PROTEIN STRUCTURE-FUNCTION RELATIONSHIP
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What are the primary structures and subcellular locations of preproinsulin, proinsulin, and insulin?
synthesis in pancreatic beta cells
preproinsulin: signal peptide, insulin B, C, and A chains (ribosomes of rough ER)
proinsulin: signal peptide CLEAVED, insulin, B, C, and A chains remain (golgi apparatus)
insulin: chain C is CLEAVED, insulin B and A chains remain connected by disulfide bonds (storage vesicles to blood)
what is the function of the signal peptide?
directs the nascent polypeptide to the ER for proper localization and synthesis, after which it undergoes post-translational modifications.
what is the structure/function of myoglobin?
O2 storing unit in muscle (cardiac and skeletal)
carries a heme
protein protects heme from oxidation and provides a pocket for O2 to fit
hyperbolic binding curve
higher affinity for O2 than Hb (left on curve)
what is the structure/function of hemoglobin?
each of four subunits in Hb carries a heme (2 alpha and 2 beta)
carries O2 from lungs to body
cooperative binding > once one O2 binds, more likely to bind to another subunit
binding changes shape of unit
R-state > O2 bound
T-state > not bound
what causes sickle cell anemia and what are the physiological consequences?
Primary structure changes via a E6V substitution in B2 subunit of hemoglobin; polymerizes Hm into long fibers > sickle cell shape; pain, anemia and infections are more likely to occur
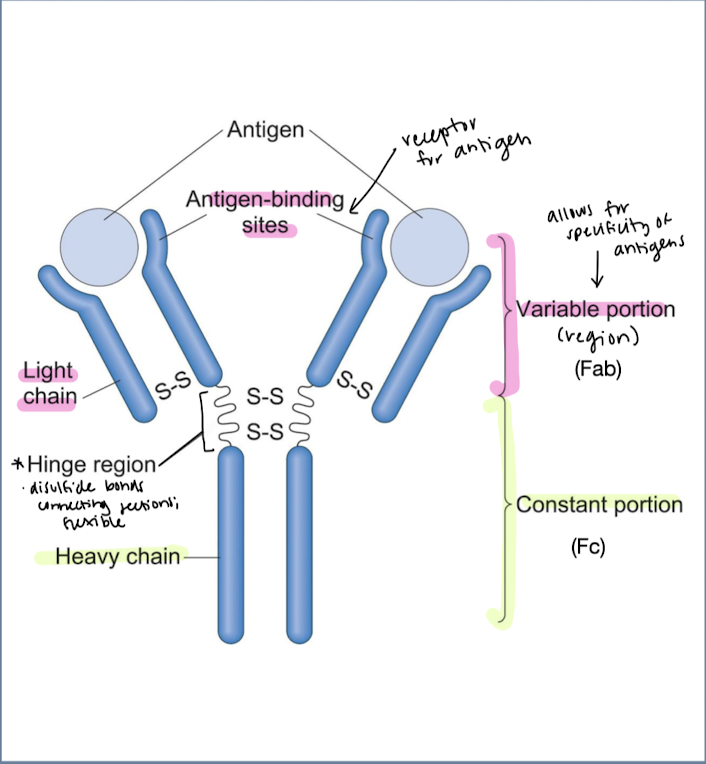
what is the quaternary structure of immunoglobulins and the functions of each feature?
Variable portion/fragment of antigen binding (Fab) - allows for specificity of antigens
antigen binding sites, light chain
Hinge region - disulfide bonds connecting sections; flexible
Constant portion/ cyrstallizable fragment (Fc) - heavy chain; turns off activity once foreign body is removed