Chem Unit 3: Organic Chemistry
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Alkanes
homologous series of hydrocarbons- organic compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon, are saturated bc contain no double carbon bond.
suffix: ane Generic formula: CnH2n+2
Alkenes
unsaturated hydrocarbons(have at least one double carbon bond, which acts as their functional group). Suffix: ene General formula: CnH2n
Carboxylic acid
a homologous series of organic compounds, weak acids, has the functional group -COOH. Suffix: anoic acid General formula: Cn H2n+1COOH
COOH at the end and take away one hydrogen because of double O=C bond
alcohols
a homologous series of organic compunds with the functional group OH(hydroxyl group). Suffix: ol General formula: CnH2n+1OH
halogenoalkanes
organic compounds that are essentially alkanes with one or more of the hydrogen atoms replaced with a hallogen
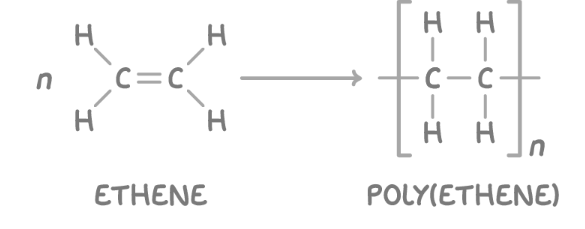
polymers
Polymers are large, chain-like molecules that can extend for thousands of atoms. Polymers are held together by:
Strong covalent bonds between atoms in molecules.
Weak intermolecular forces between molecules.
Because of the large size of polymer molecules, the intermolecular forces add up to be quite strong.
So, polymers are usually solid when at room temperature.
But, many polymers melt easily because the intermolecular forces remain less strong than chemical bonds.
add poly to the name of the monomer to name the polymer
organic compounds
his is a large group of compounds which all contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds but can also contain a small number of other atoms
homologous series
family of organic compounds that have the similar chemical properties, but the physical properties can change(gradually) eg. as the carbon chain becomes longer the boiling point increases, and they share a general formula and change by a difference of CH2(gradual change) and the same functional group.
trend in hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons with longer chains have a higher boiling point
Hydrocarbons with longer chains are less flammable
Hydrocarbons with longer chains are more viscous(thick and not runny) and are darker in colour
Hydrocarbons with longer chains create a smoky flame it burnt(not easyn to ignite tho
complete combustion
excess oxygen and thus produces carbon dioxide and water; it always produces these products(same). During this reaction, the air hole is open, so the flame is blue.
incomplete combustion
limited oxygen supply and thus produces a mixture of carbon(C), carbon monoxide(CO), carbon dioxide(CO2) and H2O and therefore, the products are not always the same(vary). During this type of combustion, the air hole is closed and the flame is yellow.
eg. 2CH4 + 2O2 —> 2CO + 4H2O
—> carbon monoxide forms because there isn’t enough O2 to fully oxidise the fuel so carbon atoms react only with 1 Oxygen molecule instead of 2.
what is fractional distillation
A process that allows us to split up crude oil into its useful fractions by separating the hydrocarbons based on their boiling points to make them useful. This is an important industrial process since crude oil provides raw materials for fuels(via combustion) and plastics(via polymerisation).
how does fractional distillation work?
Crude oil is heated up at a high temperature(outside the fractionating column) and is then pumped into the column.
Some hydrocarbons condense inside the column at the bottom, forming bitumen.
The rest of the vapour continues to rise as it is hot and the bubble caps are slowing down the rate of the rising vapour to ensure that at each level, the fractions can be separated from the mixture.
Finally, short hydrocarbon chains condense at the top and higher up in the column where the temperature is lower because their boiling point is lower due to the weak intermolecular forces, meaning less energy is needed to break the bonds(which is what starts to happen when you boil something).
functiosn of fractions
bitumen-road surfacing
kerosene-jet fuel
diesel- vehicles
naptha-chemical industry
molecular formula
indicates the number of each atom in the molecule in subscript
condensed structural formula
formula summarising how the different atoms are connected ina molecule, shows the atoms involved but not each of their bonds.
expanded structural formula
shows every single atom and every individual bonds, showing the strucutre of the molecule
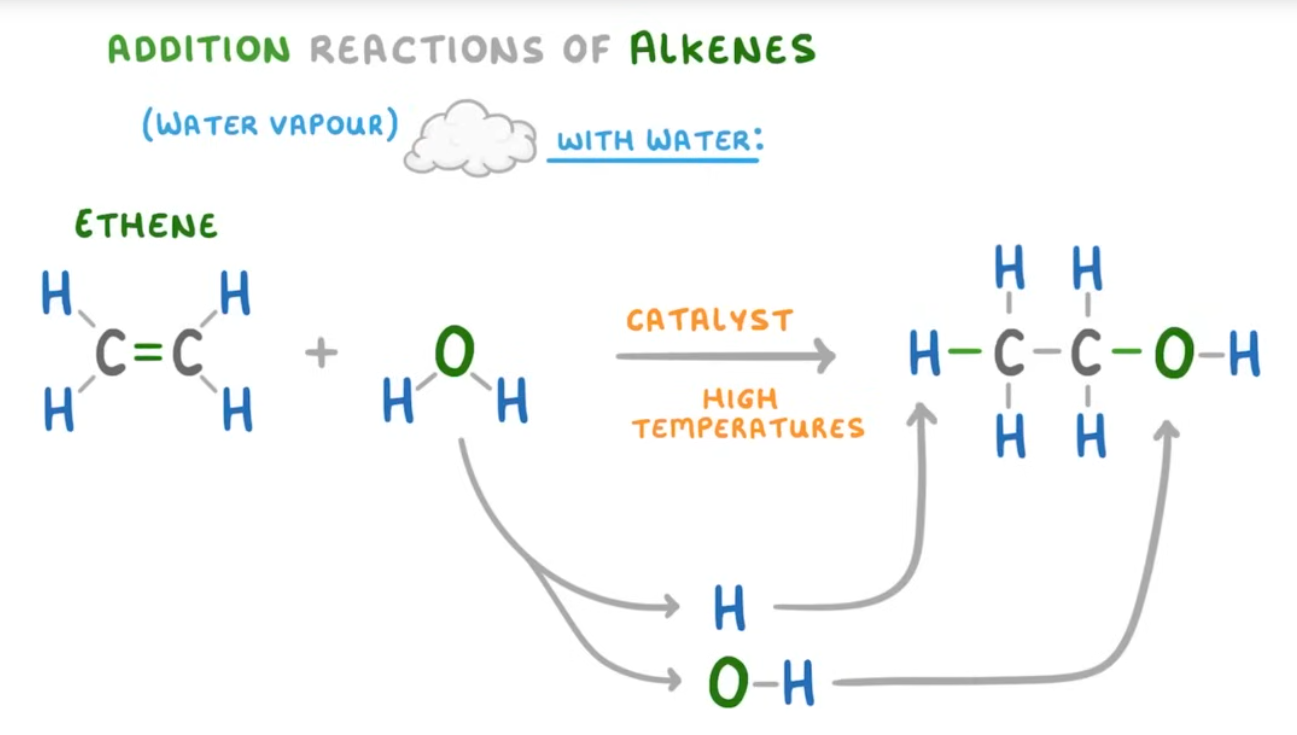
addition reactions of alkenes
an addition reaction involves atoms or molecules combining to form a single product. Alkenes do this because they are unstaturated due to their double carbon bond, they are very reactive because of this bond too. The double carbon bond can split up to allow the molecule to bodn to two additional atoms.
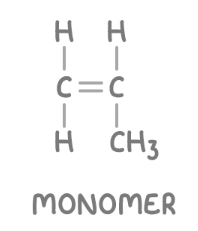
monomer + annotation
repeting units that bond together covalently to form a chain, called a polymer. Always an alkene in additiona reactions, draw with NO continuation bonds, n outside the bracket, and simiplify the alkene.
polymer naming
put poly and then in brackets the monomers name