UTA Plant Science Exam 3
1/240
Earn XP
Description and Tags
urethra!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
241 Terms
what do all seeds contain?
seed coat
food reserves
embryo
seed coat
hard, outer covering
food reserves
endosperm and/or cotyledons
embryo
axis with attached cotyledons
what are the two steps in seed development?
embryogenesis
seed maturation
embryogenesis
establishes the body plan
what are the two superimposed patterns in embryogenesis?
apical-basal pattern
radial pattern
seed maturation
build up of food reserves
desiccation
hardening of seed coat
dormant or quiescent phases
seed development image
study this image!
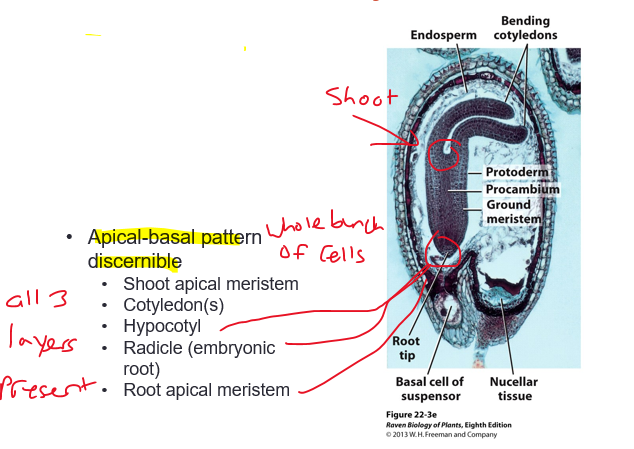
is early embryogenesis the same in ALL angiosperms?
yes all early embryogenesis is the same in all angiosperms
formation of the embryo
begins with [apical cell] and [basal cell]
establishes polarity
IMPORTANT! fixes the structural axis of the body (the backbone!)
determines arrangement of lateral appendages
results in [Embryo proper] and [Suspensor]
what does the first mitosis division establish?
it establishes polarity
what is the top vs what is the bottom
what does the apical cell develop into?
it develops into the embryo proper
what does the basal cell develop into?
it develops into the suspensor
suspensor
stalk-like, anchors the embryo
micropylar
lower end
globular stage
development of the three, concentrically arranged tissue systems
AKA [radial pattern]
what are the primary tissues of the globular stage?
protoderm
ground meristem
procambium
heart stage
[cotyledons]: seed leaf, emerge
all three primary meristems are present
notch forms at the base of emerging cotyledon
site of future apical meristem of the shoot
suspensor is still present!
metabolically active in angiosperms
provide nutrients and growth regulation
short-lived! dies before embryo matures
![<ul><li><p>[<strong>cotyledons</strong>]: seed leaf, emerge</p></li><li><p>all three primary meristems are present</p></li><li><p>notch forms at the base of emerging cotyledon</p><ul><li><p>site of future apical meristem of the shoot</p></li></ul></li><li><p>suspensor is still present!</p><ul><li><p>metabolically active in angiosperms</p></li><li><p>provide nutrients and growth regulation</p></li><li><p>short-lived! dies before embryo matures</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9cff12c3-5a49-4d80-b603-01f36763c149.png)
torpedo stage
cotyledons elongate
suspensor NO LONGER PRESENT
embryo is near maturity
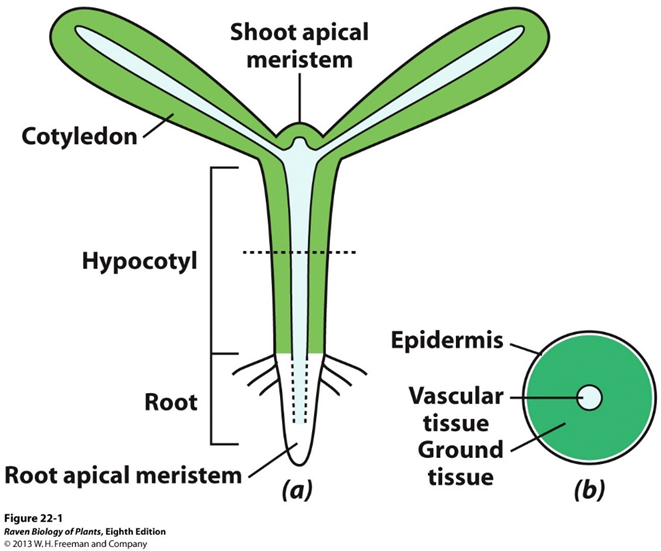
apical-basal pattern discernible
study this image!
mature embryo
consists of an axis bearing one or two cotyledons
Axis: (polar body of embryo)
epicotyl
hypocotyl
radicle
apical meristems
cotyledons: food storage, photosynthetic and/or food absorption
NOT PART OF THE EMBRYO
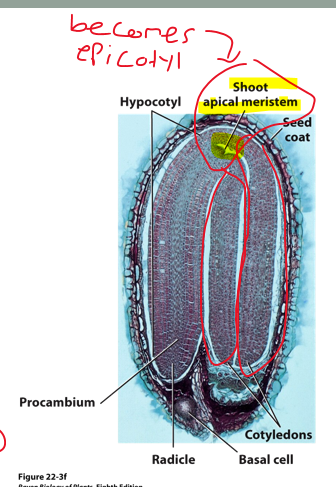
epicotyl
region ABOVE the cotyledon attachment poin
hypocotyl
region BELOW the cotyledon attachment point
radicle (embryonic root)
at terminal end of the [hypocotyl]
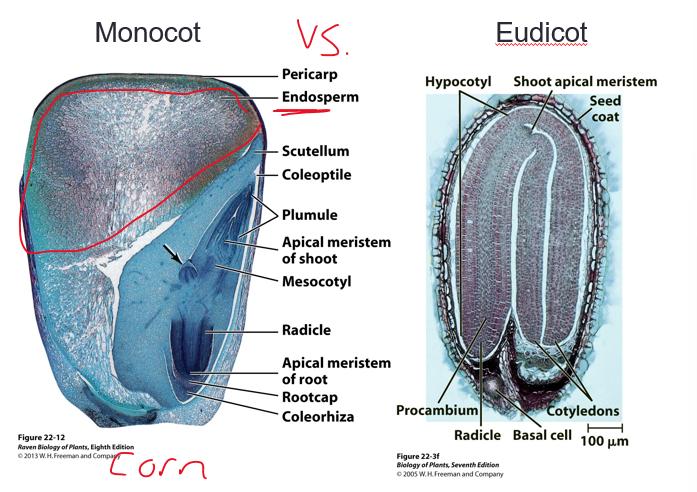
how many cotyledons are present in eudicots and basal angiosperms?
two cotyledons are present
what is the primary function of the cotyledons in eudicots and basal angiosperms?
store nutrients (pinto bean)
stored in the form of oils, starch, proteins
when embryo mature: cotyledons are large, and endosperm reserves depleted
some function to absorb nutrients (castor bean)
cotyledon is an absorptive structure
endosperm present as nutrient source
think about how peanut butter is full of lipids and protein
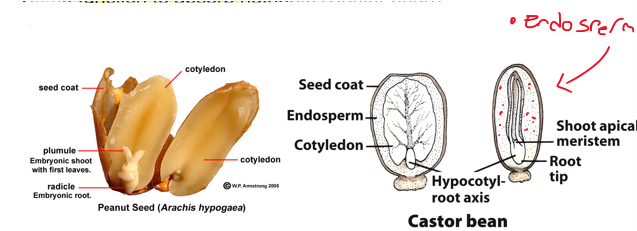
how many cotyledons are present in monocots?
one cotyledon is present
primary function is to absorb nutrients
Large reserves of endosperm remain in the seed
most of the grains we eat (rice, wheat, corn) are monocots
monocot vs eudicot
ill come back to this
seed maturation
massive buildup of food reserves in endosperm and cotyledons
flow of nutrients from parent DISCONTINUES
seed desiccates (lose 90% water)
metabolism slows
seed coat hardens
enters either a [dormant] stage or [quiescent] stage
quiescent
resting state
seeds germinate upon favorable conditions (water)
dormant
DOES NOT GERMINATE EVEN IN FAVORABLE CONDITIONS
seed-coat imposed dormancy
impermeability of seed coat
rigidity of seed coat
escape prevented by growth inhibitors
embryonic growth suppression
embryo dormancy
hormone imbalance
physiological immaturity
what are some ways you can bring a seed out of dormancy?
passing through a digestive tract (birds)
rainfall (for desert species)
mechanical cracking (stone fruit)
heat of fire
germination
resumption of growth of the embryo
cell enlargement and cell division
what are the requirements of germination?
water
oxygen
temperature
role of water in germination
resumes metabolic activity
activates enzymes
new enzymes created to synthesize and digest food stores
enlarges the seed
role of oxygen in gerrmination
respiration
is anaerobic for a period
becomes aerobic when seed coat breaks open
waterlogged soil can prevent germination
no air! can’t breathe!
role of temperature in germination
most have a wide range of Temp.
Min: 0° - 5°C
Max: 45° - 48°C
Optimum 25° - 30°C
think of how temperature affects enzyme and chemical processes!
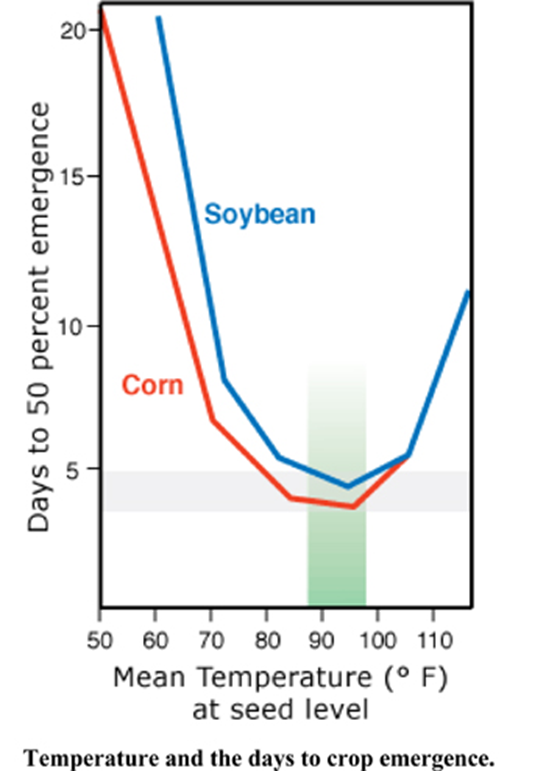
from embryo to adult plant
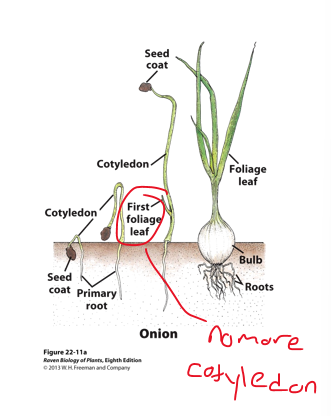
primary root (taproot, radicle)
first structure to emerge
produces [lateral roots]
[Eudicots]
maintain taproot/lateral root morphology
[Monocots]
primary root is short-lived, replaced by stem-borne roots
what is a primary root also called?
the radicle
eudicot roots
maintain taproot/lateral root morphology
monocot roots
primary root short-lived, replaced by stem-borne roots
what are the two kinds of germination that eudicots have
epigeous germination
hypogeous germination
epigeous germination
cotyledons carried Above Ground to provide nutrients
[Hypocotyl] elongates, forms a hook
shoot tip protected by being pulled from soil
![<ul><li><p>cotyledons carried Above Ground to provide nutrients </p></li><li><p>[<span style="color: rgb(255, 44, 44);"><strong>Hypocotyl</strong></span>] elongates, forms a hook</p></li><li><p>shoot tip protected by being pulled from soil</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/95a1755c-dade-46dd-ac8e-21b32257395a.png)
hypogeous germination
cotyledons remain Underground, provide nutrition
[Epicotyl] elongates and forms hook
shoot tip protected by being pulled from soil
![<ul><li><p>cotyledons remain Underground, provide nutrition</p></li><li><p>[<span style="color: rgb(71, 182, 255);"><strong>Epicotyl</strong></span>] elongates and forms hook</p></li><li><p>shoot tip protected by being pulled from soil</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ea51bbe1-f295-44eb-92fb-2d2fd8e19bc8.png)
most monocots have these characteristics
elongation of a single, tubular cotyledon
forms a hooked cotyledon
seed coat and endosperm carried Upward with cotyledon to absorb nutrients
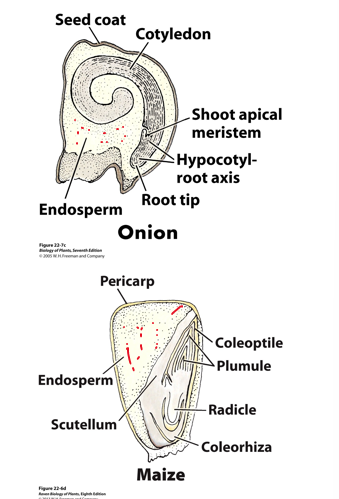
[monocots]: Corn (Zea mays)
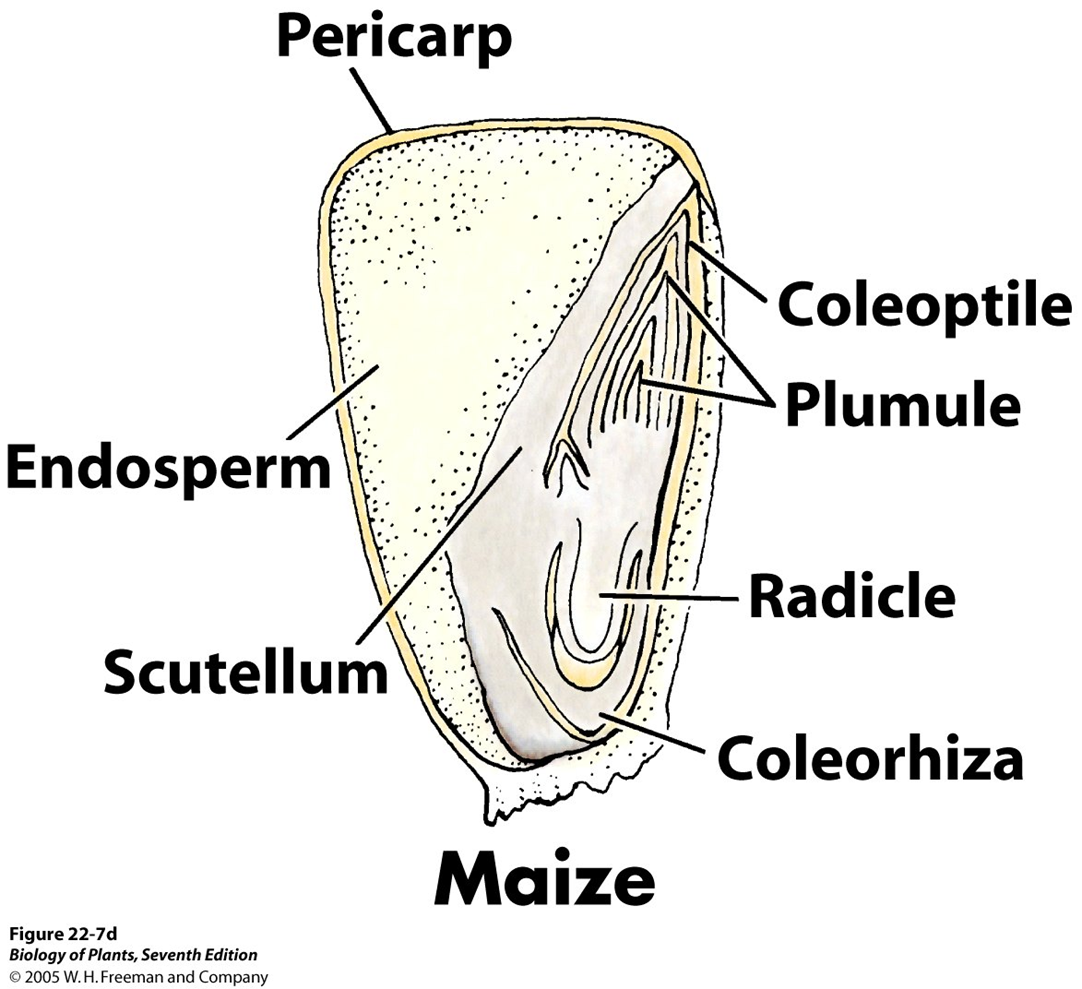
cotyledon is called a [scutellum]
highly differentiated embryo
[coleorhiza]: protective covering for radicle, emerges first
[coleoptile]: protective covering for plumule, elongates to soil surface
[plumule]: young shoot, emerges
![<ul><li><p>cotyledon is called a [<span style="color: rgb(255, 26, 26);"><strong>scutellum</strong></span>]</p></li><li><p>highly differentiated embryo</p></li><li><p>[<span style="color: rgb(230, 100, 255);"><strong>coleorhiza</strong></span>]: protective covering for radicle, emerges first</p></li><li><p>[<span style="color: rgb(46, 199, 255);"><strong>coleoptile</strong></span>]: protective covering for plumule, elongates to soil surface</p></li><li><p>[<span style="color: rgb(255, 189, 46);"><strong>plumule</strong></span>]: young shoot, emerges</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fee57b20-f786-4329-ba2b-f0c4889e3323.png)
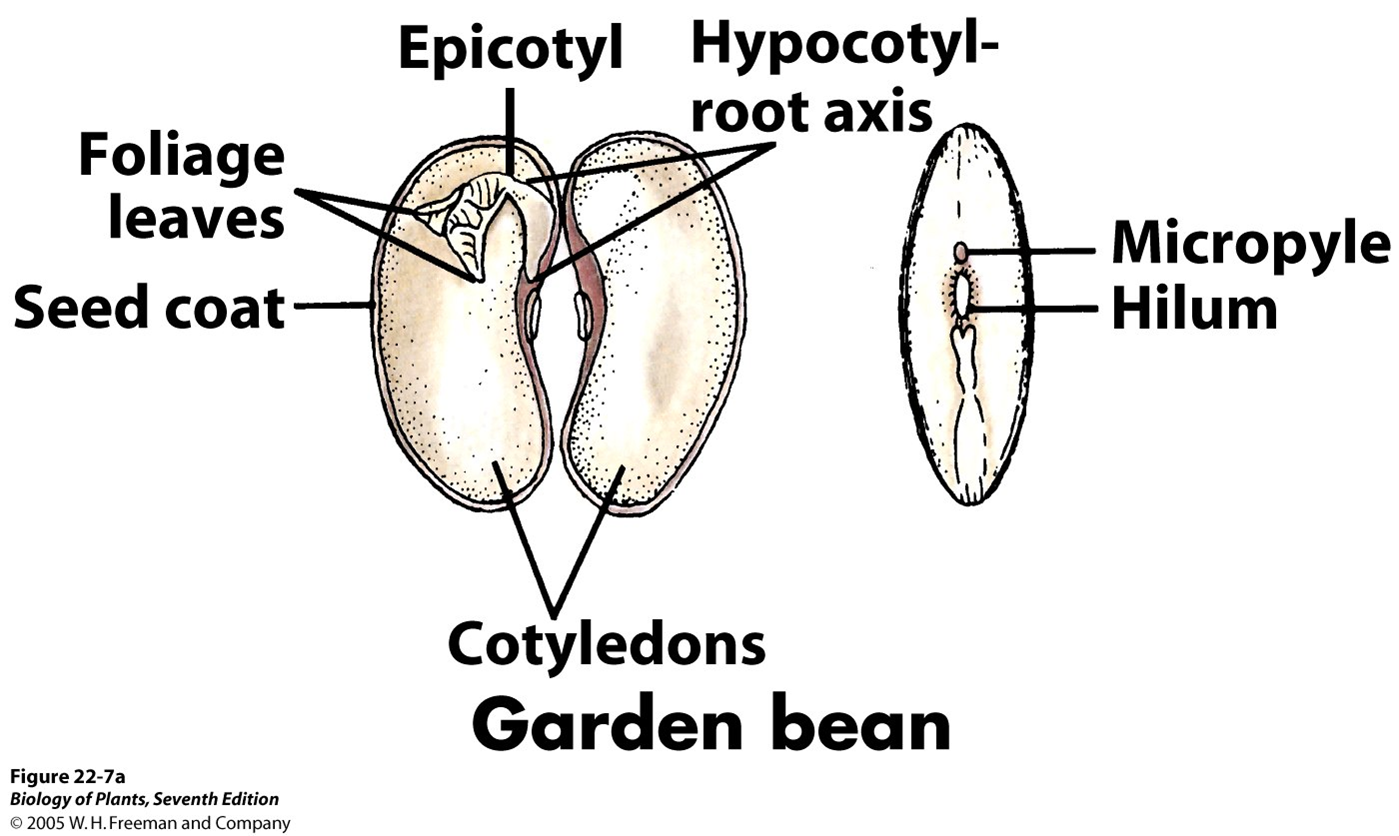
eudicot garden bean diagram
cotyledons are food!
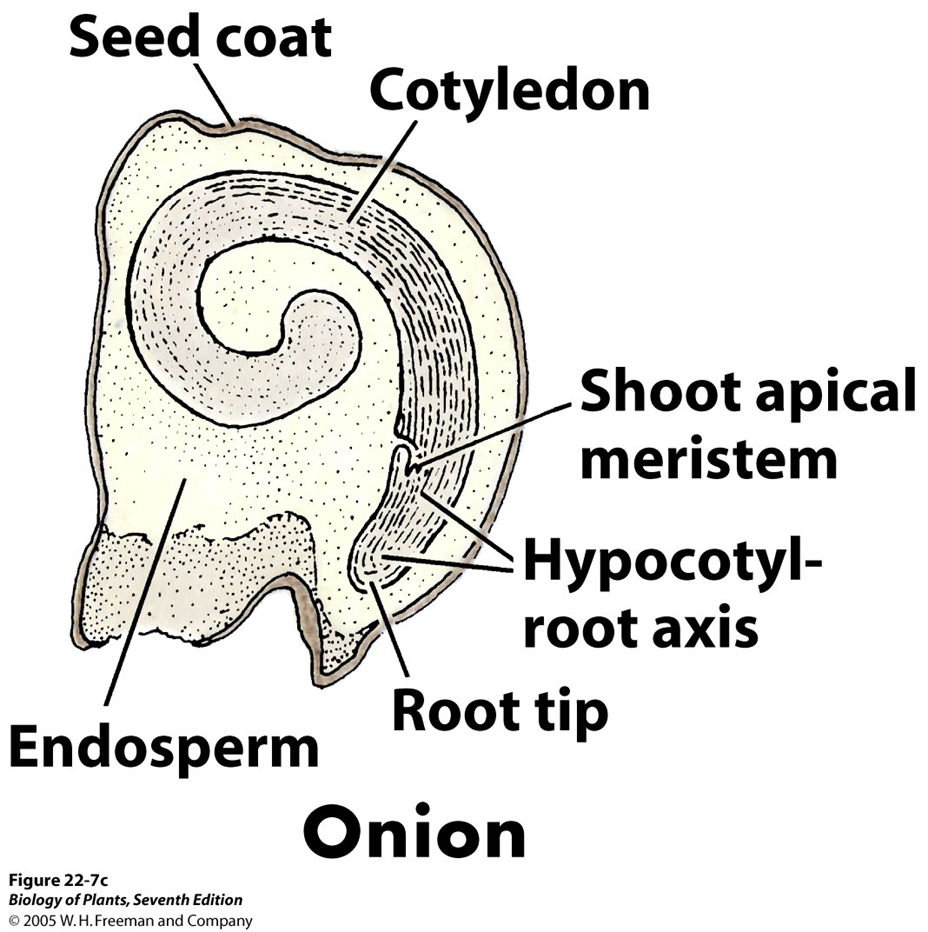
monocot onion diagram
large endosperm reserves!
maize diagram [monocot]
cotyledon is called a scutellum! in corn!
what are the three processes of development?
growth
differentiation
morphogenesis
growth
irreversible increase in size
cell division and cell enlargement
differentiation
Cells with identical genetic constituents become different from each other and from meristematic cells
fate is determined by final position in organ
morphogenesis
the Plant assumes a particular shape or form
depends on the planes in which cells divide and how tissues expand
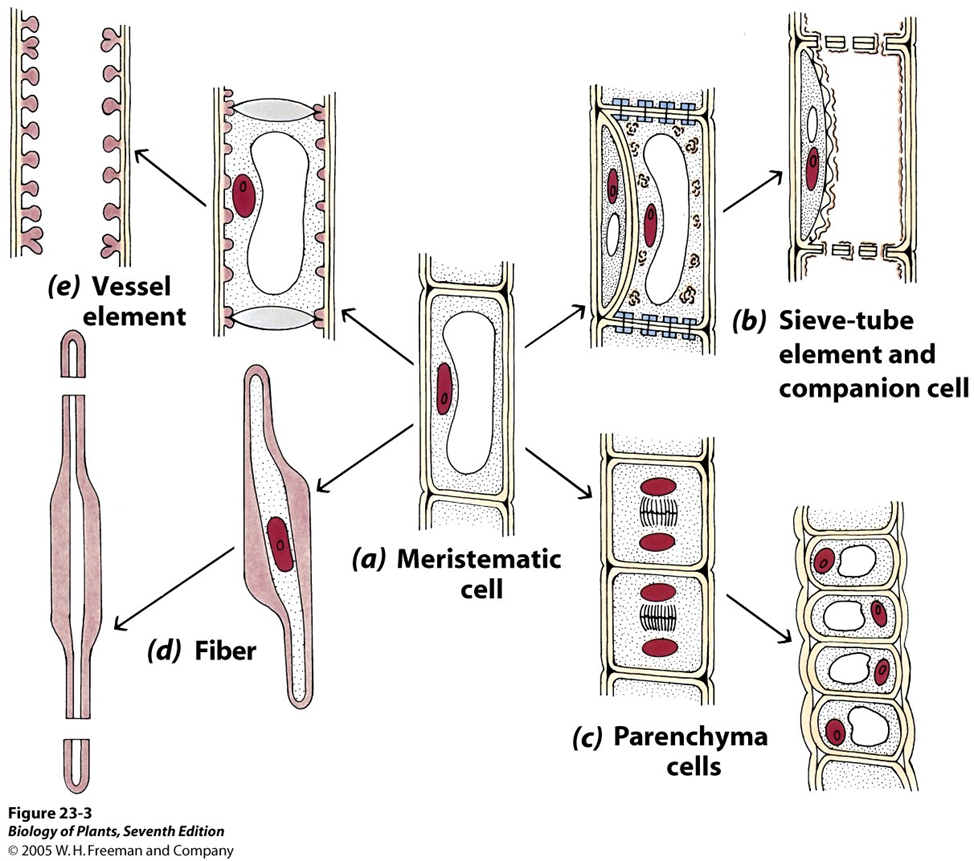
differentiation diagram
how many phases of growth are there in plants
there are up to two phases of growth
NOT ALL PLANTS WILL HAVE BOTH!
primary growth
form primary meristems and extension of the plant body
present in ALL plants (must have primary!)
responsible for elongation of the plant
occurs as a result of cell division in the apical and primary meristems
parts of the plant derived from primary growth form the primary plant body
secondary growth
NOT present in all plants
responsible for growth in diameter
occurs as a result of cell division in the secondary meristems
forms the secondary plant body
apical meristems
tips (apex) of roots and shoots
responsible for producing new cells and growth
elongation/extension of the plant body
formation of primary meristems
primary meristems
protoderm
ground meristem
procambium
secondary (lateral) meristems
vascular cambium
cork cambium
meristems
cells divide in a way so that one cell remains in the meristem as an “initial” and the other becomes part of the body as a “derivative”
initial
a cell that remains in the meristem and never differentiates
derivatives
can divide several times before differentiating
what are primary meristems derived from and where are they found
derived from apical meristem
found in the “sub-apical” region
protoderm
future epidermis
formed by divisions parallel to the surface in outermost cells of embryo
procambium
future vascular tissues
xylem
phloem
ground meristem
future ground tissue
what is the ground tissue system comprised of
parenchyma
collenchyma
sclerenchyma
parenchyma tissue (simple)
composed of parenchyma cells
living at maturity
found throughout the plant in many shapes and form
mesophyll, pith, cortex of stems, interspersed in xylem and phloem
typically only possess primary wall
parenchyma tissue functions
often metabolically active
photosynthesis
storage
secretion
regeneration
cortex
in eudicots, the mass of ground tissue between the epidermis/periderm and the vascular cylinder
composed mostly of parenchyma, some collenchyma
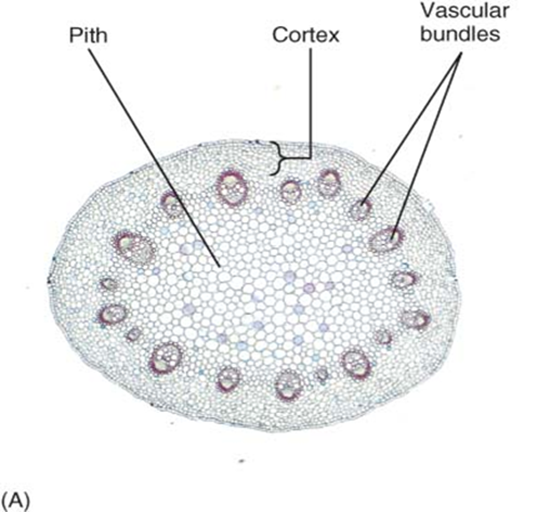
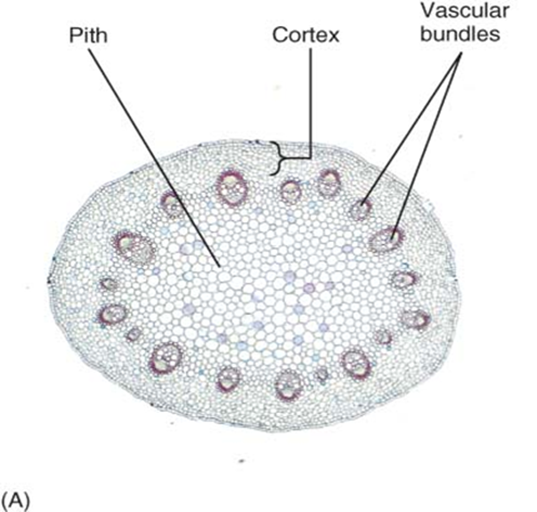
pith
the mass of ground tissue encircled by the vascular cylinder in eudicots
usually made of parenchyma
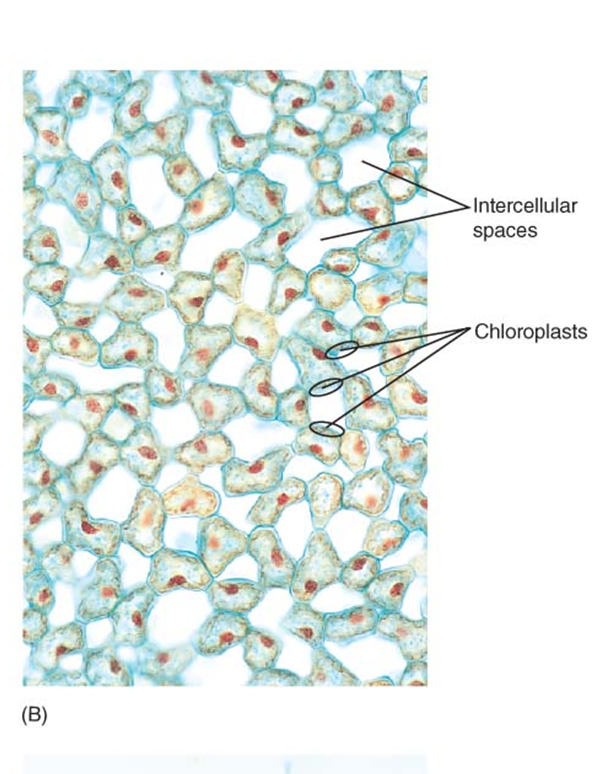
chlorenchyma cells
specialized photosynthetic parenchyma cells
thin walls allow light and CO2 to pass through to chloroplast
other types of pigmented cells are also parenchyma
petals and fruits
thin walls of parenchyma cells also allow pigments to be seen
any part of a plant that is colored, is likely parenchyma
glandular cells
contain elevated amounts of endoplasmic reticulum
transport large amounts of sugar and minerals
located throughout plant
secretes:
nectar
fragrances
mucilage
resins
oils
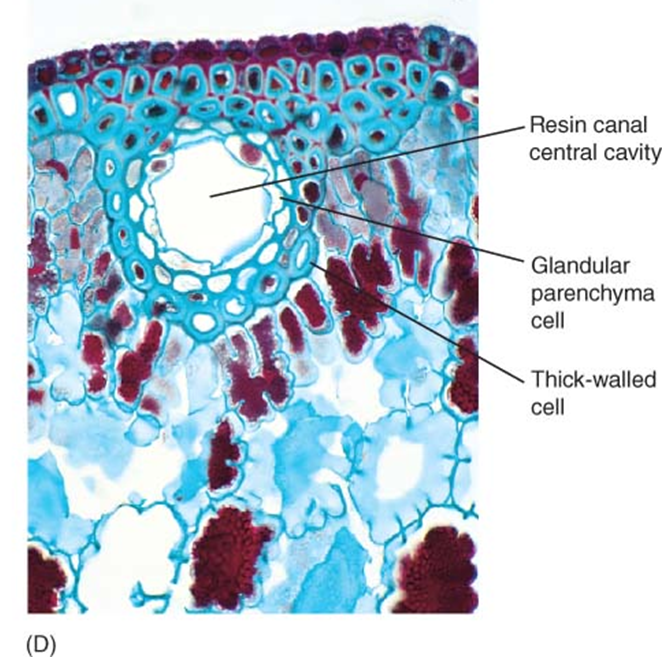
what do glandular cells secrete?
nectar, fragrances, mucilage, resins, oils
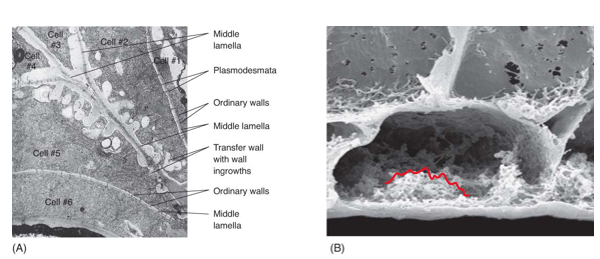
transfer cells
mediate short-distance transport of material
have many knobs/ridges on inner surface of cell wall
creates extensive plasma membrane with numerous molecular pumps
found in cotyledons, leaves reproductive structures, and glandular structures
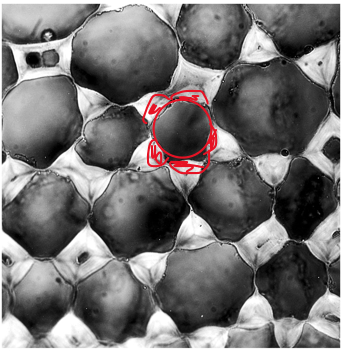
collenchyma tissue
composed of collenchyma cells
living at maturity
unevenly thickened, NONLIGNIFIED primary wall
usually found in periphery
support young, growing organs
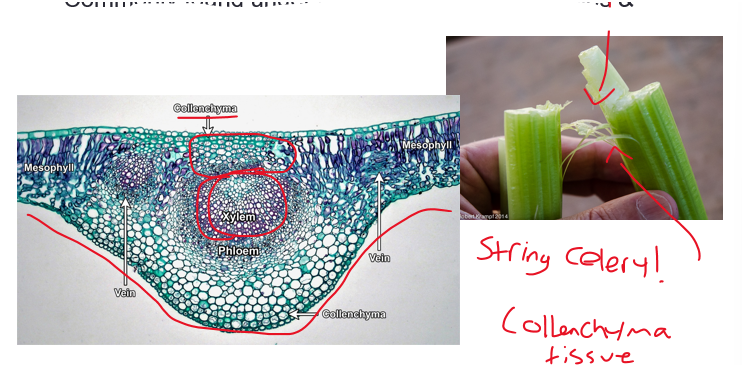
collenchyma tissue cont. celery example
commonly occur in strands or cylinders
usually elongated
commonly found under epidermis in leaves/perioles & around eudicot leaf veins
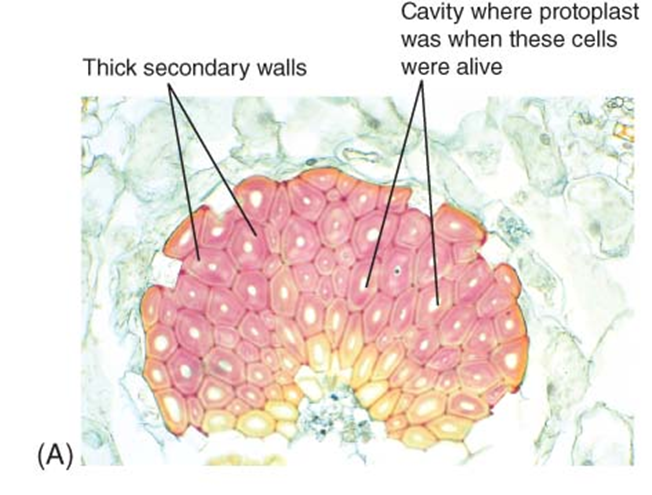
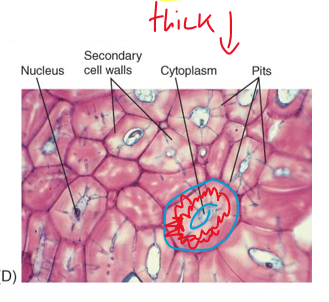
sclerenchyma tissue
composed of sclerenchyma cells
dead at maturity
thick lignified secondary wall
strength and support plant parts not elongating
two types of cells
sclereids
fibers
fibers
long and flexible
found where strength and flexibility are important such as wood
vascular tissue
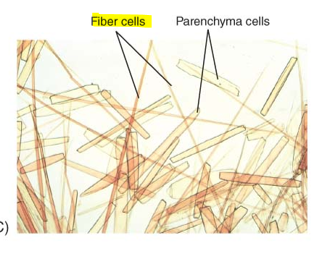
sclereids
short, “cuboidal”, inflexible, brittle
forms hard impenetrable surfaces such as shells of nuts and fruit pits
stone fruit pits!
if you can easily chew it (fruit)
parenchyma soft
if it is annoying to chew (celery strands)
collenchyma annoying
if you cannot chew it (cherry pits, seed coat on popcorn kernel)
sclerenchyma break yo tooth
dermal tissue system
composed of epidermis and periderm tissues
outermost layers of the plant
great diversity in form and function
through what tissue does interchange of material between plant and the environment occur?
through dermal tissues
true or false: dermal tissue functions in preventing water loss
true
what specialized cells does the dermal tissue system have?
trichomes
guard cells
what material is dermal tissue covered in?
it is covered in cuticle
[dermal tissue system]: epidermis tissue (complex)
cells of the aerial parts of the plant are coated with waterproof cuticle
consists of wax and cutin exuded over surface in either smooth sheets, or rods and filaments extending upwards
minimizes water loss!

what does the cuticle prevent the plant from doing?
prevents dessication
prevents gas exchange
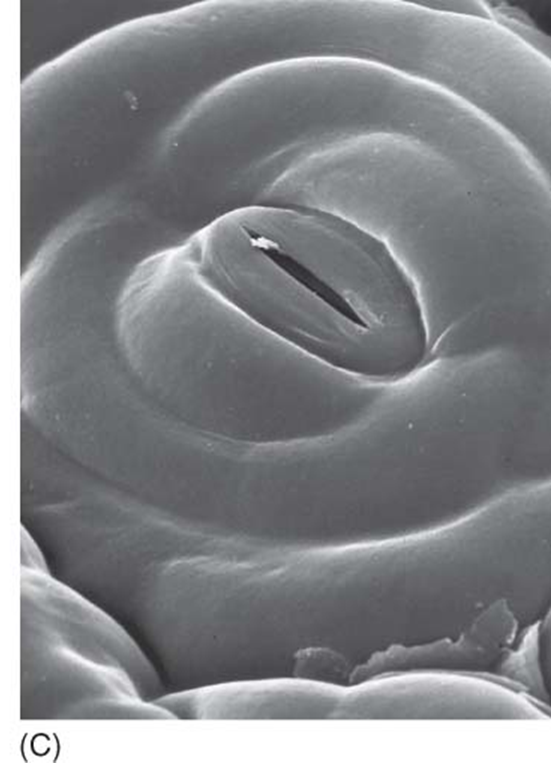
what is each stoma composed of?
guard cells
stomatal pore
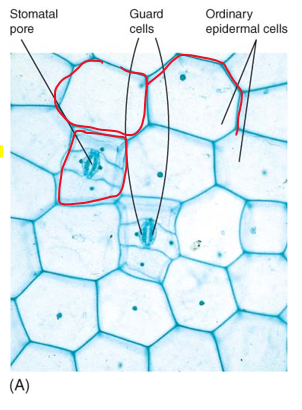
guard cells
responsible for opening/closing stomata
cells swell by water absorption
as guard cells swell, pore between them opens
to close they lose water

trichomes
epidermal cells that elongate outward into hairs
deter herbivory
minimize water loss
protect from over exposure to sunlight
absorptive roles
root hairs
epiphytic plants
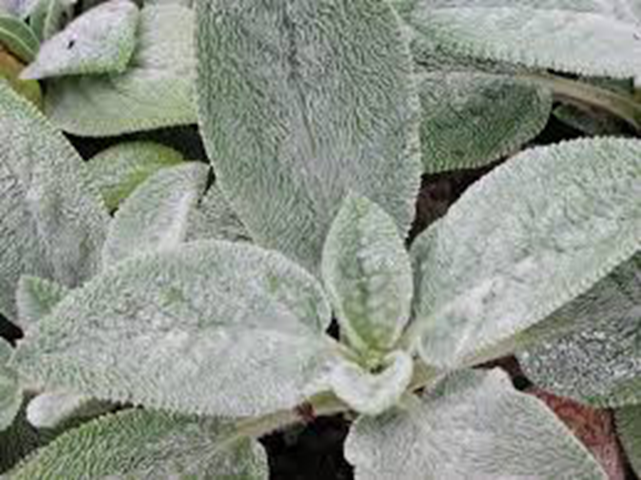

mullen leaf
mushroom shaped trichomes are [glandular], while the branched trichomes are what gives the leaf a furry texture
![<p>mushroom shaped trichomes are [glandular], while the branched trichomes are what gives the leaf a furry texture</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c11b4081-1ae9-4768-a2cb-23113c7ef4d0.png)
periderm (complex)
replaces epidermis in secondary growth
comprised of:
cork
cork cambium
phelloderm
lenticels
cork
non-living and high suberized cell (corky)
cork cambium
secondary/lateral meristem