EXP4064 EXAM 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:53 PM on 3/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
1
New cards

Information processing approach argues 2 points
Mental processes are similar to a computer, info progresses through our cog. Systems in stages
2
New cards
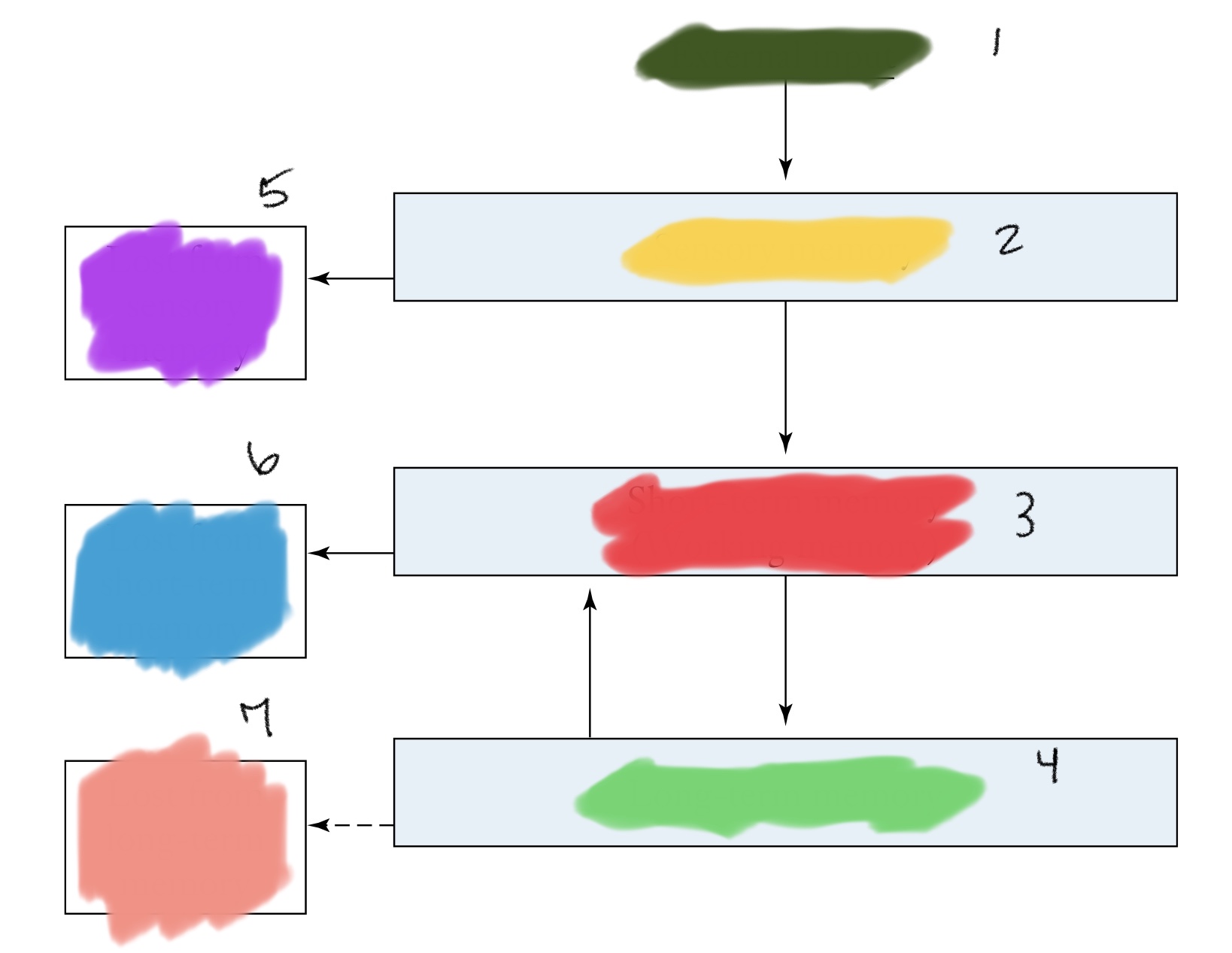
The Atkinson-Shiffrin model proposed that
Memory involves a series of separate steps
3
New cards
Fill in the blanks
External input, sensory memory, short term memory, long term memory, lost from sensory memory, lost from short term memory, lost from long term memory
4
New cards
Sensory memory is a
Storage system that records info from each of the senses with reasonable accuracy
5
New cards
Control processes are
Strategies that people may use to improve their memory
6
New cards
What are 2 characteristics of memory?
Duration,capacity
7
New cards
What are the 3 theoretical subdivisions of long term memory?
Episodic, semantic, procedural (implicit)
8
New cards
2 aspect of LTM
Encoding, retrieval
9
New cards
Encoding means to
Process info to store into LTM
10
New cards
Retrieval means to
Locate info stored in LTM
11
New cards
What are 3 effects on encoding?
Encoding specificity, depth of processing, emotional context
12
New cards
Primacy effect
Superior recall for the first items presented on the list
13
New cards
Recency effect
Superior recall for the last items presented on the list
14
New cards
Serial position effect
Likelihood item remembered depends on its position
15
New cards
3 stages of memory
Encoding, storage, retrieval
16
New cards
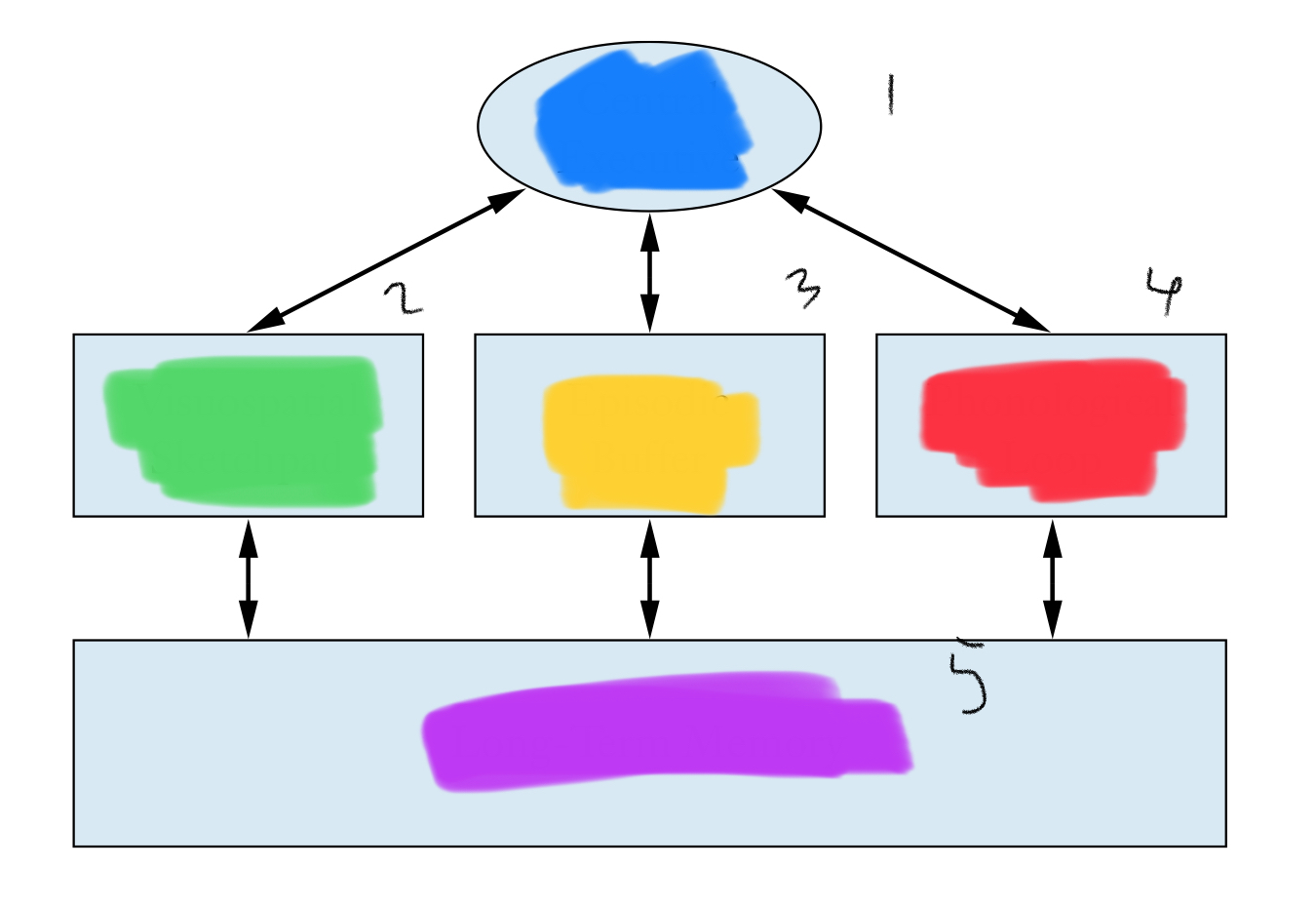
List the missing terms for the baddley and hitch memory approach
Central executive, visuospatial sketch pad, episodic buffer, phonological loop, long term memory
17
New cards
the phonological loop can
Process a limited number of sounds for a short period of time
18
New cards
Visuospatial sketch pad processes
Visual and spatial info
19
New cards
The central executive
Integrates info from the phonological loop, visuospatial sketch pad ,episodic buffer , and LTM
20
New cards
The central executive plans and coordinates but does not
Store info
21
New cards
The episodic buffer serves as a
Temporary storehouse that can hold and combine info from phonological loop, visuospatial sketch pad, and LTM
22
New cards
The episodic buffer actively
Manipulates info so that you can interpret an experience, solve new problems, and plan future activities
23
New cards
STM model =
Storage
24
New cards
WM model =
Use
25
New cards
Working memory approach
Our immediate memory is a multipart system that temporarily holds and manipulates information while we perform cognitive tasks
26
New cards
Working memory is
Immediate memory for material currently processing
27
New cards
LTM refers to
High capacity storage system that contains memories for experiences accumulated across your lifetime
28
New cards
Episodic memory focuses on
Memories for events that happened to me personally
29
New cards
Semantic memory describes
Organized knowledge of my world and facts
30
New cards
Procedural memory refers to
my knowledge about how to do something
31
New cards
Deep levels of processing encourage recall because of _ *and* _
Distinctiveness, elaboration
32
New cards
Distinctiveness means that
A stimulus is different from other memory traces
33
New cards
Elaboration processes
Meaning and interconnected concepts
34
New cards
Encoding specificity states that
Recall better if retrieval is similar to the context during encoding
35
New cards
Emotions and mood can serve as
Contex
36
New cards
___ memories tend to be recalled more
Pleasant
37
New cards
Retrieval of a memory can never occur before storage of a memory?
True
38
New cards
Priming is
Unconscious influence
39
New cards
What subtype of LTM is associated with remembering skills?
Implicit memory
40
New cards
Anterograde means that
new mems cannot be formed
41
New cards
Schemas are
Expectations about objects, events, or situations
42
New cards
Autobiographical memory is
Memory about yourself
43
New cards
Source monitoring refers to
Not sure of the origin of a memory
44
New cards
reality monitoring refers to
Unsure memory actually happened
45
New cards
Flashbulb memories are
Vivid, details mems of emotional events
46
New cards
Explicitly memories are retrieved ____ and are easy to__ __
Consciously, verbalize
47
New cards
Retrograde is
Loss of prior memories
48
New cards
Experts are
Context specific
49
New cards
Retrospective memory is
Remembering info that you acquired in the past
50
New cards
Prospective memory is
Remembering that you need to do something in the future
51
New cards
The term metacognition refers to
Knowledge and control of our cognitive processes
52
New cards
Metamemory refers to
Knowledge, monitoring, and control of mems
53
New cards
Foresight bias
General tendency to be overconfident
54
New cards
Keyboard method
Vocabulary learning or names
55
New cards
What are the two approaches to forming concepts?
Prototype , exemplar
56
New cards
Semantic memory models focus mainly on
Organized knowledge about the world
57
New cards
Situated cognition approach means that
Knowledge depends on context
58
New cards
What is a category?
A set of objects that all belong to the same group
59
New cards
what is a semantic concept?
Mental representation of category
60
New cards
what is the definition of a concept prototype?
a mental item that best represents a category
61
New cards
which of the following is an accurate criticism of the Classical Theory of concept formation?
It inaccurately predicts all elements in a concept will be defined by some key feature
62
New cards
Semantic priming refers to the finding that accessing the meaning of a word is faster if
It is preceded by another word that is related to it in meaning
63
New cards
What are the levels of categorization?
Superordinate, basic, subordinate
64
New cards
What are the 3 characteristics of prototype approach?
Typicality, semantic priming, family resemblance
65
New cards
How does a neural network learn?
Fire together, wire together
66
New cards
What are the basic components necessary for a parallel distributed model of knowledge?
Nodes, connections
67
New cards
According to most network models of semantic memory
When a node is activated by presented info, activation spreads to other nodes to which it is connected
68
New cards
Spontaneous generalization
Creates stereotypes
69
New cards
Default assignment allows for
Stereotyping
70
New cards
abstraction means to
Store the gist of a message
71
New cards
What is proactive interference?
Previously learned material hinders new learning
72
New cards
An implicit memory task is is __ and _
unconscious, automatic
73
New cards
What are the 2 elements of expertise?
Context specific, strategic memory patterns
74
New cards
A heuristic is a
default interpretation
75
New cards
The pragmatic approach argues that
Verbatim memory does occur
76
New cards
A definition to stereotyping is due to the
influence of implicitly held schemas
77
New cards
Carry is trying to memorize her PantherID number. She is having trouble because the number is 9 digits long. _____________ would BEST help Carry learn the number.
A. Repeating the digits over and over to himself
B. Saying the digits out loud
C. Chunking the digits
D. Reading the digits to a friend
A. Repeating the digits over and over to himself
B. Saying the digits out loud
C. Chunking the digits
D. Reading the digits to a friend
Chunking the digits
78
New cards
If people are presented a series of items, their percent recalled typically shows a U-shaped function across serial positions. The recency effect seen in such data is usually attributed to information that:
A. was transferred to long-term memory at the time of presentation.
B. remains in short-term (working) memory at the time of recall.
C. was extremely well remembered because it was associated with earlier information in the series.
D. All of the above are correct.
\
A. was transferred to long-term memory at the time of presentation.
B. remains in short-term (working) memory at the time of recall.
C. was extremely well remembered because it was associated with earlier information in the series.
D. All of the above are correct.
\
Remains in short term (working) memory at the same time of recall
79
New cards
A subject is shown an image of a turtle and asked to keep that item in their WM. After waiting silently for 2 mins, the subject is asked what they remember seeing. The subject responds “a turtle”. Which of the following is likely true?
A. The study shows the Visuospatial Sketchpad has a duration of 2 mins.
B. The subject may have converted the image to a verbal code to rehearse it.
C. The subject could not have performed this tasked while simultaneously singing “row row your boat”
D. Visuospatial Sketchpad duration would have been longer if the subject had to maintain two images in WM.
A. The study shows the Visuospatial Sketchpad has a duration of 2 mins.
B. The subject may have converted the image to a verbal code to rehearse it.
C. The subject could not have performed this tasked while simultaneously singing “row row your boat”
D. Visuospatial Sketchpad duration would have been longer if the subject had to maintain two images in WM.
The subject may have converted the image to verbal code to rehearse it
80
New cards
Visual information cannot be rehearsed in working memory without being transformed into a verbal code.
A. True
B. False
A. True
B. False
False
81
New cards
The component of the working-memory system that combines information from the phonological loop, the visuospatial sketchpad, and long-term memory, which is involved in interpreting earlier experiences, solving new problems, and planning future activities, is called the:
A. perceptual buffer
B. visuospatial sketchpad
C. episodic buffer
D. phonological loop
\
A. perceptual buffer
B. visuospatial sketchpad
C. episodic buffer
D. phonological loop
\
Episodic buffer
82
New cards
According to a recent approach proposed (Baddeley, 2000, 2006), working memory:
A. involves procedural memory, even for information that may also be encoded semantically.
B. is not influenced by attention, by consciousness, or by long-term memory processes.
C. consists of a central executive, a visuospatial sketchpad, an episodic buffer, and a phonological loop.
D. maintains all information in a phonological loop, even if the information is visual or meaningful.
\
A. involves procedural memory, even for information that may also be encoded semantically.
B. is not influenced by attention, by consciousness, or by long-term memory processes.
C. consists of a central executive, a visuospatial sketchpad, an episodic buffer, and a phonological loop.
D. maintains all information in a phonological loop, even if the information is visual or meaningful.
\
Consists of a central executive, a visuospatial sketchpad, an episodic buffer, and a phonological loop
83
New cards
Compared to people who are not depressed, people suffering from major depression:
A. have difficulty with some working memory tasks.
B. show a surprising increase in ability to concentrate on tasks.
C. show an increased span on short-term memory tasks.
D. All of the above are correct.
A. have difficulty with some working memory tasks.
B. show a surprising increase in ability to concentrate on tasks.
C. show an increased span on short-term memory tasks.
D. All of the above are correct.
Have difficulty with some working memory tasks
84
New cards
Research reveals that people's scores on working-memory tasks are correlated with:
A. overall intelligence and grades in school
B.. verbal fluency and reasoning ability.
C. reading ability.
D. All of the above are correct.
A. overall intelligence and grades in school
B.. verbal fluency and reasoning ability.
C. reading ability.
D. All of the above are correct.
All of the above are correct
85
New cards
The region of the brain that it most strongly activated when a person works on tasks that require the central executive component of working memory is the:
A. frontal lobe
B. temporal lobe
C. parietal lobe
D. occipital lobe
\
A. frontal lobe
B. temporal lobe
C. parietal lobe
D. occipital lobe
\
Frontal lobe
86
New cards
The part of the brain that it most strongly activated when a person performs visual and spatial tasks is the:
A. left cerebral hemisphere, especially the frontal and occipital lobes, but including the cerebellum.
B. right cerebral hemisphere, especially the frontal and parietal lobes, but including the occipital lobe.
C. cerebellum.
D. lateral hypothalamus.
A. left cerebral hemisphere, especially the frontal and occipital lobes, but including the cerebellum.
B. right cerebral hemisphere, especially the frontal and parietal lobes, but including the occipital lobe.
C. cerebellum.
D. lateral hypothalamus.
right cerebral hemisphere, especially the frontal and parietal lobes, but including the occipital lobe.
87
New cards
A driver who is listening to a football game on the radio and forming clear images of the action may experience difficulty driving. This interference may be attributable to the limited capacity of a working-memory component called the:
A. central executive.
B. visuospatial sketchpad.
C. episodic buffer.
D. phonological loop.
A. central executive.
B. visuospatial sketchpad.
C. episodic buffer.
D. phonological loop.
Visuospatial sketchpad
88
New cards
The functioning of the phonological loop:
A. may give rise to acoustic confusions in working-memory tasks, especially when rehearsal is involved.
B. is related to a person's "inner voice," or his or her use of subvocalization to perform a task.
C. involves activation or information storage in the left hemisphere of the brain, including frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes
D. All of the above are correct.
\
A. may give rise to acoustic confusions in working-memory tasks, especially when rehearsal is involved.
B. is related to a person's "inner voice," or his or her use of subvocalization to perform a task.
C. involves activation or information storage in the left hemisphere of the brain, including frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes
D. All of the above are correct.
\
All of the above are correct
89
New cards
The effects of proactive interference are decreased if
A. you know more information at the beginning.
B. you keep studying the same list.
C. you learn different items from the same category.
D. you shift to a different category of items to learn.
A. you know more information at the beginning.
B. you keep studying the same list.
C. you learn different items from the same category.
D. you shift to a different category of items to learn.
You shift to a different category of items to learn
90
New cards
What has a bigger impact on your LTM?
A. The intention & desire to remember
B. What you think about while you are studying
C. Time you spend studying
A. The intention & desire to remember
B. What you think about while you are studying
C. Time you spend studying
What you think about while you are studying
91
New cards
Research on levels of processing reveals that deep processing levels enhance recall as a result of two main factors:
A. Distinctiveness & elaboration
B. Distinctiveness & bizarreness
C. Elaboration & interference
D. Bizarreness & interference
A. Distinctiveness & elaboration
B. Distinctiveness & bizarreness
C. Elaboration & interference
D. Bizarreness & interference
Distinctiveness & elaboration
92
New cards
Which of the following facts is Tony most likely to remember next week about the hero Hercules from Greek myth? Why?
A. Hercules rhymes with Achilles
B. Hercules defeated the Hydra, which both start with the letter “H”
C. Hercules captured a Boar and a Bull, which are both similar creatures
D. Hercules fought Tony’s favorite animal, a Lion
A. Hercules rhymes with Achilles
B. Hercules defeated the Hydra, which both start with the letter “H”
C. Hercules captured a Boar and a Bull, which are both similar creatures
D. Hercules fought Tony’s favorite animal, a Lion
Hercules fought Tony’s favorite animal, a lion
93
New cards
Dayna felt consistently stressed while preparing for her final exam. The day of her final, her mood’s surprisingly relaxed throughout the test. Which of the following outcomes might you predict is likely?
A. Dayna will struggle to remember much of the material she studied
B. Her relaxed mood will make it easier to retrieve her exam knowledge from memory
C. Negatively worded questions on the exam will be easier for her to answer
D. Her mood will have no effect on her performance, just her knowledge
A. Dayna will struggle to remember much of the material she studied
B. Her relaxed mood will make it easier to retrieve her exam knowledge from memory
C. Negatively worded questions on the exam will be easier for her to answer
D. Her mood will have no effect on her performance, just her knowledge
Dayana will struggle to remember much of the material she studied
94
New cards
Retrieval of a memory can never precede storage of a memory.
A. TRUE
B. FALSE
A. TRUE
B. FALSE
True
95
New cards
Which of the following is an example of priming?
A. Julia is shown rapid subliminal messages and asked to report which ones she remembers.
B. Joshua unconsciously checks his blindspots before merging after seeing another car hit a bike in its blindspot.
C. Jane is able to still walk on a suspended tightrope even though she has not tried it for many years.
D. Jason is reminded of the first time he went to the Harry Potter theme park in Orlando by a book.
A. Julia is shown rapid subliminal messages and asked to report which ones she remembers.
B. Joshua unconsciously checks his blindspots before merging after seeing another car hit a bike in its blindspot.
C. Jane is able to still walk on a suspended tightrope even though she has not tried it for many years.
D. Jason is reminded of the first time he went to the Harry Potter theme park in Orlando by a book.
Joshua unconsciously checks his blindspots before merging after seeing another car hit a bike in its blindspot.
96
New cards
What subtype of long-term memory is associated with remembering skills?
A. Episodic memory
B. Implicit memory
C. Prospective memory
D. Semantic Memory
A. Episodic memory
B. Implicit memory
C. Prospective memory
D. Semantic Memory
Implicit
97
New cards
Omar tells his friend Chris an interesting fact about the Center for the Arts. Chris replies, “I was the one who told you about that in the first place.” In this situation, Omar is suffering from a lapse in ________.
A. flashbulb memory
B. source monitoring
C. proactive interference
D. encoding specificity
A. flashbulb memory
B. source monitoring
C. proactive interference
D. encoding specificity
Source monitoring
98
New cards
Leigh studied French in high school and Italian in college. While communicating with a **French** business associate, she often found herself using some *Italian words* in her e-mail messages. This type of memory failure is called _______________.
A. Proactive interference
B. Retroactive interference
C. Decay
D. Consolidation
A. Proactive interference
B. Retroactive interference
C. Decay
D. Consolidation
Retroactive interference
99
New cards
A person (such as H.M.) who receives damage to the hippocampus and suffers from anterograde amnesia will show considerable difficulty:
A. performing implicit memory tasks, such as word-guessing games and word-completion tasks.
B. encoding new events into long-term memory so that they can be explicitly recalled later.
C. retrieving information from long-term memory that was encoded prior to the hippocampal damage.
D. learning new motor skills, such as skiing, and automatic behaviors, such as classical conditioning.
A. performing implicit memory tasks, such as word-guessing games and word-completion tasks.
B. encoding new events into long-term memory so that they can be explicitly recalled later.
C. retrieving information from long-term memory that was encoded prior to the hippocampal damage.
D. learning new motor skills, such as skiing, and automatic behaviors, such as classical conditioning.
encoding new events into long-term memory so that they can be explicitly recalled later.
100
New cards
A middle-school teacher places words such as "calm" and "success" on the walls of his classroom to make his students feel more at ease and improve their drive for achievement. This teacher is trying to take advantage of the effects of _____________.
A. procedural memory
B. priming
C. retroactive interference
D. encoding specificity
A. procedural memory
B. priming
C. retroactive interference
D. encoding specificity
Priming