Pre-AP_Biology_2025_Midterm_Exam_Review
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pre-ap bio mid term review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Ecology
The study of interactions among organisms and their environment.
Ecosystem
A community of living organisms and their physical environment interacting as a system.
Biotic factors
Living components of an ecosystem, such as plants and animals.
Abiotic factors
Non-living components of an ecosystem, such as climate and soil.
Cycling of Matter
The process by which matter is recycled in an ecosystem.
Energy Flow
The transfer of energy through an ecosystem, typically from sunlight to producers and then to consumers.
Geosphere
The solid Earth, including rocks, minerals, and landforms.
Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding Earth.
Hydrosphere
All the water on Earth, including oceans, rivers, and groundwater.
Biosphere
The global sum of all ecosystems; the zone of life on Earth.
Biogeochemical cycle
The movement of elements and compounds through living organisms and the environment.
Water Cycle
The continuous movement of water through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
Carbon Cycle
The series of processes by which carbon compounds are interconverted in the environment.
Nitrogen Cycle
The process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms.
Population
A group of individuals of the same species living in a specific area.
Growth Rate
The change in population size over time.
Density
The number of individuals per unit area.
Distribution Patterns
The way in which individuals are spaced within an area.
Exponential Growth Model
A growth model that describes populations that grow rapidly when resources are plentiful.
Logistic Growth Model
A growth model that describes populations whose growth slows as resources become limited.
r-selected species
Species that reproduce quickly and often in unstable environments.
K-selected species
Species that reproduce more slowly and have fewer offspring in stable environments.
Trophic Levels
The hierarchical levels in an ecosystem, comprised of producers, consumers, and decomposers.
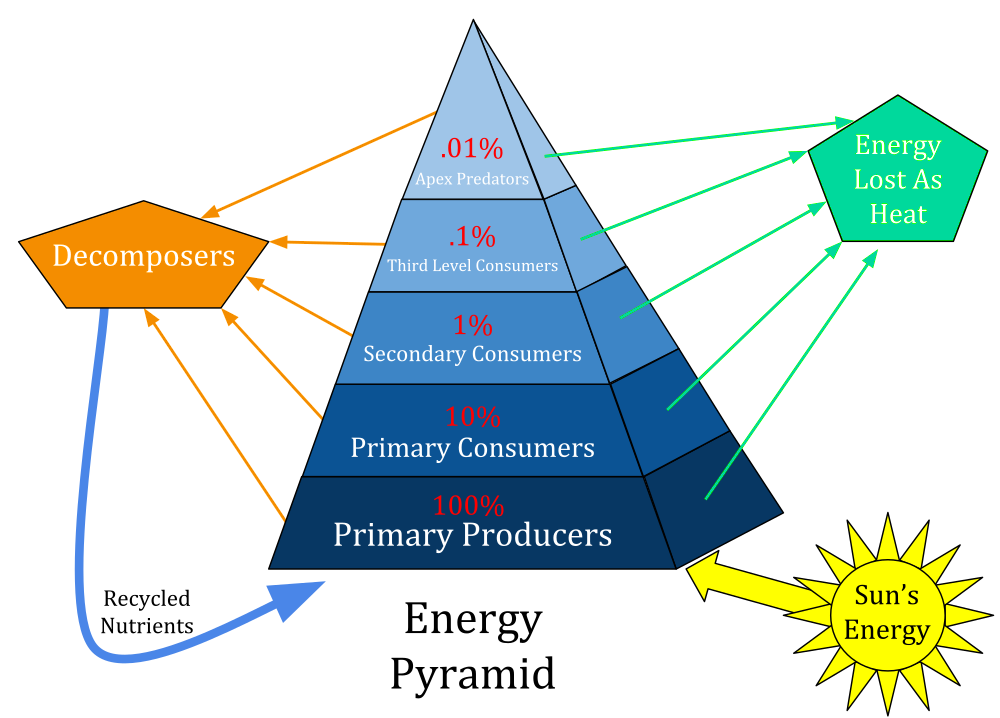
Energy Pyramid
A graphical representation of energy flow in an ecosystem, depicting energy at different trophic levels.
10% Rule
The ecological principle stating that only about 10% of the energy from one trophic level is passed on to the next.
Biodiversity
The variety and variability of life forms within a given ecosystem.
Genetic Diversity
The variety of genes within a species.
Species Diversity
The variety of species within a given area.
Ecosystem Diversity
The variety of ecosystems in a given area.
HIPPO
An acronym representing the threats to biodiversity: Habitat destruction, Invasive species, Pollution, Population growth, Overharvesting.
Biome
A large geographic biotic unit, a major community of plants and animals with similar life forms and environmental conditions.
Primary Succession
The process of community development on previously uninhabited land.
Secondary Succession
The process of ecosystem recovery after a disturbance.
Climax Community
A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species composition.
Pioneer Species
The first species to colonize previously uninhabited land.
Natural Selection
The process by which individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Survival of the Fittest
The concept that the individuals best adapted to their environment survive and reproduce.
Adaptation
A trait that enhances an individual's fitness in a particular environment.
Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequencies in a population, often having a significant effect in small populations.
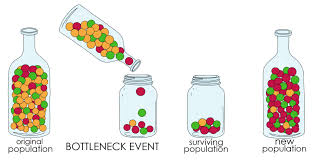
Bottleneck Effect
A sharp reduction in population size due to environmental events or human activities.
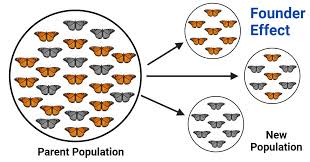
Founder Effect
A situation in which a small group becomes isolated from a larger population, leading to a reduced genetic diversity.
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
A principle stating that allele and genotype frequencies in a population remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary influences.
Speciation
The formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.
Prezygotic Barriers
Reproductive barriers that occur before fertilization.
Postzygotic Barriers
Reproductive barriers that occur after fertilization.
Allopatric Speciation
Speciation that occurs when populations are geographically isolated.
Sympatric Speciation
Speciation that occurs without geographic separation.
Homologous Structures
Body parts in different species that share a common ancestry.
Analogous Structures
Body parts in different species that have similar functions but different evolutionary origins.
Vestigial Structures
Body parts that have lost their original function through evolution.
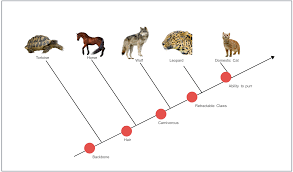
Cladogram
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species.
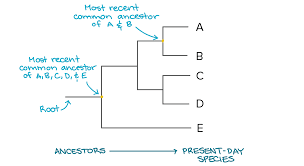
Phylogenetic Tree
A branching diagram that represents the evolutionary history of a group of organisms.
Ecological Succession
The process of change in the structure of a community over time.
Trophic Structure
The feeding relationships among the various species in an ecosystem.
Community
An assemblage of different species living together in a defined area.
Fundamental Niche
The full range of environmental conditions under which a species can survive.
Realized Niche
The actual conditions and resources in which a species exists due to biotic interactions.
Optimum Range
The range of environmental conditions that are most favorable for a species.
Keenstone Species
A species that has a disproportionately large effect on its environment relative to its abundance.
Symbiosis
A close, long-term interaction between two different biological species.
Mutualism
A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit.
Commensalism
A symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Parasitism
A symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits at the expense of another.
Climate Change
Long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions.
Invasive Species
Non-native species that disrupt local ecosystems.
Habitat Destruction
The process by which natural habitat becomes unable to support the species present.
Evolutionary Scientists
Researchers who study the processes and evidence of evolution.
Lamarck
An early evolutionary scientist who proposed the theory of inherited characteristics.
Charles Darwin
The scientist known for his theory of evolution through natural selection.
Common Ancestor
An ancestor shared by two or more descendants in the evolutionary lineage.
Homology
Similarity in structure due to shared ancestry.
DNA Evidence
Genetic material that provides insights into evolutionary relationships.
Comparative Embryology
The study of the similarities and differences in the embryos of different species as evidence of evolution.
Diversity of Aquatic Biomes
The varied ecosystems found in water environments, such as lakes, rivers, and oceans.
Tropical Rainforest
A biome characterized by high rainfall and a vast diversity of species.
Savanna
A grassy plain in tropical and subtropical regions, with few trees.
Desert
A biome that receives very little precipitation and has a distinct temperature and plant ecosystem.
Temperate Grassland
A biome characterized by grasses and few trees, found in temperate regions.
Temperate Forest
A biome characterized by deciduous trees that lose their leaves in winter.
Boreal Forest
A biome consisting mostly of coniferous forests, found in northern regions.
Tundra
A biome characterized by cold temperatures and a short growing season.
Community Dynamics
The interactions and changes in a community over time.
Fundamental vs. Realized Niche
Difference between the full potential habitat of a species and the actual habitat it occupies.
Tolerance Range
The range of conditions within which a species can survive.
Pioneer Species
Species that first colonize previously disrupted or damaged ecosystems.
Main Processes of Water Cycle
Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, and runoff.
Natural Selection Conditions
Overproduction, heritable variation, and variable fitness among individuals.
Five Conditions of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Large population size, no migration, no mutations, random mating, and no selection.
Main Processes of Carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion.
Main Processes of Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, and ammonification.
Three Types of Distribution Patterns
Clumped, uniform, and random distribution.
Biodiversity Value
Biodiversity is important for ecosystem services, resilience, and human well-being.
Mass Extinctions
Events in which a significant percentage of all life on Earth became extinct.
Ecosystem Engineers
Species that significantly modify their environment and create new habitats.
Mass Extinctions Impact
Mass extinctions lead to significant changes in biodiversity and ecosystem structure.
Ecological Niches Importance
Different niches help minimize competition for resources among species.
Predation
The interaction where one organism (the predator) kills and eats another (the prey).
Competition
The struggle between organisms for the same resources in a given habitat.
Thomas Malthus
An economist whose theories on population growth influenced Darwin's concepts of natural selection.
Alfred Russel Wallace
A naturalist who independently proposed a theory of evolution through natural selection, co-publishing with Darwin.