AP Chem Chapter 14-15 Titration, Acids and Bases 2021
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
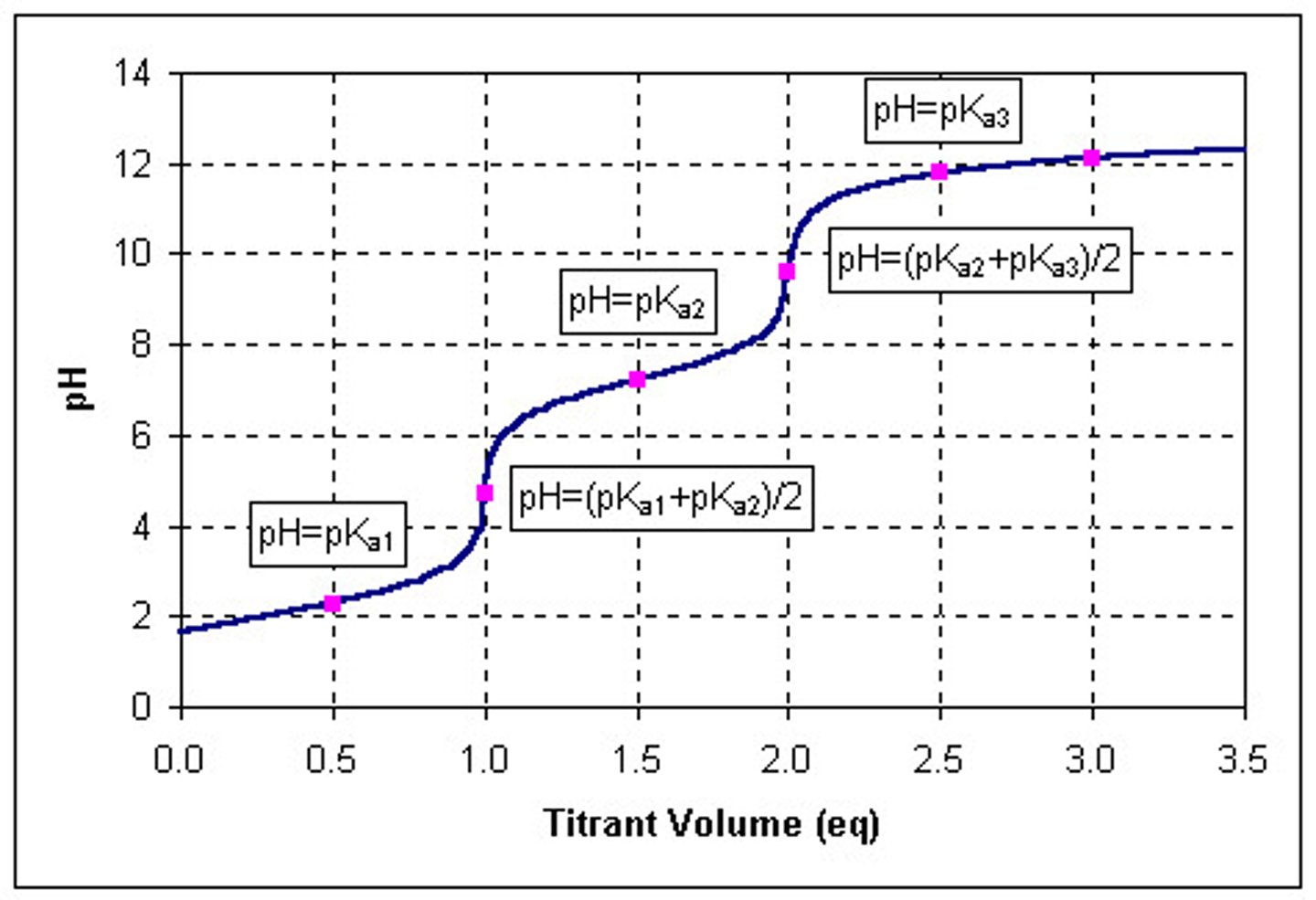
What is the name of the point of the curve where pH = pKa?
Halfway point
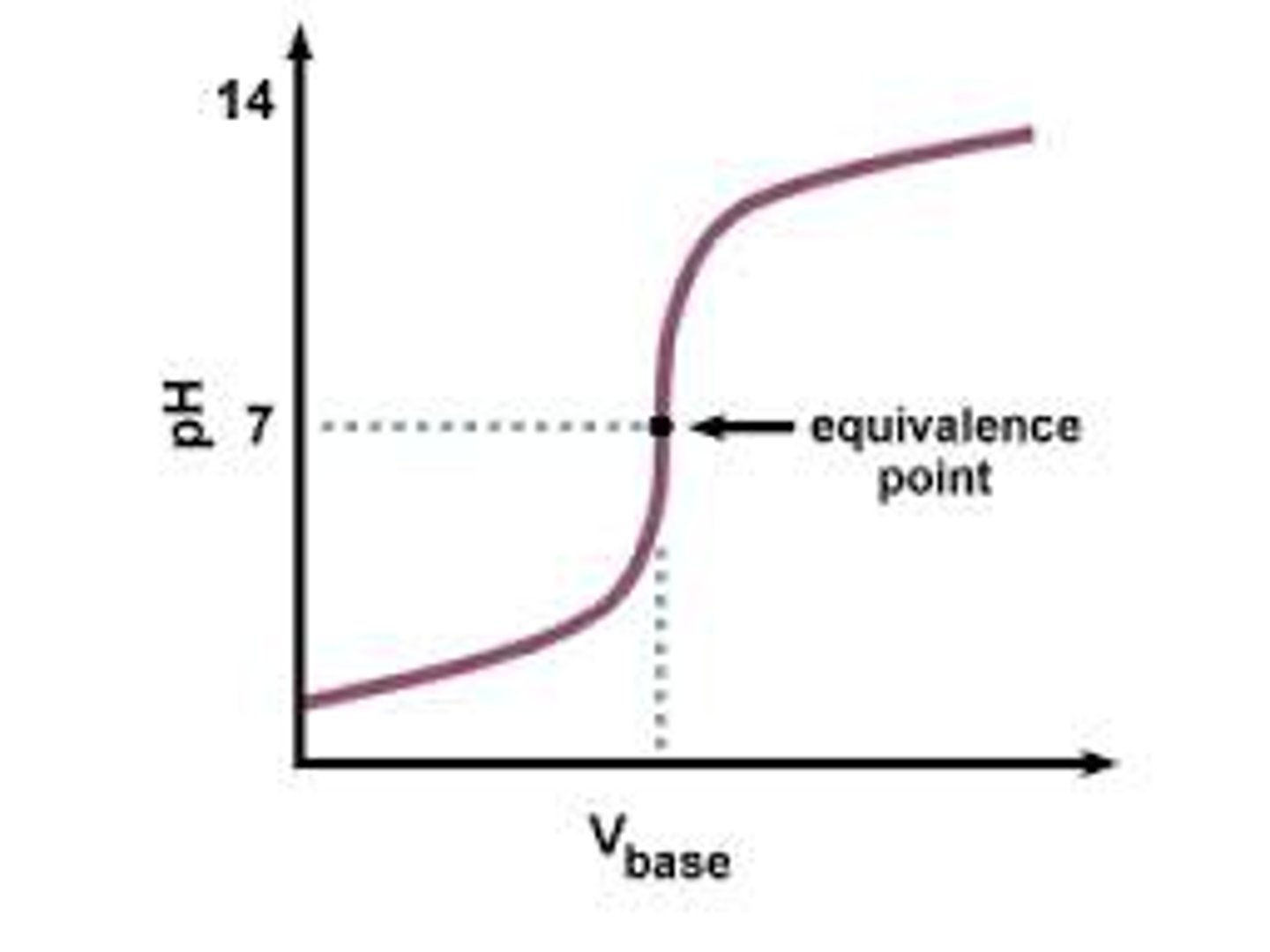
At what point will [H] = [OH]?
Equivalence point
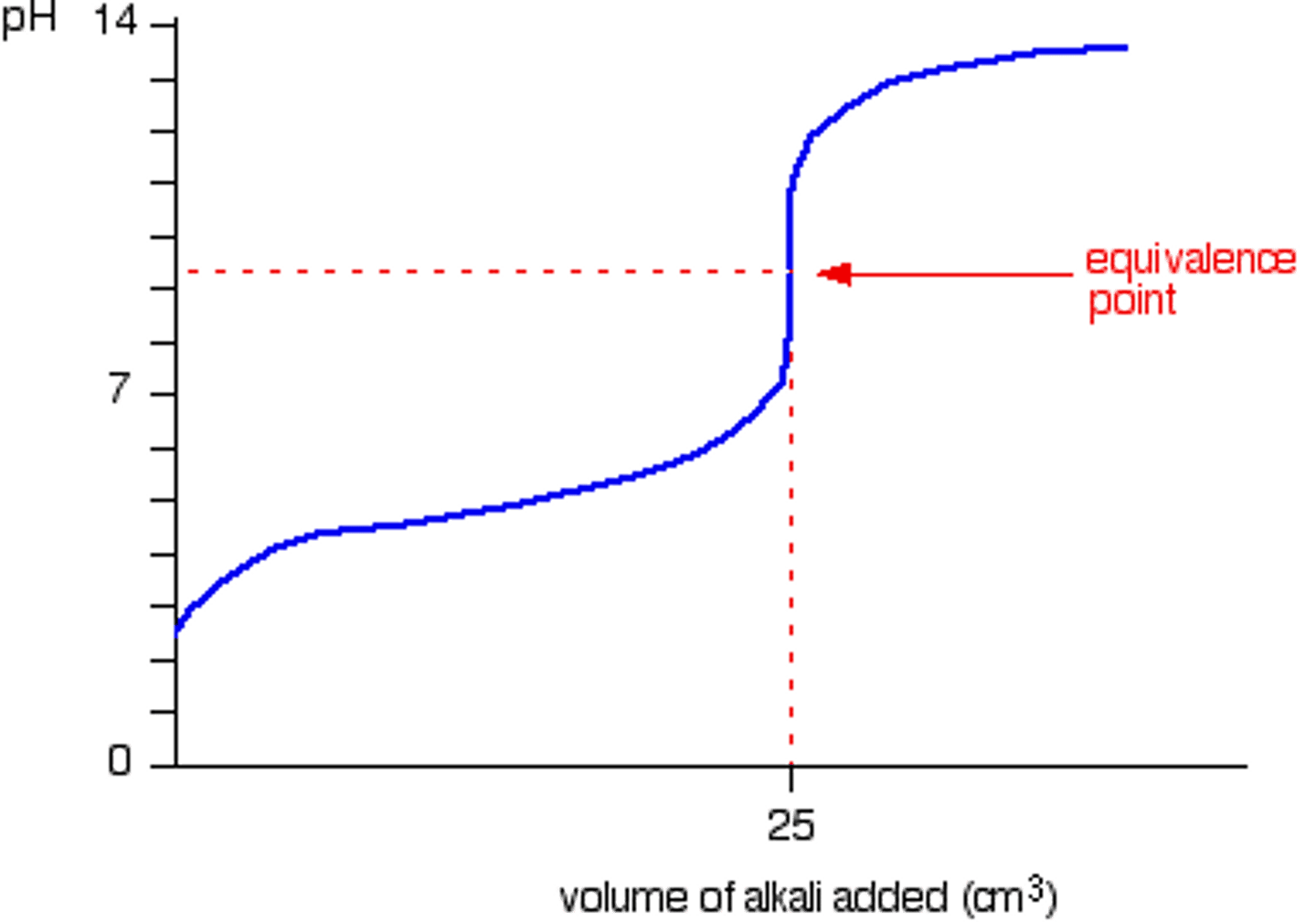
If a weak acid is titrated with a strong base
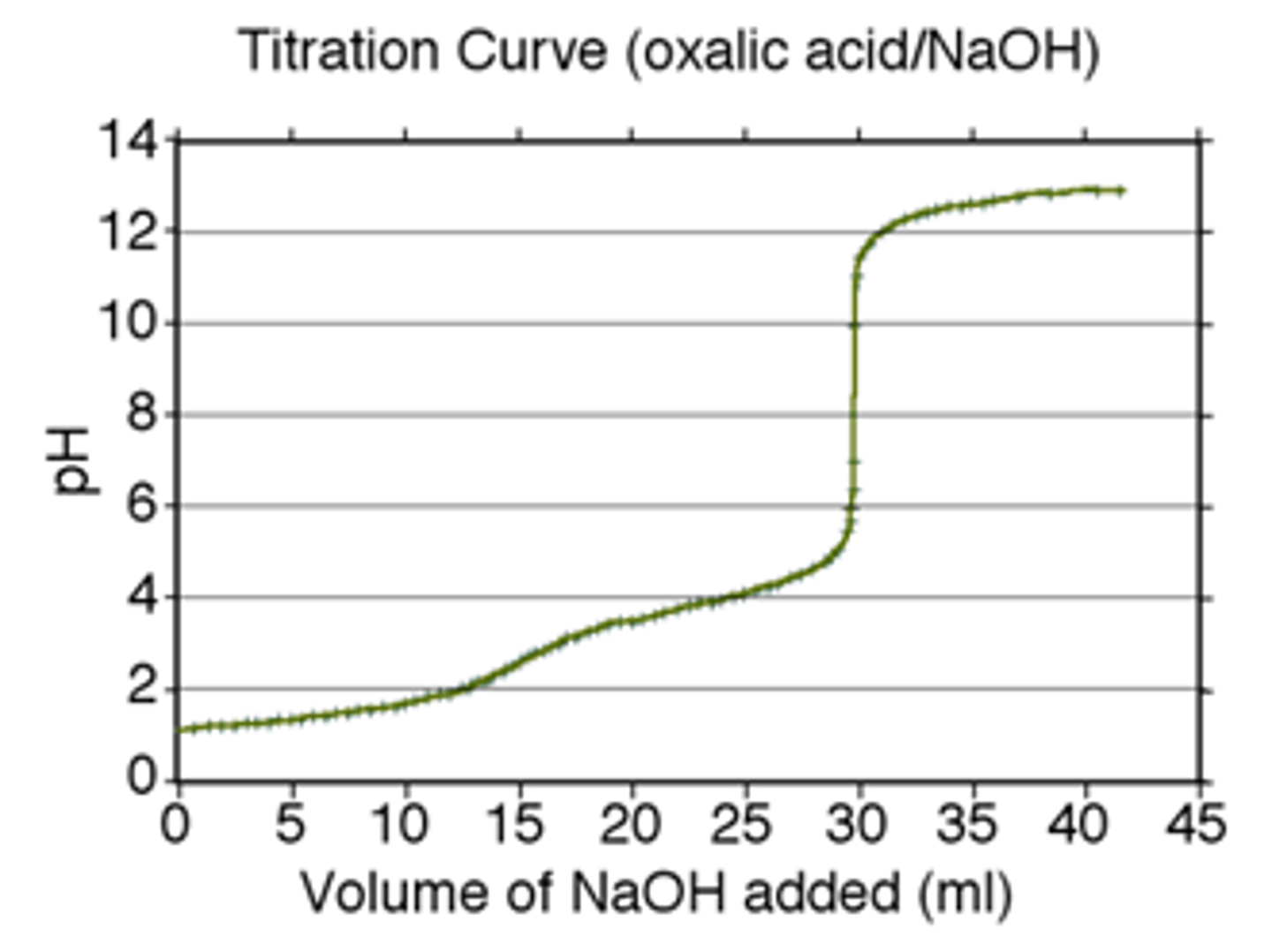
What is the definition of a Buffer ?
A solution which contains a weak acid (or weak base) and its conjugate base (or acid)
Given a titration curve, determine the Ka of the acid
anti-log of the negative value of the solution's pH at the halfway point
Why does the titration of a weak acid with a strong base have an equivalence point that is greater than 7?
the acid's conjugate base makes the solution basic
What is the definition of the equivalence point?
The spot on the titration curve where moles of acid = the mole of base . The pH at this point is not necessarily 7
Which indicators would be the most useful when titrating a weak acid with a strong base?
Pink phenolphthalein or thymol blue. Both change colors at pH's between 7.6 and 9. These are the values between which the equivalence
Given an unmarked titration curve, how would you identify the equivalence point?
Isolate the section of the curve where the slope is steepest. Look for the center point
arrhenius acid
they are the acids that dissociate in water to produce H+ ions
arrhenius base
they are the bases that dissociate in water to produce OH- ions
bronsted-lowery acid
acids that are proton donors
they are willing to give up H+
t
bronsted-lowry base
bases that are proton(H+) acceptors
conjugate base
what the acid becomes once the proton(H+) has been donated
conjugate acid
what the base becomes after it accepts the proton(H+)
strong acids
HNO3
HI
HBr
HCl
H2SO4
HClO4
what defines a strong acid
they completely(100%) dissociate in water
what defines a weak acid
acids that only partially dissociate
has a relatively strong conjugate base
strong bases
soluble compounds containing the hydroxide ions
NaOH
KOH
LiOH
RbOH
Mg(OH)2
Ba(OH)2
Ca(OH)2
Sr(OH)2
How # of oxygens on oxyacids affects acid strength
acid strength increases as more oxygens are added to the central Y
increasing the number of electronegative oxygen atoms increases the electrons attraction toward the Y. This will reduce the forces of attraction in the O-H bond making ti easier to remove a H+
Kw
1.0 X 10^-14 at 25 degrees Celsius
how to find pH when given [H3O+]
pH=-log[H3O+]
how to find pOH when given [OH-]
pOH=-log[OH-]
how to find the pH when given the pOH
14-pOH
how to find pOH when given the pH
14-pH
neutral
[H+] = [OH-]
larger Ka value means what
stronger acid because the acid is going more into completion
neutralization SA + SB reaction net ionic equation
H+ + OH- ---> H2O
hydrolysis
states that salts (ionic compounds) can make a solution acidic, basic, or even have no effect on the pH