Medical Terminology - Chapter 6
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:40 PM on 4/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
agglutino
clumping
2
New cards
baso
base
3
New cards
chromo
color
4
New cards
coagulo
clotting
5
New cards
eosin
rosy red
6
New cards
fuso
pouring
7
New cards
granulo
granules
8
New cards
hemo/ hemato
blood
9
New cards
morph
shape
10
New cards
myelo
bone marrow
11
New cards
neutr
neutral
12
New cards
phag
eat/swallow
13
New cards
sanguino
blood
14
New cards
septic
infection
15
New cards
\-apheresis
removal, carry away
16
New cards
\-crit
separation of
17
New cards
\-cytic
pertaining to cells
18
New cards
\-cytosis
more than normal
19
New cards
\-emia
blood condition
20
New cards
\-globin
protein
21
New cards
\-oid
resembling
22
New cards
\-penia
abnormal decrease, too few
23
New cards
\-phil
attracted to
24
New cards
\-philia
condition of being attracted to
25
New cards
\-philic
being attracted to
26
New cards
\-plastin, -poiesis
formation
27
New cards
\-stasis
standing still
28
New cards
blood composition
erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, plasma
29
New cards
hematopoiesis
how blood cells are produced in there’d bone marrow
30
New cards
plasma
composes 55% of blood volume
90-92 % water
8-10% is plasma proteins (albumin, globulins and fibrinogen)
\
90-92 % water
8-10% is plasma proteins (albumin, globulins and fibrinogen)
\
31
New cards
albumin
helps transport fatty substances that cannot dissolve in the water plasma
32
New cards
globulins
gamma globulin: act as antibody
33
New cards
fibrinogen
a blood clotting protein
34
New cards
Substances found in plasma
calcium, potassium , sodiums, glucose, amino acids, fats, urea, creatine
35
New cards
erythrocytes
enucleated, contain hemoglobin
average lifespan of 120 days
bilirubin: waste product disposed of by liver
average lifespan of 120 days
bilirubin: waste product disposed of by liver
36
New cards
leukocytes
provide protection against the invasion of pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or other toxins
granulocytes (with granules in cytoplasm) and agranulocytes (without granules)
granulocytes (with granules in cytoplasm) and agranulocytes (without granules)
37
New cards
platelets
modern term for thrombocyte
play a critical role in blood clotting or hemostasis
thromboplastin + prothrombin = thrombin
works to convert fibrinogen to fibrin which becomes a blood clot
play a critical role in blood clotting or hemostasis
thromboplastin + prothrombin = thrombin
works to convert fibrinogen to fibrin which becomes a blood clot
38
New cards
agglutinate
clump together (platelets)
39
New cards
blood typing
following ABO system
type A: anti-B antibodies, surface protein antigen A
type B: anti-A antibodies, surface protein antigen B
Type AB: both surface antigens, no antibodies (universal recipient)
Type O: no surface antigens, produced all antibodies (universal donor)
type A: anti-B antibodies, surface protein antigen A
type B: anti-A antibodies, surface protein antigen B
Type AB: both surface antigens, no antibodies (universal recipient)
Type O: no surface antigens, produced all antibodies (universal donor)
40
New cards
Rh factor
Rh positive: with Rh factor
Rh negative: no Rh factor will produce anti-Rh antibodies
Rh negative: no Rh factor will produce anti-Rh antibodies
41
New cards
basophilic
a leukocyte that attracts a basic pH stain
42
New cards
eosinophilic
pertaining to a leukocyte that attracts a rosy red stain
43
New cards
monocytic
pertaining to a white cell with a single large nucleus
44
New cards
sanguineous
pertaining to blood
45
New cards
thrombocytes
pertaining to a clotting cell
46
New cards
thrombotic
pertaining to a clot
47
New cards
hematology
study of blood
48
New cards
coagulate
to convert from liquid to a gel or solid (blood coagulation)
49
New cards
dyscrasia
general term indicating presence of a disease affecting blood
50
New cards
hematoma
collection of blood under skin as result of blood escaping into tissue from damaged blood vessels
51
New cards
hemorrhage
blood flowing out of a blood vessel
52
New cards
thrombus
hard collection of fibrin blood cells and tissue debris that is a result of hemostasis
53
New cards
hemophilia
hereditary blood disease in which blood clotting time is prolonged due to lack of one vital clotting factor
54
New cards
hyperlipidemia
condition of having too high a level of lipids such as cholesterol in blood stream, risk factor for atherosclerosis
55
New cards
pancytopenia
having too few of all cells
56
New cards
septicemia
having bacteria or their toxins in bloodstream
57
New cards
anemia
large group of conditions characterized by reduction in number of RBCs
58
New cards
aplastic anemia
severe form of anemia that develops as a consequence of loss of functioning red bone marrow
59
New cards
erythocytosis
too many RBCs
60
New cards
eryhtopenia
condition of having too few RBCs
61
New cards
hemolytic anemia
anemia that develops as result of destruction of erythrocytes
62
New cards
hemolytic reaction
destruction of patient’s erythrocytes that occurs when receiving a transfusion
63
New cards
hypochromic anemia
anemia resulting from having insufficient hemoglobin in erythrocytes
64
New cards
pernicious anemia (PA)
anemia associated with insufficient absorption of vitamin B12
65
New cards
polycythemia vera
production of too many RBCs by bone marrow, blood becomes too thick to easily flow through blood vessels
66
New cards
thalassemia
genetic disorder in which body is unable to make functioning hemoglobin
67
New cards
leukocytosis
condition of having too many WBCs
68
New cards
leukopenia
condition of having too few WBCs
69
New cards
myeloid leukemia
type of leukemia (cancer located in red bone marrow, large and abnormal leukocytes) in which abnormal leukocytes are granulocytes
70
New cards
thrombocytopenia
condition of having too few platelets
71
New cards
prothrombin time
indicates bloods coagulation abilities by measuring how long it takes for a clot to form about prothrombin has been activated
72
New cards
phlebotomy
incision into vein in order to remove blood for diagnostic test
73
New cards
adenoid/o
adenoids
74
New cards
immune
protection
75
New cards
inguino
groin region
76
New cards
lympho
lymph
77
New cards
lymphadeno
lymph node
78
New cards
lymphangio
lymph vessel
79
New cards
spleno
spleen
80
New cards
thymo
thymus gland
81
New cards
tonsillo
tonsils
82
New cards
\-globulin
protein
83
New cards
\-phage
to eat
84
New cards
\-toxic
pertaining to poison
85
New cards
lymphatic system
network of vessels that picks up excess tissue fluid and absorbed fats
Organs: lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, the spleen, thymus gland, tonsils
\
* collects and purifies excess, tissue fluid called lymph
* works with the immune system to form body’s defence
* assist with fat absorption
\
Organs: lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, the spleen, thymus gland, tonsils
\
* collects and purifies excess, tissue fluid called lymph
* works with the immune system to form body’s defence
* assist with fat absorption
\
86
New cards
immune system
immune system fights disease and infections
\
lymph nodes, appendix, bone marrow, thymus, spleen, peers patch, tonsils and adenoids
\
lymph nodes, appendix, bone marrow, thymus, spleen, peers patch, tonsils and adenoids
87
New cards
lymphatic vessels
in green, pick up excess tissue fluid, purify it in lymph nodes and return it to circulatory system
* form network of ducts throughout body
* one way pipes
* form network of ducts throughout body
* one way pipes
88
New cards
lymphatic ducts
a low pressure system that uses valves to prevent back flow
begin as a very small lymph capillaries n tissues
merge into large lymph vessels
drain into one of two large lymphatic ducts:
* the right lymphatic duct
* the thoracic lymphatic duct
begin as a very small lymph capillaries n tissues
merge into large lymph vessels
drain into one of two large lymphatic ducts:
* the right lymphatic duct
* the thoracic lymphatic duct
89
New cards
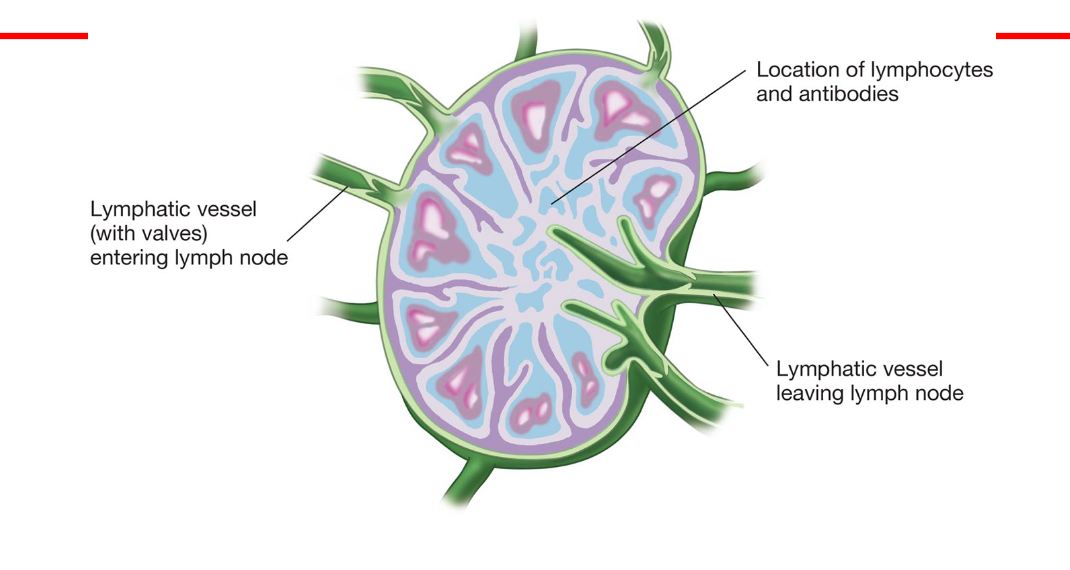
lymph nodes
small organs of lymphatic tissue
house lymphocytes and antibodies
* remove pathogens and cell debris from lymph
* trap and destroy cells form cancerous tumors
* concentrated in: cervical, mediastinal, axillary, inguinal
house lymphocytes and antibodies
* remove pathogens and cell debris from lymph
* trap and destroy cells form cancerous tumors
* concentrated in: cervical, mediastinal, axillary, inguinal
90
New cards
tonsils
collection of lymphatic tissue on each side of throat
3 sets:
* palatine tonsils
* pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
* lingual tonsils
\
tonsils act as filters to protect the body from pathogen invasion
not essential organs
3 sets:
* palatine tonsils
* pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
* lingual tonsils
\
tonsils act as filters to protect the body from pathogen invasion
not essential organs
91
New cards
spleen
location the left upper quadrant
consists of lymphatic tissue that is highly infiltrated with blood vessels
vessels spread out into slow moving blood sinuses lines with macrophages
destroys old RBCs, recycles iron and stores blood
not essential BUT: can be at risk for serious infections,
consists of lymphatic tissue that is highly infiltrated with blood vessels
vessels spread out into slow moving blood sinuses lines with macrophages
destroys old RBCs, recycles iron and stores blood
not essential BUT: can be at risk for serious infections,
92
New cards
thymus gland
located in the upper portion of the mediastinum
essential for immune development
secretes thyroxin, which changes lymphocytes to T lymphocytes
active through adolescence then it begins to shrink
essential for immune development
secretes thyroxin, which changes lymphocytes to T lymphocytes
active through adolescence then it begins to shrink
93
New cards
Peyer’s patches
small masses of lymphatic tissue found through the ileum region of the small intestine
also known as aggregated lymphoid nodules
monitoring intestinal bacteria populations
also known as aggregated lymphoid nodules
monitoring intestinal bacteria populations
94
New cards
Natural immunity
nonspecific and does not require pathogen exposure
95
New cards
Acquired immunity
bodies response to a specific pathogen
1. active: develops following direct exposure to a pathogen (vaccines)
2. passive acquired immunity: results when a person receives protective substances produced by another human or animal (maternal antibodies, gamma globulin injections)
1. active: develops following direct exposure to a pathogen (vaccines)
2. passive acquired immunity: results when a person receives protective substances produced by another human or animal (maternal antibodies, gamma globulin injections)
96
New cards
Plague
a disease that affects humans and other mammals
caused by bacterium Yersinia pestis
exposure: bite of a rodeo flea that is carry the plague bacterium or by handling animals infected with plague
Ex: Bubonic plague
caused by bacterium Yersinia pestis
exposure: bite of a rodeo flea that is carry the plague bacterium or by handling animals infected with plague
Ex: Bubonic plague
97
New cards
98
New cards
99
New cards
100
New cards