Lecture 2 - Introduction to Basic Physics: MRI Image Characteristics & Atomic Physics (Fill-in-the-Blank)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fill-in-the-blank flashcards covering MRI image characteristics (voxels, FOV, matrix size, resolution, PSF, noise, SNR, CNR, windowing), scientific notation, SI units, and basic atomic physics (quarks, Rutherford, Bohr model, and particle properties) from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
In MRI, the unit element of an image is the __.
voxel
The voxel represents the MR signal in a volume __.
element
The matrix size determines the number of __ in an MRI image.
voxels
The Field of View (FOV) is essentially the image __.
dimensions
Resolution = __ / matrix size.
FOV
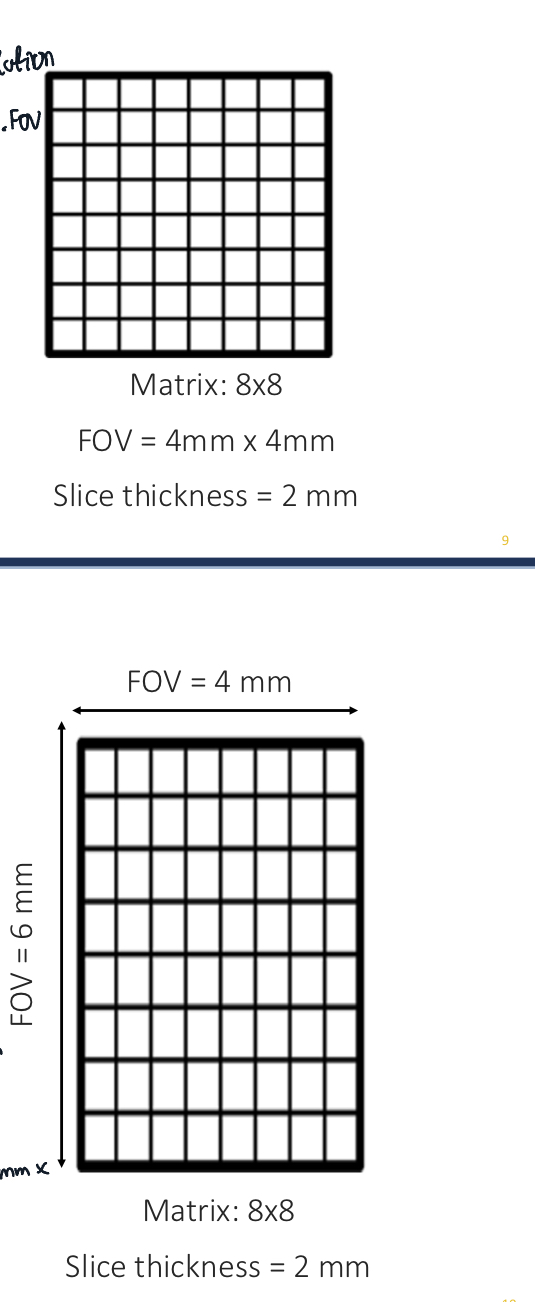
For an 8x8 matrix with a 4 mm FOV, the resolution is 4 mm / 8 = __ mm.
0.5
Larger matrix sizes = more __ but longer scan times.
detail
Examples of FOV values include 270 mm, 200 mm, and __ mm.
160
One way to measure resolution is to stimulate the detector system with a single point input; the resultant output image is the __.
point spread function
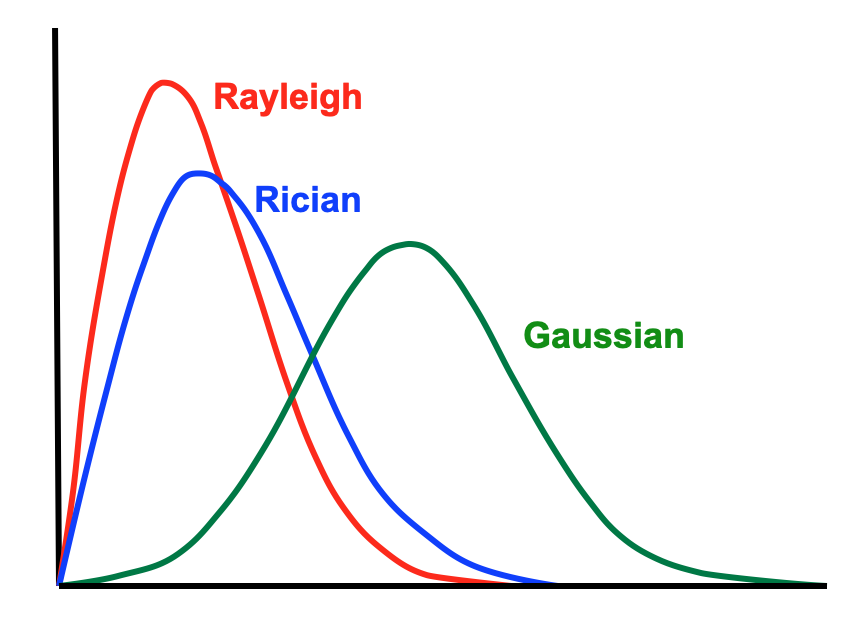
Noise in MRI can follow Gaussian, Rician, or __ distributions.
Rayleigh
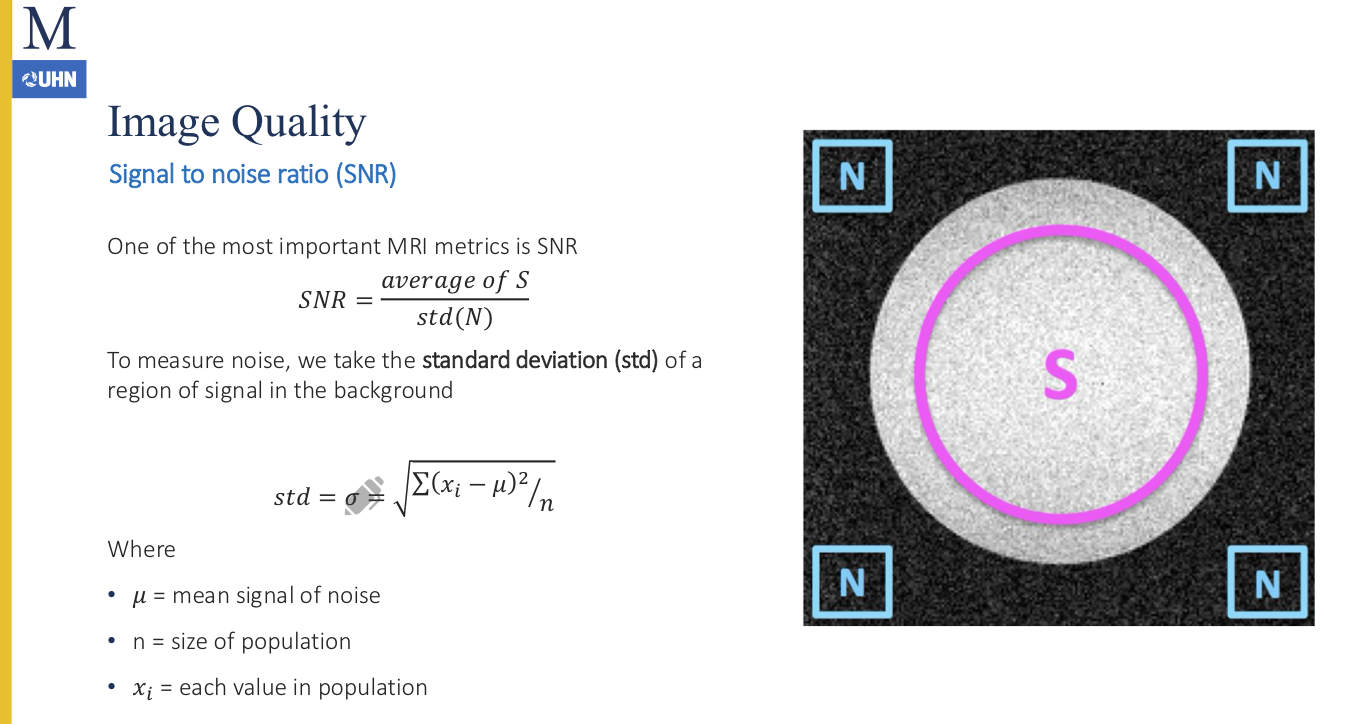
SNR = average of S divided by the __.
standard deviation of the noise
Contrast = difference in pixel values divided by the __.
average pixel intensity
Windowing is the process of manually changing __ to adjust contrast.
contrast
CNR = SNR(A) – SNR(B).
the difference between the SNR of region A and region B
In physics, we prefer to use SI units; all SI units can be broken down into SI __.
constants
19,394,000 written in scientific notation is __.
1.9394 × 10^7
15 mm equals __ μm.
15000
25 MHz equals __ GHz.
0.025
All matter is comprised of atoms; the nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while electrons __ around.
orbit
Protons and electrons are spin __.
1/2
Thomson's plum pudding model depicted a sphere of positive charge with embedded __.
electrons
Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the charge is concentrated at the atom's __.
center
Bohr described electrons orbiting the nucleus in fixed __ energy levels.
quantized
Electrons will 'give off' light when falling to a lower energy level and will '' light when jumping up energy levels.
absorb
In Bohr's model, the number of protons equals the number of __.
electrons
Mass of a proton is approximately __ kg.
1.6726 x 10^-27
Mass of a neutron is approximately __ kg.
1.6749 x 10^-27
Mass of an electron is approximately __ kg.
9.109 x 10^-31
Charge of a neutron is __.
0
Charge of a proton is __.
+1
Charge of an electron is __.
-1
Resolution equation
Resolution (x/y) = FOV/MS
Note: there is x/y because FOV can have two different x/y dimensions
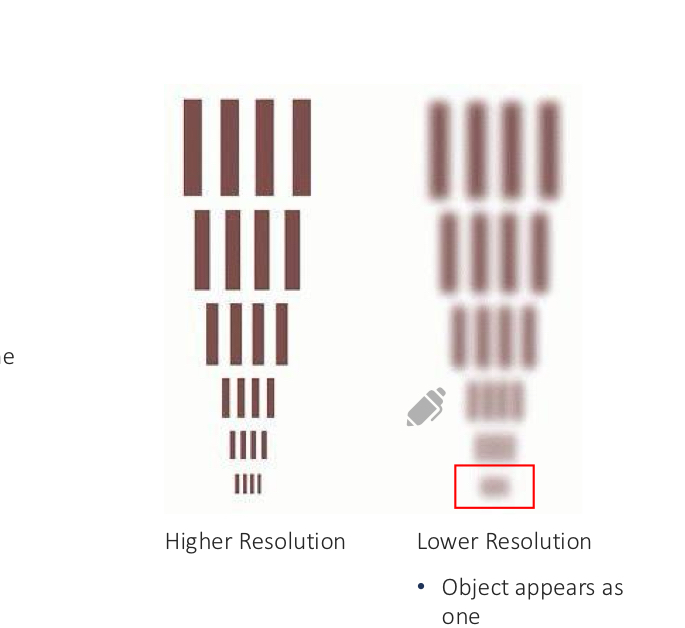
Higher resolution yields _____; lower resolution causes _____
separation of closely spaced features;
merging
How to generate points from the imaging system (meaning, how to avoid blurring/point spread function)
System can include:
Tiny hole in lead plate (X-ray)
Point source of radioactivity (Nuclear medicine)
Thin metal wires (CT)
Small hole filled with h20 (MRI)
Gaussian statistical distribution follows
normal distribution or bell curve, symmetrical, with most values close to the mean.
Rician statistical distribution is ______
Asymmetrical
Rician distribution measures the ____ of background noise, which can only be _____
magnitude
Positive
Increasing signal of Rician distribution makes the curve more ____
Gaussian-like
Rayleigh distribution is purely _____ w/ no _____
Background noise
Underlying signal strength
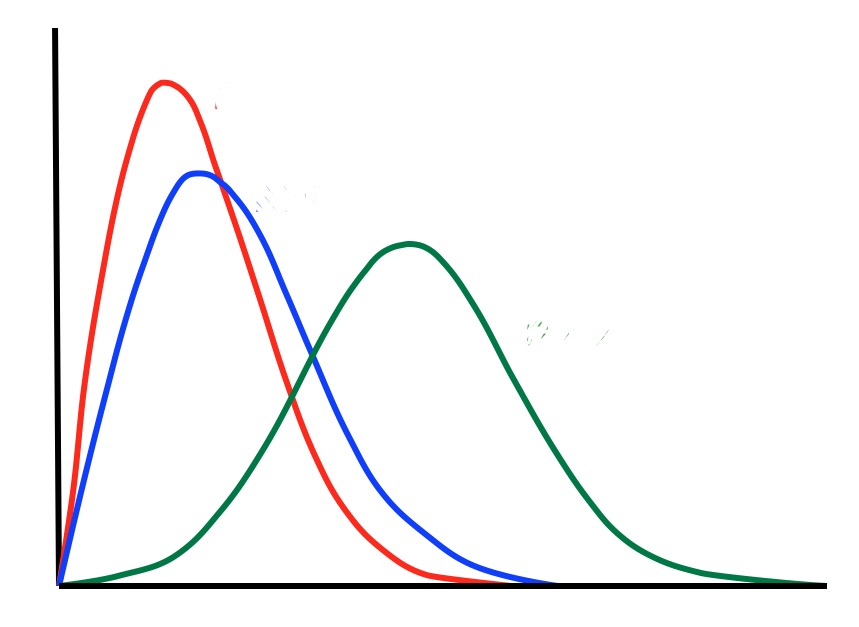
Name the SNR statistical distributions
Human eye can deal with which CNR?
>5

Improving contrast to noise ration (CNR) will _______
improve the perception of the distinct differences between two clinical regions of interest

CNR =

SNR =

Based on this equation, what happens to the resolution if FOV and MS double
Resolution remains the same, because there is no difference between 4/2 vs 8/4
If MS increases by two, resolution___
Decreases by 2

If FOV decreases by two, resolution ___
Decreases by two

Isotropic resolution means that___
That Rx = Ry = thickness of the image voxel dimensions, resulting in uniform resolution in all directions.
