Financial Markets
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
CML
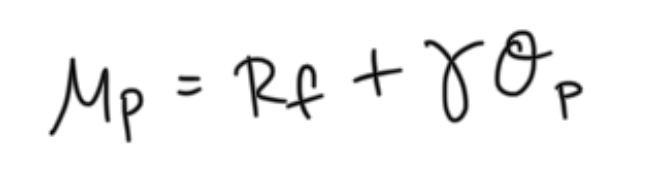
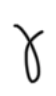
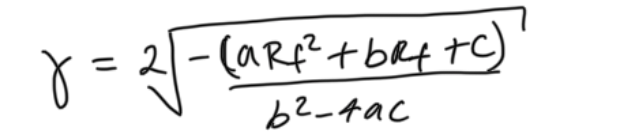
market expected return
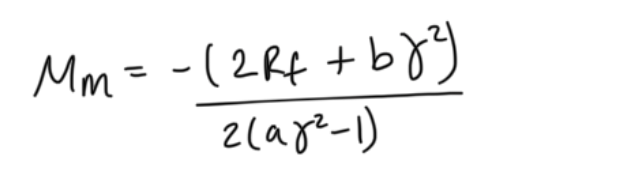
beta
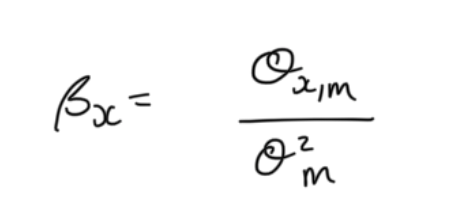
ARA
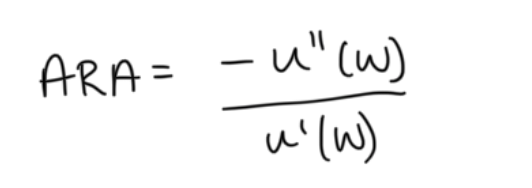
continuous return from discrete
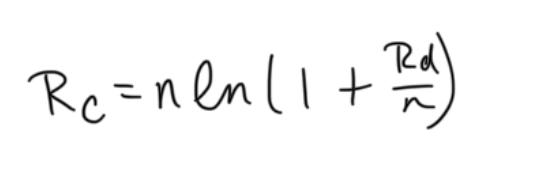
duration

change in price using duration
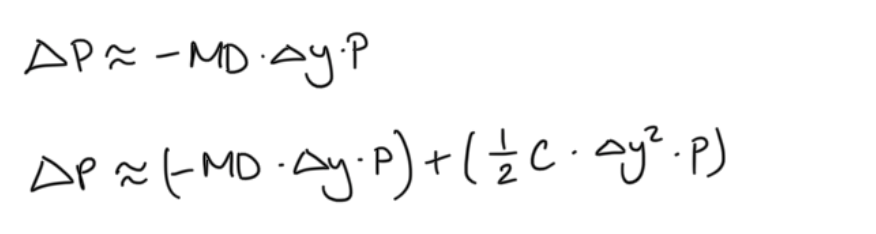
convexity using discrete compounding
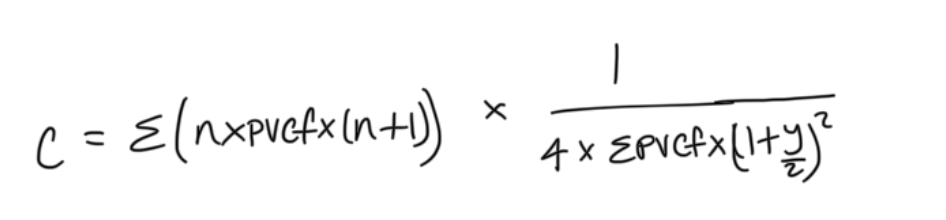
convexity using continuous compounding
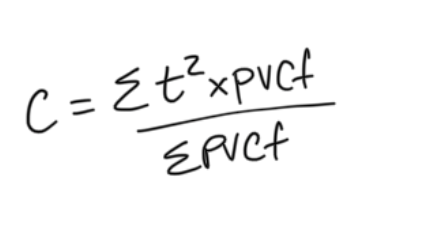
hedge ratio
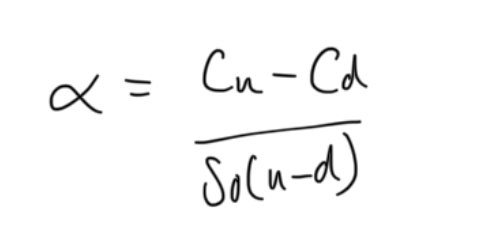
Pseudo probability, p
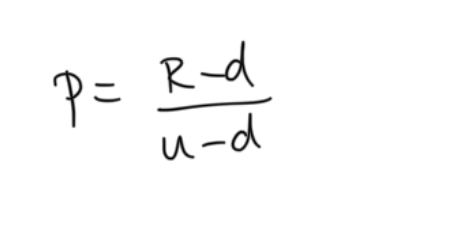
price of call option

min. number of ups to get positive payoff
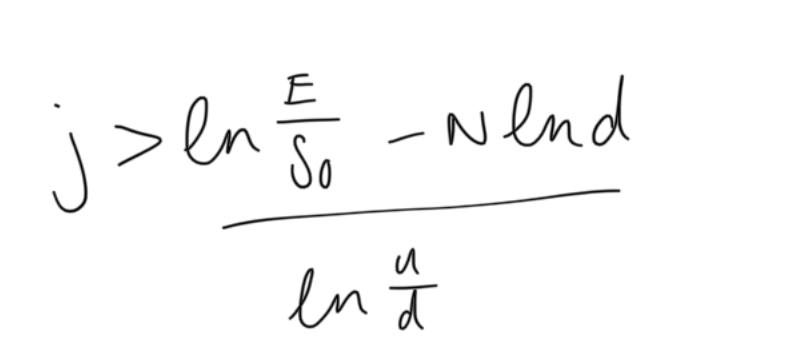
RRA
= ARA*w
amount you would be willing to give up in a fair bet
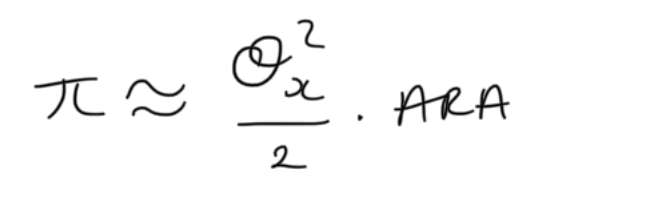
market variance
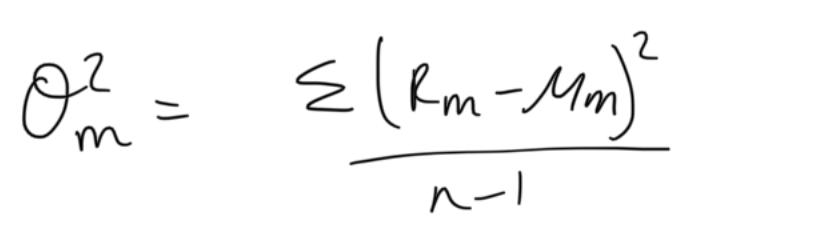
covariance
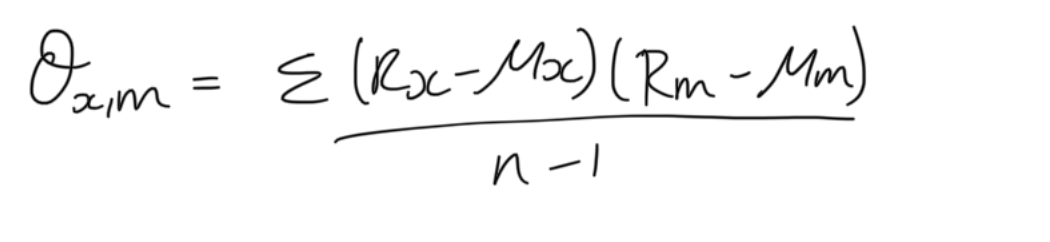
put-call parity
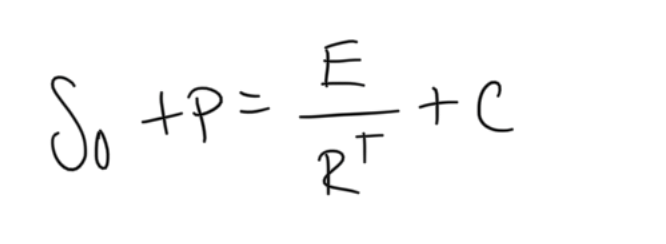
call pricing using binomial approximation
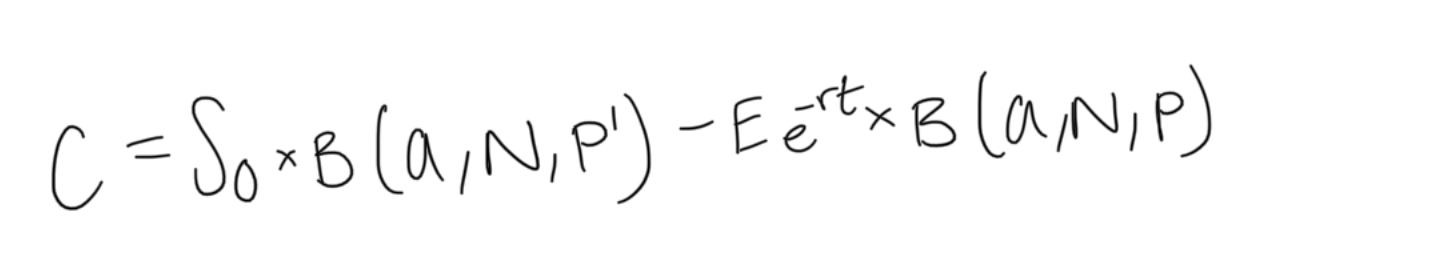
Z1
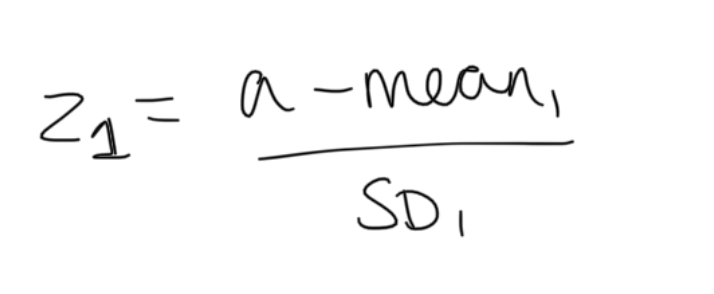
SD1

PI
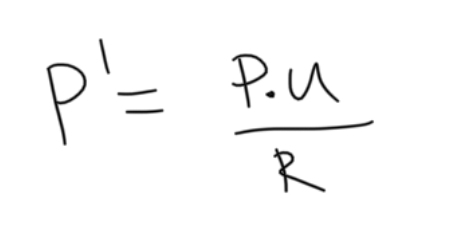
upper bound for call option
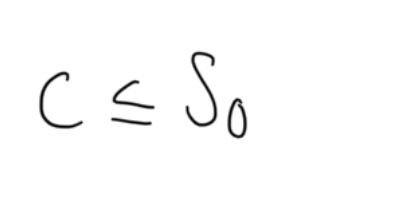
upper bound for put option
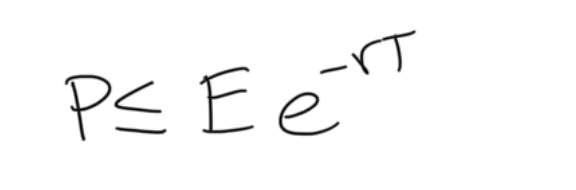
lower bounds of call option
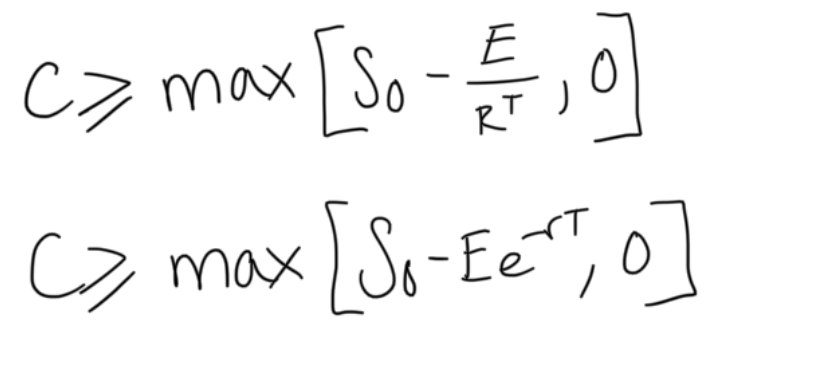
lower bounds for put options
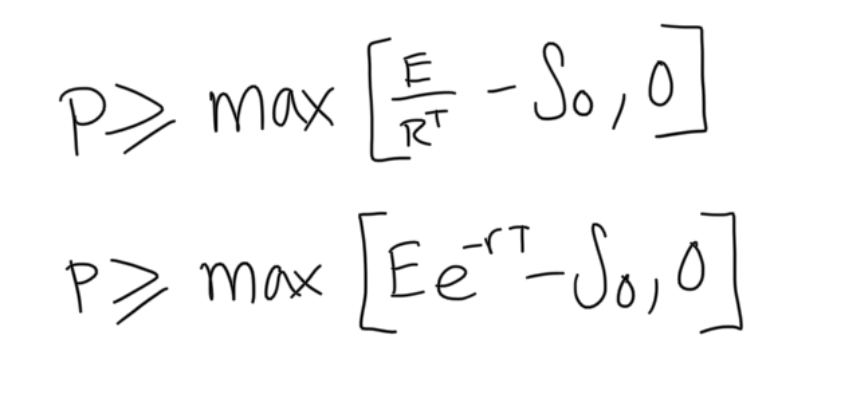
two period binomial option pricing
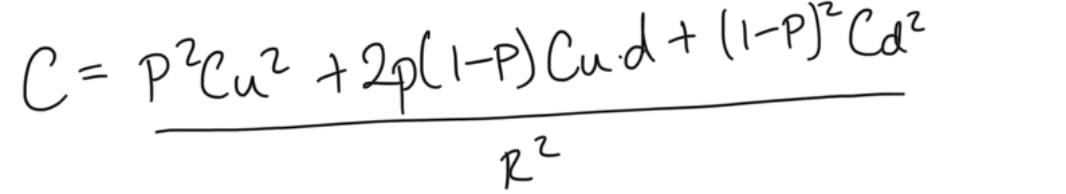
three period binomial option pricing
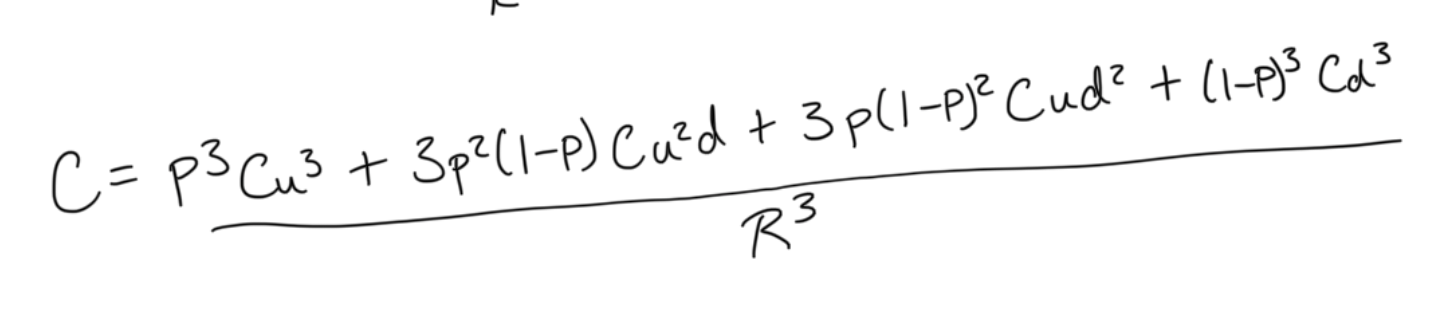
risk neutral probabilities, q
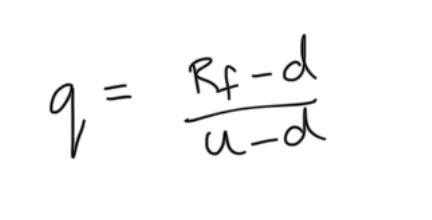
forward prices, no income

forward prices, predictable income
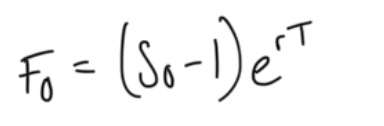
forward prices, predictable yield
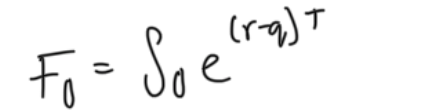
value of long forward
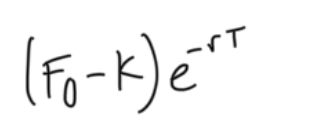
value of short forward
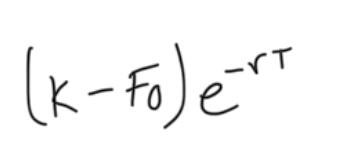
forward rate on currencies
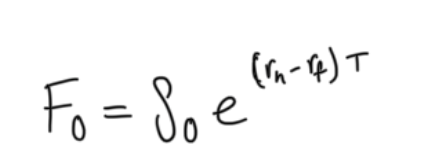
forward rate on investment commodities
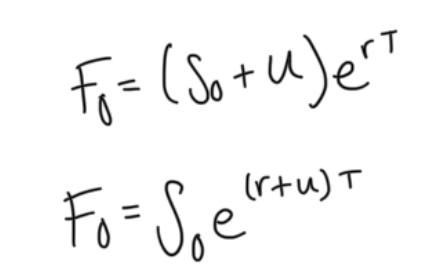
forward rate on consumption commodities
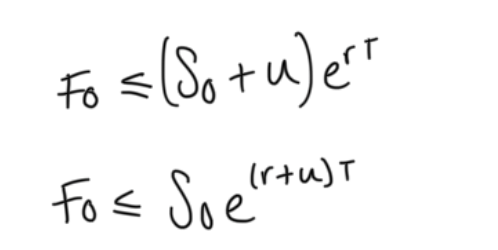
d1
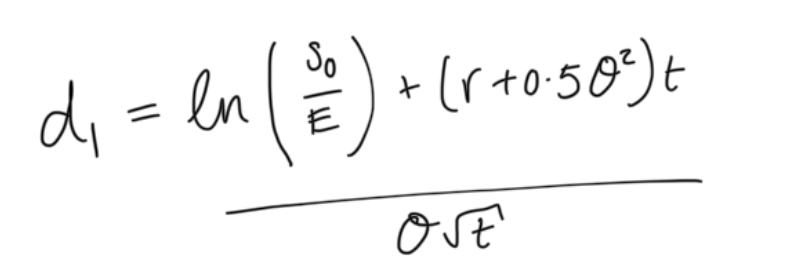
d2

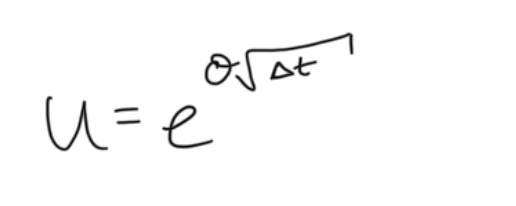
u =
d =
1/u
CAPM Assumptions
no transaction costs
all assets are infinitely divisible
no personal taxes
markets are purely competitive
investors choose portfolios purely on expected return and standard deviation
short sales permitted
unlimited borrowing and lending at the risk free rate
investors have homogenous expectations
arithmetic returns
discrete compounding
multiplicative cumulation
non-symmetric reversal in return
not normally distributed
logarithmic returns
continuous compounding
additive cumulation
reversal in return is symmetric
more normally distributed
fama French model
extends CAPM to include two additional factors that capture systemic risk that is not explained by the market alone
factors: market, size, value
largely empirical
explains more of the variation in average returns than CAPM
empirically supported across many markets and long time periods
lacks strong theoretical foundations
interpretations of size and value factors still debated
carhart four factor model
extends on mama French by adding momentum factor
strong empirical support: captures size, value and momentum effects
widely used in performance evaluation
lacks deep theoretical foundation
momentum may arise from behavioural biases rather than risk premia
CAPM vs APT
CAPM is one factor only, APT has multiple factors
CAPM has market risk only, several system risks priced in APT
CAPM has weak empirical performance but APT has stronger
core idea of CAPM = excess returns depend on exposure to market portfolio
core idea of APT = expected returns are determined by multiple sources of systemic risk. condition of no arbitrage prevents mispricing.
effect of a decrease in market interest rate on utility of borrowers and lenders
market interest rate = -(1+r)
a fall in r makes the budget line flatter
can now access a higher utility curve
consumers consume more this period and next
effect of a decrease in market interest rate on the present wealth of borrowers and lenders
pv of future income = income*1/1+r
as r falls, pv of future income rises
borrower has negative future net income, lower r reduces the pv of loan repayments, increasing the present wealth of borrowers
lender has positive future income, lower r reduces pv of returns from lending - present wealth of lenders decreases
strategy for arbitrage
buy the undervalued option
short the stock if the option is a call
buy the stock if the option is a put
do this without borrowing - borrow cash if necessary
credit default swaps
derivative contract that transfers credit risk of a borrower from one party to another
protection buyer pays premium
protection seller compensates buyer if credit event occurs
settlement may be physical or cash
mainly used to hedge credit risk, speculate on changes in credit quality, and improve pricing efficiency between bond and credit markets
CDS involves counterparty risk, may encourage excessive speculation and can contribute to systemic risk if poorly regulated
Explain the nature and properties of Brownian motion(BM); and explain the relevance of the standard form of scaled BM with drift to the pricing of options
stochastic process with following properties:
W0 = 0
independent increments: movements over non-overlapping time intervals are independent
normally distributed increments
continuous paths
stationary increments: distribution depends only on the length of the time interval
in finance it is used calculate stock prices
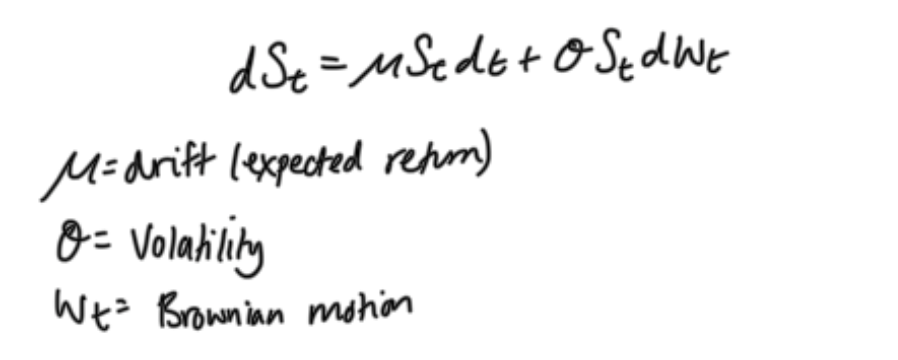
Itos lemma
applying Ito’s lemma gives the stochastic differential equation for option price
decomposition separates random part from deterministic part
by forming a hedged portfolio that eliminates dwt, creating a riskless portfolio
no arbitrage arguments lead directly to the Black-Scholes partial differential equation
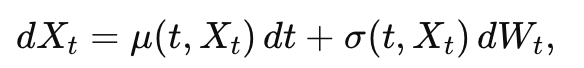
complete vs incomplete market
complete = every possible payoff across all states of the world can be replicated exactly using traded assets
incomplete = some contingent payoffs cannot be replicated
redundant assets
if its payoff can be exactly replicated by a portfolio of other traded assets
its presence does not expand the set of attainable payoffs
removing it does not affect market completeness
Type 1 vs Type 2 arbitrage
type 1 = zero initial cost, non-negative payoff in every state, strictly positive payoff in at least one state
type 2 = negative or zero initial cost, non-negative payoff in every state, weak arbitrage
Arrow-Debreu security
hypothetical asset that pays 1 unit of consumption in one state of the world, and 0 in all other states
state price vector
is the vector of prices of all arrow debreu securities
each element gives the todays price of receiving 1 unit of payoff in a specific state tomorrow