Electronegativity and polarity
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
Electronegativity
The attraction of a bonded atom for the pair of electrons in a covalent bond.
Elctonegativity is caused by:
The nuclear charges are different
The atoms being different sizes
The shared pair of electrons are closer to one nucleus than another.
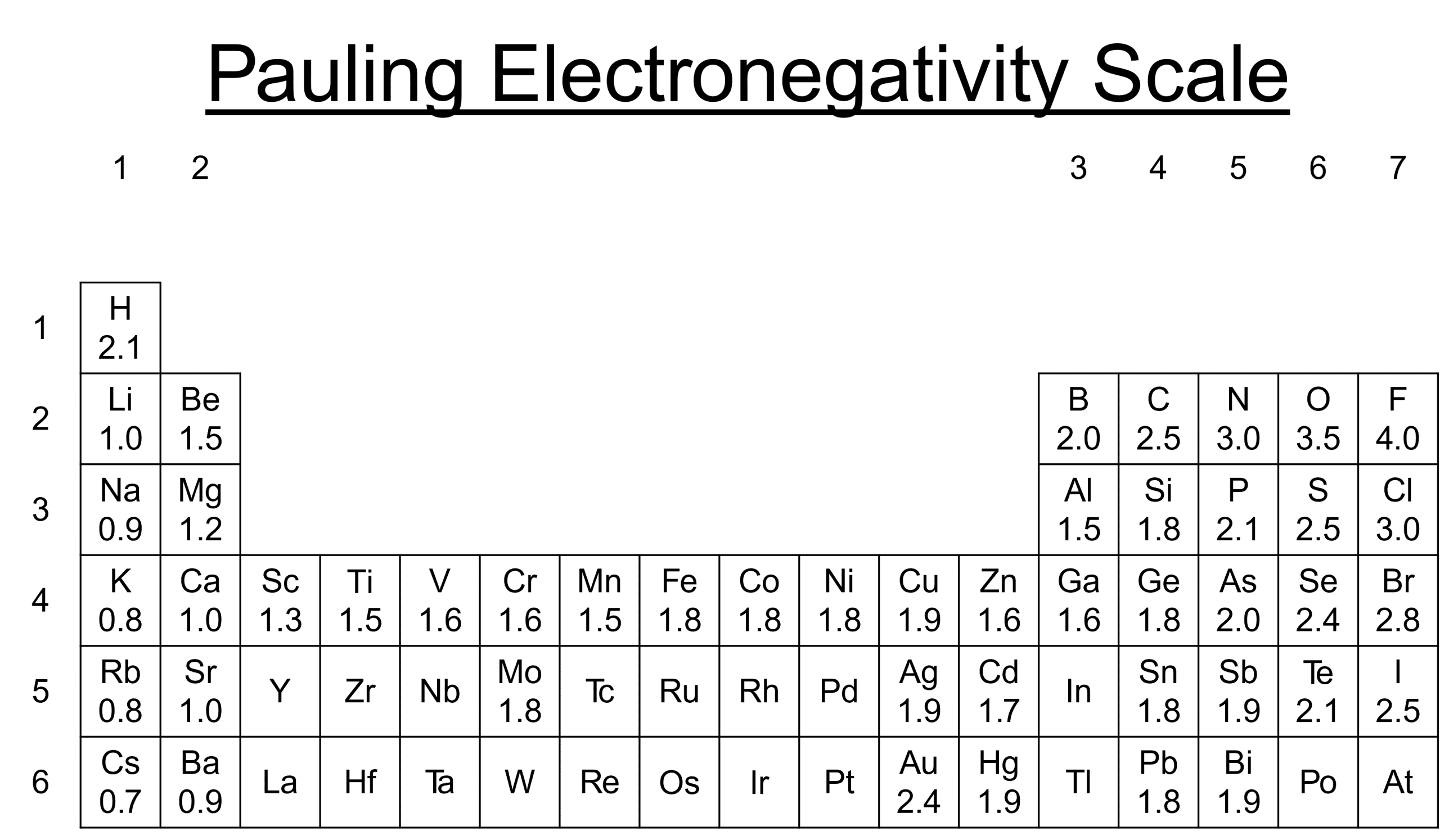
The Pauling scale
The Pauling scale compares the electronegativity of atoms. The greater the Pauling value, the greater the electronegativity.
Electronegativity increases going across a period from left to right and also as you go up a group. This is because as you go across nuclear charge increases as atomic radius decreases.
This makes fluorine the most electronegativity element at 4.0 along with nitrogen and oxygen.
Electronegativity effect on bonding
If the electronegativity difference is large, one bonded atom will have a much greater attraction for the shared pair than another bonded atom. This will change the bonding from covalent to ionic.
Bond type | Electronegativity difference |
Covalent | 0 |
Polar covalent | 0 to 1.8 |
Ionic | greater than 1.8 |
Polar bonds
A polar bond is when the electrons are shared unequally between the two bonding atoms. This is caused by a difference in electronegativity. This leads to separation of charge and the formation of a dipole.
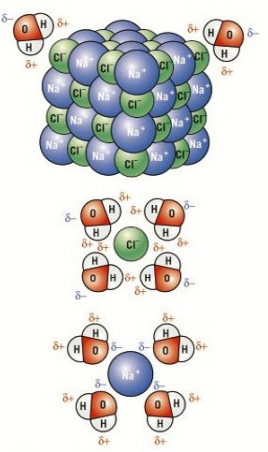
Polar solvents and solubility
Polar solvents like water can dissolve polar molecules like sodium chloride by the opposite attraction of the dipoles.
This is breaks down the ionic lattice as it dissolves.