AP Bio Unit 6 - Gene Expression and Regulation
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself.

DNA Polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
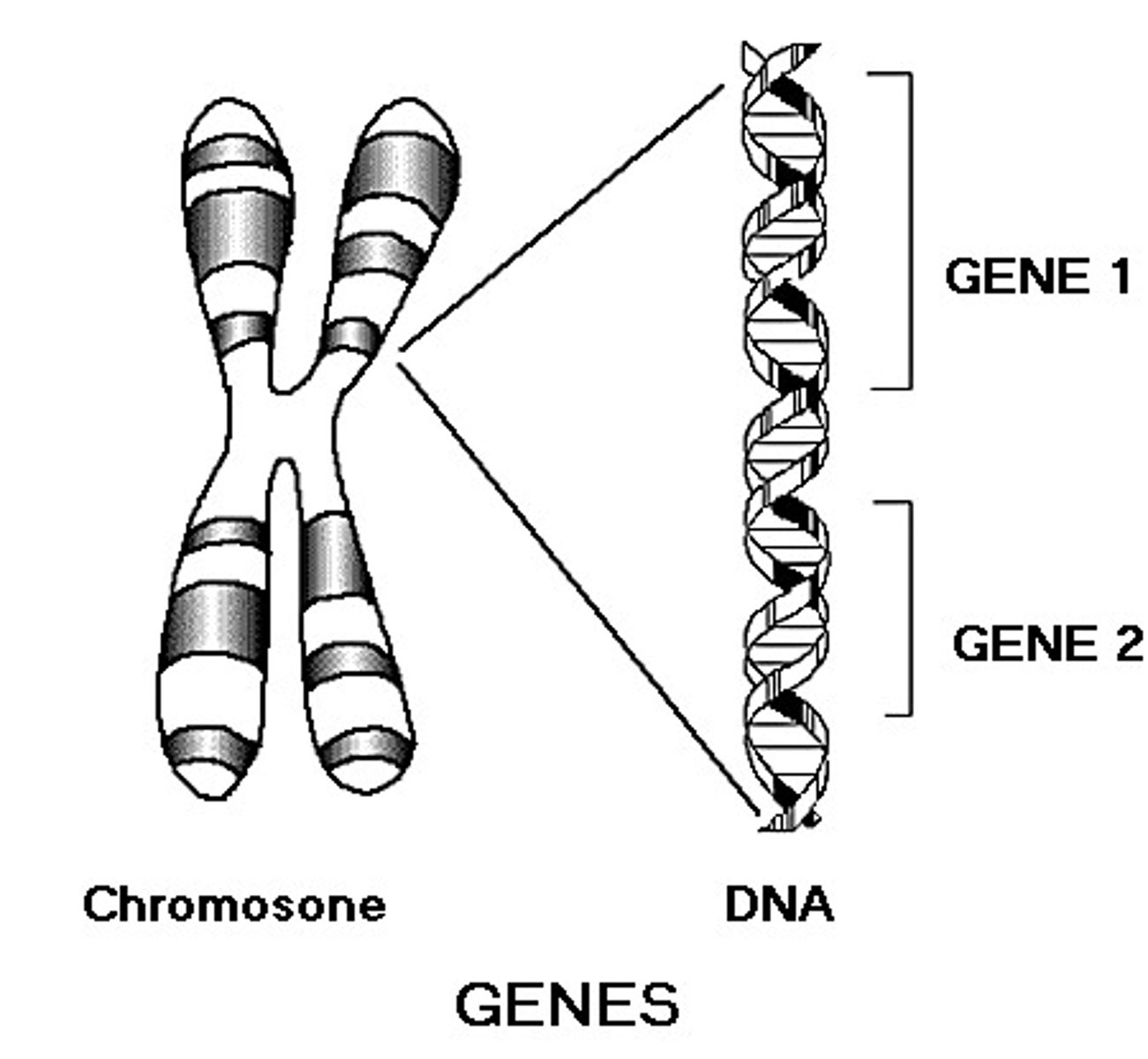
genes
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
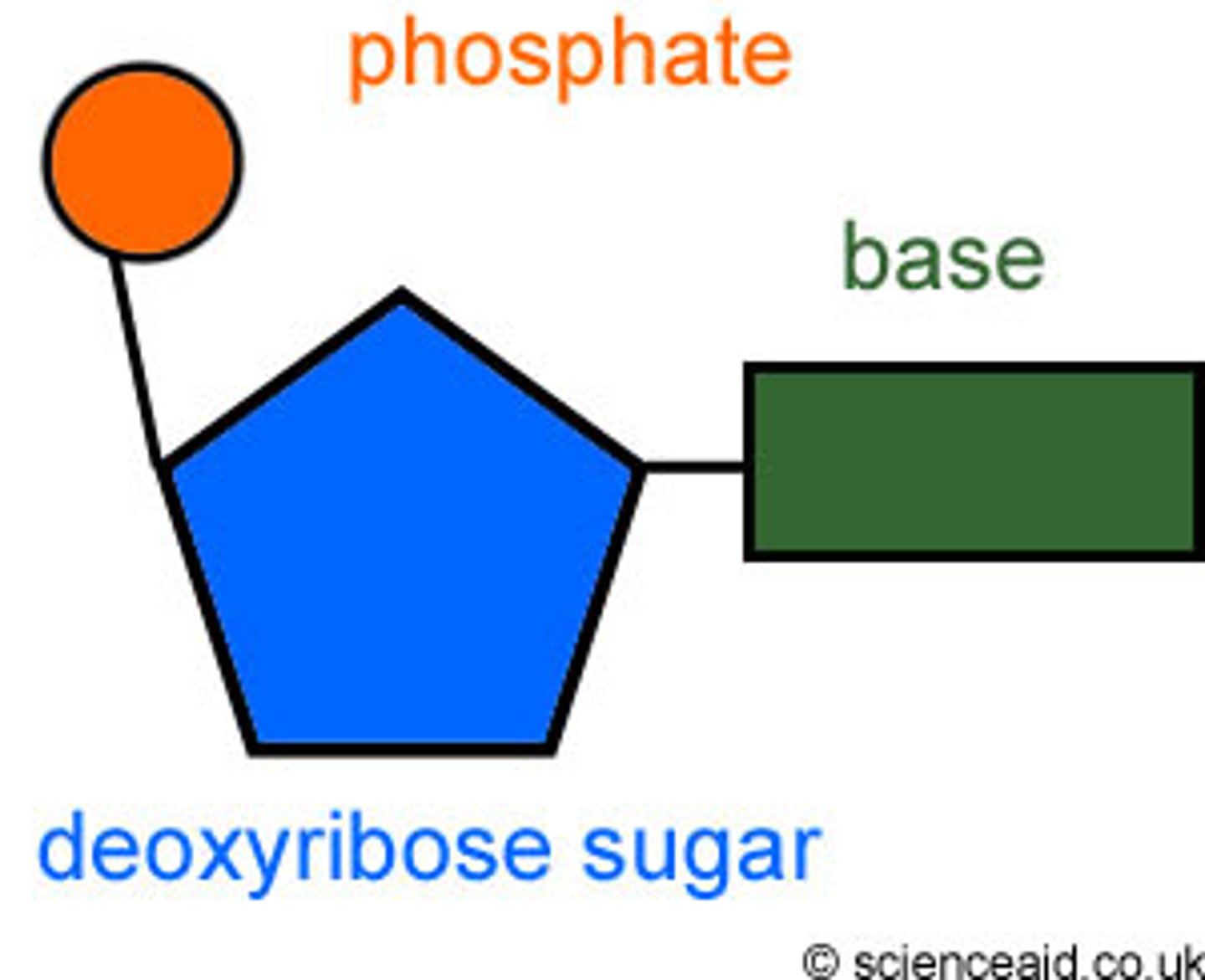
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
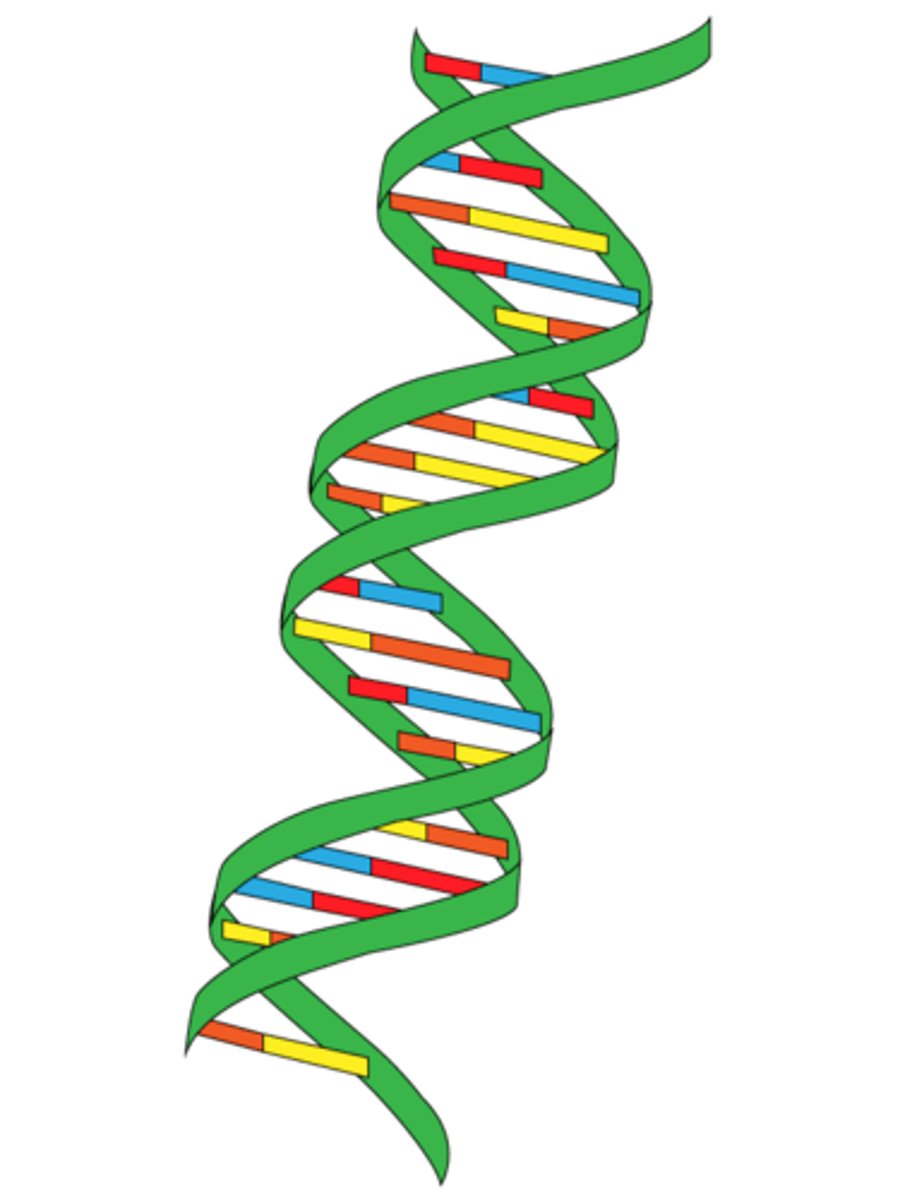
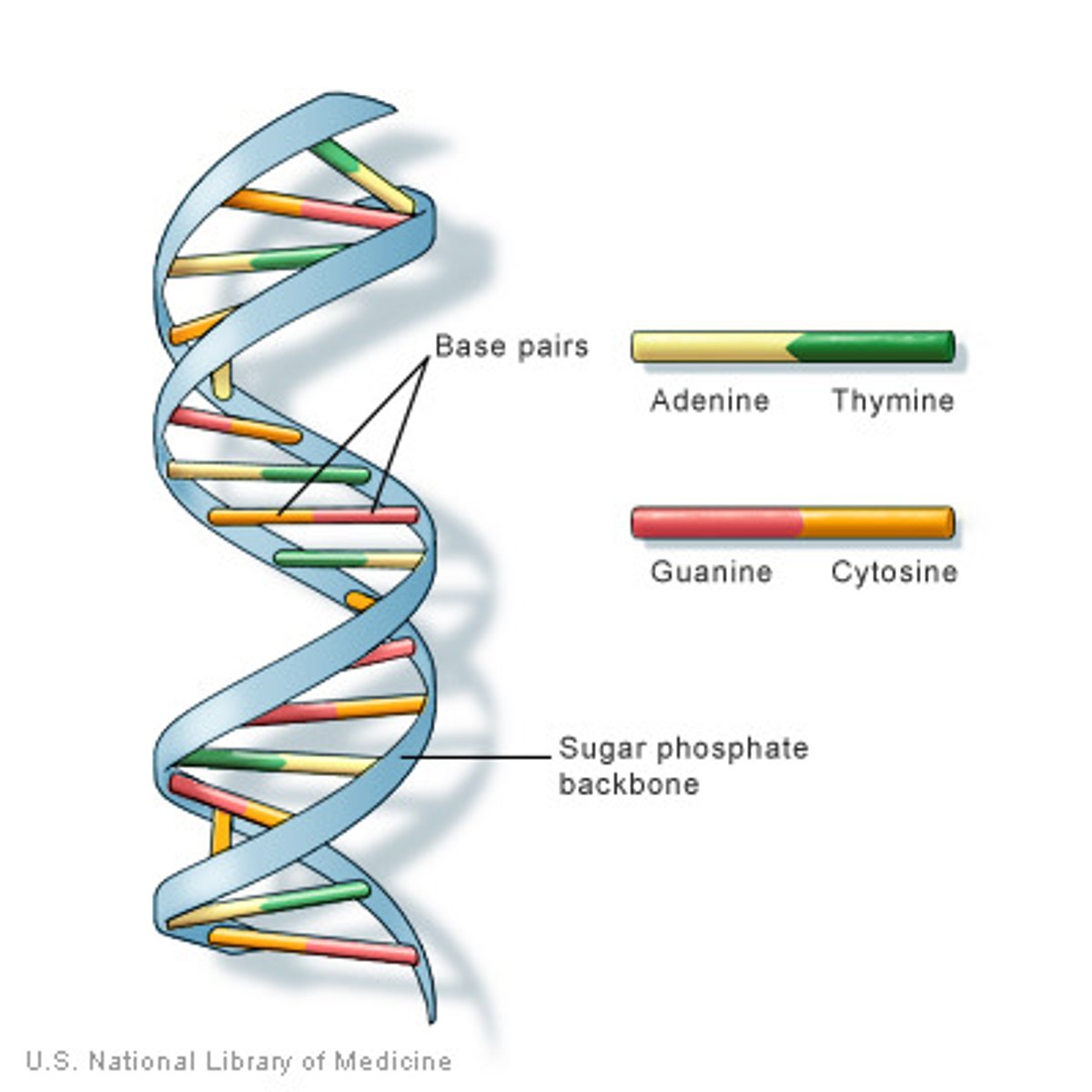
double helix
two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure/shape of DNA
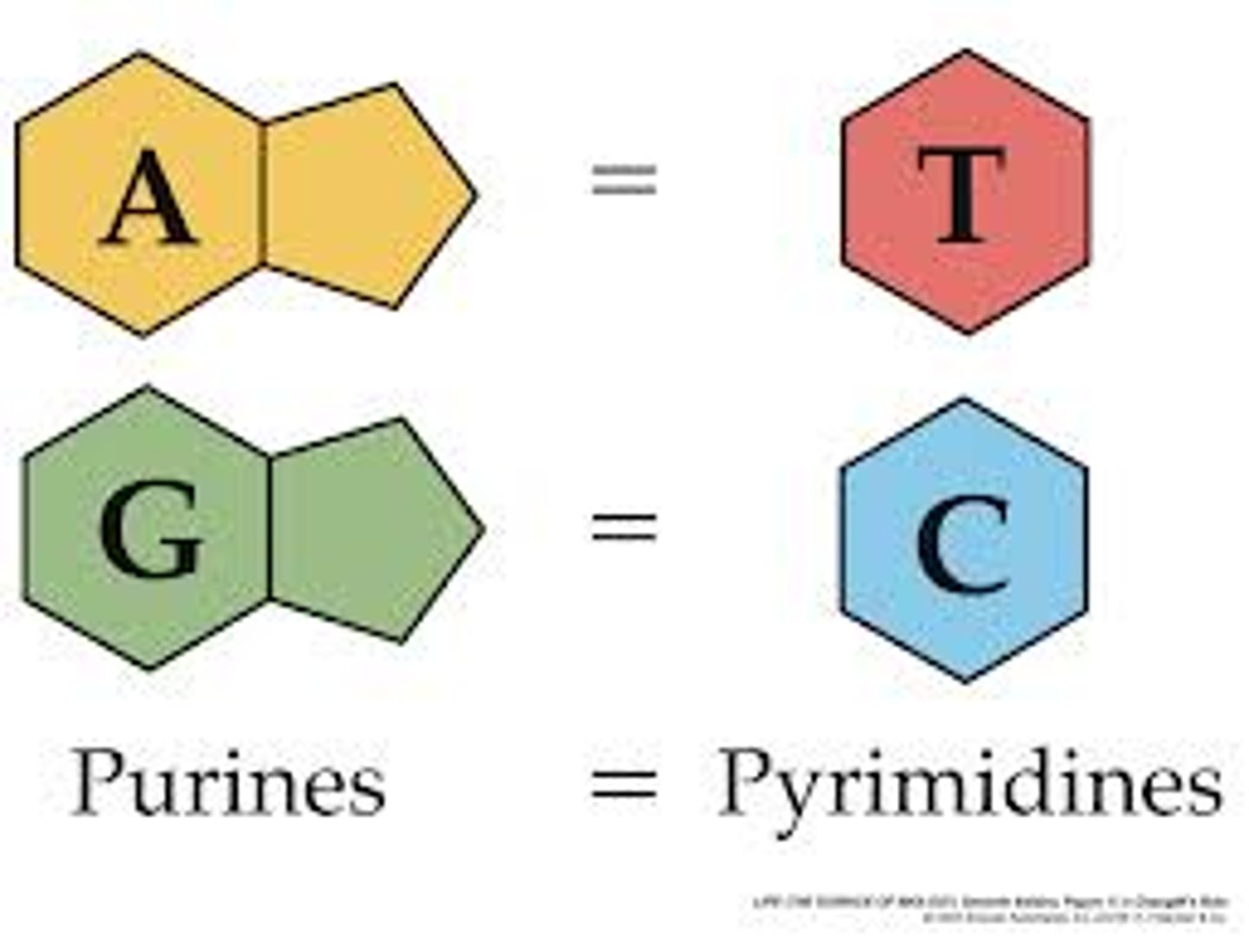
adenine
nitrogen base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA
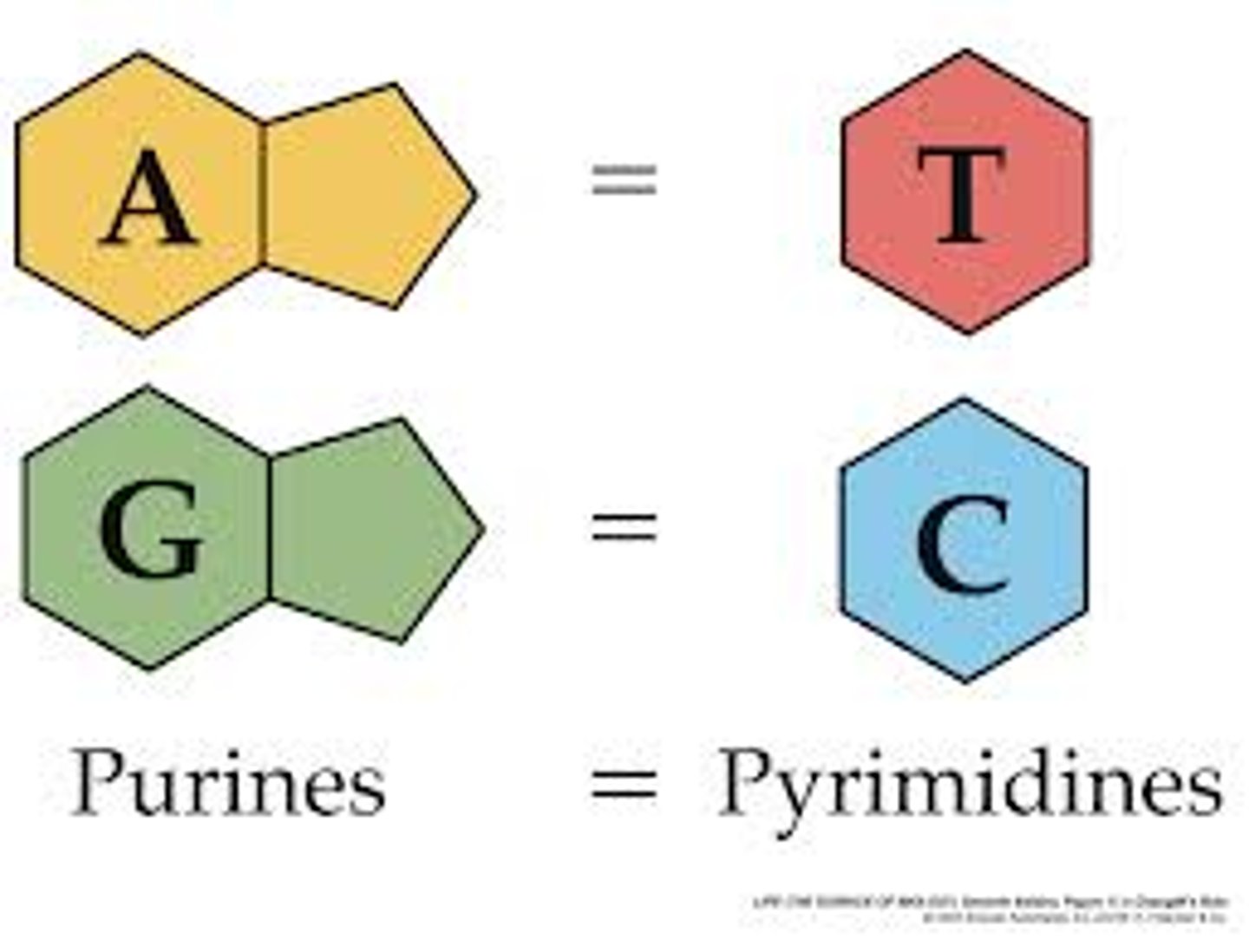
cytosine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with guanine
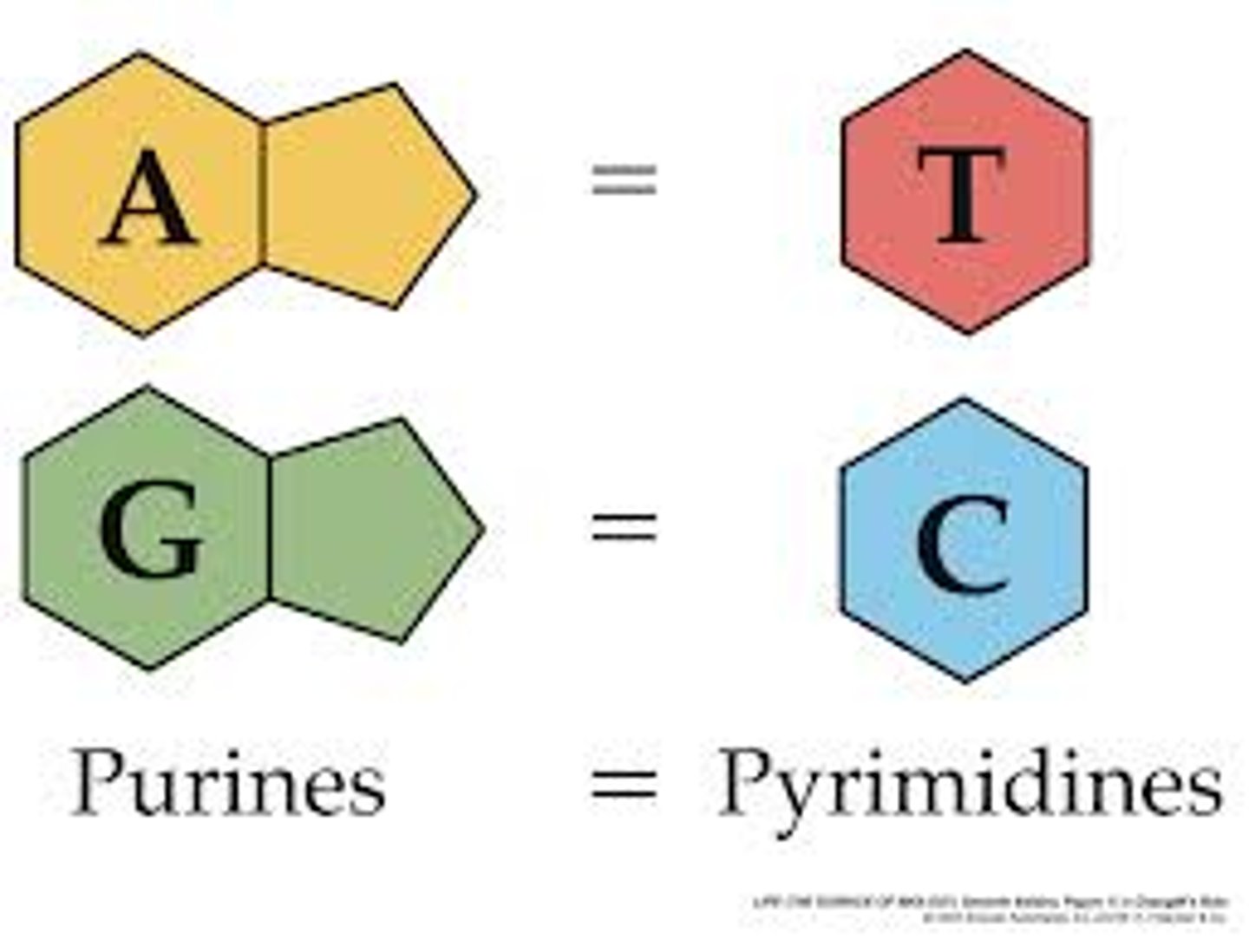
guanine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with cytosine
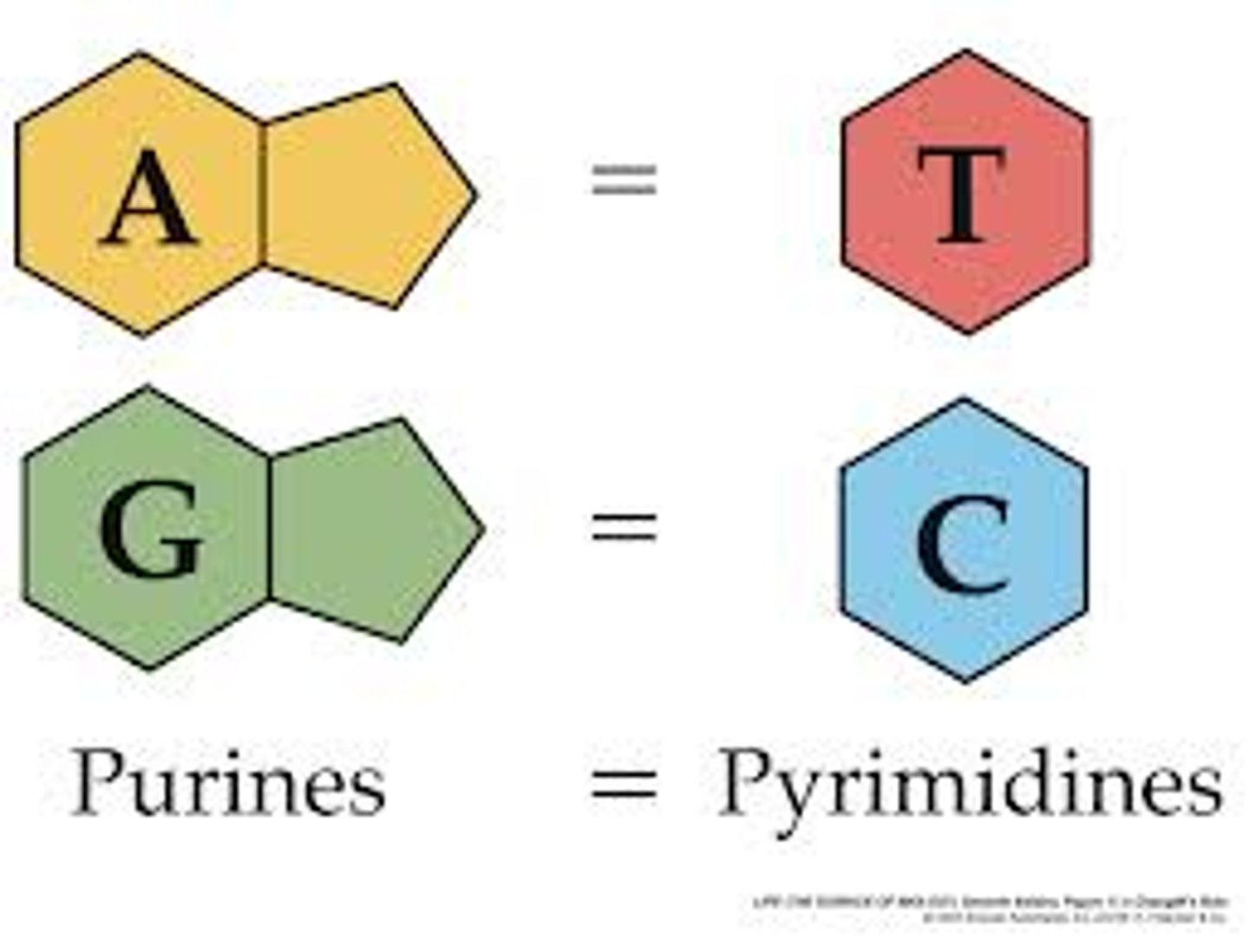
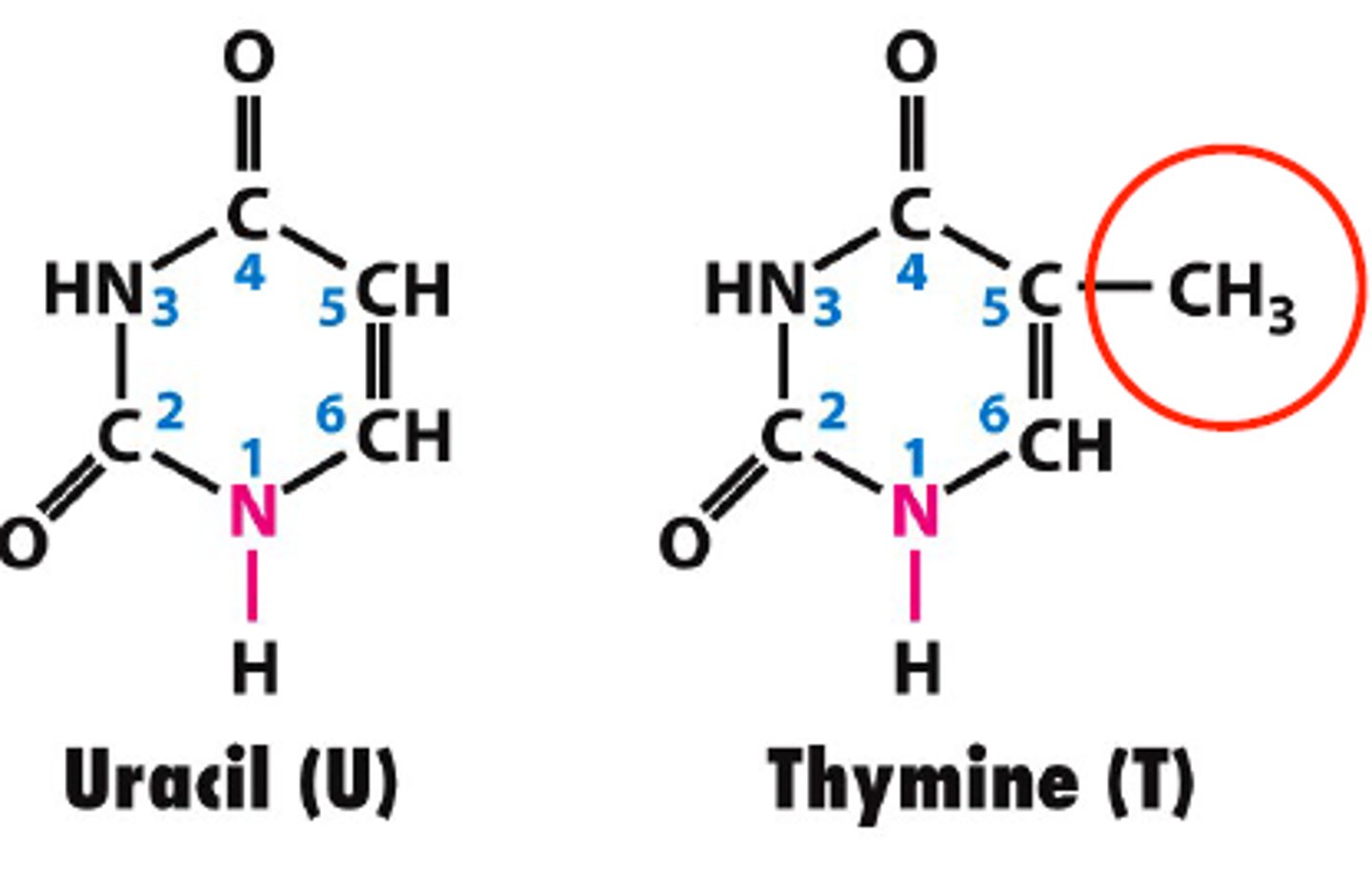
thymine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA (but not in RNA); pairs with adenine
uracil
A nitrogenous base found in RNA (but not in DNA); pairs with adenine
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes,
deoxyribonucleic acid
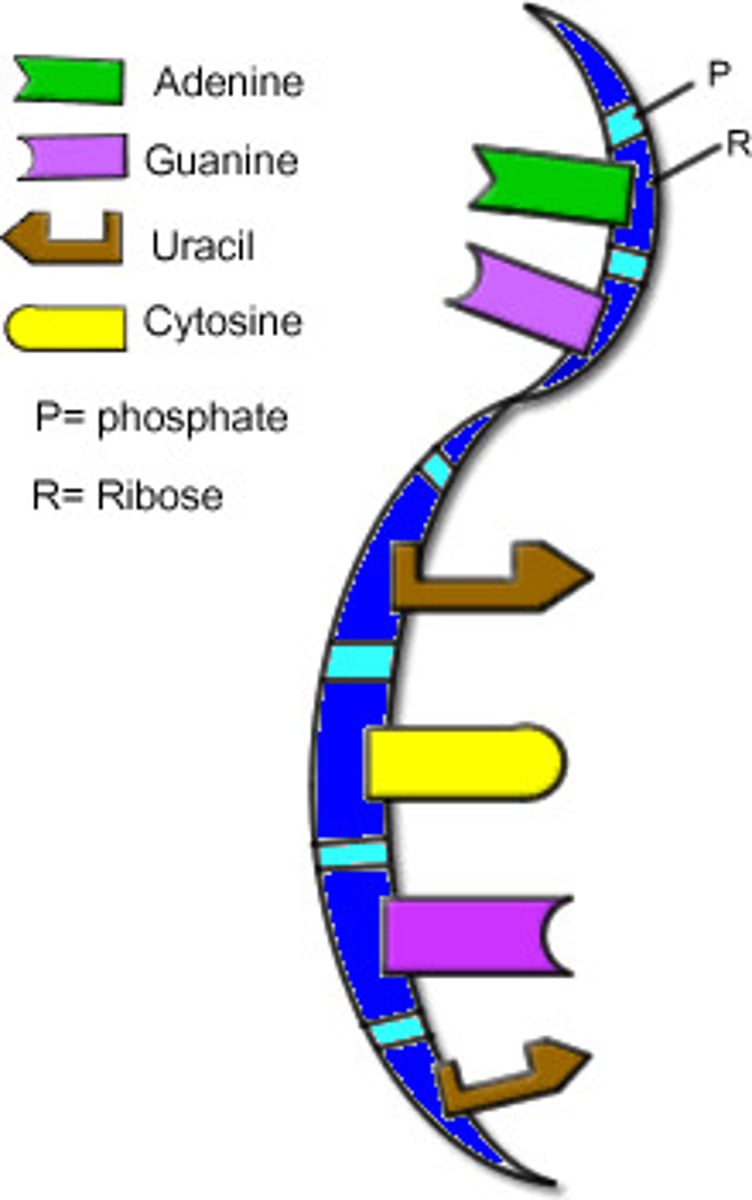
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages,
ribonucleic acid
deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
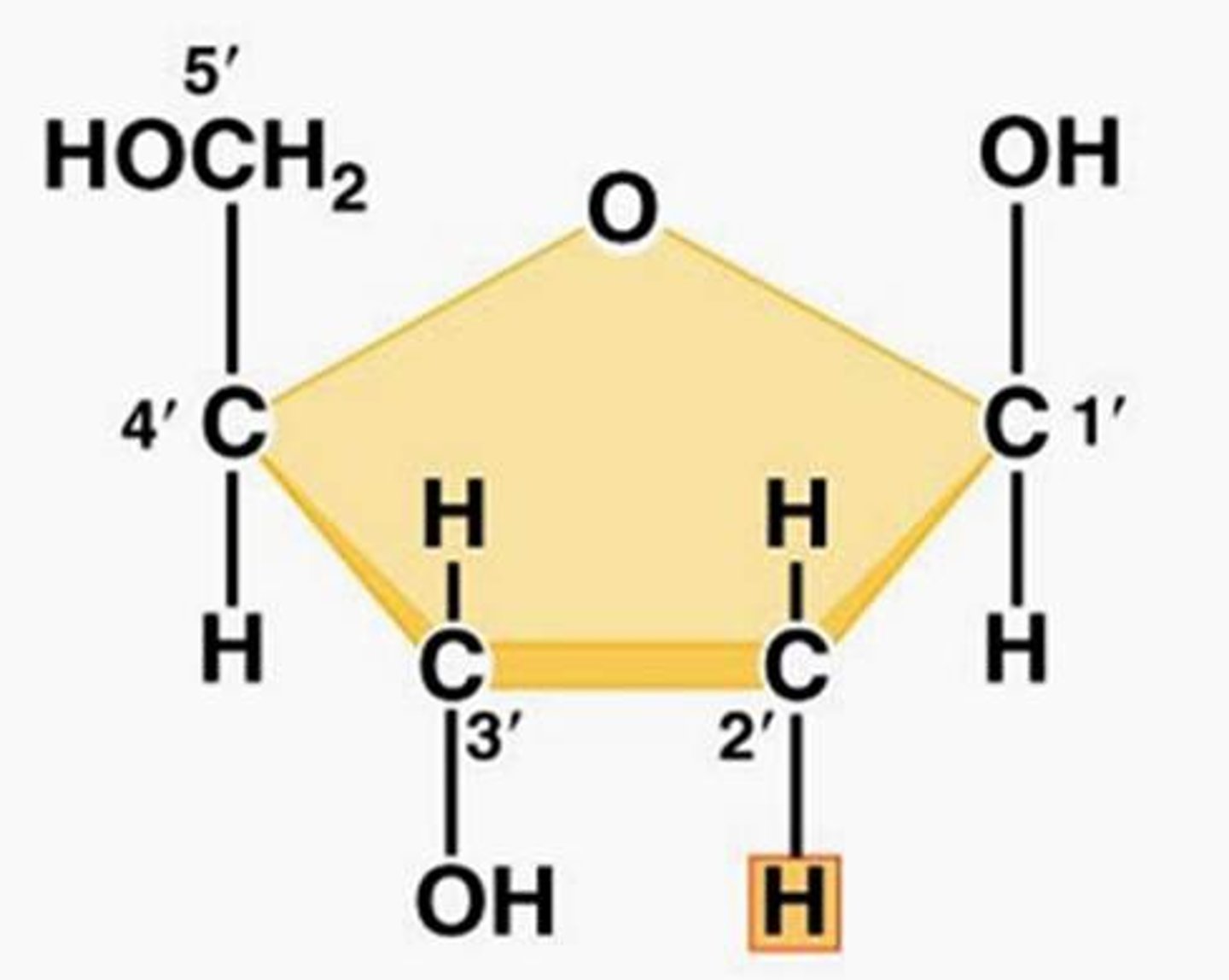
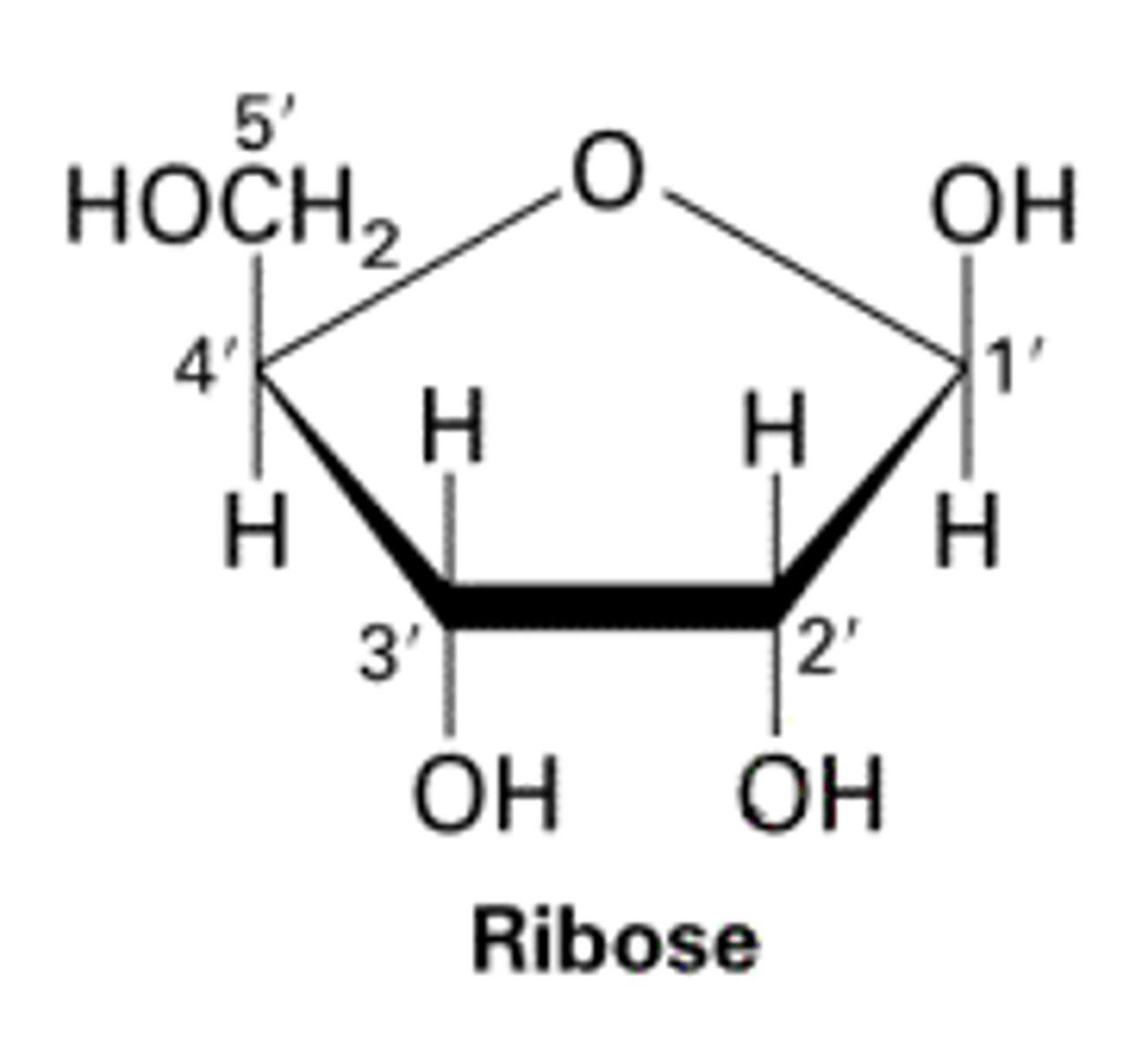
ribose
a five-carbon sugar present in RNA
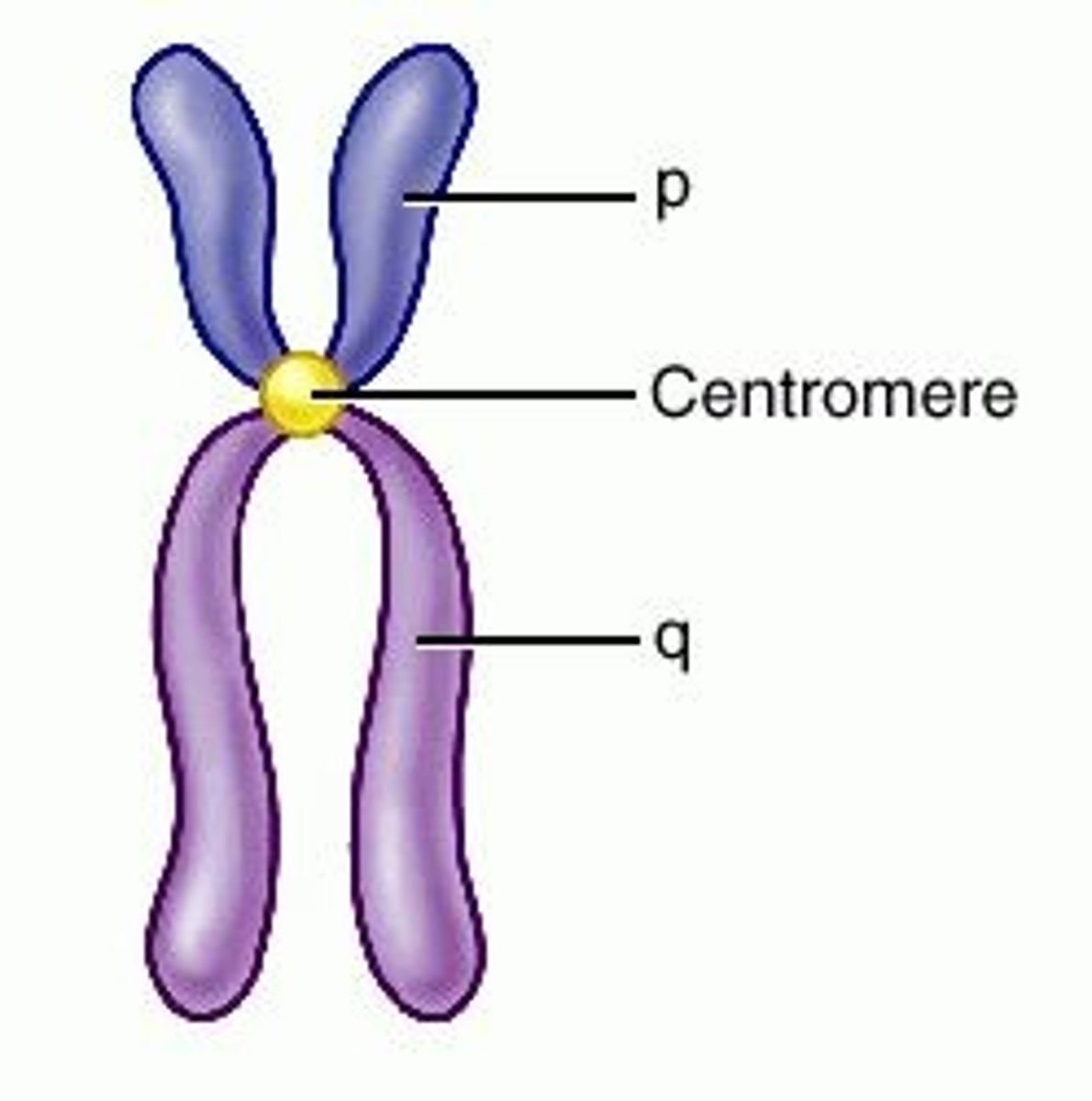
chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome

rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
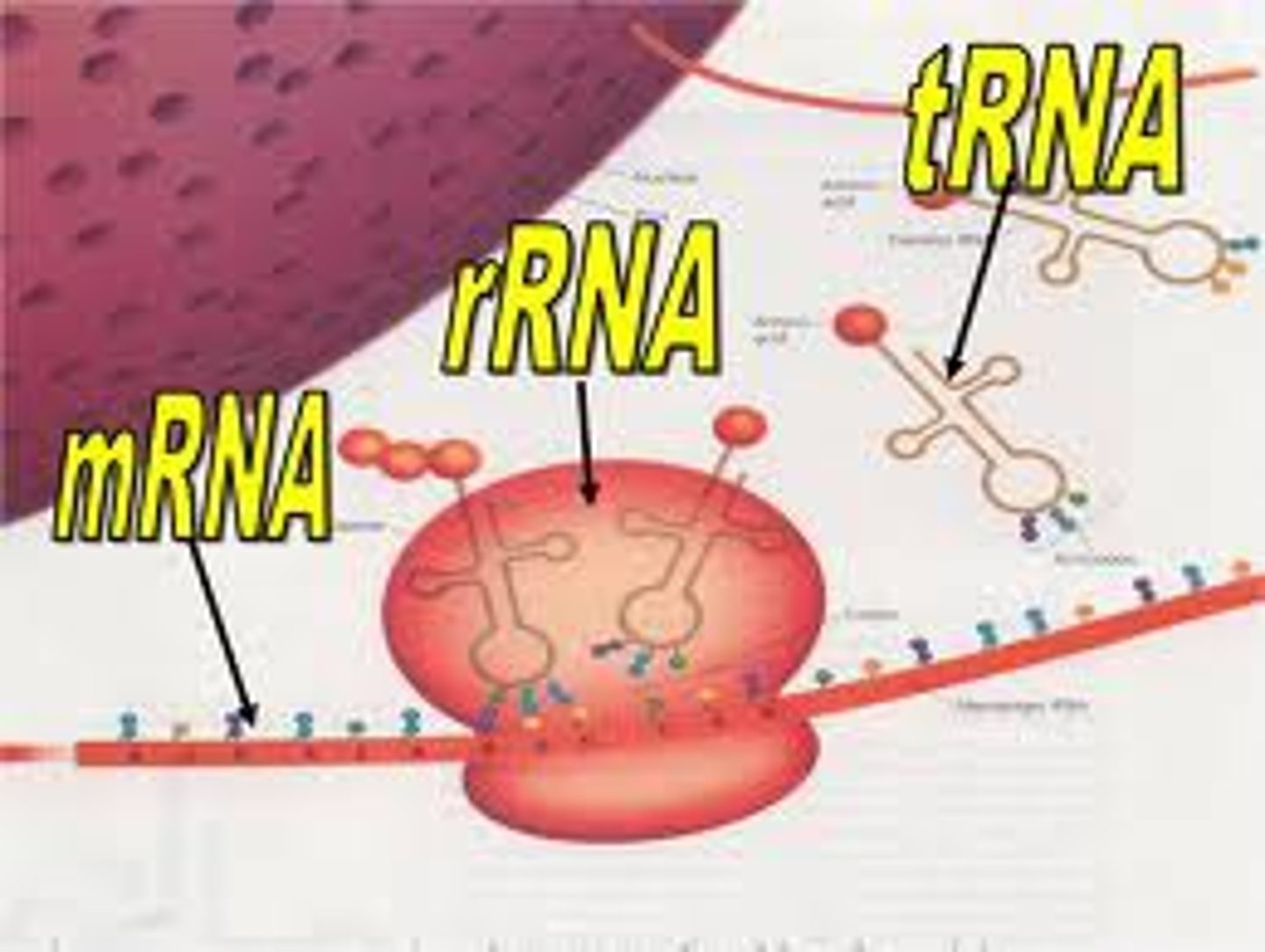
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
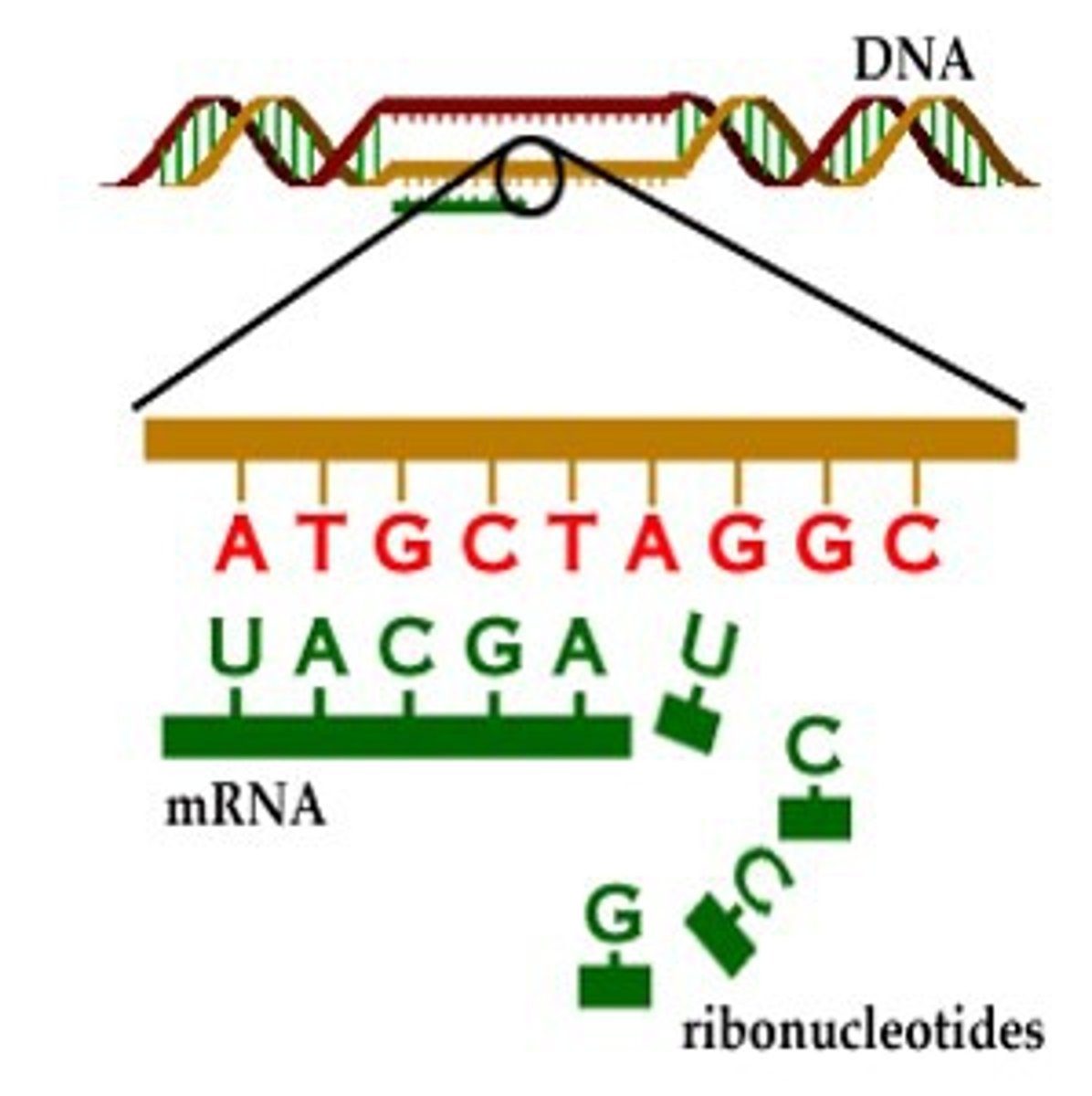
transcription
process where the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
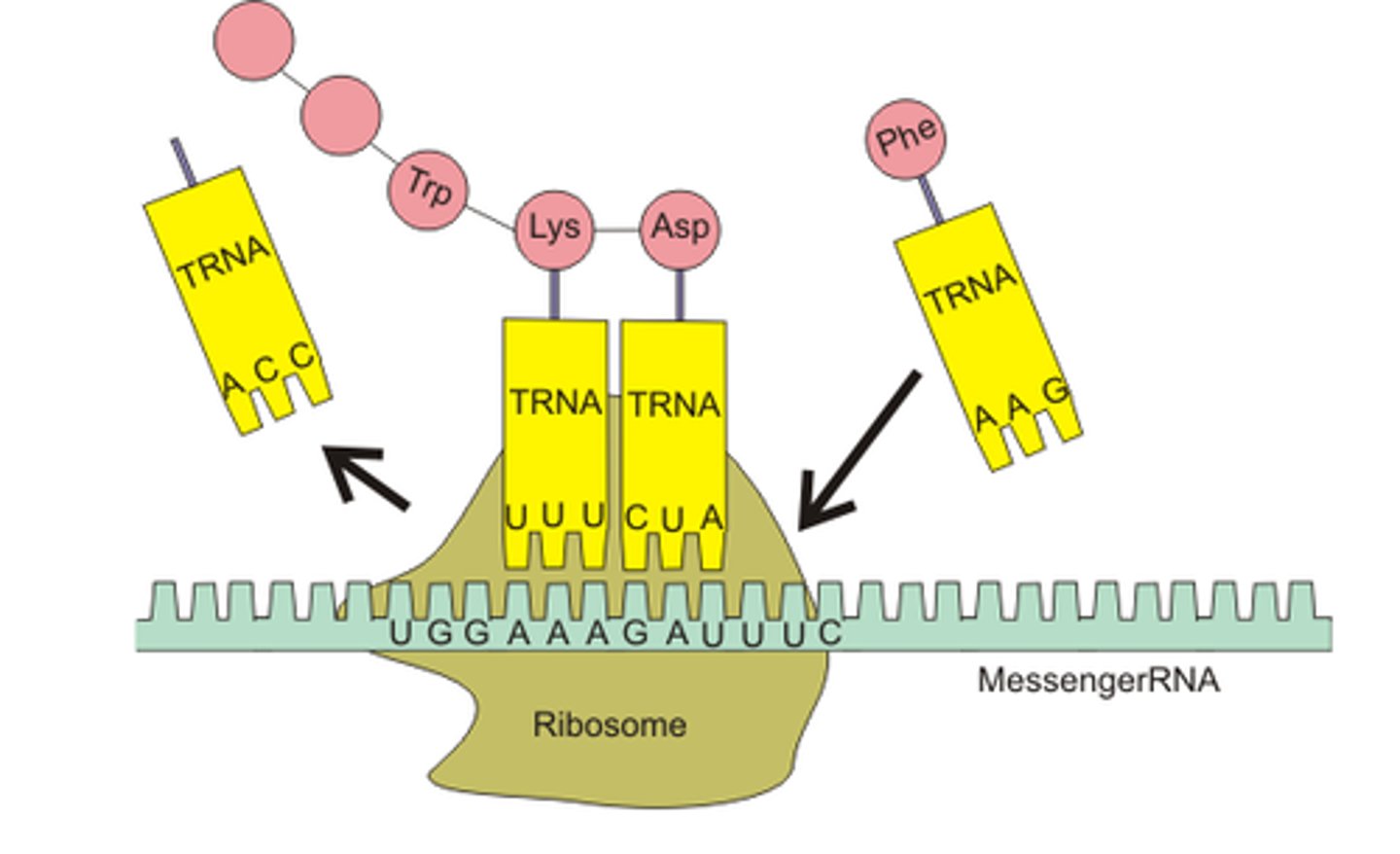
translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
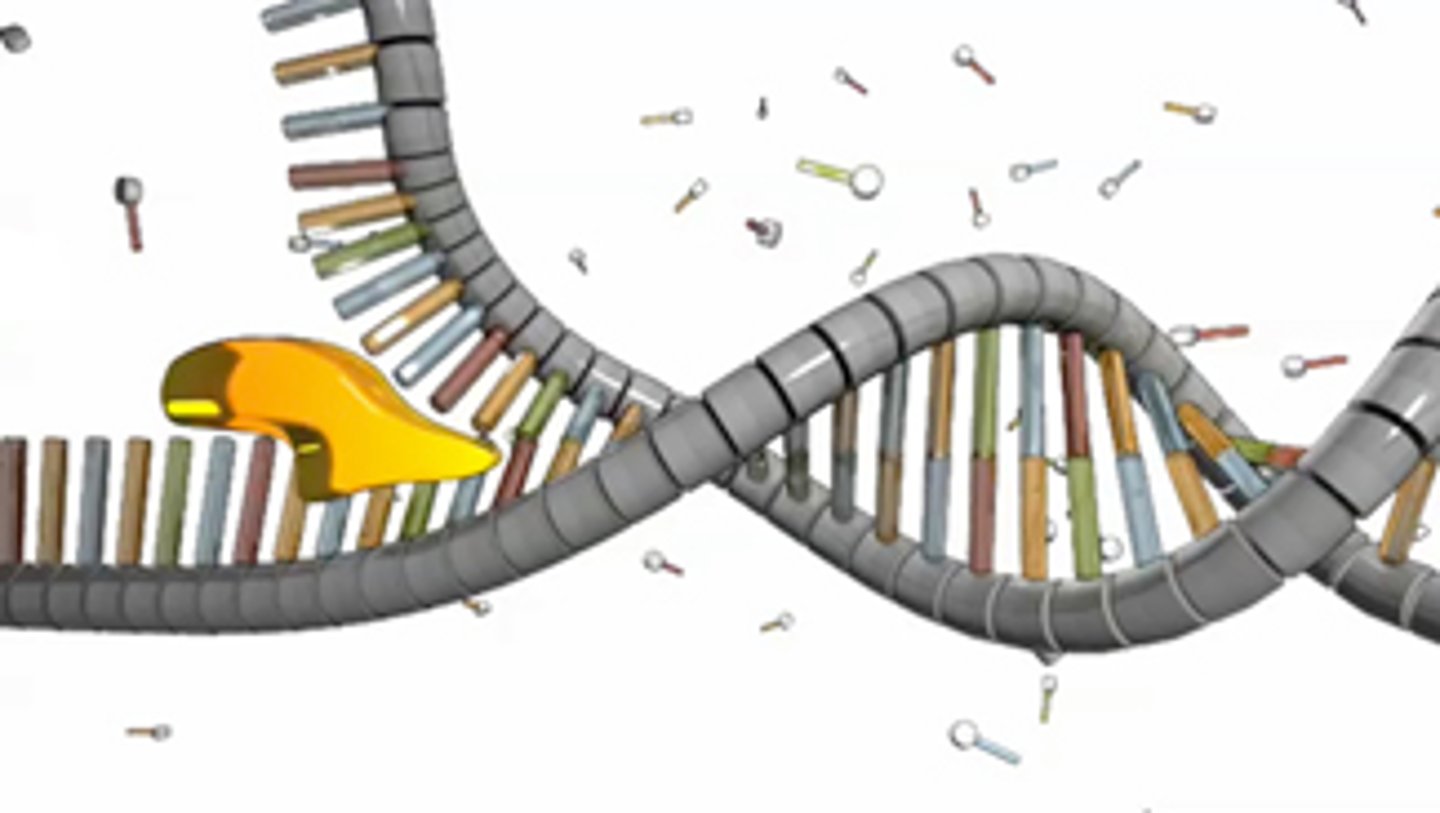
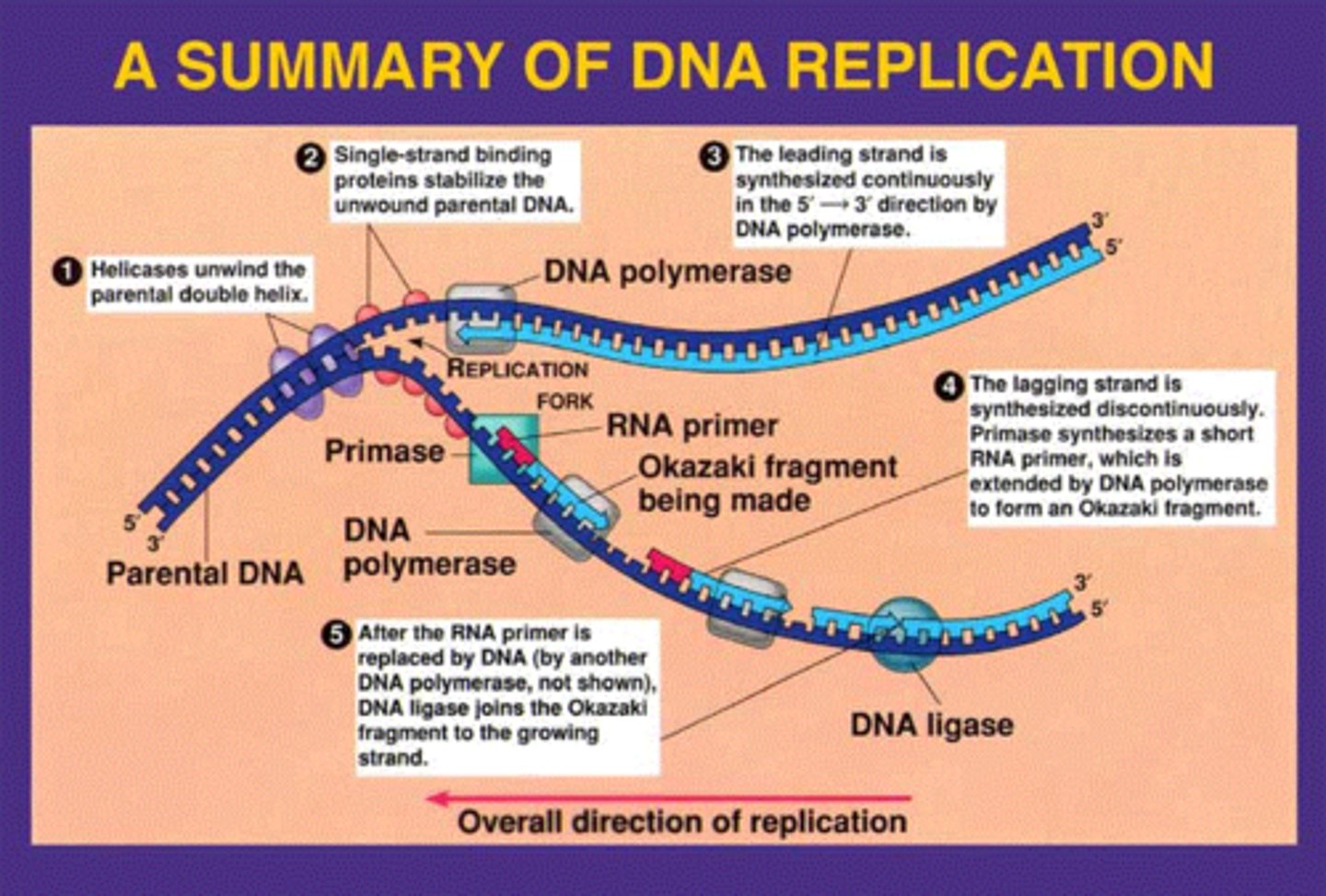
DNA helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix during DNA replication
mutation
A change in a gene or chromosome.
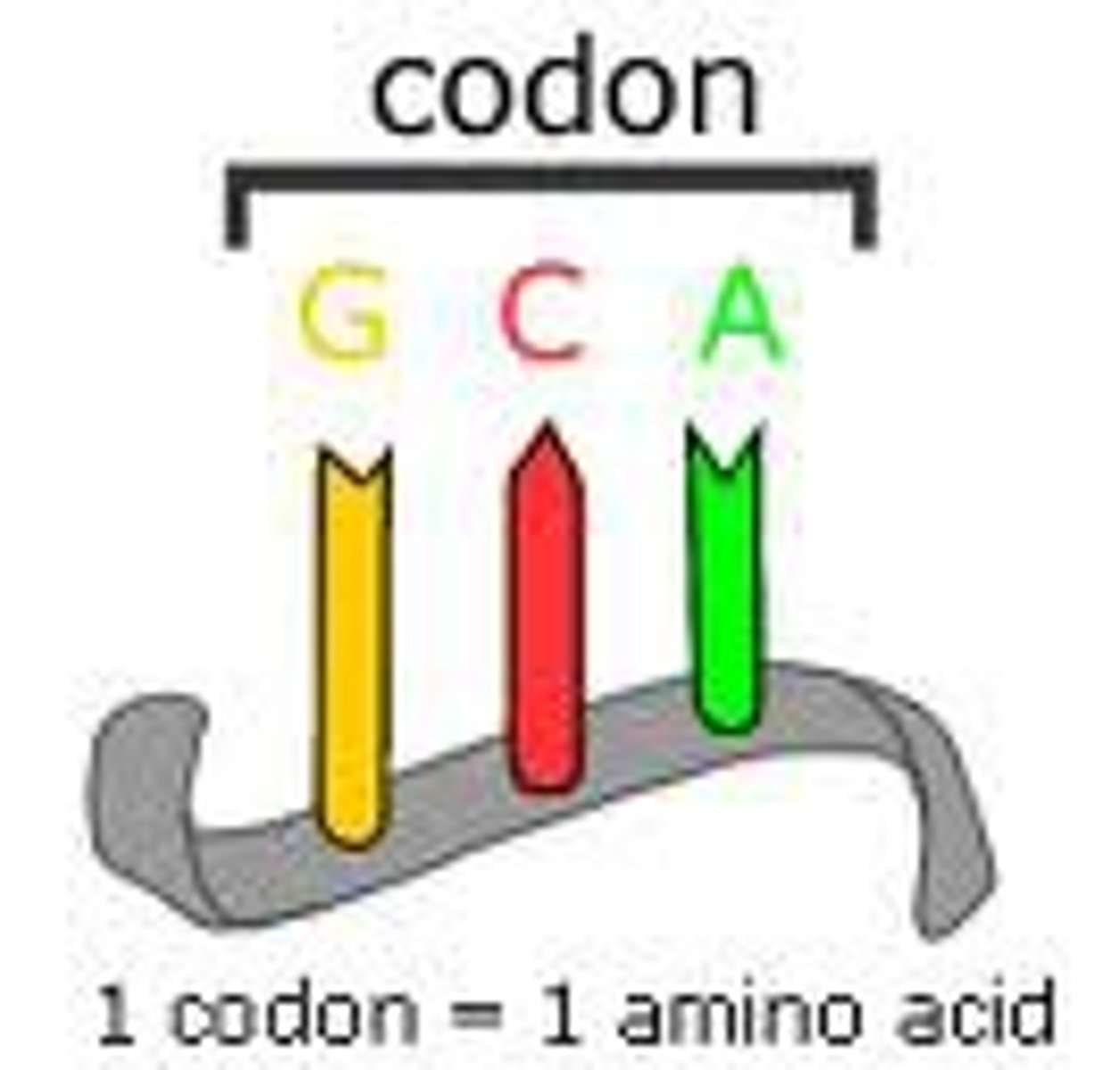
codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger mRNA that codes for a single amino acid
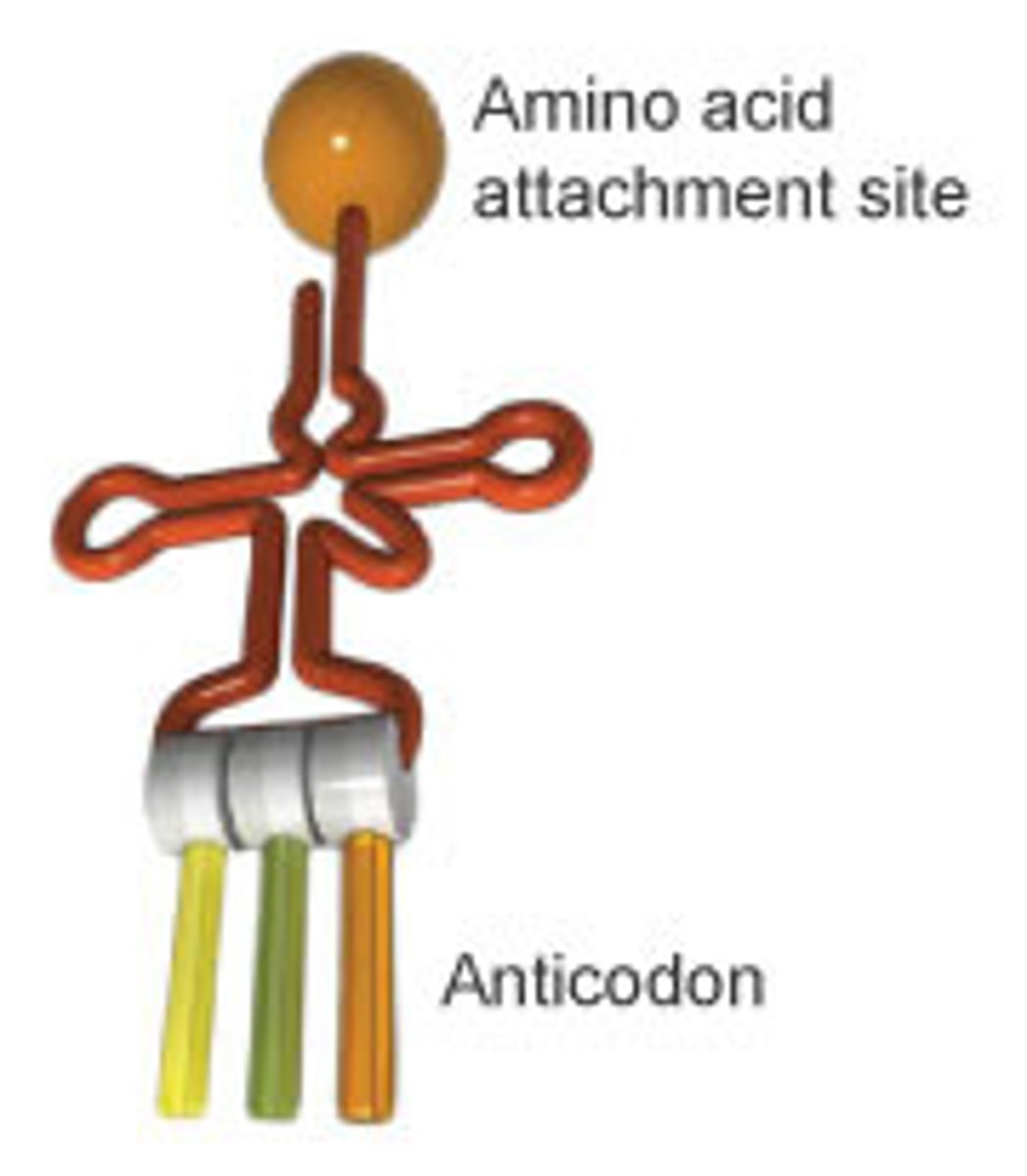
anti-codon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
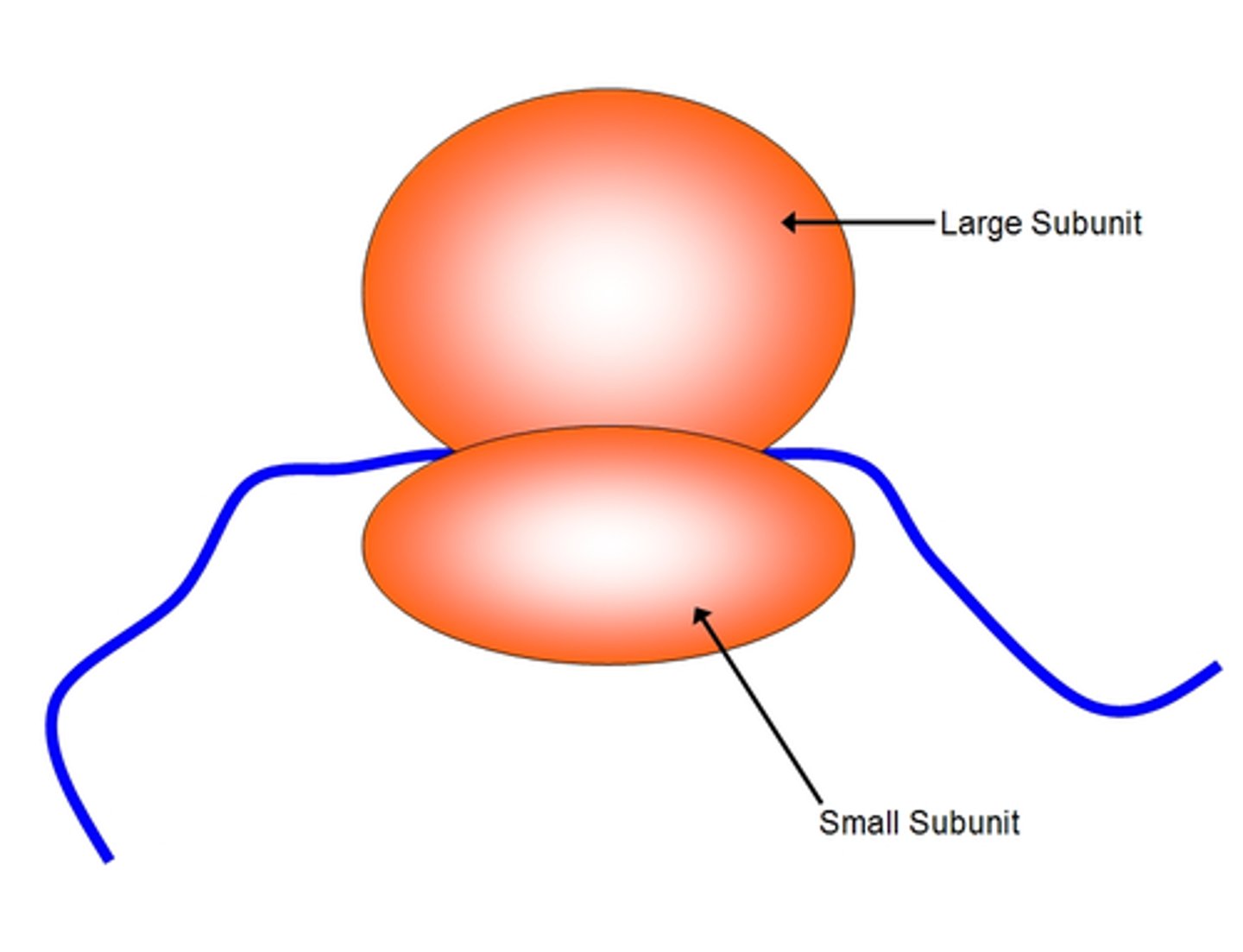
ribosome
site of protein synthesis
semi-conservative replication
in each new DNA double helix, one strand is from the original molecule, and one strand is new

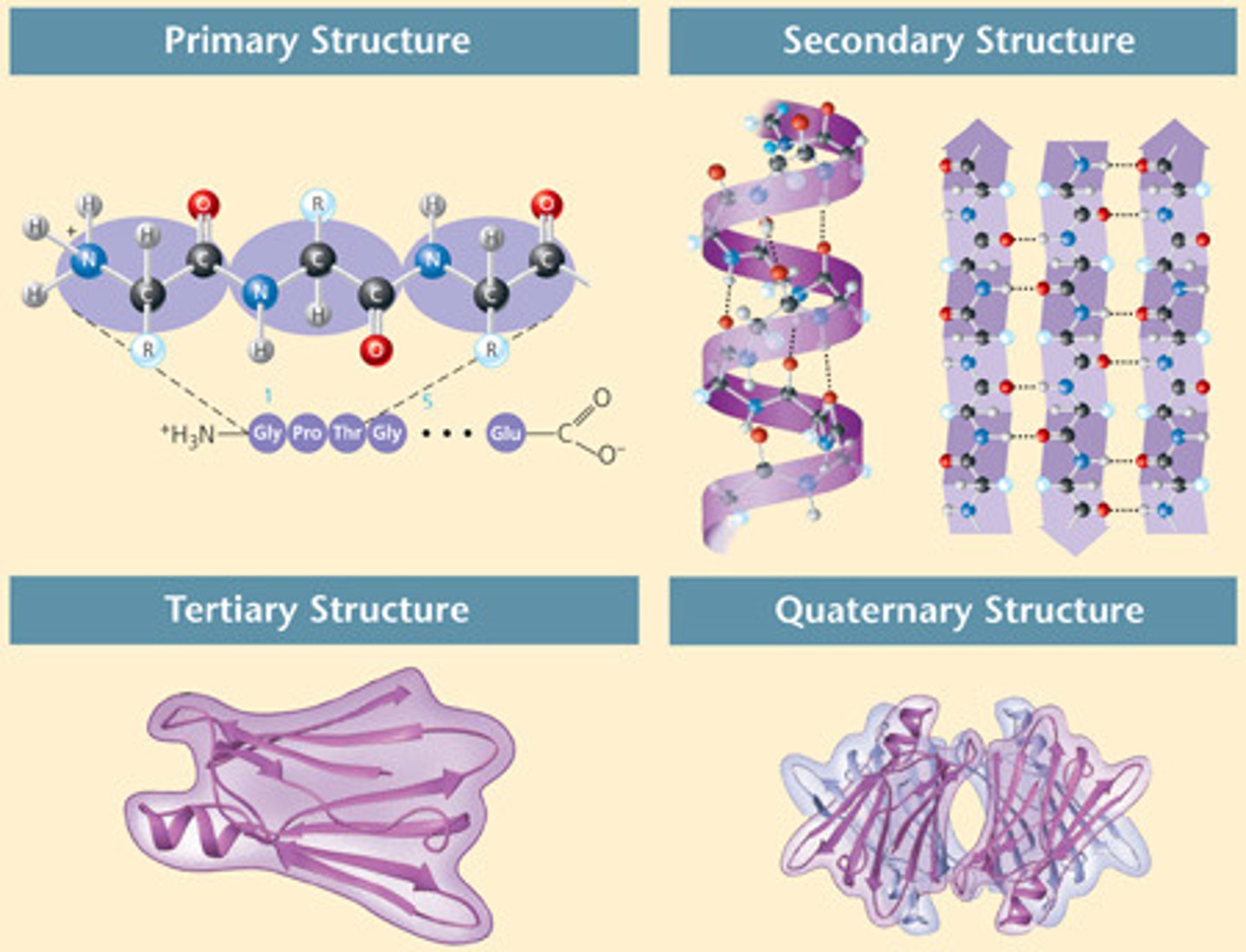
protein
An organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
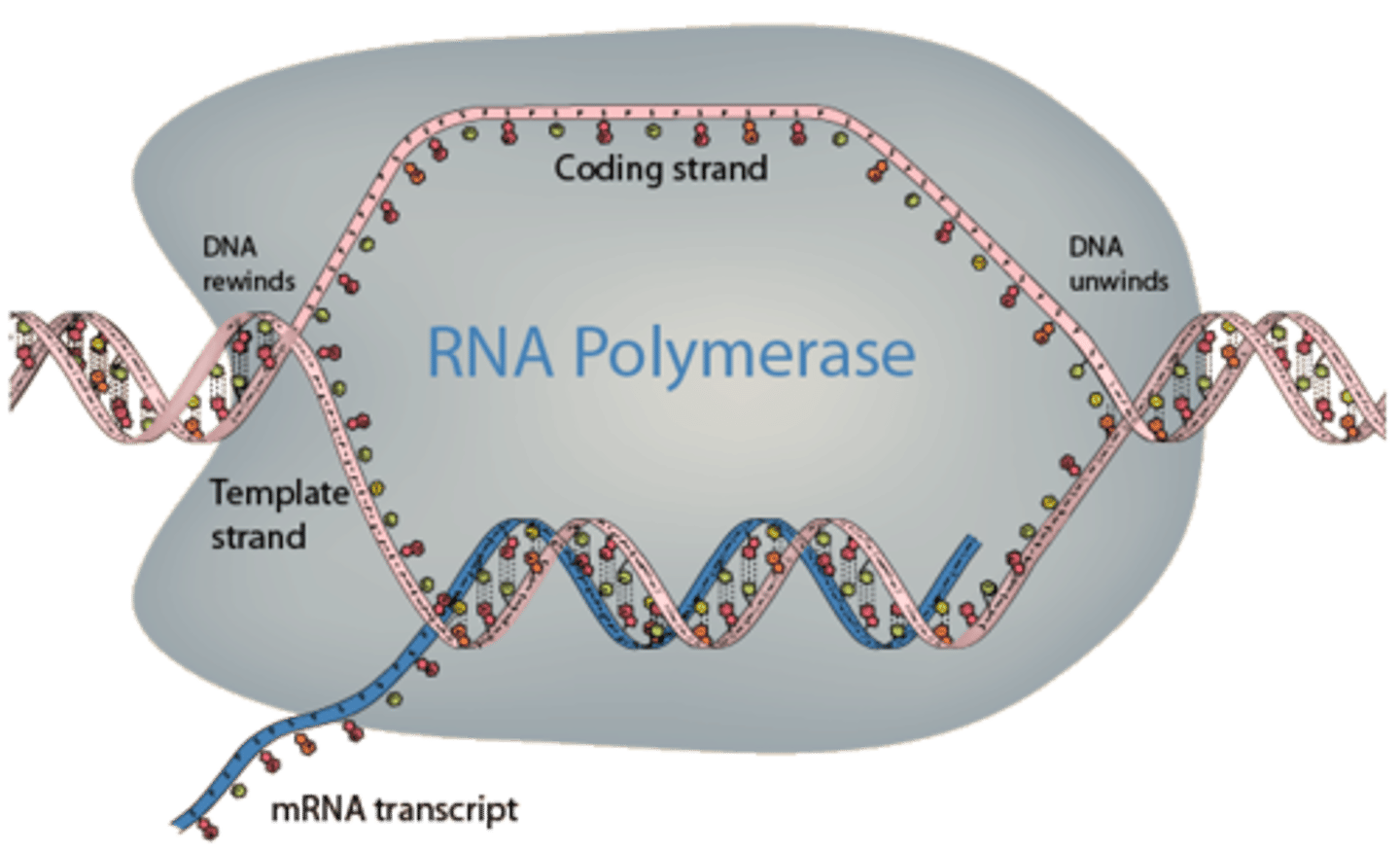
RNA polymerase
Enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands during transcription
start codon
AUG (methionine)

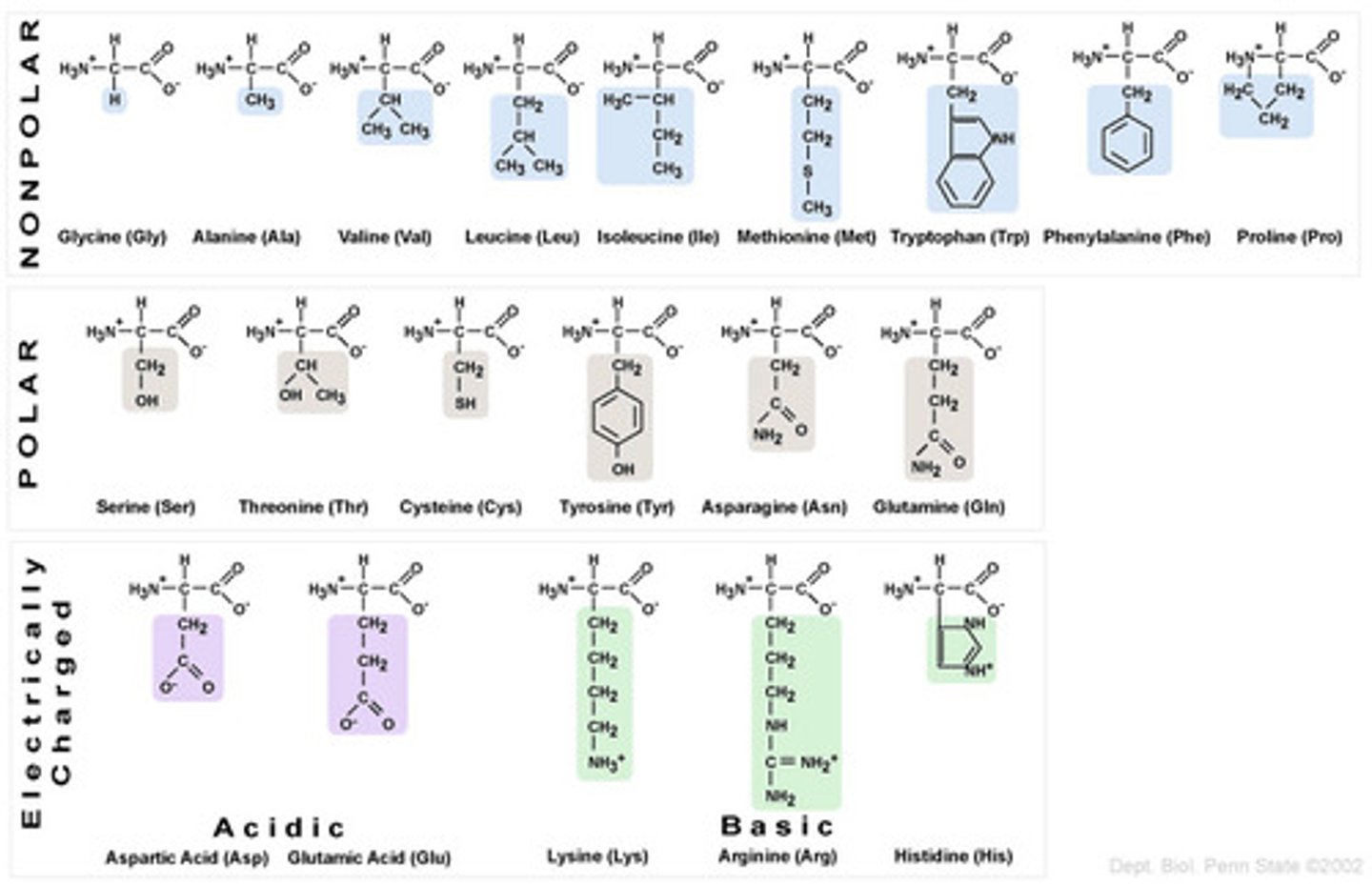
amino acids
monomers/building blocks of proteins
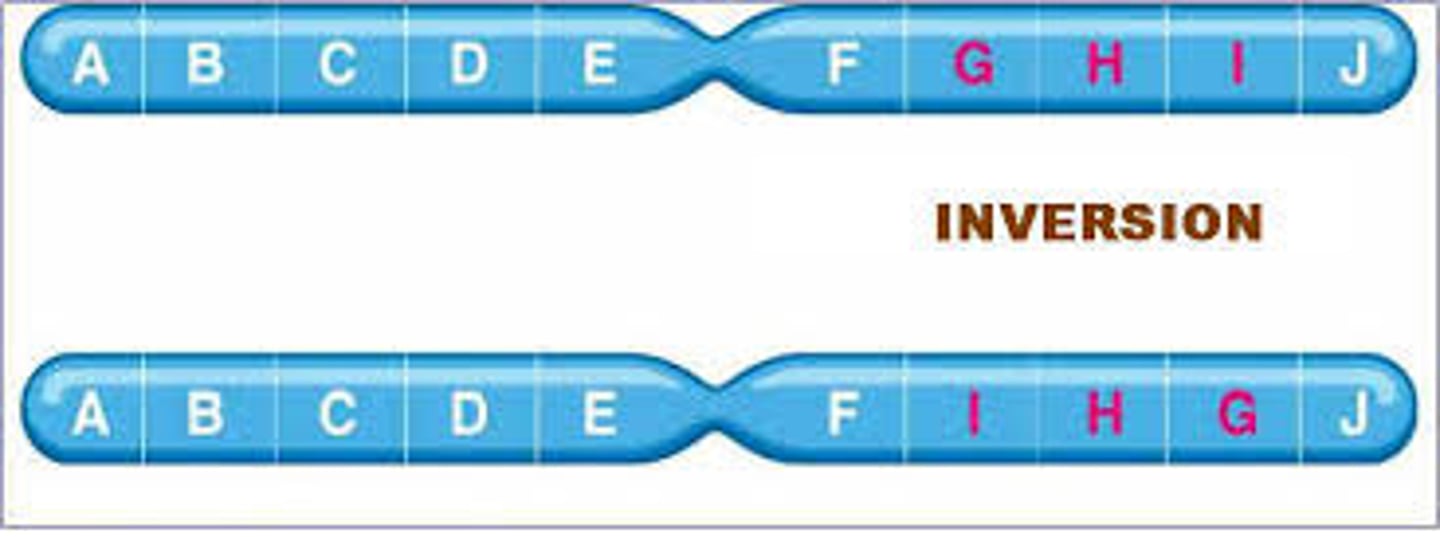
inversion mutation
A mutation involving a piece of a chromosome that breaks off and reattaches in reverse orientation.
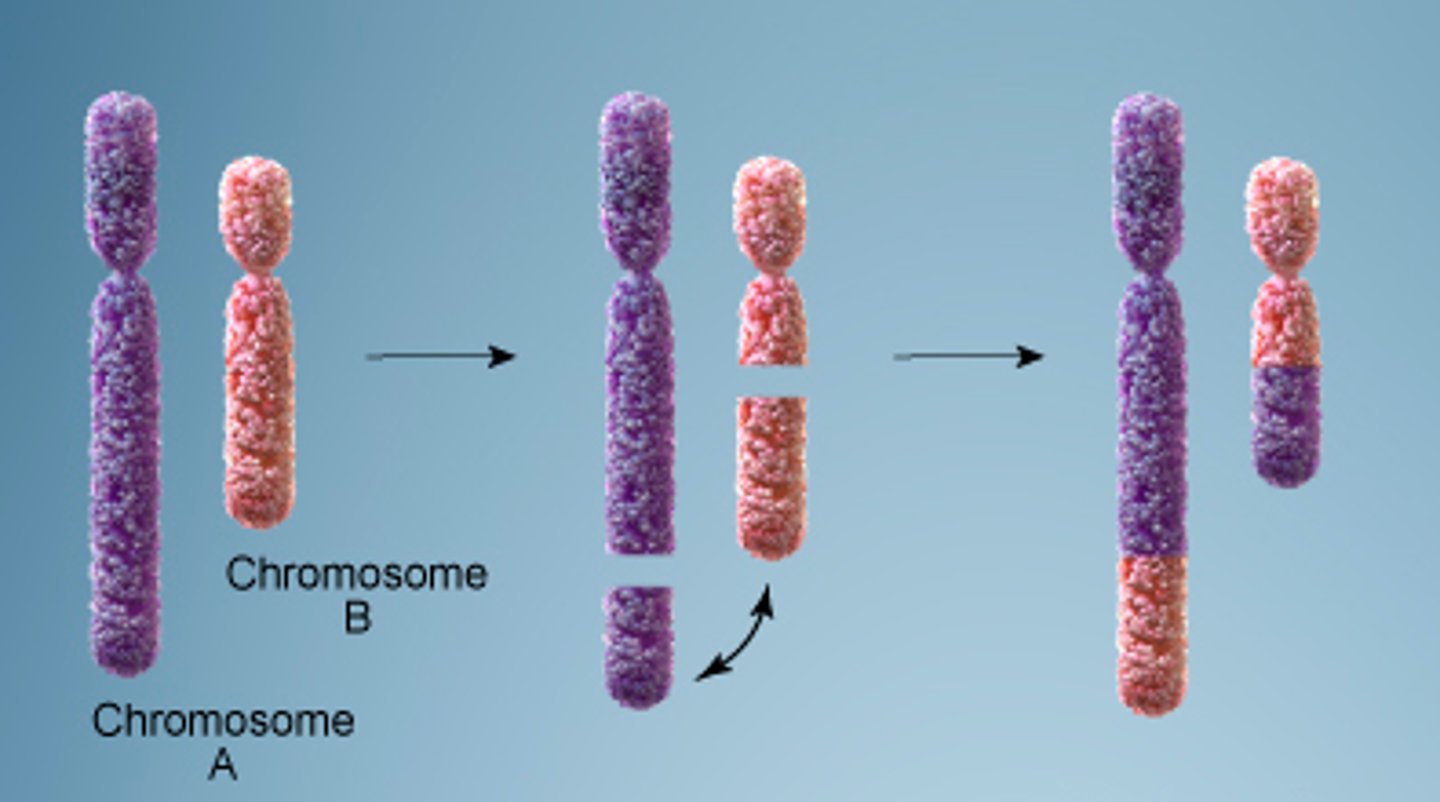
translocation mutation
mutation in which one part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome
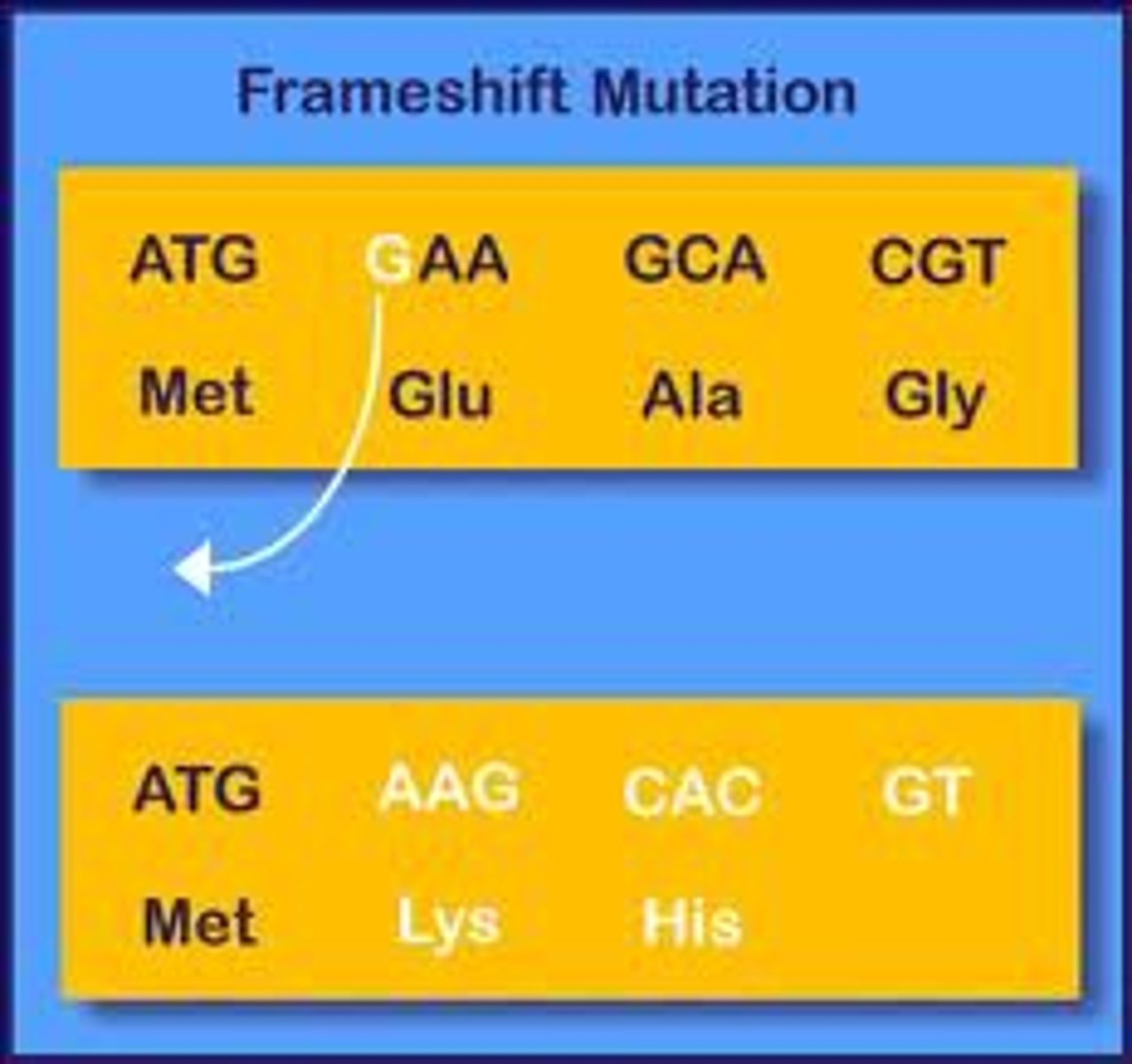
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
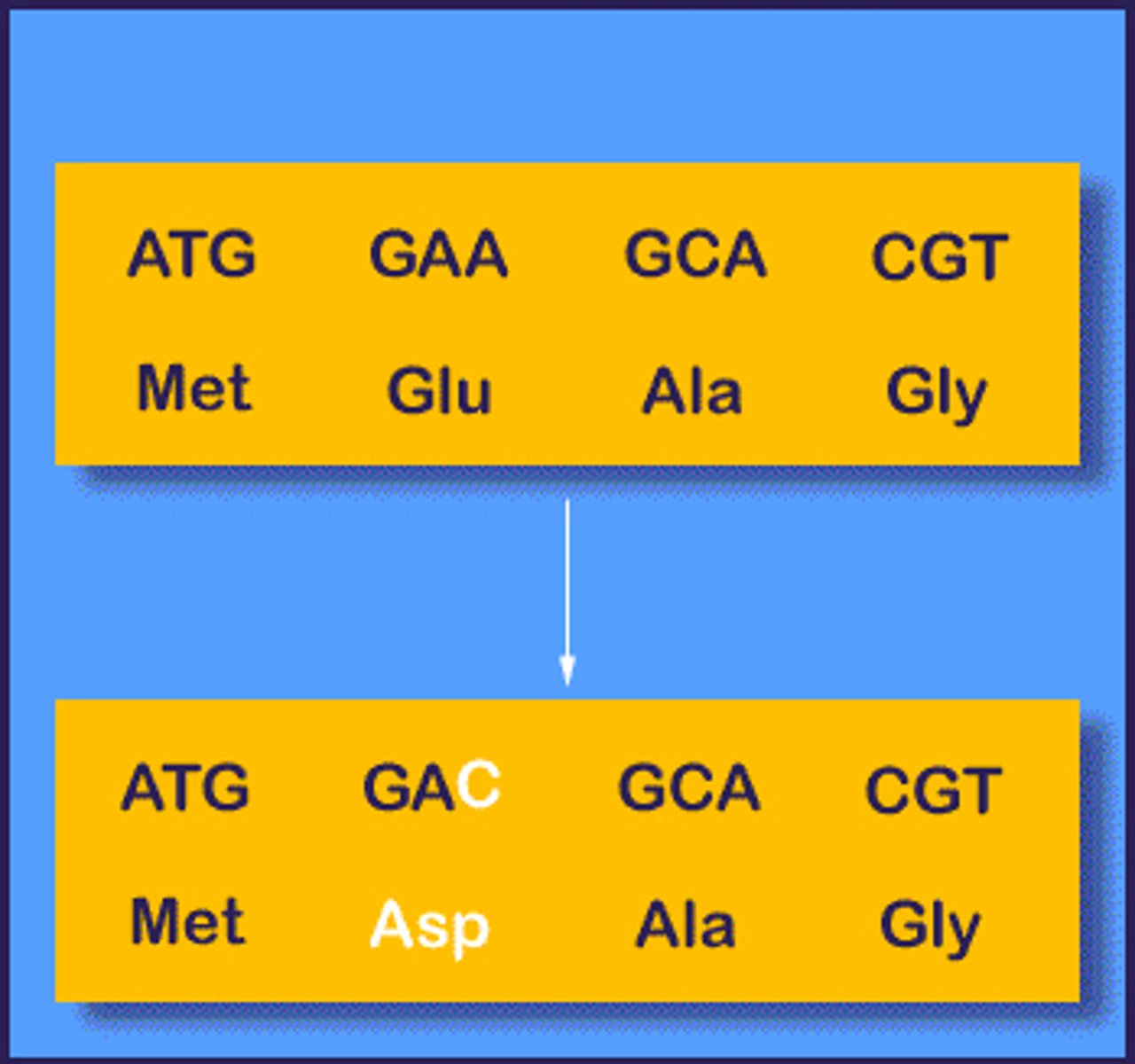
point mutation (substitution)
one nucleotide is replaced with a different nucleotide.
Watson and Crick
Developed the double helix model of DNA.

DNA ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment during DNA Replication

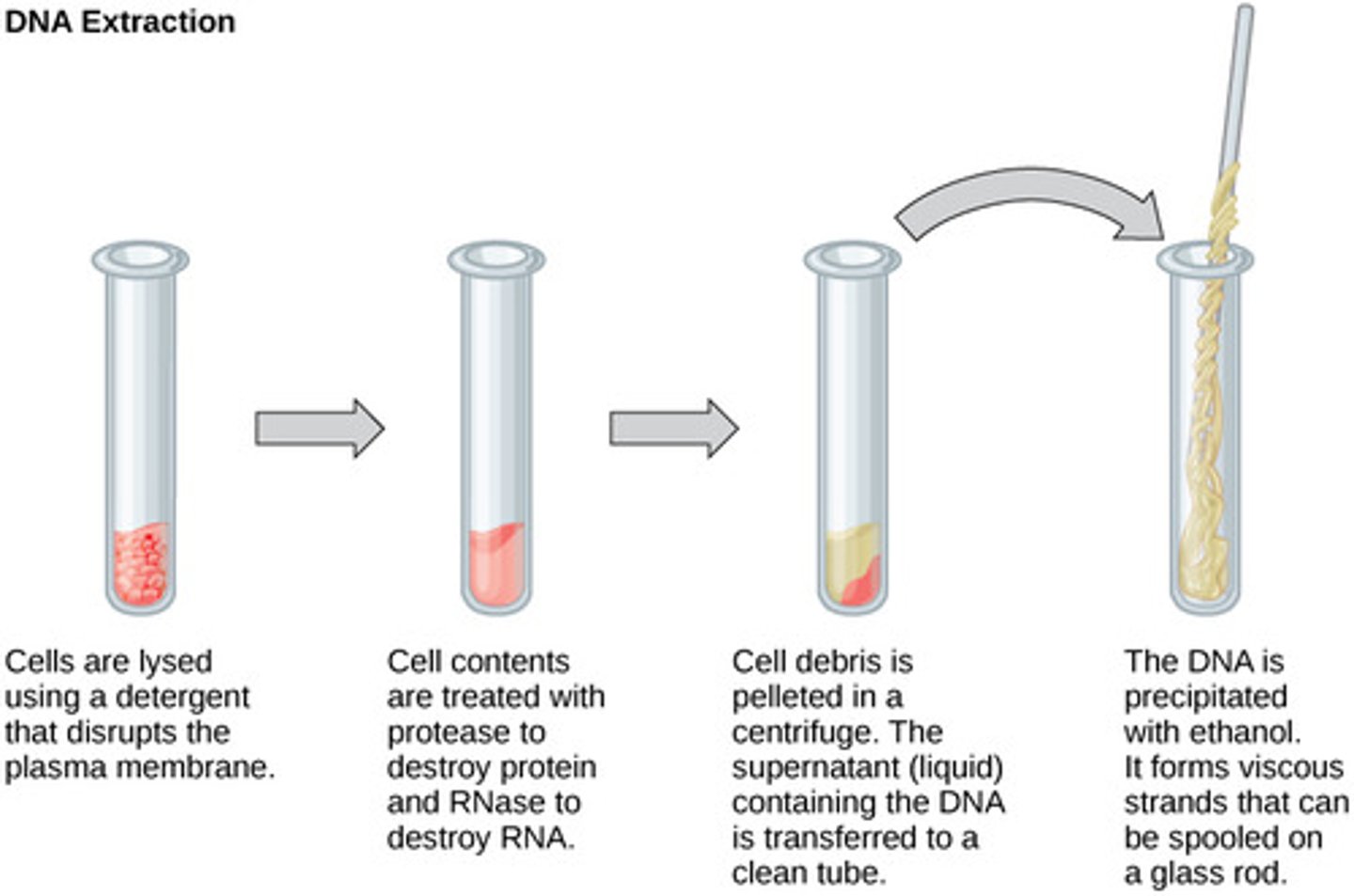
DNA extraction
the opening of cells to separate/isolate DNA from other cell parts
Primase (RNA polymerase)
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer using the parental DNA strand as a template.
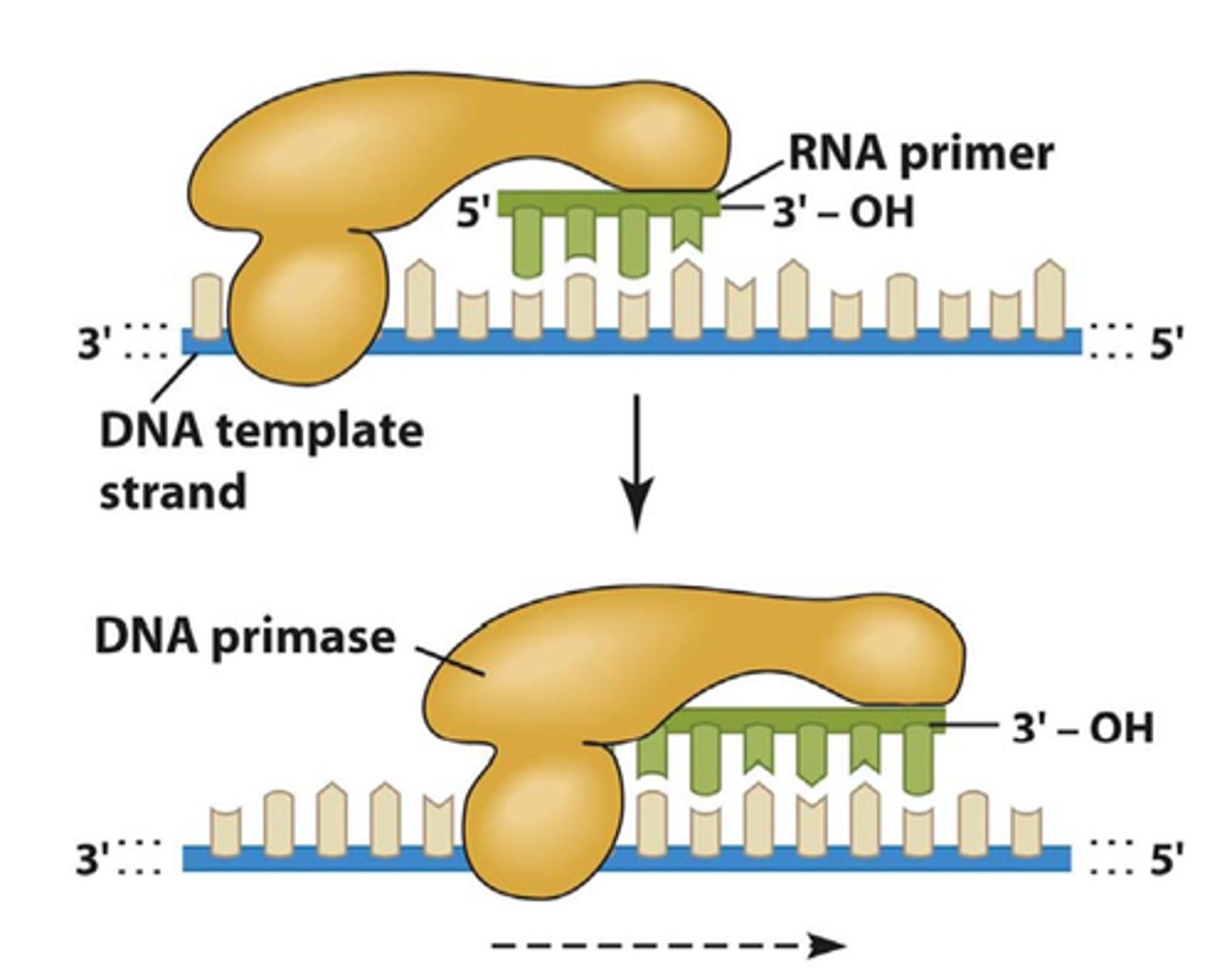
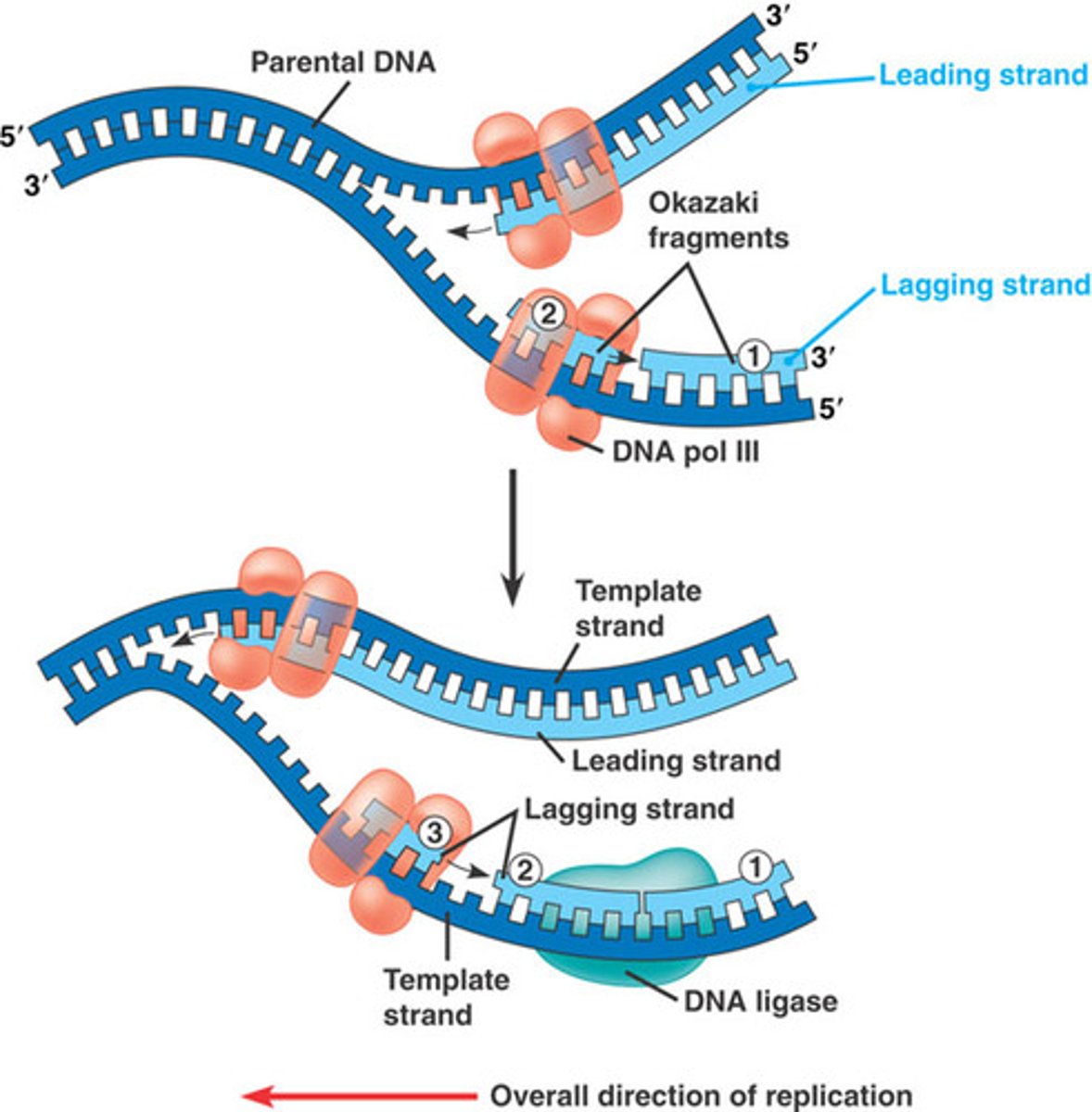
leading strand
the new complementary DNA strand synthesized continuously along the template strand toward the replication fork in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction
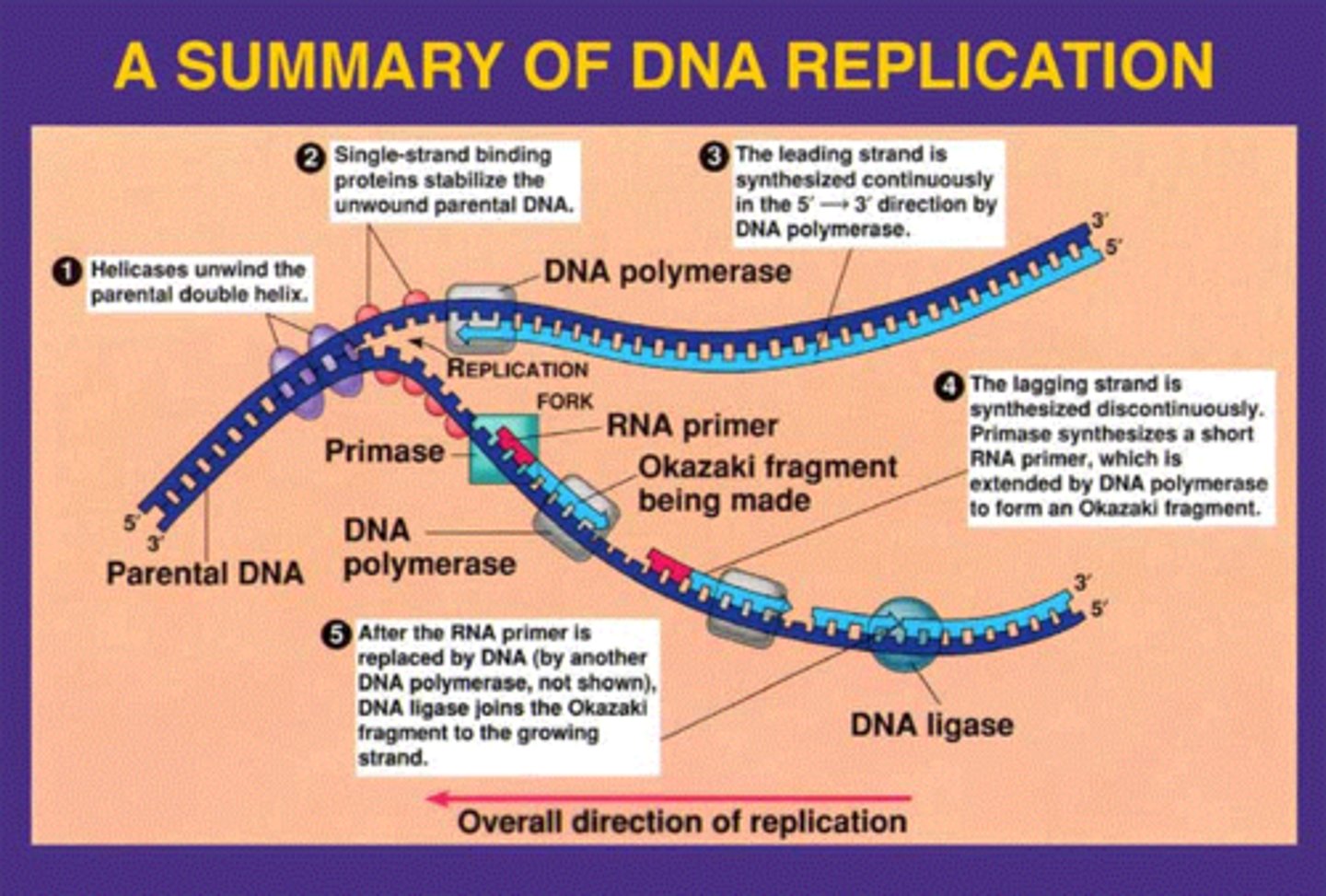
lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
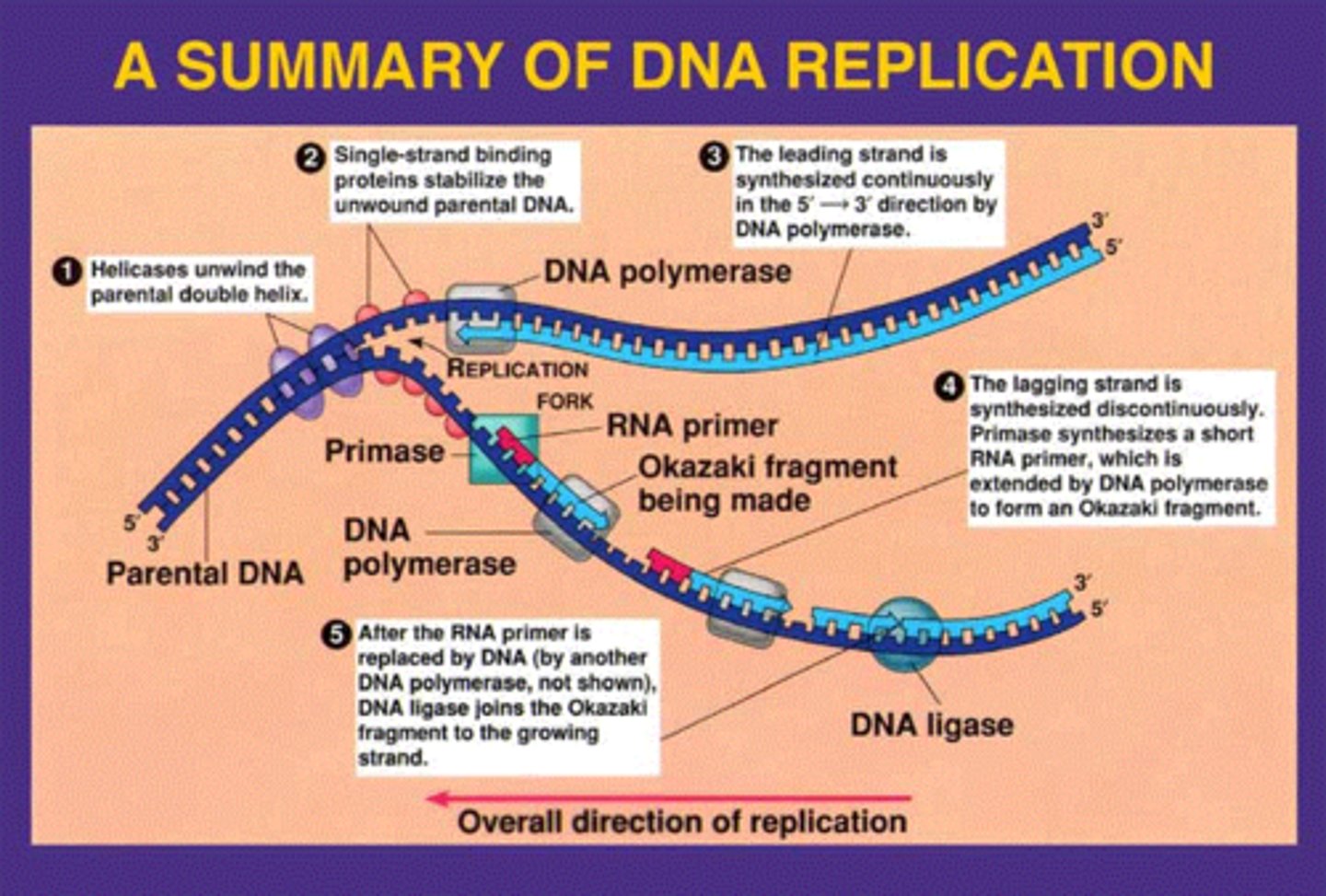
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
pre-mRNA
precursor mRNA; the first strand of mRNA produced by gene transcription that contains both introns and exons
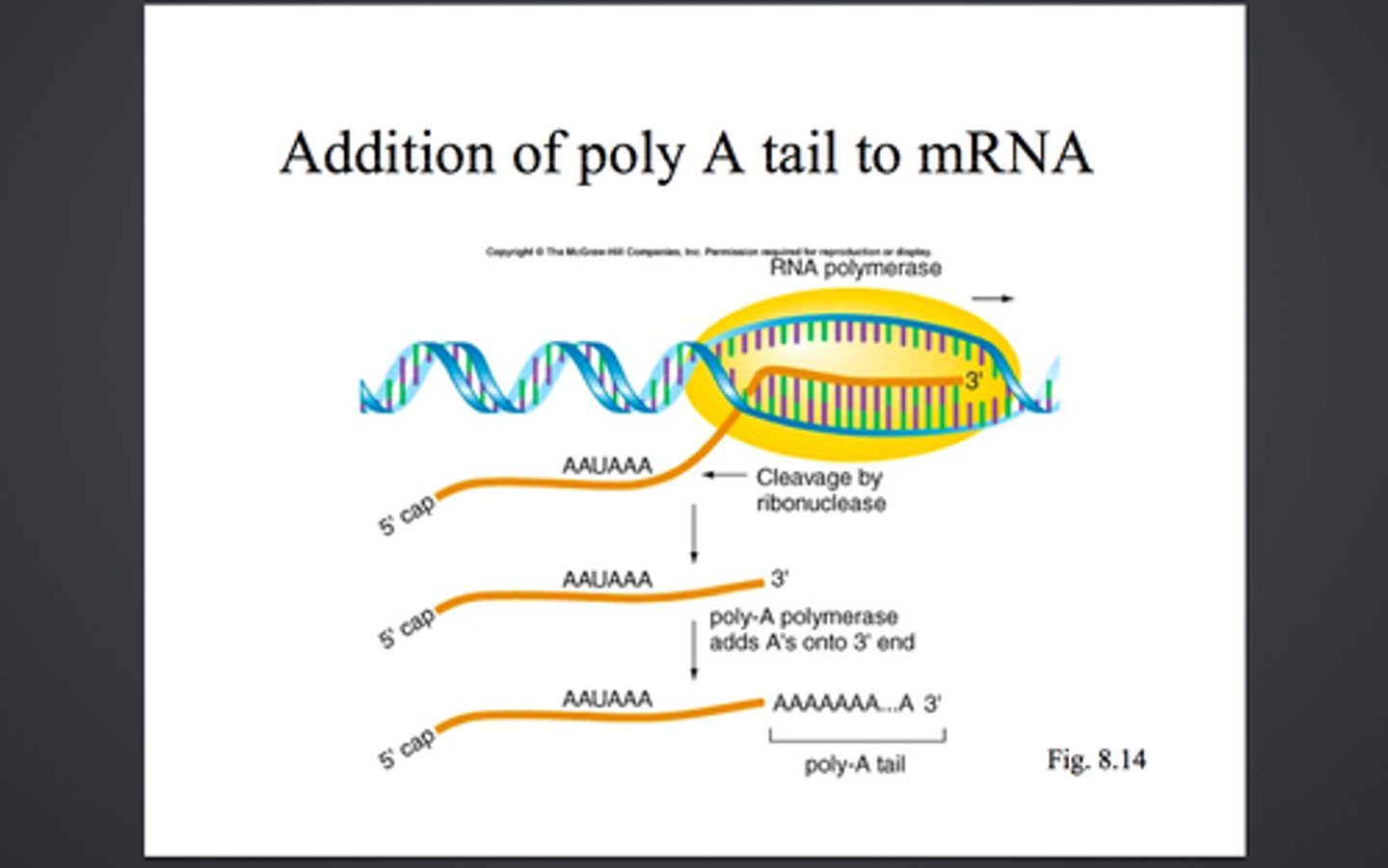
poly-A tail
a sequence of 50-250 adenine nucleotides added onto the 3' end of a pre-mRNA molecule
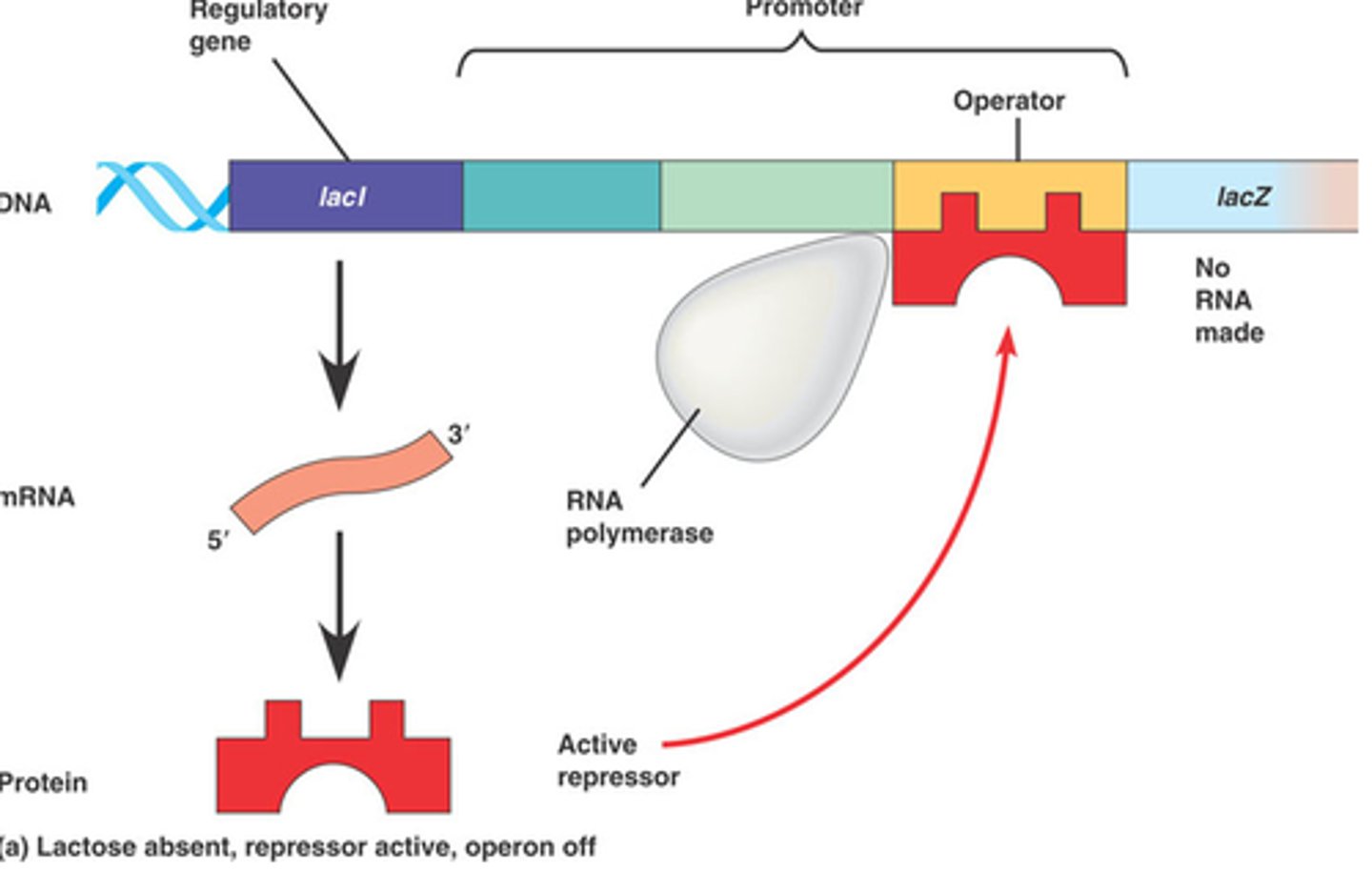
operon
group of genes operating together
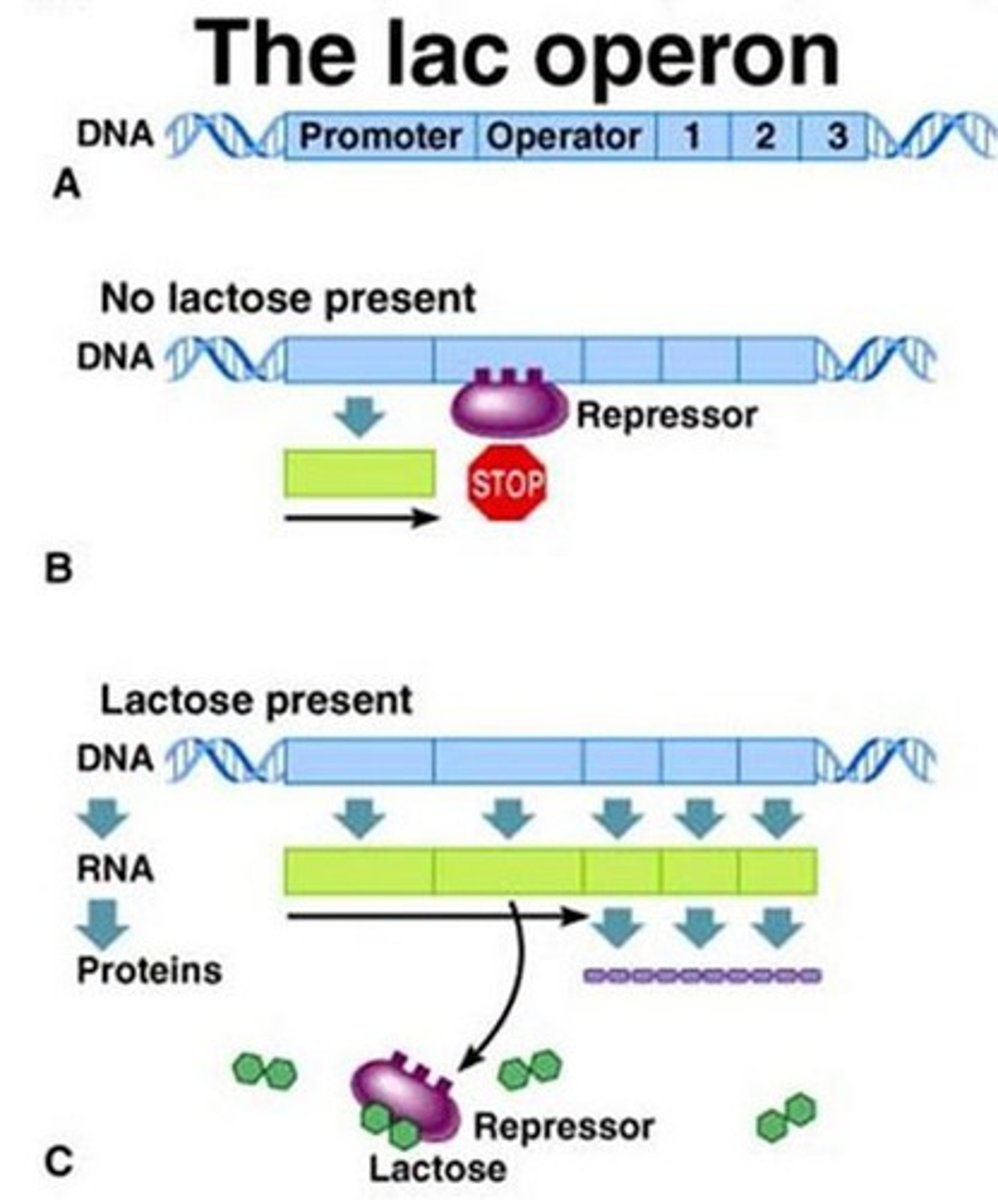
promotor
A region of DNA with a specific sequence that tells RNA polymerase where to begin transcription.
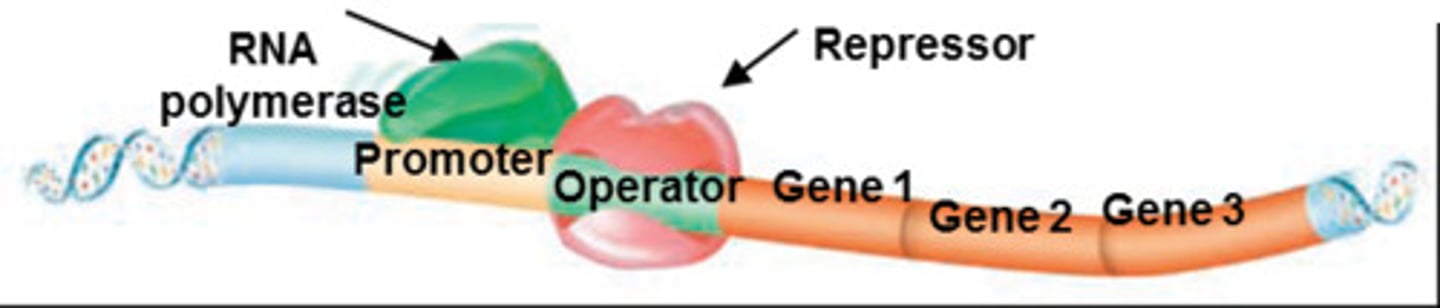
repressor
A protein that binds to an operator and physically blocks RNA polymerase from binding to a promoter site
Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.

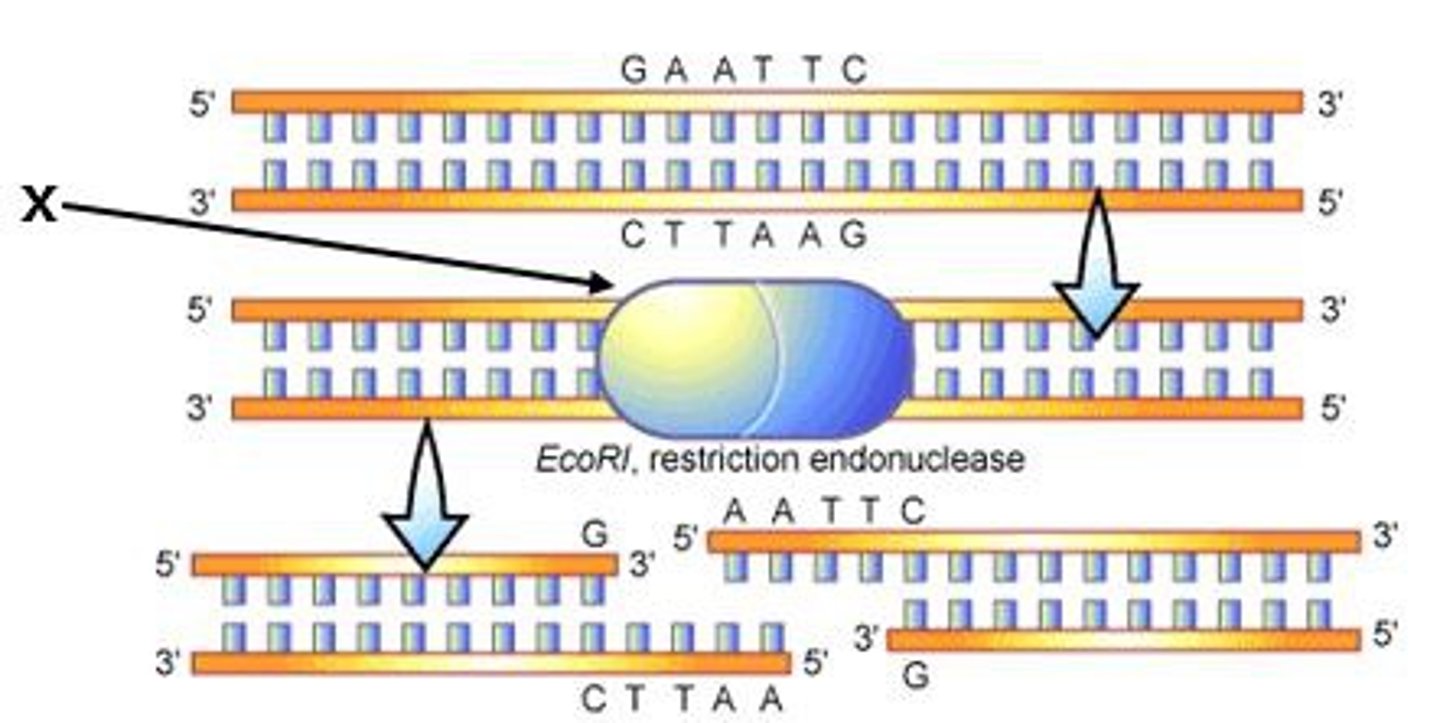
restriction enzymes
Enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides
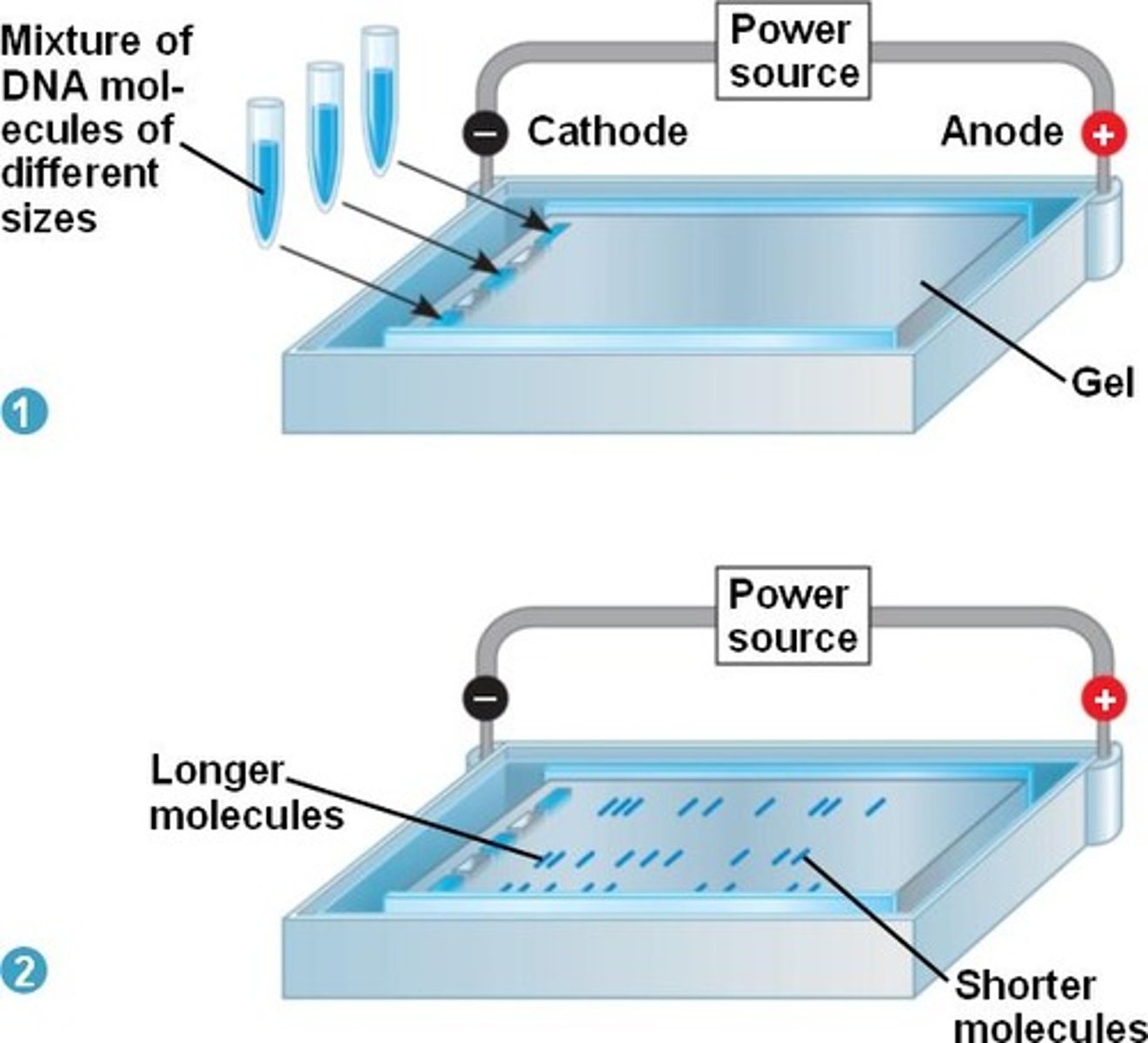
gel electrophoresis
Procedure used to separate and analyze DNA fragments by placing a mixture of DNA fragments at one end of a porous gel and applying an electrical voltage to the gel
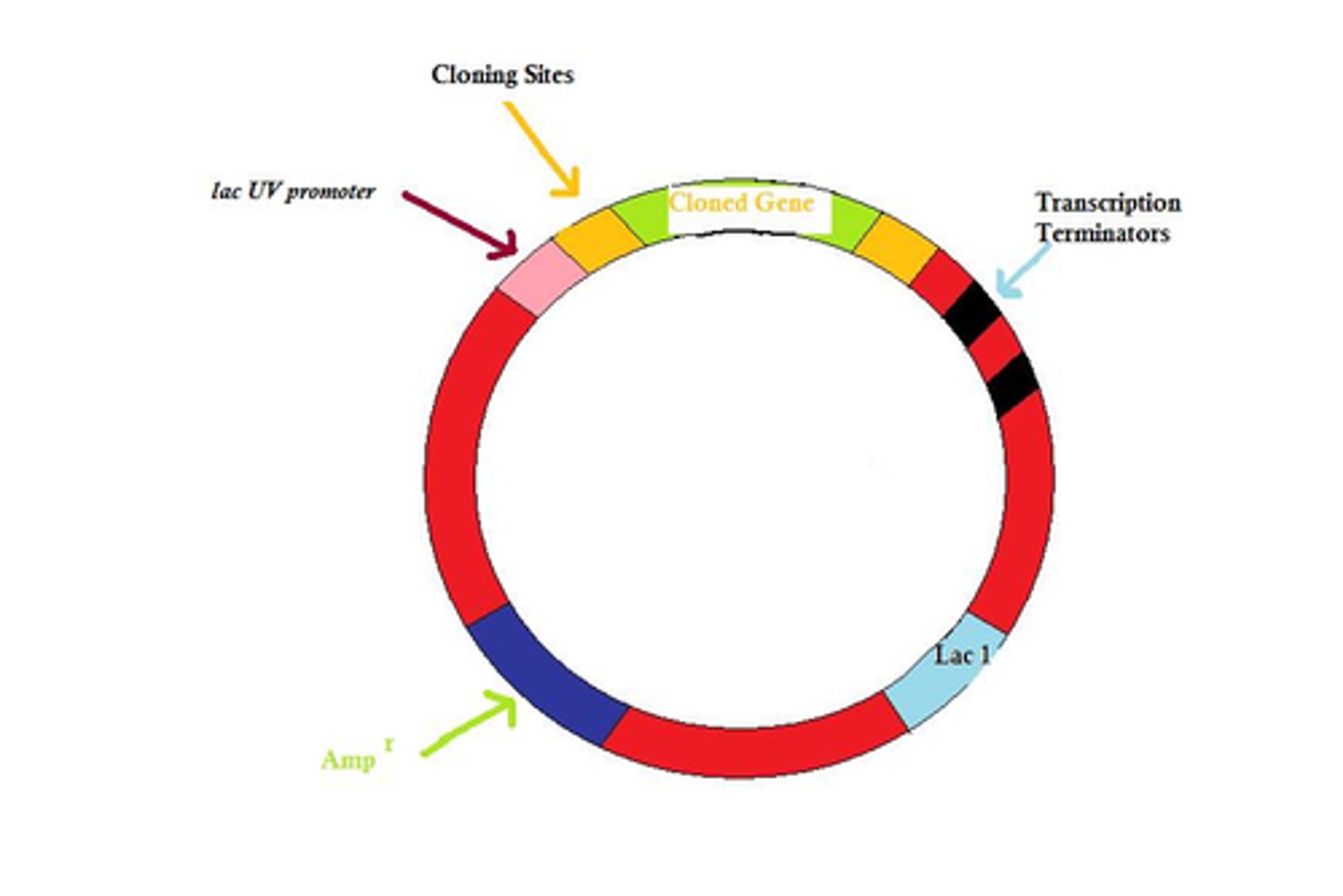
Recombinant DNA
DNA that has been formed artificially by combining constituents from different organisms.
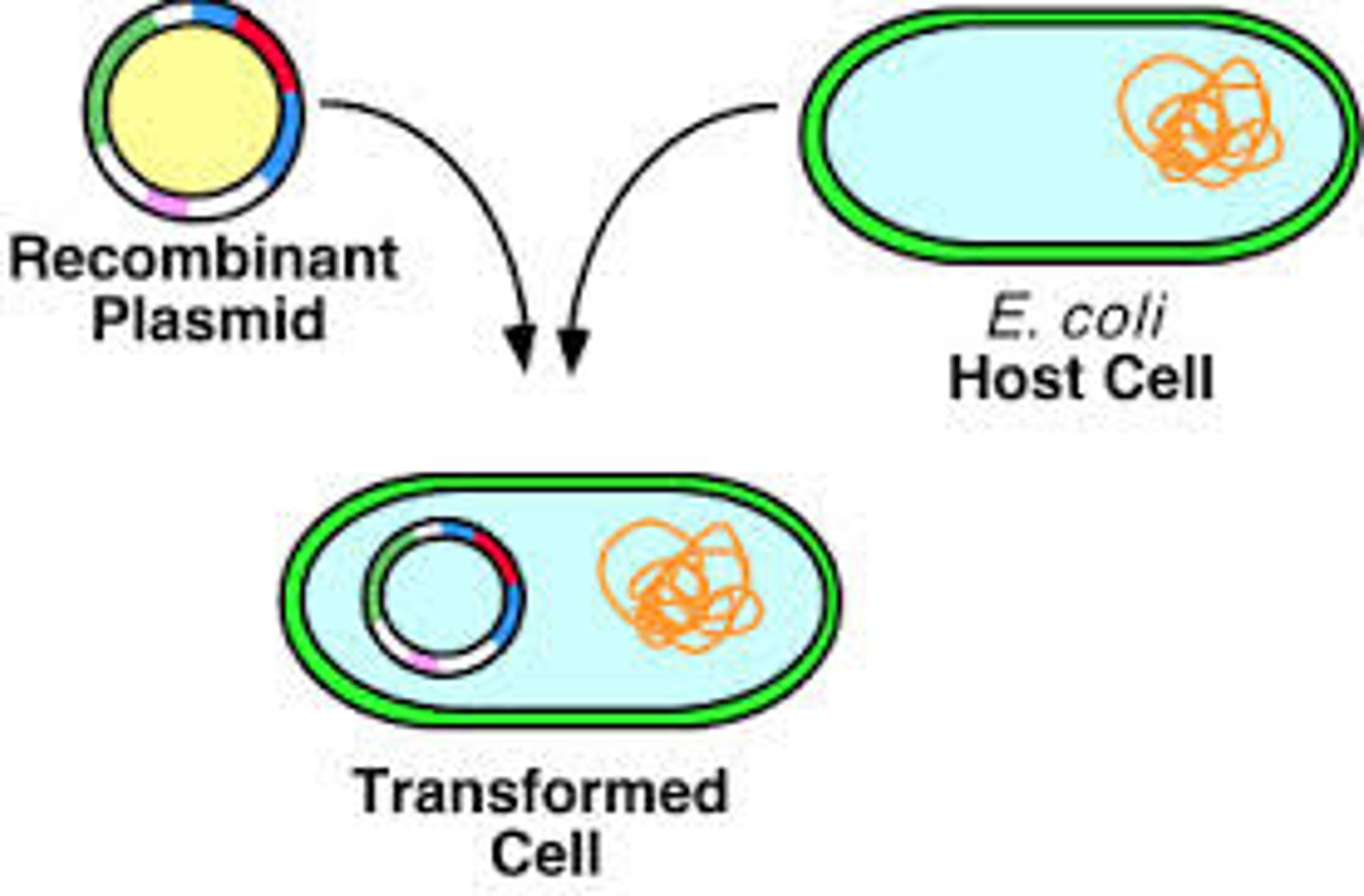
transformation
insertion of foreign DNA into host cells, in order to have the host produce new proteins and traits
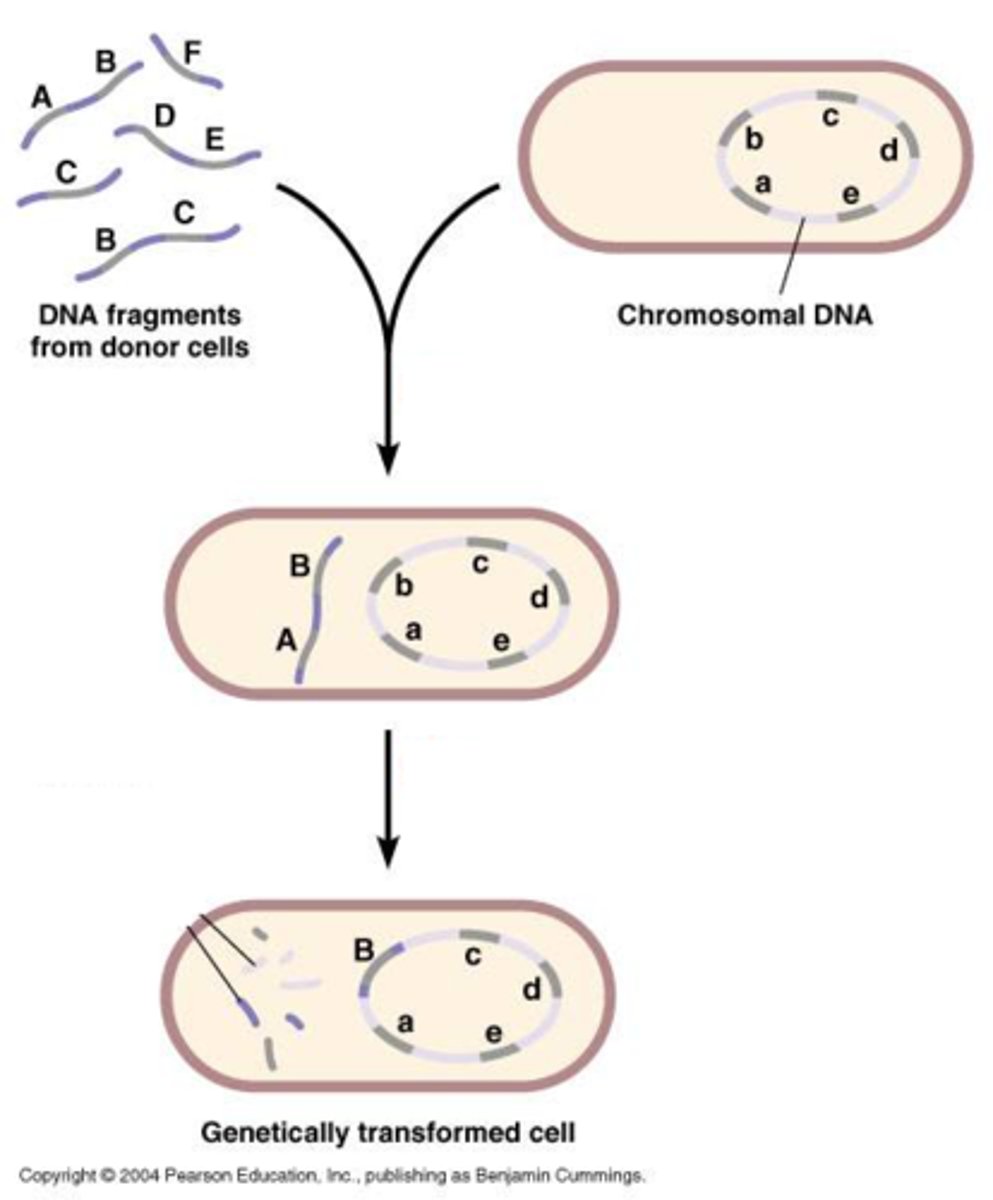
vectors
An organism that transmits DNA or disease by conveying DNA or pathogens from one host to another, ex. bacteriophages and viruses
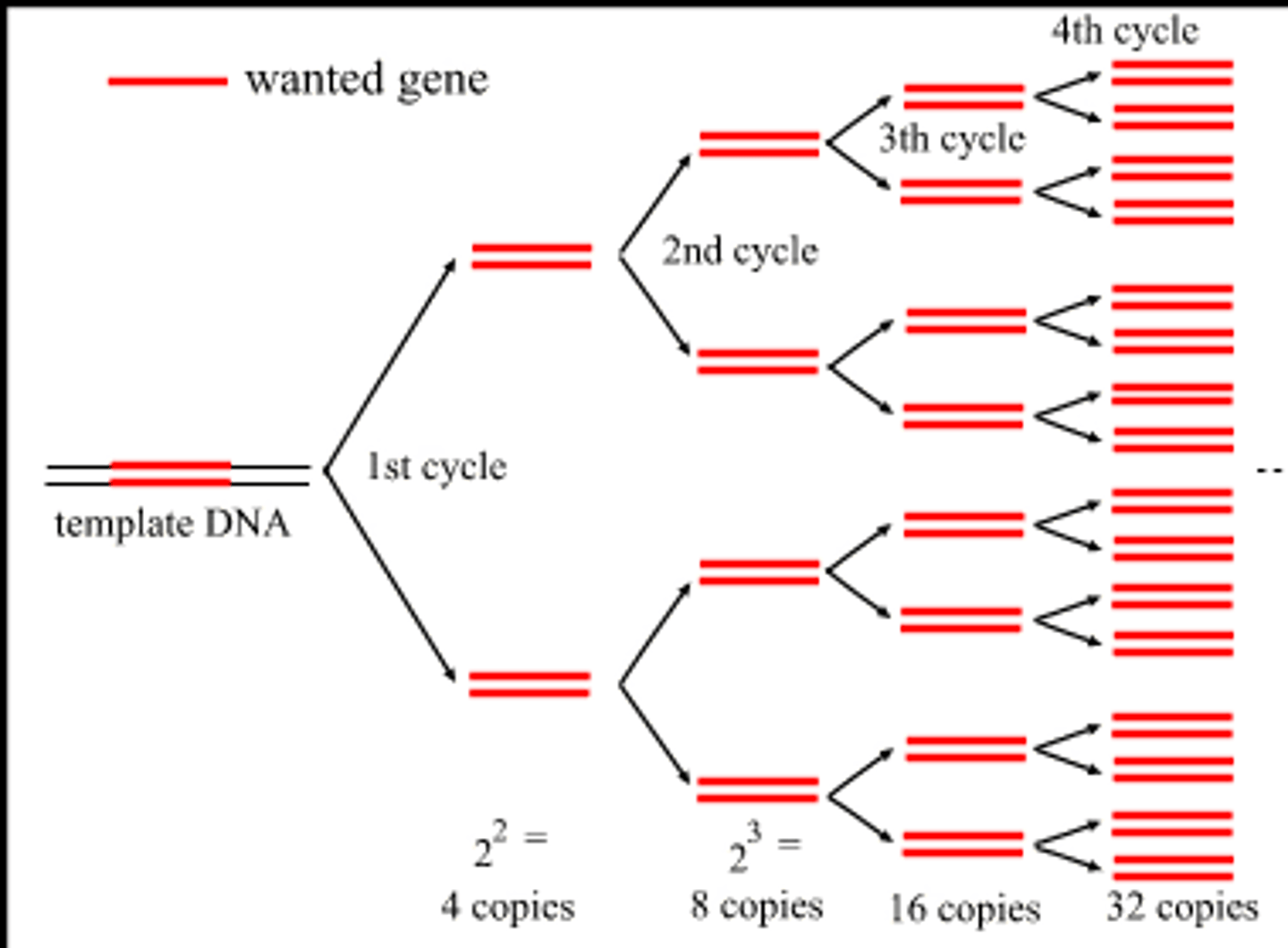
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
A laboratory technique for amplifying DNA in vitro (testtube) by incubating with special primers, Taq polymerase molecules, and nucleotides.
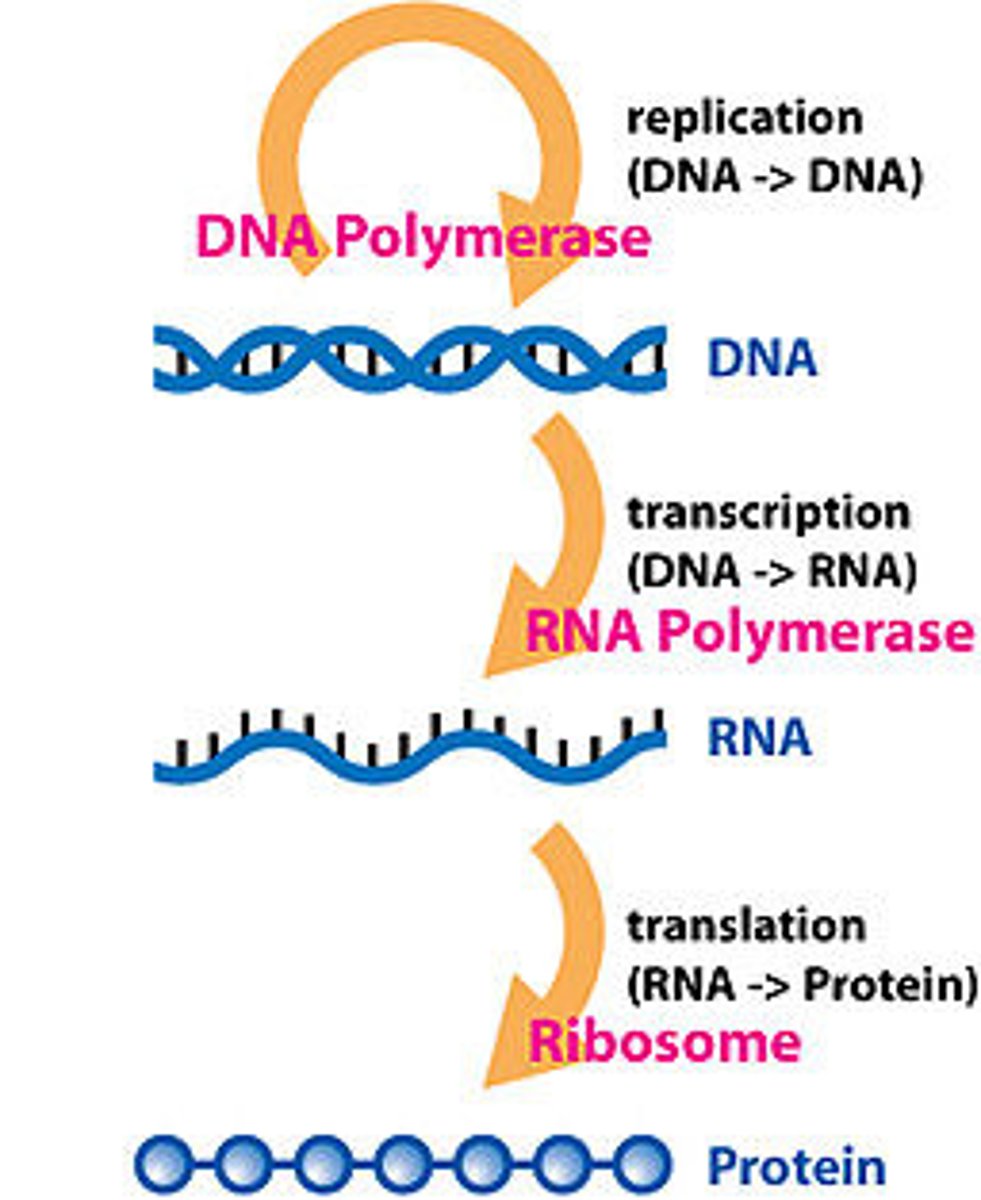
Central Dogma
DNA-transcription-RNA-translation-protein-trait
transcription factors
A regulatory protein that binds to DNA and affects transcription of specific genes.
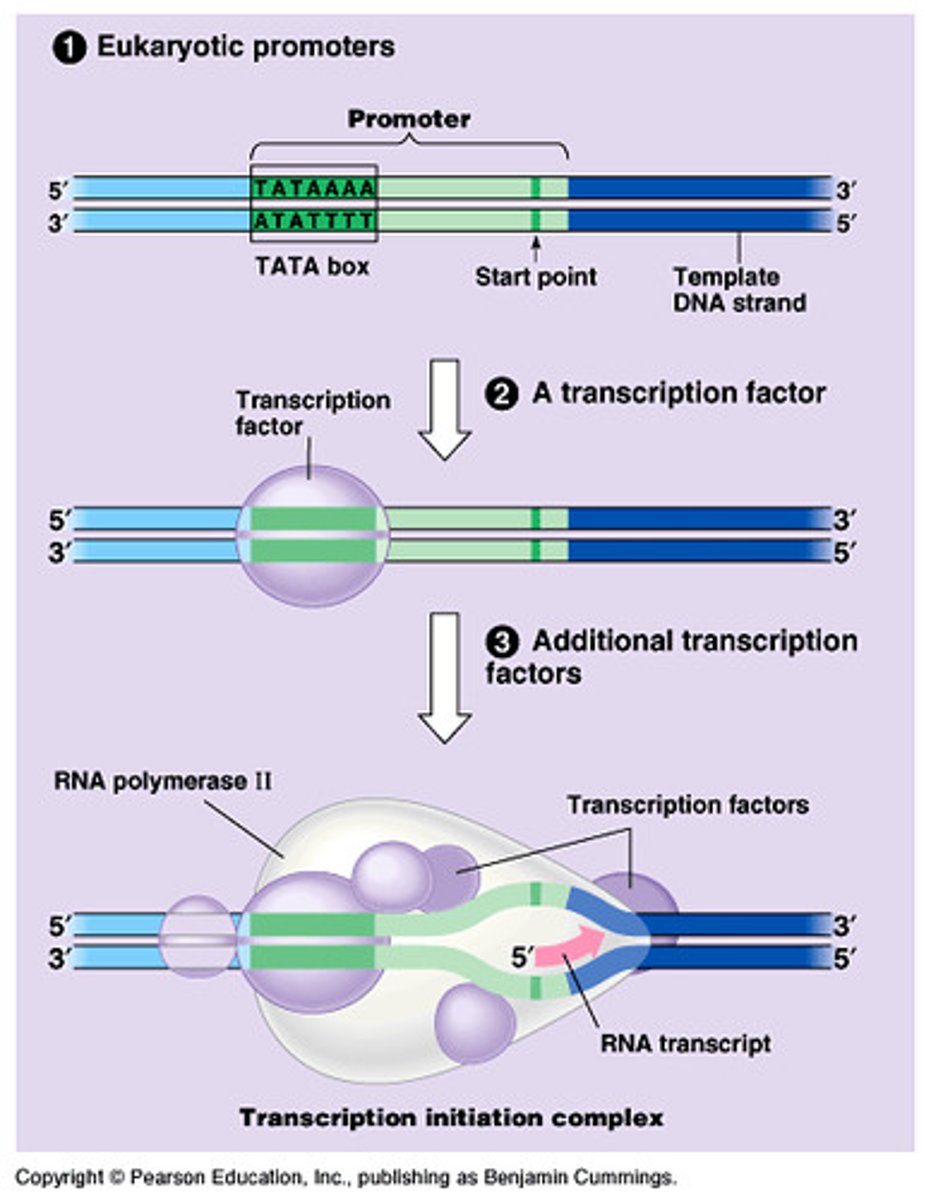
inducible operon
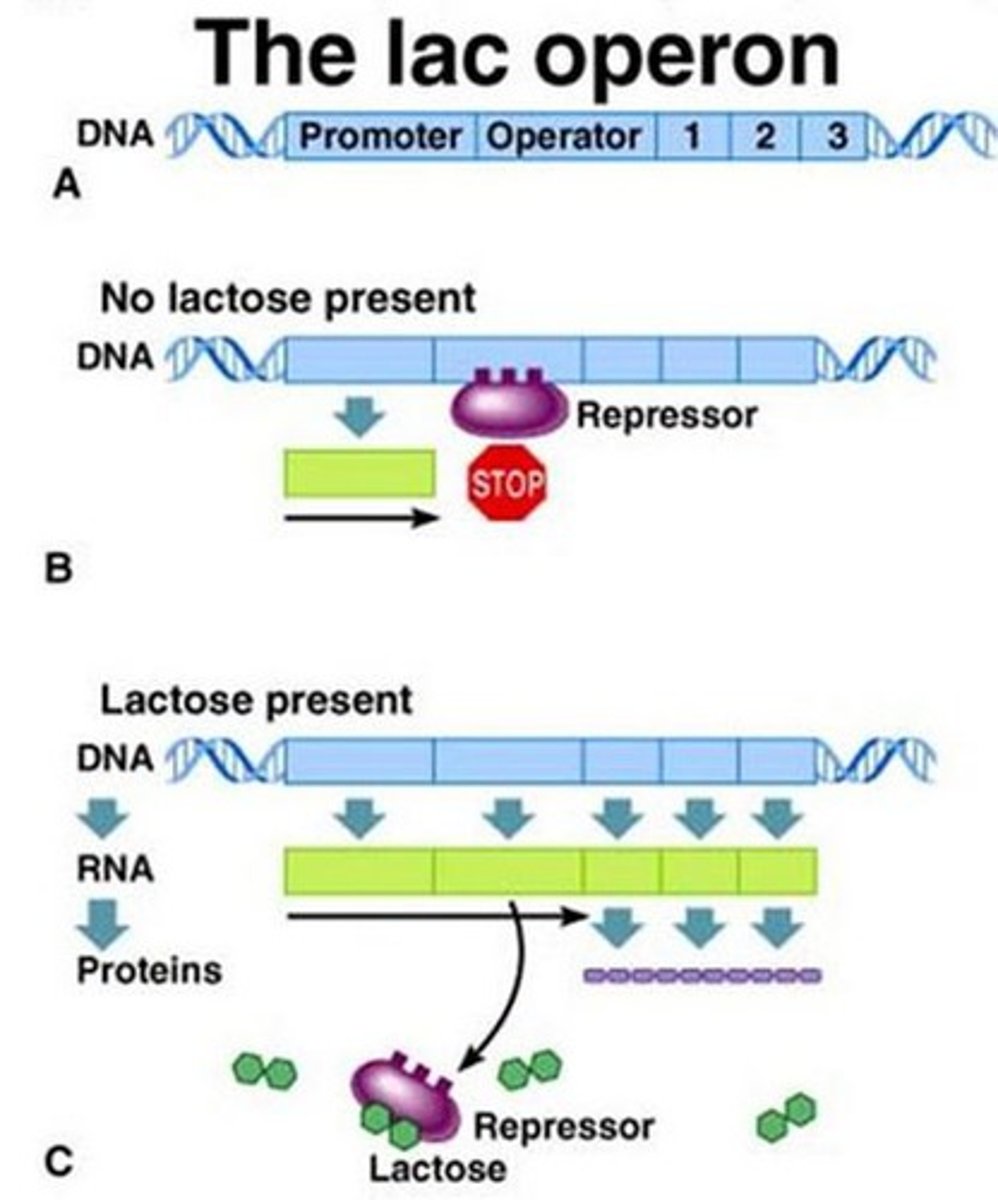
usually off, but can be stimulated (induced) when a specific small molecule interacts with a regulatory protein (example lac operon)
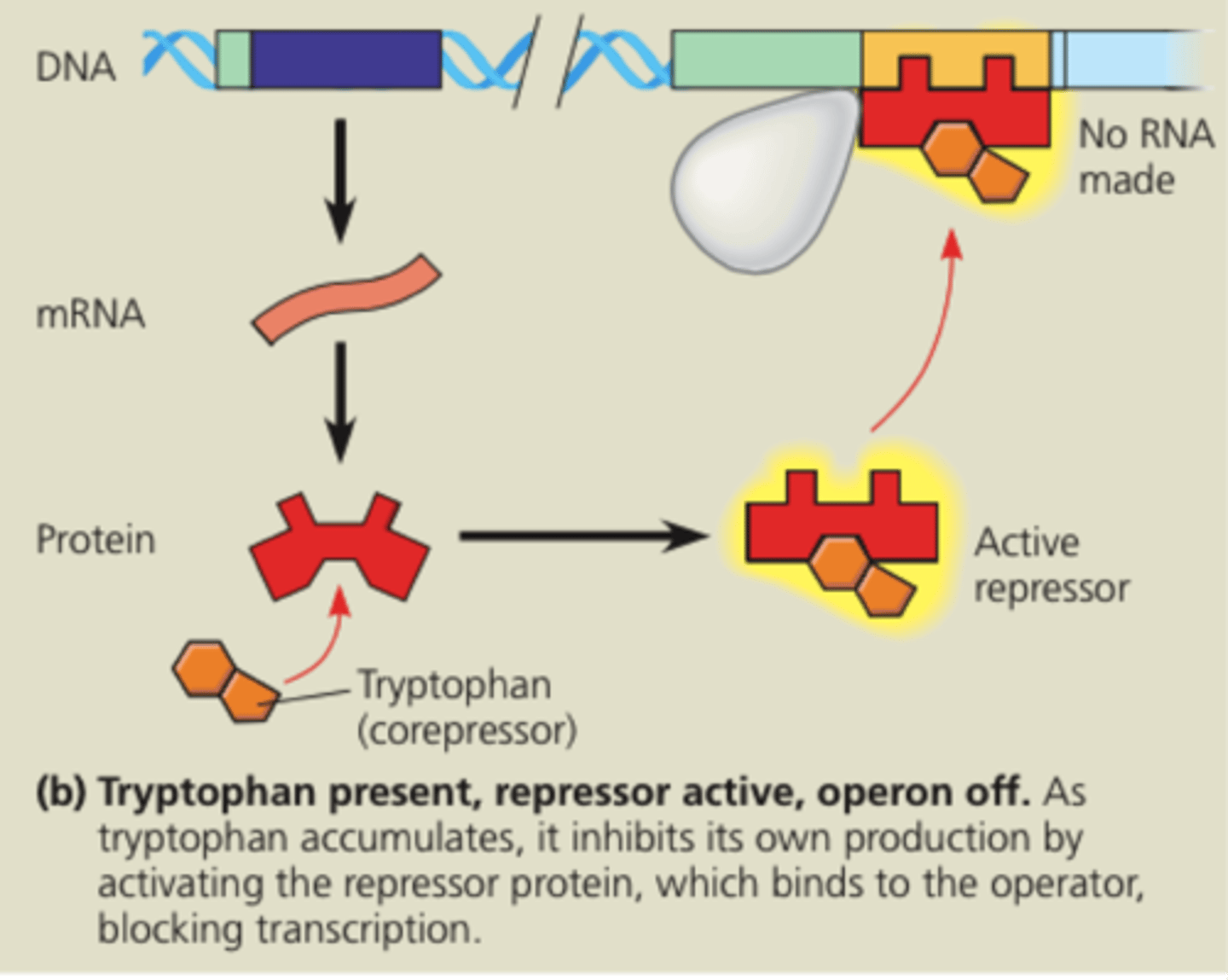
repressable operon
transcription is usually on but it an be inhibited
activators
proteins that turn operons on by binding to DNA, make it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter
endonuclease
An enzyme that cleaves its nucleic acid substrate (DNA) at internal sites in the nucleotide sequence.
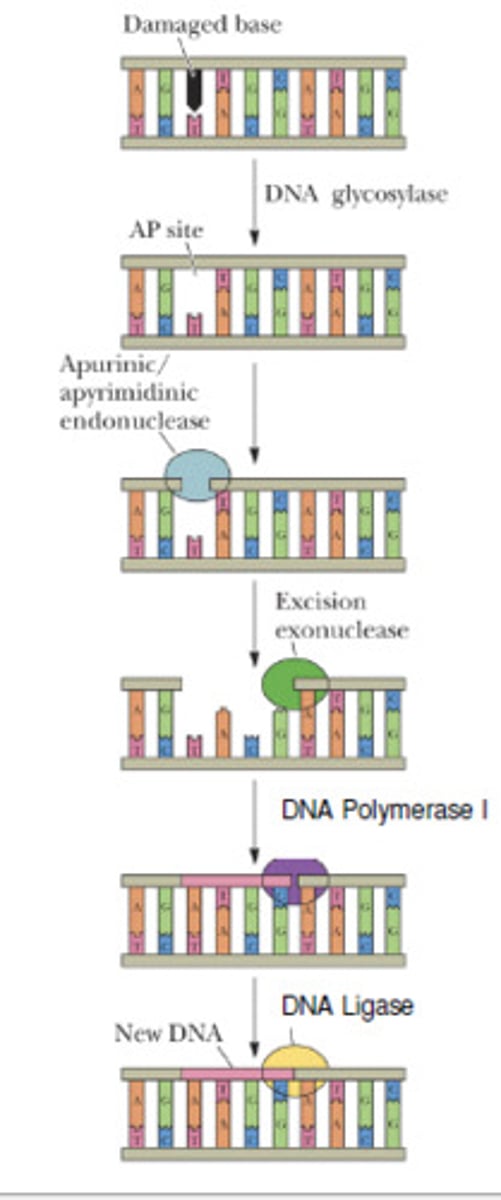
template strand
The DNA strand that provides the pattern, or template, for ordering, by complementary base pairing, the sequence of nucleotides in an RNA transcript, the 3' to 5' strand.
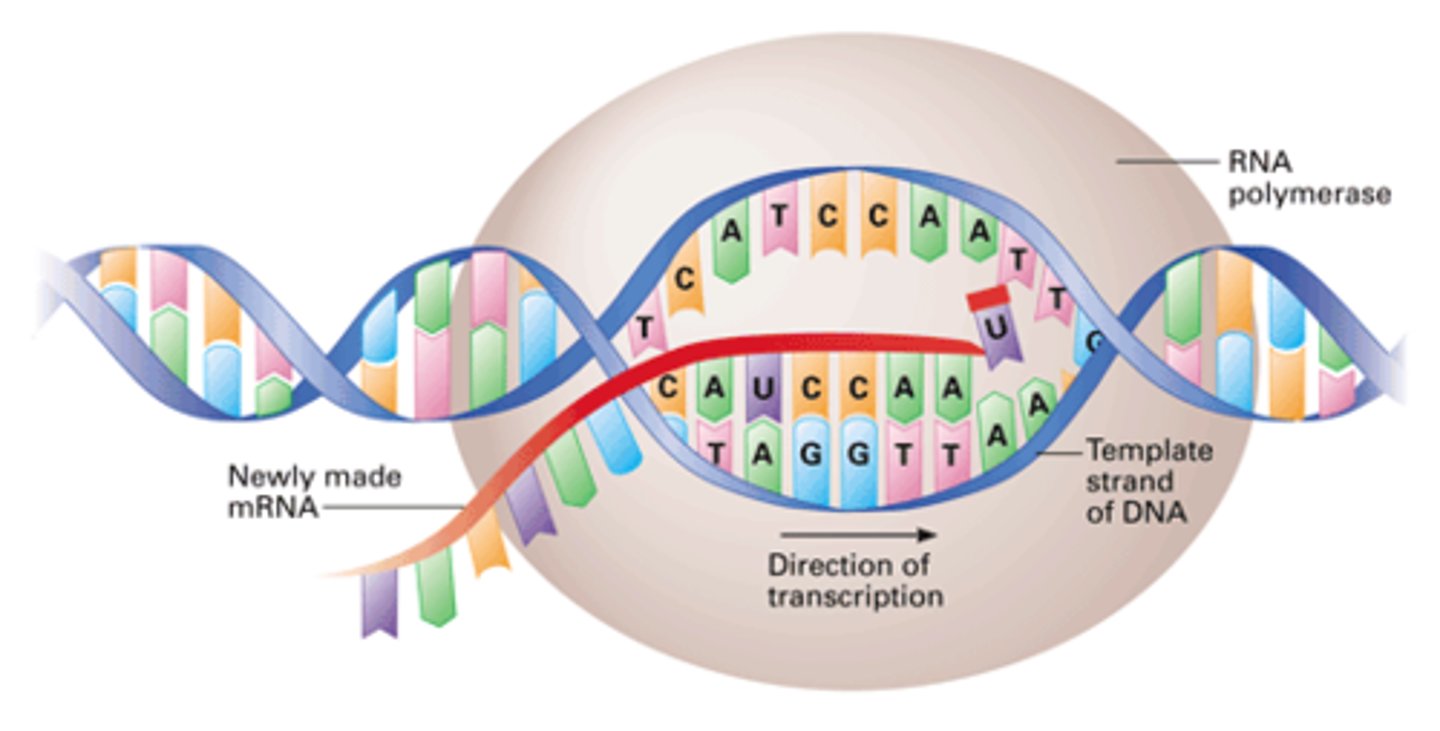
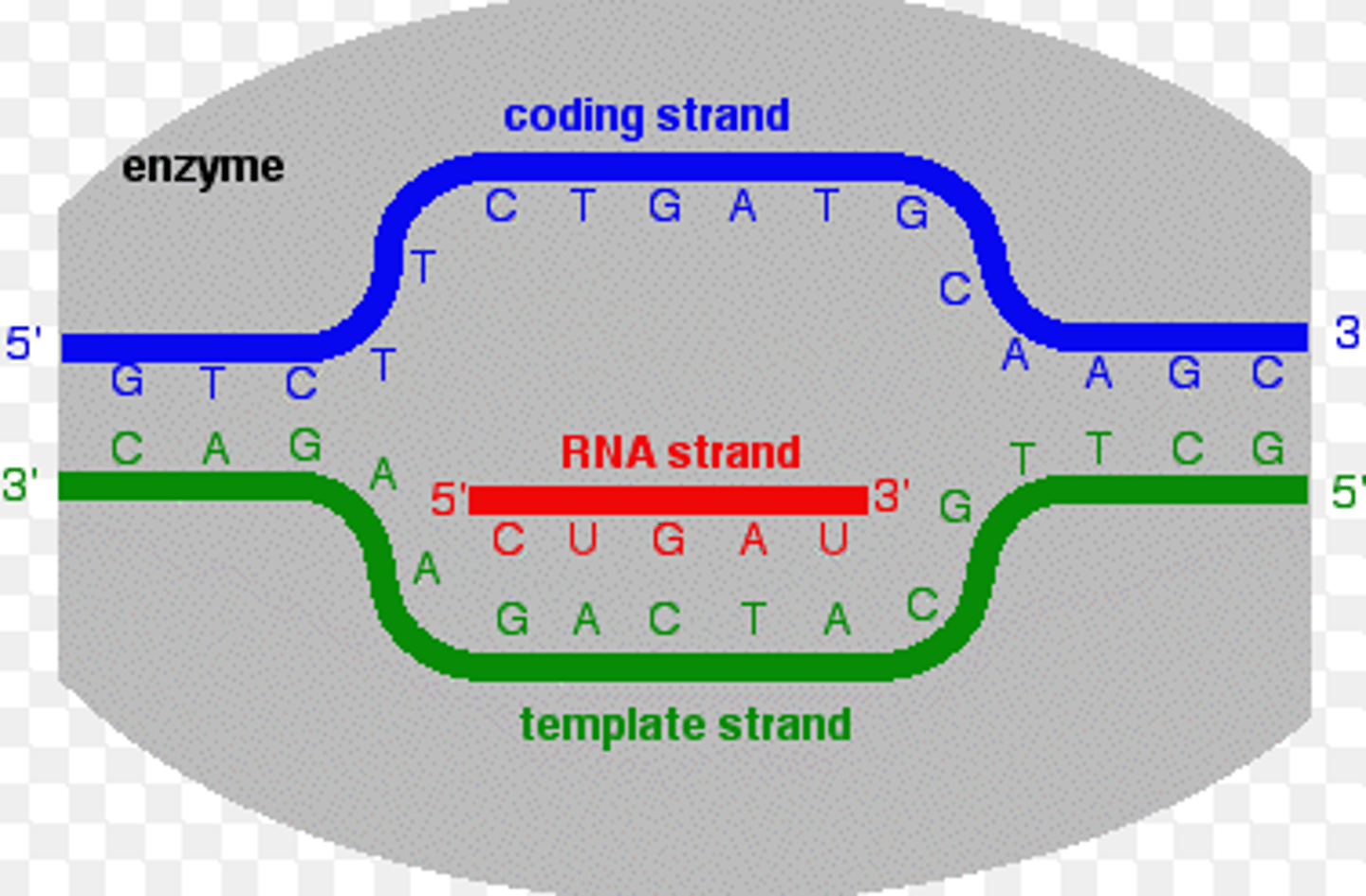
coding strand (sense strand)
the strand of DNA that is not used as a template during transcription, because it is already complimentary to the Template strand, the 5' to 3' strand.
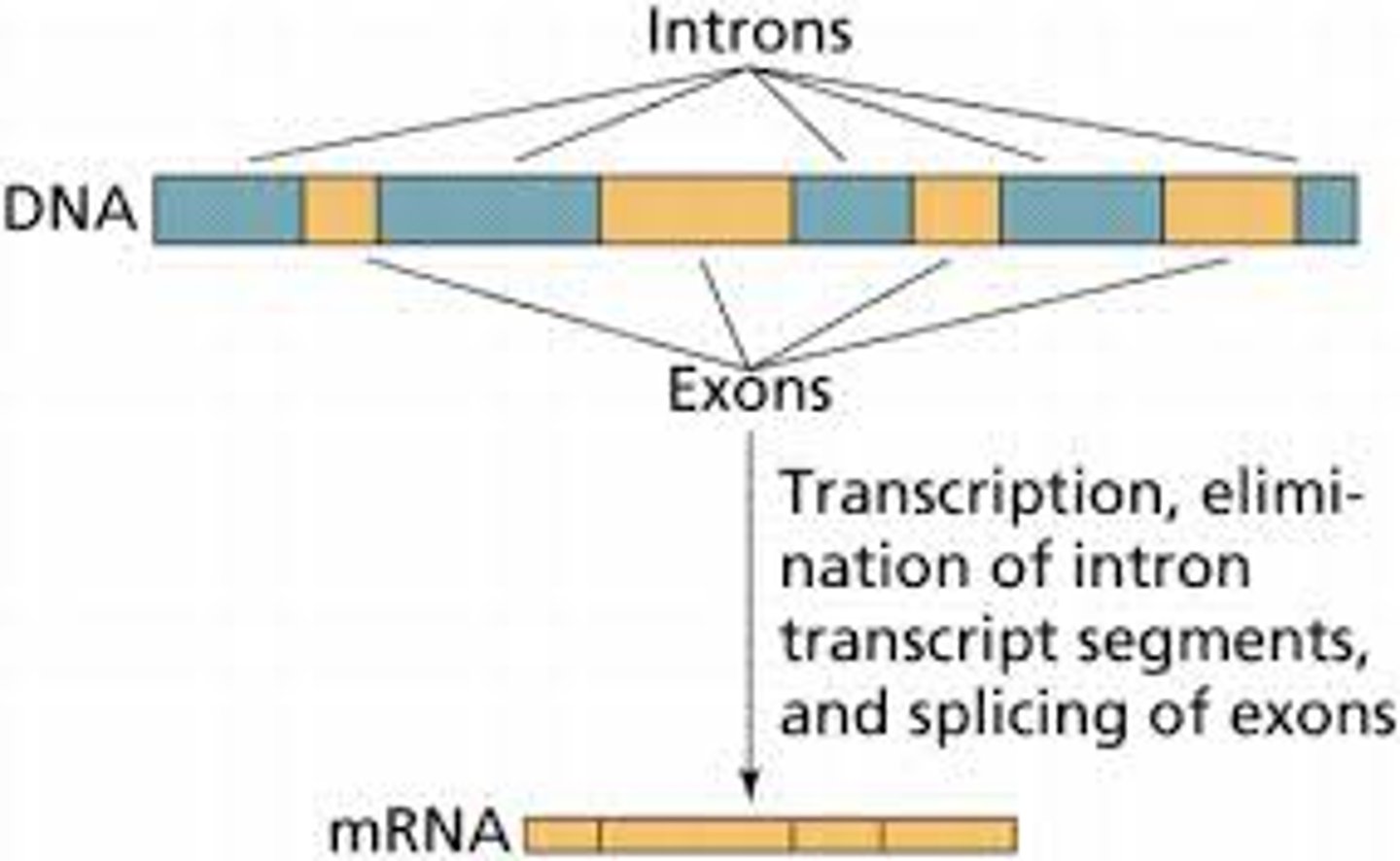
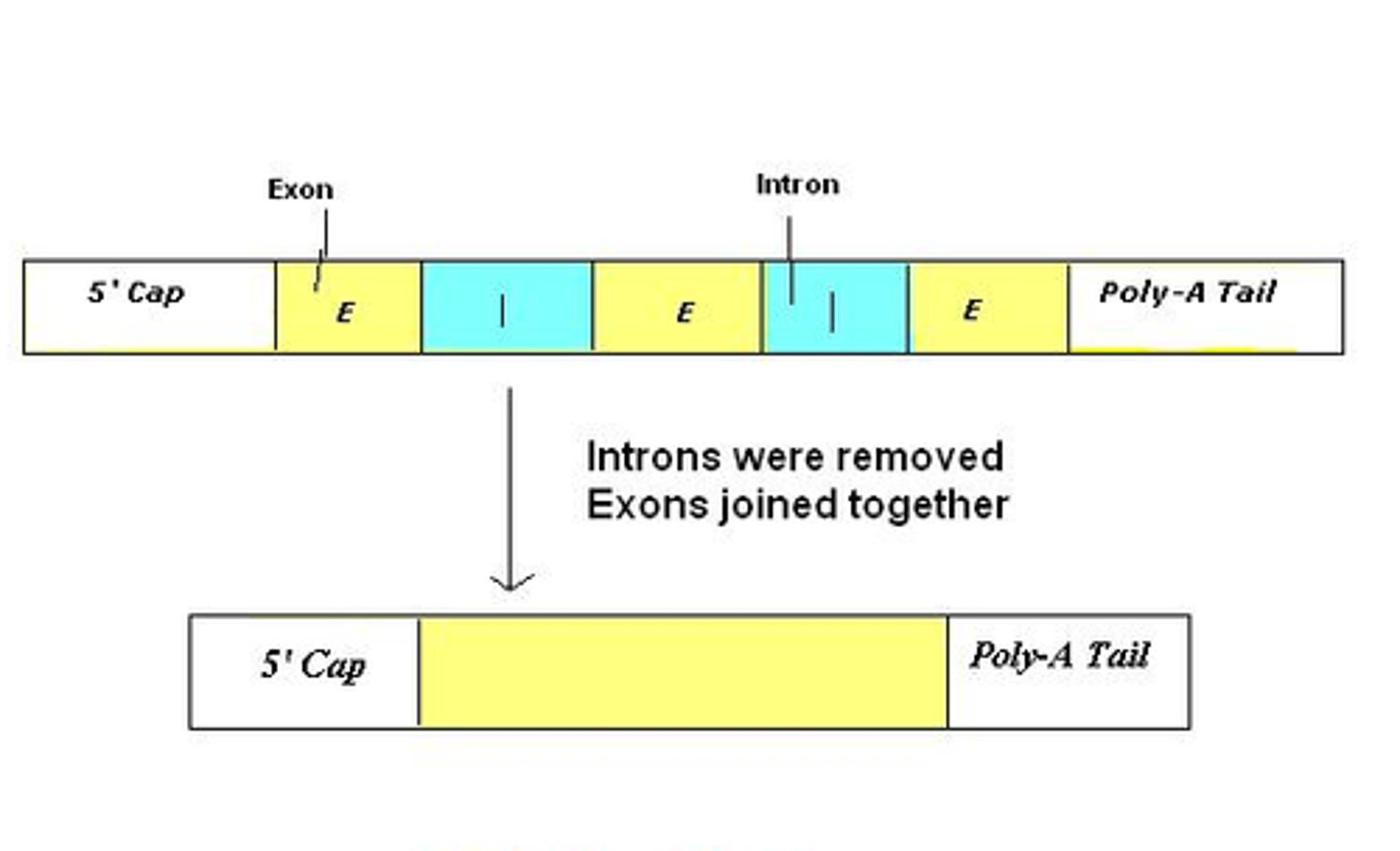
introns and exons
In most eukaryotic genes, coding regions (exons) are interrupted by noncoding regions (introns). During transcription, the entire gene is copied into a pre-mRNA, which includes exons and introns. During the process of RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons joined to form a contiguous coding sequence, before leaving the nucleus.
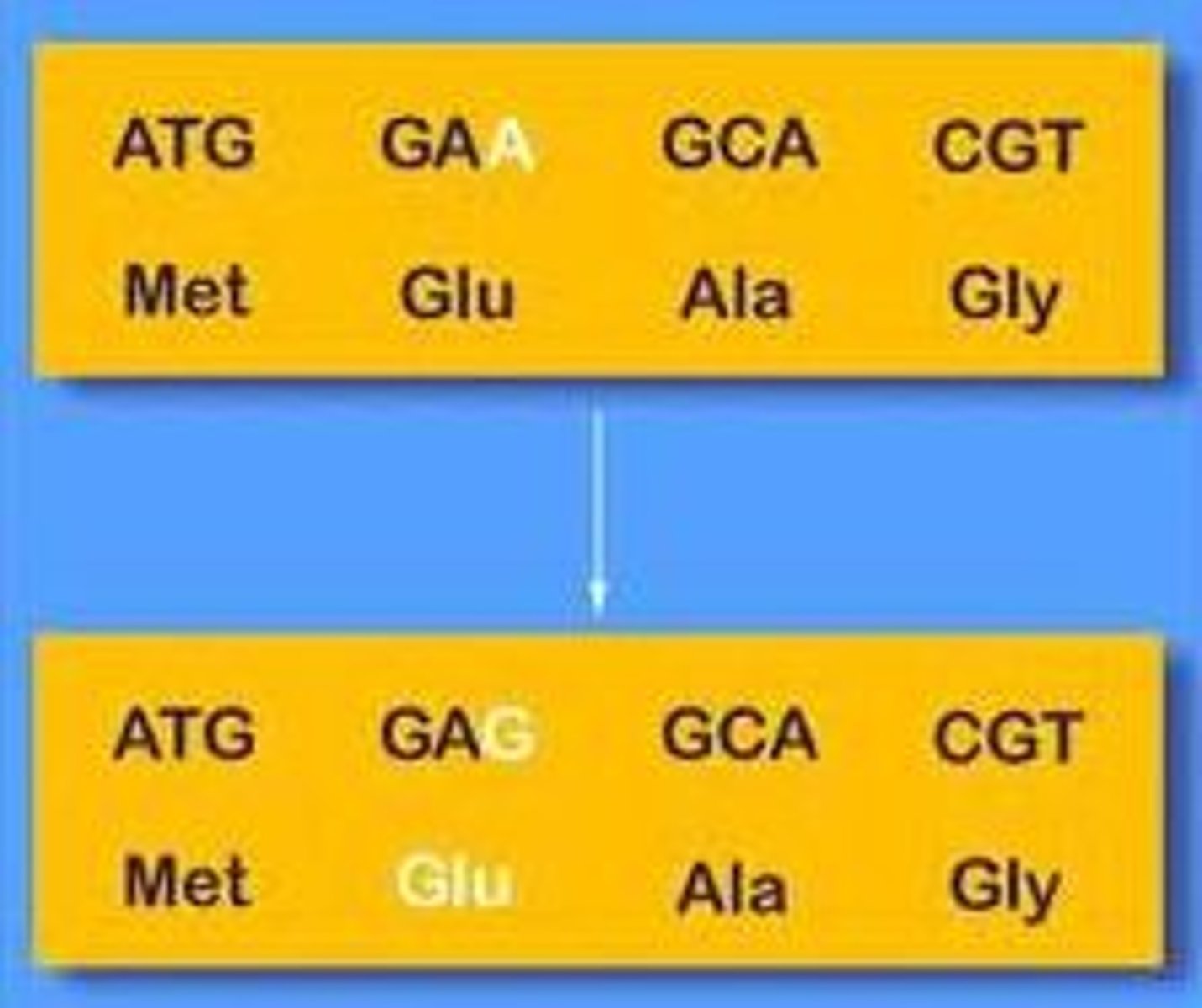
silent mutation
A mutation that changes a single nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created.
missense mutation
A base-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
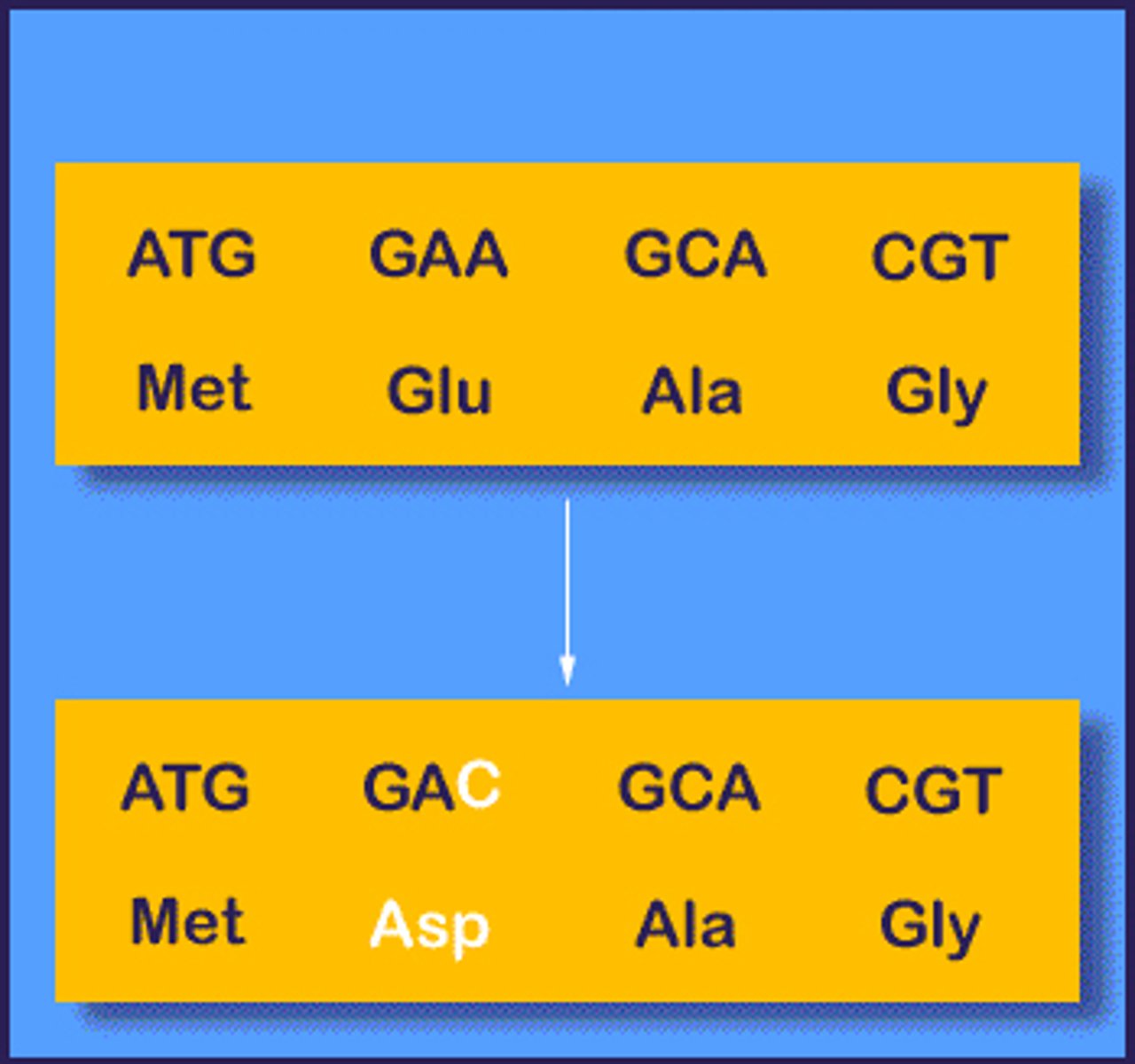
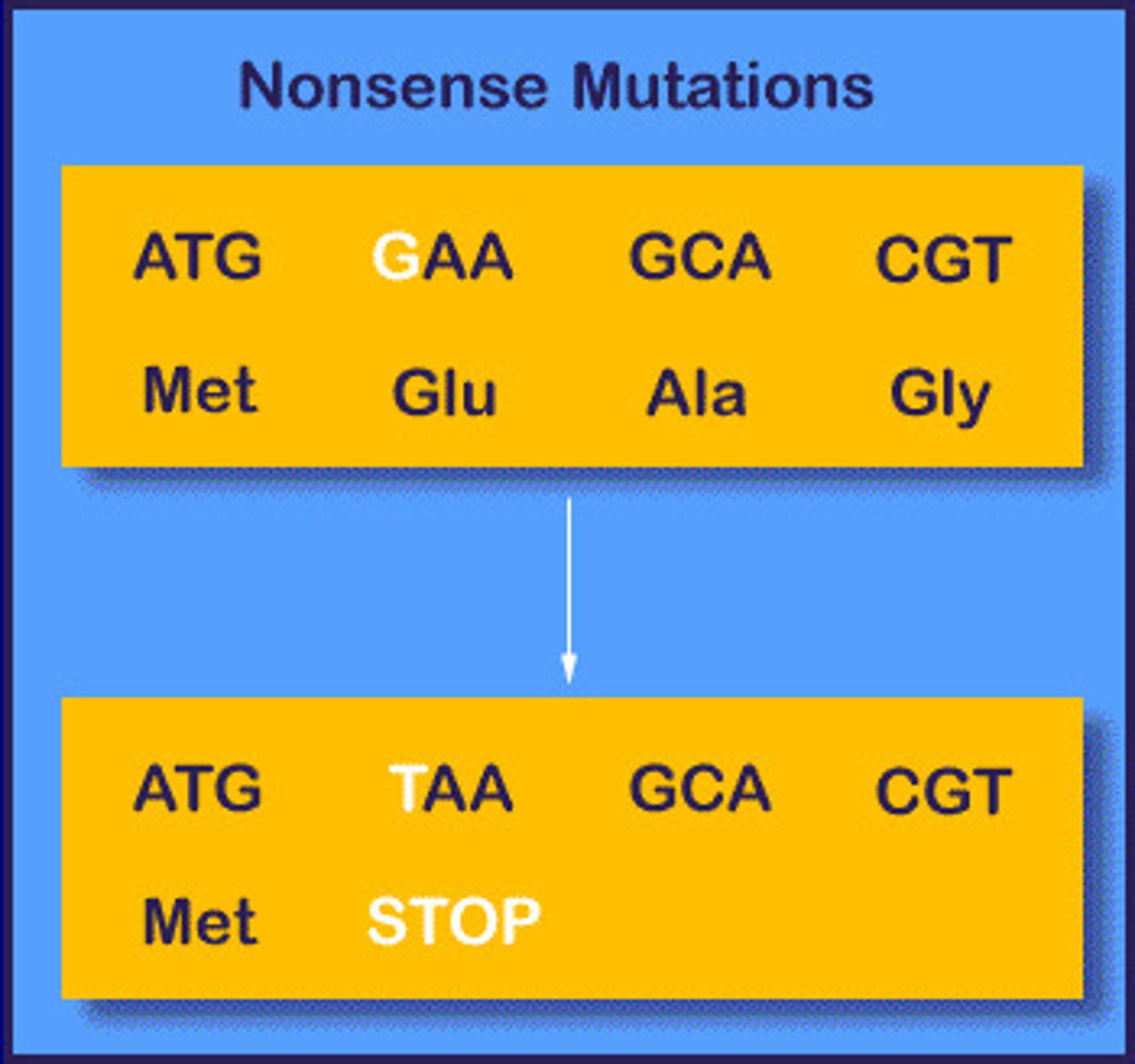
nonsense mutation
A mutation that changes an amino acid codon to one of the three stop codons, resulting in a shorter and usually nonfunctional protein.