/speech
infants with ____ will display CNS damage and ID
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Which hormone is associated with the brain’s reward system?
dopamine
T/F: ACE scores do not correlate with health risks and social problems later in life
False