TTU Chem 1307 Exam 3 Notecards
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Sublimation Energy
energy require to change state from solid to gas directly
Angular Momentum Number (l)
An integer range from 0-(n-1) and indicates shape of orbital, multiple possible values of l
ex: if n=3, l= 0,1,2.
if n=1, l=0.
Aufbau Principle
e- occupy the lowest energy orbitals first (1s2, then 2s2, then 2p6, then 3s2...etc.)
Pauli Exclusion Principle
1. no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers
2. No more than 2 e- can occupy an orbital
3. e- that occupy same orbital must have different values for ms (ms= +1/2 and ms= -1/2)
Periodic Trends: Atomic Radius
Highest in lower left corner, lowest in top right corner

Lattice Energy
(only have to know definition) The enthalpy change that takes place when a gaseous ion forms a solid ion
Execptions to Electron Configuration
Copper - 4s1 3d10
Chromium - 4s1 3d5
Change of Enthalpy (ΔH)
Used for heat transfer/capacity questions. Quantifies heat flow in or out of system.
ΔH = H(products) - H(reactants)
Exothermic
Heat flows out of system (-ΔH)
Endothermic
Heat flows into system (+ΔH)
Heat calculation formula
q=mc∆T
q=heat absorbed or released by substance
m=mass
c=specific heat capacity
ΔT= change in temp. (final-initial)
Specific Heat of H2O
c=4.184
Calorimetry Solving Process
q=mcΔT, slove for water first, then use the q for the alloy equation. Flip sign (-/+) at the end of solving process.
Bomb Calorimetry
energy of reaction = ΔT - Heat capacity of Calorimeter
Hess's Law
using two reactions to achieve desired equation
rules: 1.if you reverse equation, reverse sign of ΔH associated with that equation, 2. if you multiple/divide equation, divde/multiple ΔH by the same
Standard Enthalpy of Formation
ΔH(rxn) = Sum of ΔH products (ΔHfproducts) - Sum of ΔH reactants (ΔHfreactants)
element in standard form (Xe, H2, etc.) has an sum of ΔHf of zero
Most compounds have -ΔHf
Wavelength (λ)
The distance between any point on a wave and the corresponding point on the next crest(or trough) of the next wave.
Frequency (v)
The number of cycles of the wave in a give amount of time (ex:5.65x1o^14 Hz)
Amplitude
The height of crest, or depth of trough, of a wave from the middle line.
c = v x λ
Speed of light = frequency x wavelength
Nanometers --> Meters conversion
10^-9
Speed of light (c)
3.0 x 1o^8 m
E = hv = hc/λ
energy of light (J)
h= planks constant
c= speed of light
Plank's Constant (h)
6.626 x 10^-34
Concept of Photoelectric Light
electrons are emitted as electromagnetic radiation(eg.light) hits the surface of a metal
De Broglie's Equation
λ=h/mv
*mass is in Kg here, only here
Bohr's Model of the Atom
"electron cloud model" Electrons occupy a definite amount of orbitals that require specific energies to occupy.
Emission
Electrons moving from a higher shell to a lower shell emit energy(light)
Absorption (Evolving) (Excited)
Electrons moving from a lower energy shell to a higher shell absorb energy to do so.
Energy Level Formula
En = RH(1/n^2)
n = energy level outmost e is occupying, quantum number
RH = Rydberg's Constant
Rydberg's Constant
-2.178 x 10^-18
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
It is impossible to simultaneously know an electron's location AND speed of orbit
Principle Quantum Number (n)
a positive integer(1,2,3..) indicating size and relative distance from nucleus, specifies the energy level
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
Integer range from -l to 0 to +l, indicates orientation of the orbital in the space around the nuclues
ex: if l=2, ml= -2, -1, 0, 1, 2.
Level (Shell)
denoted by (n), defined further by subshells
Sublevel (Subshell)
designates the orbital shape, denoted by l quantum number
l= 0 -- s sublevel
l= 1 -- p sublevel
l= 2 -- d sublevel
1= 3 -- f sublevel
Orbital shapes
s = spherical shaped
p = dumbbell shaped
d = clover leaf shaped
Hund's Rule
when filling orbitals, e- go into separate orbitals with parallel spins until all of the orbitals are occupied by one e-, then they pair up.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom
ex: [Ne] 3s23p4 (everything following [Ne] is valence b/c it is not full)
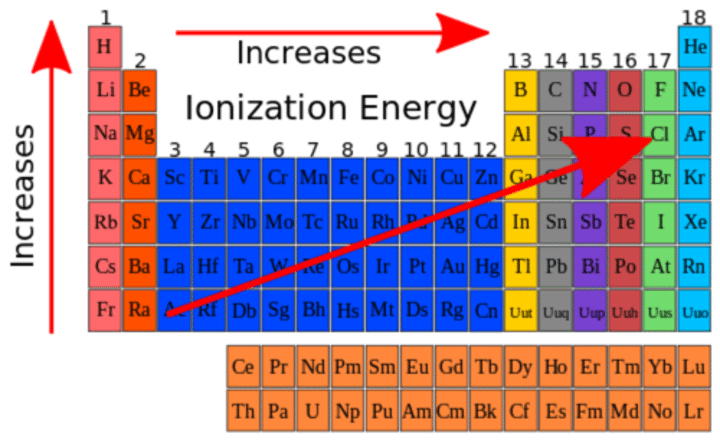
Periodic Trends: Ionization Energy
Lowest IE in left bottom corner, highest in right upper corner.
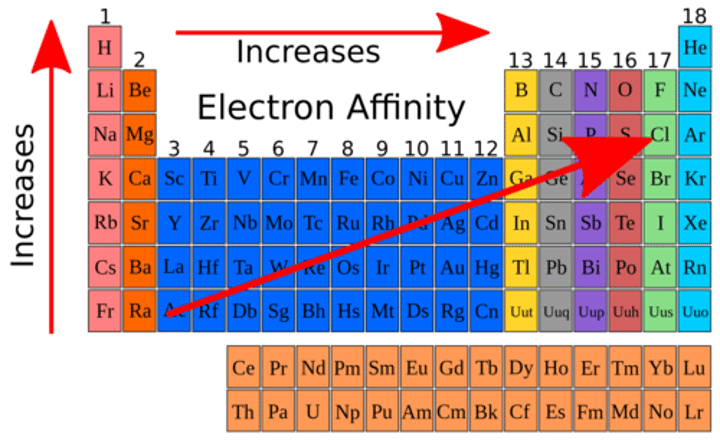
Periodic Trends: Electron Affinity
Amount of energy required to add an e- to a gaseous ion/atom
Lowest in bottom left corner, highest in top right corner
Ionic Bonds
Metal and nonmetal, >1.7 electronegativity difference
Polar Covalent Bond
Nonmetals, 0.7-1.7 electronegativity difference
(non-polar) Covalent Bond
Nonmetals >0.7 electronegativity difference
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself
ex: H=2.1
B=2.0
C=2.5
N=3.0
O=3.5
S=2.5
F=4.0
Bond Polarity
Difference in EN, results from an unequal distribution of electrons
Molecular Polarity (dipole moement)
When the entire atom has a partially positive and partially negative charge.
Indicated by lewis structure, symmetric=nonpolar
Isoelectric Ions
Ions with the same number of electrons in the configurations after incorporating ionic charges. ex. Al^3+ and O^2- are isoelectric
Ion size decreases as atomic number(z) increases when comparing isoelectric ions
Ion size rules
1. Cations (positive ion) is smaller than parent atom
2. Anions (negative ions) are larger than parent atom (more e-)
3. Size generally decreases down a group
Dissociation Energy
energy required to break apart a compound (breaks bond)
Heat of formation
heat energy released or evolved when an electron is added to a neutral atom(Hf)
Exceptions to Octet rule
more than octet- Anything after P can have more than 8 e- if it is the central atom
Less than octet- boron
Resonance
occurs when two or more Lewis structures are valid and stable for a particular molecule
Transition metals lose e- from --- orbital before --- orbital
s orbital before d orbital
Formal charge
the difference between the number of valence electrons on a free atom and the number of electrons on the atom in the molecule (use lewis structures)
Bond order
number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms in a molecule
single
double
triple
Bond energy
the energy required to break a bond
breaking bond - positive enthalpy
creating bond - negative enthalpy