Protein Synthesis
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
The Genetic Code (extra notes)
Bases are read in triplets (groups of 3) called codons
There are 64 codons (4³) but only 20 amino acids, so multiple codons can code for the same amino acid
Example: CCA, CCC, CCG, CCT all → proline
Important Features of Genetic Code
Linear: read in one direction (5' → 3' on mRNA)
Non-overlapping: each base belongs to only one codon
Universal: almost all organisms use the same code
Start codon: AUG (methionine)
Stop codons: UAA, UAG, UGA (don’t code for an amino acid)
When a certain protein of the body is in high demand…
numerous RNA transcripts of its gene will be produced
ex: when we eat sugar → our body needs insultin protein
DNA is stored and protected in the…
nucleus
Protein Synthesis (chain of events)
DNA →RNA → Endoplasmic Reticulum → Ribosomes →Amino Acids →Protein
ONE GENE =
ONE POLYPEPTIDE
When multiple amino acids join together they form a
they form a polypeptide chain, which can then fold into a specific three-dimensional shape to become a functional protein.
Genes (at a molecular level) are…
a sequence of nucleotides from DNA
**DISCLAIMER → this is just for clarification and not to confuse genes for pure DNA. nucleotides also differ from
What do proteins do?
They:
Run cellular processes (like metabolism)
Control physical traits
Can cause genetic disorders if missing or changed
Archibald Garrod
studied a disease called alkaptonuria — people’s urine turned black because it had a chemical called alkapton.
He thought people with alkaptonuria had a defective enzyme that couldn’t break down alkapton.
This defect was inherited.
🧩 Conclusion: A problem in a gene → defective enzyme → disease
Beadle and Tatum
→Discovery with Arginine/Mold
Some mutant molds only grew when given arginine (an amino acid).
This showed that one or more enzymes that make arginine were defective.
🧩 Conclusion: Each gene controls one enzyme in a chemical pathway.
Identify the roles of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
1. mRNA (messenger RNA)
Acts as a template of the gene.(only one)
Carries the instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome.
Has codons (triplets) that tell the cell which amino acids to put in order.
➡ Role: Brings the genetic message to the ribosome.
2. rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
Forms the ribosome, along with proteins.
The ribosome is the place where the protein is built.
rRNA helps:
hold the mRNA in place
connect amino acids together
➡ Role: Makes up the ribosome and helps build the protein.
3. tRNA (transfer RNA)
Brings the correct amino acids to the ribosome.
Each tRNA has an anticodon that matches with an mRNA codon.
➡ Role: Delivers the amino acids and matches them to mRNA codons.
When something goes wrong in protein synthesis it can lead to:
No protein being made
OR
Protein being made incorrectly → wrong shape and function
**5 key differences between DNA and RNA
Sugar
Bases
Strands
Length
Location
Genes don’t just code for proteins they also code for:
(probably not important)
antibodies
hormones
structural proteins
→ these all affect an organism’s physical traits
4 scientists :
Mendel
Garrod Archibald
Beadle & Tatum
Vernon Ingram
Vernon Ingram’s Experiment
Vernon Ingram studied hemoglobin
In normal hemoglobin, the β chain has this sequence:
Valine – Histidine – Leucine – Threonine – Proline – Glutamic acid – Glutamic acid
In sickle cell anemia, one glutamic acid is replaced by valine:
Valine – Histidine – Leucine – Threonine – Proline – Valine – Glutamic acidThis tiny change causes red blood cells to become sickle-shaped → blocking blood flow → serious disease.
🧩 Conclusion: A single amino acid change → major health effect.
mRNA
carries the DNA “message” to the ribosome
“consists of nucleotides that can be read as codons and translated into proteins”
transcribed in nucleus and translated outside
single stranded
only contains the code for ONE GENE
has a short life →destroyed when no longer needed
t-RNA
1st comes due to signal triggered by the mRNA and ribosome match/link up
brings amino acid to the ribosome
they come based on whatever codon needs its anti codon and they bring the corresponding amino acid
r-RNA
binds to mRNA
used to help build/make ribosomes cuz for some reason they need help being made
act as a base for building the proteins
varies in length?
DEFINE Transcription
Transcription is the process where a cell makes an mRNA copy of a gene.
happens purely in the nucleus
STEPS of Transcription
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Capping and Tailing
Splicing
Translation
happens in RIBOSOME
Initiation
ribosome clamps onto the mRNA
reads the code in codons (3 nucleotides at a time)
Elongation
t-RNA brings the correct amino acid
The amino acids join together form a polypeptide chain
Termination
Ribosome reaches a stop codon
The completed protein is released
The genetic code///RNA polymerase both move in one direction
5’ →3’
Transcription Voice Note in detail
True or False: Introns are recycled
True. The diff nucleotides are recycled for more mRNA
Alternative Splicing
can join different combinations allowing one gene to make many different proteins
tRNA structure
At the tip of each tRNA, is an anticodon a 3 base sequence
it is complementary to the mRNA codon
Basically da same as the DNA triplet but ofc U replaces T
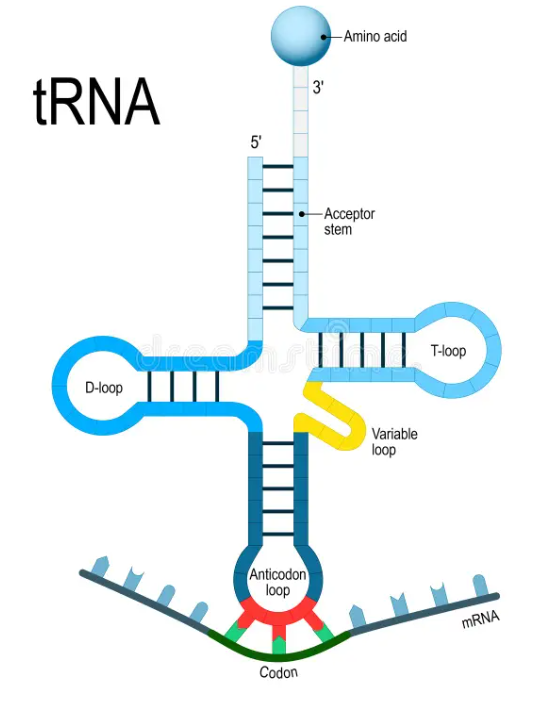
Wobble Hypothesis
There are 61 possible codons (combinations of 3) but we do NOT have 61 different tRNAs….
Some tRNAs can match for more than one codon
EX: UAU and UAC both code for tyrosine. So if a tRNA anticodon is AUA it can still bind to UAC even though it shouldddd bind to UAU
This flexibility is called the Wobble Hypothesis
Termination of Trancsription
When RNA polymerase reaches the terminator sequence it stops copying.
**The exact terminator varies by the gene
As transcription ends RNA polymerase releases the newly born mRNA transcript.
**although RNA polymerase job ends here it can still be reused for more jobs
Capping and Tailing
The newly transcribed mRNA is scared and needs protection and signals
A 5’ end cap (of methylguanosine) is added to the start of the mRNA during translation
These protect mRNA from the enzymes that will fight it in the nucleus.
It also helps the ribosome recognize mRNA during translation!
A “poly-A-tail” of 50-250 adenfines are added to the 3’ end by poly-A polymerase
also protects the mRNA from fights and degration
Splicing
The mRNA contains introns and exons.
Introns are cutout and recycled in the spliceosome
splicing happens inside a spliceosome (made up of the small ribonucleoprotein)
Alternative splicing → can join exons in diff combinations allowing one gene to make many diff proteins.
After Transcription is complete
the MATURE mRNA leaves the nucleus through nucleus pore → to the cytoplasm to be translated
Initiation of Transcription
Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of DNA.
The promoter tells the enzyme where to start and which DNA strand to copy.
Most promoters contain a TATA box, a sequence high in A’s and T’s which is easier to open bc A and T pairs only have 2 hydrogen bonds
**RNA polymerase binds at the promoter (BEFORE UTR) and does not transcribe the promoter itself
Elongation for Transcription
RNA polymerase builds the mRNA strand in the 5’ → 3’ direction.
Coding strand →Identical, Template strand → being synthesized on
mRNA is complementary to the template DNA strand (…Thymine →Uracil)
RNA polymerase moves along the gene, adding nucleotides to grow the mRNA chain
Aminoacyl-tRNA
basically the thing circled in the picture
The amino acid is attached to the 3’ end and is called/named “Aminoacyl-tRNA”
aminoacyl-tRNA synthase
The enzyme responsible for adding the appropriate A.A to each tRNA (aminoacyl-tRNA synthase)
The are about 20 of these enzymes (one for each amino acid)
The Ribosome(s)
When mRNA reaches the cytoplasm, the ribosome recognizes its 5’ cap
The ribosome has 2 subunits (large + small/the flat one) both made up of rRNA and proteins
The big subunit clamp onto the mRNA (+ short rRNA) and moves from 5’ → 3’
It reads the codons one (3 bases) at a time AND
links new amino acids to the growing chain - this is the “reading frame”
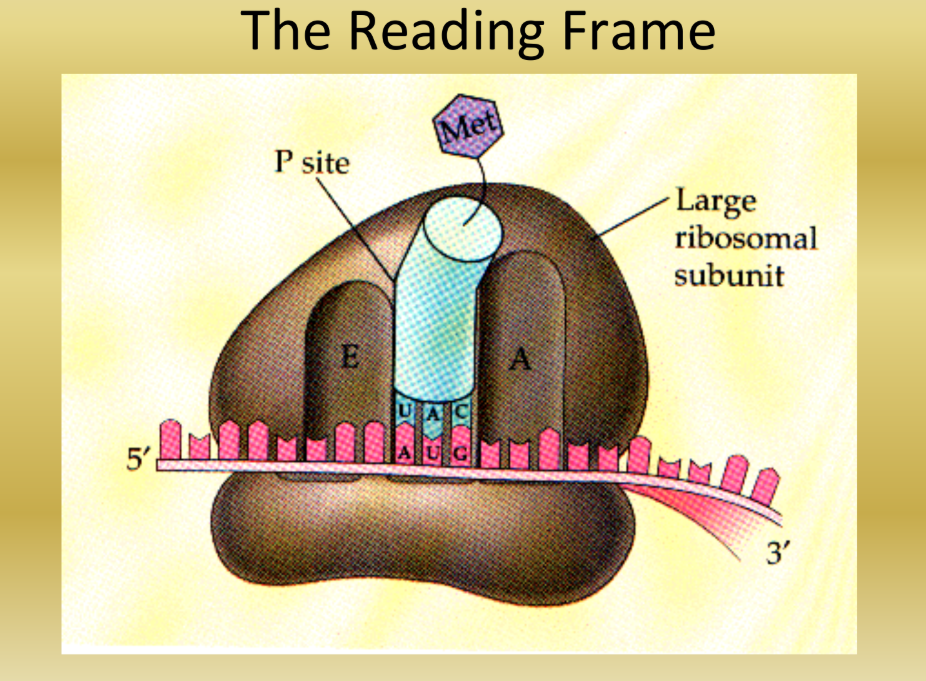

Three Binding Sites (The Reading Frame)
Inside the ribosome:

A site
Where the aminoacyl tRNA enters
P site (Peptidyl?)
Holds the tRNA with the growing chain of amino acids (polypeptide)
E site (Exit)
Where empty tRNA leaves the ribosome
Stages of TRANSLATION**
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Extra Polysomes?????
Post Translational Modifications??
Initiation of Translation
Begins at AUG the start codon (AUG = Methionine)
The Met tRNA binds near the 5’ cap
The ribosome moves along the mRNA in a process called scanning
Elongation of Translation
Met tRNA lies in the P site.
A second tRNA enters the A site
The enzyme peptidyl transferase forms a bond between Met and the next amino acid (basically links Met and next A.A)
The Met is released from its tRNA and that empty tRNA moves to the E site.
The ribosome keeps moving forwards repeating this process
Termination of Translation
The ribosome eventually reaches a STOP codon
Stop codons have no amino acids
A release factor binds and helps free the completed polypeptide protein from the ribosome
Polysomes
Many ribosomes can translate the same mRNA at once…
This group of ribosomes is called polysomes
********“Post-Translational Modifications”
After translation, proteins often need changes to become functional
These changes may include:
Cutting the chain
Adding phosphatase or methyl groups…
Adding sugar →becomes glycoproteins
Adding lipids → becomes lipoproteins
housekeeping genes
Some genes are always active because the cell needs them all the time.
These are called housekeeping genes.
Cells can turn genes on or off depending on what they need.
There are 4 levels of control:
Transcriptional Control
Controls which genes get copied from DNA → mRNA.
Post-transcriptional Control
Controls which introns and exons are kept or removed when mRNA is edited (splicing).
Translational Control
Controls how often or how fast mRNA is translated into a protein.
Post-translational Control
Some proteins must be modified or sent through membranes before they work.
This affects how quickly they become active.
Two main categories of Mutations:
Single-gene mutations
Affect one gene’s nucleotide sequence
Chromosome mutations
Affect big sections of chromosomes (many genes)
Somatic vs Gamete Mutations
Somatic cells (body cells): mutations usually go unnoticed; not passed to children
Gametes (egg/sperm): more serious because they can be inherited
The following are point mutations (affect 1 base pair):
🎯 Silent Mutation
A change in DNA that does NOT change the amino acid
No change in phenotype
Sometimes it happens in introns (which are cut out). Wrong thingy is transcribed but its cut out anyway
Example:
UUU → UUC
Both code for Phe, so the protein stays the same.
🎯 Missense Mutation
A DNA change that replaces one amino acid with another
Can cause diseases like:
Sickle cell anemia
Some cases of Cystic Fibrosis
Can also be helpful when your body makes new antibodies.
🎯 Nonsense Mutation
A mutation that changes a codon into a STOP codon
Translation stops too early → incomplete protein
Often lethal to the cell
Both missense & nonsense come from substitution mutations.
Deletion Mutation
Removes one or more nucleotides
Changes the reading frame → changes amino acids → defective protein
Example:
AUG GGA UUC AAC
→ remove one base → AUG GAU UCA AC (shifted)
Insertion Mutation
Adds an extra nucleotide
Also causes a frameshift mutation
(Similar effect to deletion)
Translocation
A piece of a chromosome breaks off and is moved to a non-homologous chromosome
Can create fusion genes with completely altered function
🔁 Inversion
A piece of a chromosome flips its direction
No DNA lost or gained
But the gene wont be read/ read wrong
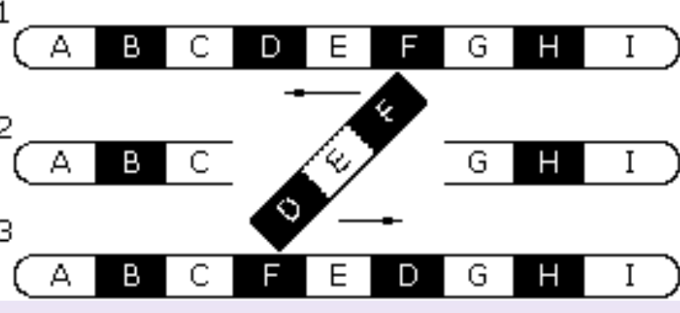
Deletion & Duplication (Chromosomal)
A part of the chromosome is lost (deleted)
Or copied twice (duplicated)
Causes of Mutations
✔ Spontaneous mutations
Natural mistakes by the cell’s machinery
✔ Induced mutations
Caused by mutagens like:
UV light
Benzene
Radiation (nuclear energy)
Other chemicals
Cancer
Cancer = diseases with uncontrolled cell division.
Two main gene problems:
❌ Tumor suppressor genes (like p53)
Normally stop bad cells from dividing
In cancer, they are turned off or broken
❌ Proto-oncogenes
Normally control cell growth
In cancer, they are stuck ON
This leads to:
Fast, uncontrolled division
Tumor (mass of abnormal cells)
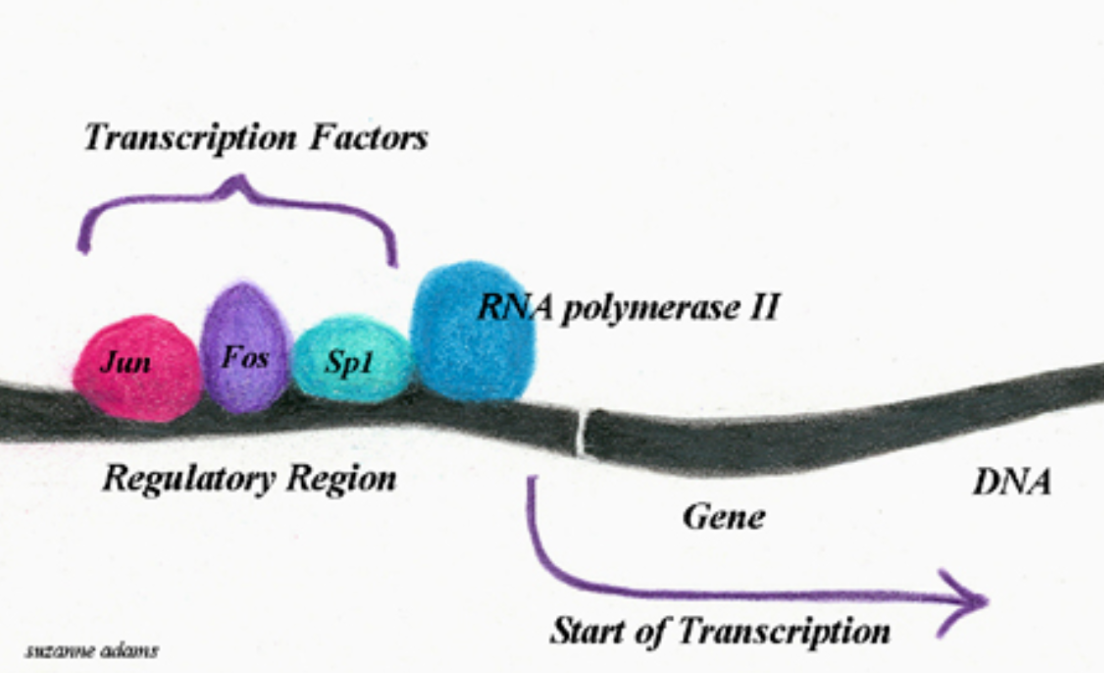
Transcription Factors
proteins that turn genes on.
They do this by binding to DNA and helping RNA polymerase start transcription.

Galinda would be the Transcription Factors
Types of Point Mutation
Silent Mutation
Missense Mutation
Nonsense Mutation