science midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:10 AM on 1/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
1
New cards
what are the two types of electrical charges?
positive and negative
2
New cards
what is it called when you have an even number of positive and negative charges?
neutral
3
New cards
what is the law of charges?
opposites attract, likes repeal
4
New cards
a positively changed object has more what than what?
has more positive than negative
5
New cards
a negatively changed object has more what than what?
has more negative then positive
6
New cards
what is the list that ranks objects to take negative charges called?
electrostatic series
triboelectric
triboelectric
7
New cards
is it the top or bottom of the
triboelectric series that take negative charges?
triboelectric series that take negative charges?
the top of the list takes the negative charges and the bottom of the list loses them
8
New cards
what charge moves?
negative
9
New cards
what is ohm’s law used for?
used to calculate the resistance of a electrical circuit
10
New cards
what is the ohm’s law formula?
R= V/I
11
New cards
explain each symbol in the ohm’s law formula?
R= is the resistance in ohms
V= voltage in volts
I= current intensity in amps
V= voltage in volts
I= current intensity in amps
12
New cards
what 2 other thing use the same formula as resistance and are closely linked?
current intensity and potential difference
13
New cards
A circuit has a resistance of 10Ω & a current intensity of 5A. What is the potential difference?
V = 50V
14
New cards
A circuit has a resistance of 20Ω & a potential difference of 100V. What is the current intensity?
I= 5 A
15
New cards
A circuit has a potential difference of 16V & a current intensity of 2A. What is the resistance?
R= 8 Ω
16
New cards
where is an Ammeter placed in a circuit?
* In order to measure the **current** traveling through a circuit, an **ammeter** must be inserted into the circuit.
17
New cards
what does an ammeter read?
the current intensity of it
18
New cards
in what type of circuit can an ammeter be placed anywhere and read the same current intensity?
In a **series** circuit an ammeter can be placed anywhere along the wire and it will have the **same current intensity** reading.
19
New cards
will the ammeter read the same anywhere in a parallel circuit?
no
20
New cards
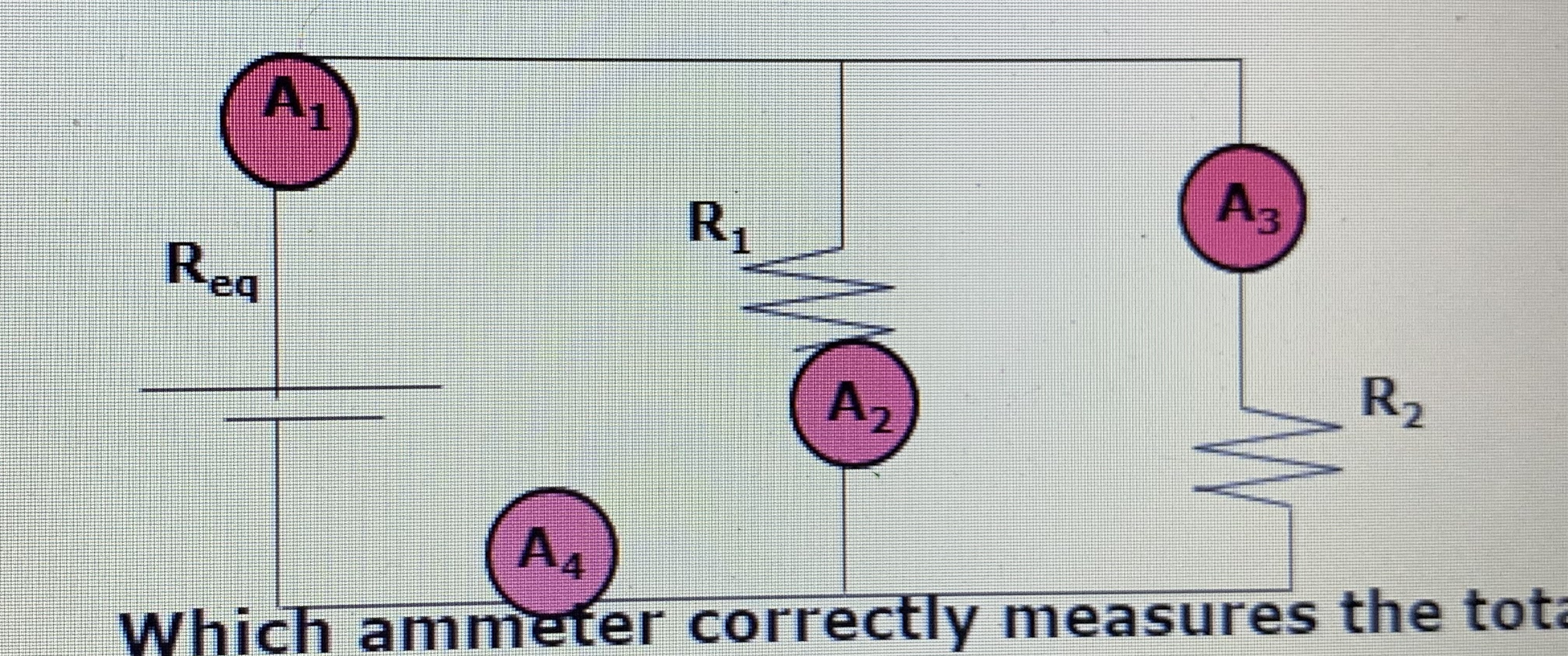
**Which ammeter correctly measures the current flowing through R1?**
**Which ammeter correctly measures the current flowing through R2?**
**Which ammeter correctly measures the total current?**
**Which ammeter correctly measures the current flowing through R2?**
**Which ammeter correctly measures the total current?**
1. 2
2. 3
3. 1 and 4
21
New cards
what does a voltmeter read?
voltage or potential difference
22
New cards
where is a voltmeter always placed in a parallel?
outside of the circuit
23
New cards
is a series circuit does the voltmeter read the same everywhere?
no it does not
24
New cards
in a parallel circuit will the potential difference/voltmeter read the same along the circuit?
yes
25
New cards
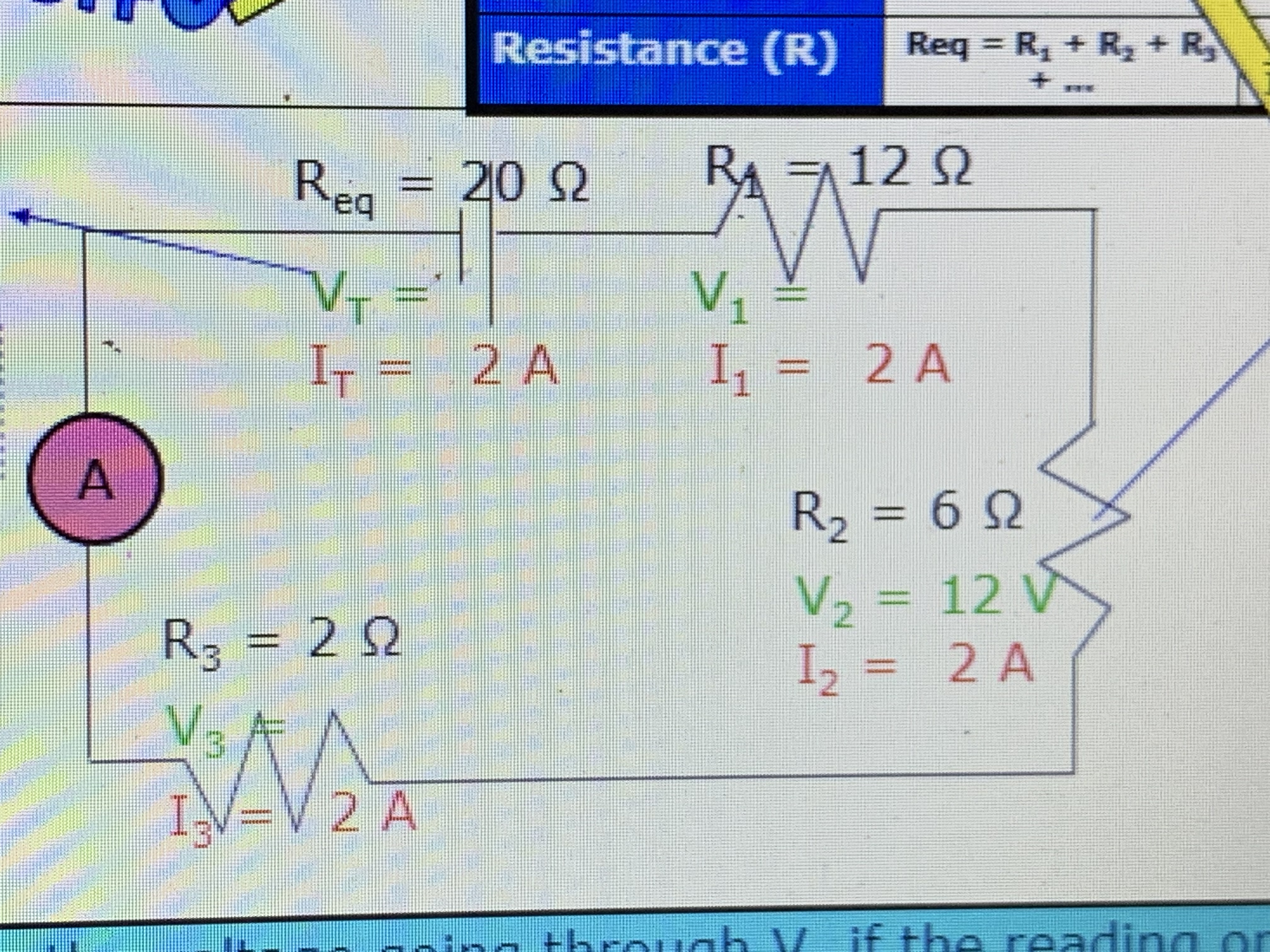
What is the voltage going through V2 if the reading on the ammeter is 2 amps?
What is the voltage going through VT if the reading on the ammeter is 2 amps?
What is the voltage going through VT if the reading on the ammeter is 2 amps?
12v and 40v
26
New cards
what is energy? give 2 examples
energy is the ability to do work. all appliances need energy to work. hair dryer needs to be plugged in to get energy to work and a light bulb needs electrical energy to shine bright.
27
New cards
what is power?
the rate in which power is used. it is the product of potential difference (voltage) and current intensity.
28
New cards
what is the symbol and unit for energy?
E and joules J
29
New cards
what is the symbol and unit for power?
p and watts W
30
New cards
what is the formula for energy?
power times time
31
New cards
A hair dryer has a power rating of 425W & is used for 10 minutes. How much energy is used?
255,000 Joules of energy were used to work the hair dryer
32
New cards
what is the formula for power?
p=v times I
33
New cards
An appliance requires 120V & 12A to work. It is used for 900 seconds. How much energy is used?
P = 1440 W and energy =1,296,000 J
34
New cards
how do you calculate cost? what units
cost= cost of electricity times power(kw) times time(hours)
35
New cards
how many watts make up 1 kw?
1000w
36
New cards
A 3.9 kilowatts curling iron is used for 10 minutes once a day. Electricity costs $0.05/kW•h. How much does it cost to use this curling iron for a week?
cost= $0.23
37
New cards
very electrical appliance has what? what does that do?
**rating plate. gives us the info so we can calculate the cost**
38
New cards
what is the unit ***ampere?***
a quantity of charges per time
39
New cards
what is the unit volt?
energy per unit charge
40
New cards
what are all the units for energy?
Joules
W•s
kw•h
V•A•s
W•s
kw•h
V•A•s
41
New cards
what are the units for power?
watts and kw
42
New cards
A circuit has a resistance of 10Ω & a current intensity of 5A. What is the potential difference?
V=50v
43
New cards
A circuit has a resistance of 20Ω & a potential difference of 100V. What is the current intensity?
5A
44
New cards
what is a circuit?
it is made up of a power supply, connecting wires and various elements that allow electrons to leave the power source travel through the elements and back to the power source.
45
New cards
what are the 2 types of circuits? what is the difference?
series pen has to follow wire and parallel pen can go in different directions
46
New cards
what is Equivalent Resistance?
the total resistance of the circuit.
47
New cards
what is the formula for Req (equivalent resistance) for series and parallel?
**Series –** ***Req = R1 + R2 + R3***
parallel - 1/req= 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
parallel - 1/req= 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
48
New cards
what is current intensity?
what is __***A***__***mpere?***
what is an ammeter?
what is __***A***__***mpere?***
what is an ammeter?
1. the rate of flow of **electrons** through a wire.
2. coulomb of electrons per second
3. *the instrument used to measure current intensity*
49
New cards
what is potential difference?
what are volts?
what is a voltmeter used for?
what are volts?
what is a voltmeter used for?
1. energetic force that **causes electrons** **to flow**
2. joule per coulomb of electrons. Provided by a battery or power supply
3. used to measure potential difference
50
New cards
what is conductance?
**how easily current flows** through a wire.
51
New cards
formula for conductance?
G= I/V
52
New cards
what is the unit and symbol for conductance?
Units = Siemens Symbol = G Conductance of 1S = 1 amp per volt
53
New cards
hat is the conductance of a circuit with a current intensity of 20A & a potential difference of 5V?
4s
54
New cards
how do you solve conductance on a graph?
***G =* __*∆I (I*__*2*__*– I*__*1*__*)*__**
***∆V (V2-V1)*** use this formula and plug in your 2 points
***∆V (V2-V1)*** use this formula and plug in your 2 points
55
New cards
what is resistance? what is a resistor used for?
how **difficult** it is for current to flow . Resistance is the opposite of conductance. to slow current down.
56
New cards
resistor has? conductor has?
1. high resistance & low conductance
2. low resistance & high conductance
57
New cards
what phenomenon has been used to create electromagnets?
Whenever electricity flows through a wire, a magnetic field is created.
58
New cards
what are the 2 types of conductors that form a magnetic filed from the flow of electrons.
“straight-line” conductor (an uncoiled wire) or a solenoid or a coil (coiled wire)
59
New cards
give info on solenoids
wire rapped around core (tube), they have a current flowing through them, have a magnetic filed, magnetic filed looks like the one of a bar magnet.
60
New cards
what is a core? what influence the strength of the electromagnet? what are some metals that can be used for a core? why is iron used the most and not metals like steal?
1. is the object that is inserted into the solenoid, creating an electromagnet.
2. different materials
3. iron, steel, nickel or cobalt
4. because when you turn off the electricity it demagnetizes.
5. Metals like steel remain magnetized thus creating a permanent magnet.
61
New cards
what are some Factors that affect the Magnetic field of an Electromagnet?
the core metal= ferromagnetic core will increase the strength of the magnetic field
the current intensity= higher current stronger the magnetic field
number of loops/number of turns= more loops strong field
the current intensity= higher current stronger the magnetic field
number of loops/number of turns= more loops strong field
62
New cards
what are some good metals for cores?
**Ferromagnetic cores** strengthen the magnetic field Steel, nickel & cobalt Iron is a VERY GOOD core.
Wood, plastic and aluminum cores do not increase the strength of the magnetic filed.
Wood, plastic and aluminum cores do not increase the strength of the magnetic filed.
63
New cards
To find the strength of the electromagnet scientists use what formula?
F=IN
64
New cards
electromagnet formula what does f n and i stand for?
* ***F*** is force or strength of the electromagnet
* ***I*** is the current intensity traveling through the wire
* ***N*** is the number of loops around the core
* ***I*** is the current intensity traveling through the wire
* ***N*** is the number of loops around the core
65
New cards
explain the Solenoid Rules Right Hand Rule
1. Place palm of right hand on positive end.
2. At the positive end, look to see if the wire is in front or behind the middle tube.
3. If the wire is in front of the tube at the positive end, place your hand on top of the core. If the wire is behind the tube at the positive end, place your hand under the tube.
4. Double check both palm and fingers.
5. Thumb points towards North. The other end is South.
\
66
New cards
where does the needle on the compass point to?
**needle is North** and is attracted to **South.**
67
New cards
what to do When the **+** and the **–** are not given on a diagram
remember that the longer line on the battery is always positive.
68
New cards
explain the Straight Line Conductor \n Right Hand Rule
1. Using your right hand, point your thumb towards the **negative** post hand behind the conductor As long as the thumb points to
negative
2. With your hand open, your finger nails are South and your knuckles are North.
3. If your hand is behind the wire and you cannot see your finger nails, close your hand. **Knuckles are up (N)**
**Nails are down (S)**
69
New cards
what are the 3 types of magnets?
magnet, Ferromagnetic and non-magnet
70
New cards
what is a Ferromagnetic?
is attracted by a magnet, can be magnetized, Most common ferromagnetic substances are **iron**, **nickel** and **cobalt**.
71
New cards
what is a non magnet?
* Is not attracted by a magnet
* Example: glass, plastic, wood, and most metals
* Example: glass, plastic, wood, and most metals
72
New cards
what are the lines around the magnet called give the rules
force that have direction and strength ***magnetic field.***
the **lines never cross**
* they always go from **North to South**
* the **closer** the lines, the **stronger** the attraction
the **lines never cross**
* they always go from **North to South**
* the **closer** the lines, the **stronger** the attraction
73
New cards
what are the 2 types of chemical changes?
physical and chemical
74
New cards
what is a physical change?
it does not change the chemical composition or the nature of the substance. easily reversible. (The substance is still there it only changes the way it appears.)
75
New cards
what are some key words that tell you a physical change has accord?
* Crush/Pulverize
* Melt
* Evaporation
* Condensation
* Sublimation
* Solidification
* Dissolve
* Melt
* Evaporation
* Condensation
* Sublimation
* Solidification
* Dissolve
76
New cards
what are chemical changes?
changes the chemical composition or make up of the substance. new substances are formed with new properties. not easily reversed Reversible only through chemical means or reactions
77
New cards
what are some signs of a chemical change?
formation of a gas, formation of a precipitate, change in color, production heat and or light and increase or decrease in mass.
78
New cards
what do chemical equations consist of what?
reactants and products
79
New cards
what is the law of conservation of mass?
in a chemical reaction mass is neither created nor destroyed.
80
New cards
In a chemical reaction below, how many grams of oxygen (O2) was used given the following information.
O2 = 107 grams
81
New cards
37 grams sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is neutralized with calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
During the reaction, calcium sulphate (CaSO4), a salt, and water are produced. If 14g of water & 51g of salt are produced, how much calcium hydroxide was initially used?
During the reaction, calcium sulphate (CaSO4), a salt, and water are produced. If 14g of water & 51g of salt are produced, how much calcium hydroxide was initially used?
**Ca(OH)2 = 28 grams**
82
New cards
what is the formula for the conservation of matter?
MASS OF REACTANTS = MASS OF PRODUCTS
83
New cards
what are nuclear transformations?
affect the nucleus of the atom where it splits to form new elements. The particles are rearranged.
84
New cards
what are the two types of chemical changes?
oxidation and combustion
85
New cards
what does s, l, g, aq?
solid, liquid, gas and aqueous
86
New cards
what is oxidation?
* Many substances oxidize when they __react with the oxygen in the air or a substance with similar properties to oxygen.__
* __Combustion is a form of oxidation that releases a large amount of energy.__
* Presence of air, light, water and salt can accelerate oxidation
* rust is a form of oxidation
* __Combustion is a form of oxidation that releases a large amount of energy.__
* Presence of air, light, water and salt can accelerate oxidation
* rust is a form of oxidation
87
New cards
what are ways to slow/prevent oxidation?
* Galvanize the metal (coat in Zinc)
* Oil coating
* Rust proofing
* Water proofing
* Add preservatives to food which may oxidize
* Oil coating
* Rust proofing
* Water proofing
* Add preservatives to food which may oxidize
88
New cards
what is combustion?
a form of oxidation that releases a large amount of energy. some examples are Burning wood, cellular respiration, Burning fossil fuels, Principle of the “internal combustion engine”.
89
New cards
what are the 3 types of combustion?
rapid, spontaneous and slow
90
New cards
what is rapid combustion? examples
spectacular and in a short time. it releases a lot of energy in the form of heat or light. ex. candle, log fire, explosion, car engine
91
New cards
what is spontaneous combustion? examples
rapid and without energy from outside sources it unpredictable. ex. dry wood catches fire by itself, hay heats up, some forest fires, oil coated rags
92
New cards
what is slow combustion? examples
occurs over a long period of time and energy is released gradually into the environment. ex. decomposition, fermentation, cellular respiration, metal corrosion
93
New cards
what are the 3 conditions to promote combustion?
1. fuel something to burn such as wood, propane, oil and gas.
2. oxidation agent it causes the fuel to react such as oxygen in the air that’s most common.
3. ignition temperature that’s the minimum temp that combustion starts. its different for each type of fuel.
94
New cards
what is the fire triangle?
its a triangle with the 3 conditions. heat on top then oxygen and fuel.
95
New cards
liquid to solid
freezing or solidification
96
New cards
solid to liquid
melting
97
New cards
solid to gas
sublimation
98
New cards
gas to solid
deposition
99
New cards
gas to liquid
condensation
100
New cards
liquid to gas
evaporation