FIN453 Lecture 5
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key vocabulary related to private debt, its characteristics, and its role in investment strategies.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
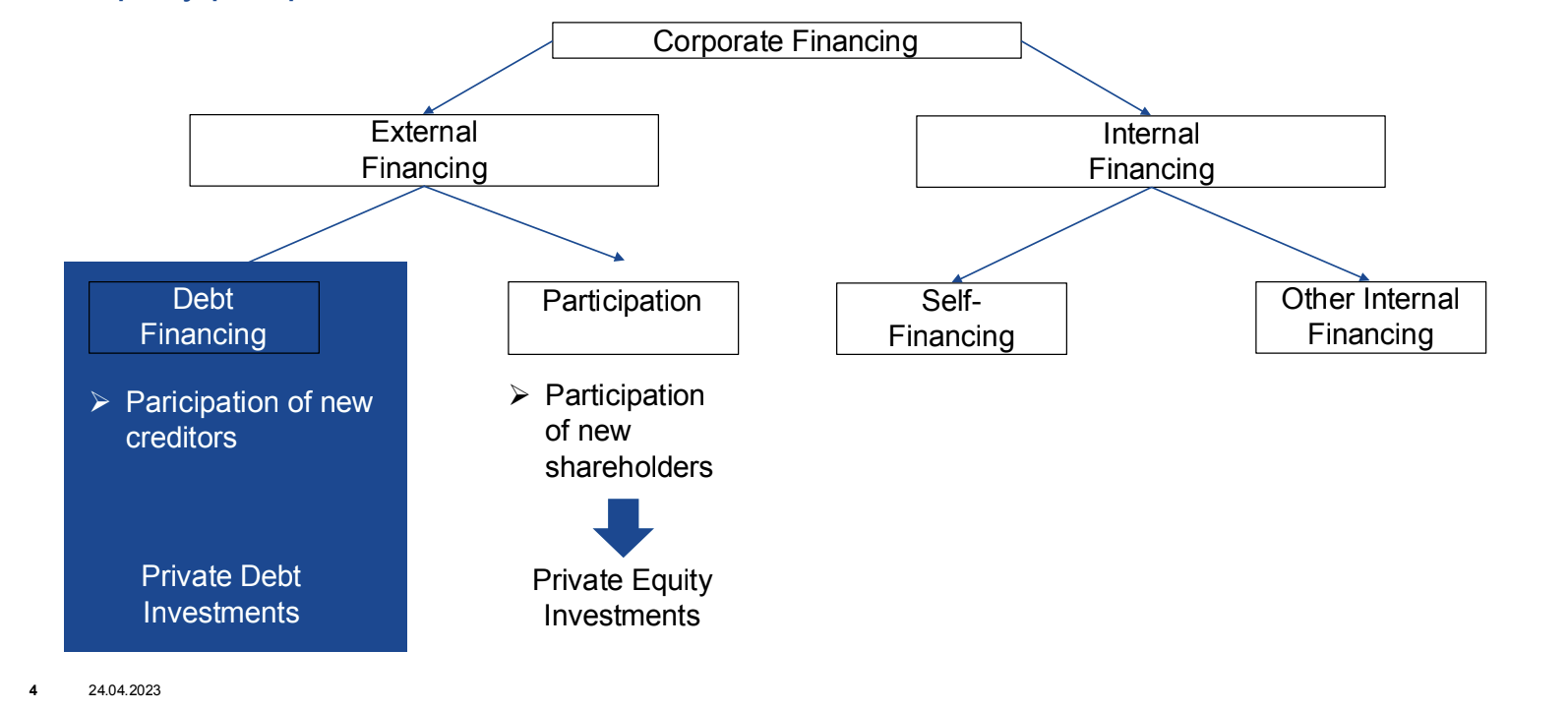
Private Debt
Loans that are privately negotiated between a lender and a borrower, often characterized by various types of securities like senior, junior, or mezzanine.
Direct Lending
A form of private debt where nonbank asset managers issue loans directly to companies.
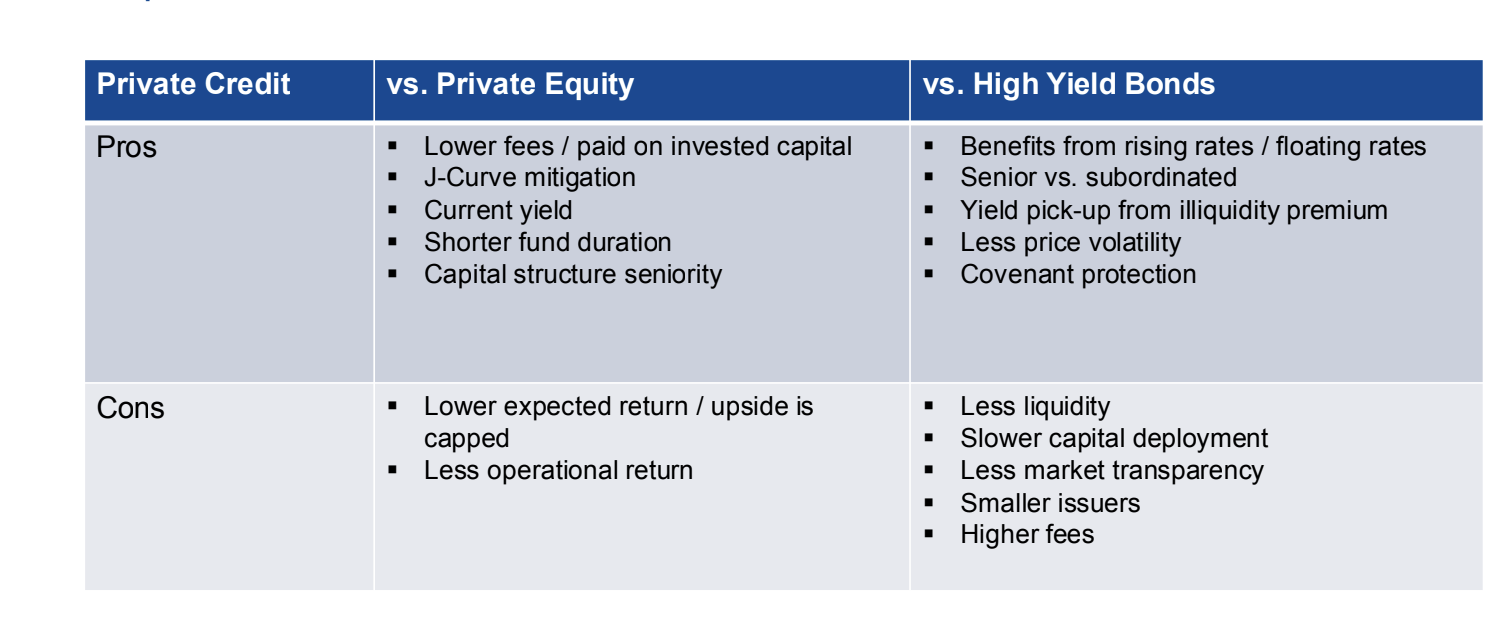
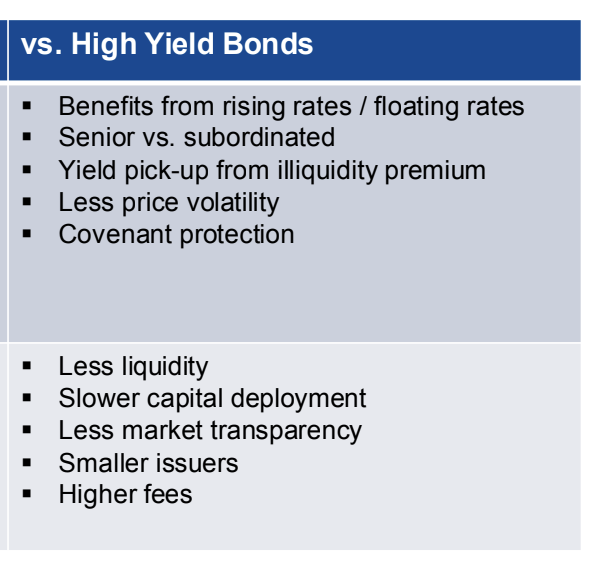
Illiquidity Premium
Higher yields offered by private debt due to illiquidity, compensating investors for the inability to quickly sell loans.
Mezzanine Debt
A subordinated (junior) debt that typically has a higher risk compared to senior loans but offers higher returns.
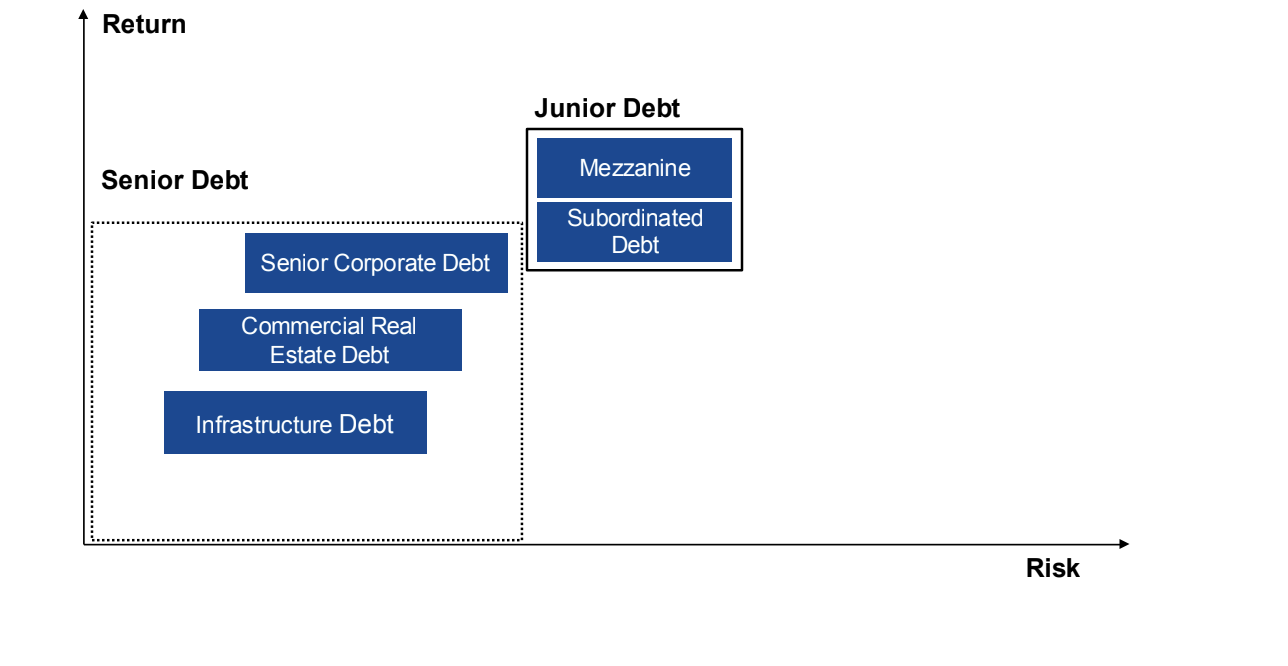
Tranche
A portion, piece, or slice of a pool or series of securities, often with different risk levels and returns.
Senior (like a classic bank loan), junior (either structured together with the senior tranche or is often taken up as further additional debt) and subordinated (Not used as a uniform term. In general, it is a tranche that is subordinated to any other debt capital and is structured without collateral)

Covenants
Conditions that borrowers agree to abide by in a loan agreement, helping reduce default risk.
Credit Risk
The risk of loss due to a borrower's failure to make payments on any type of debt.
Portfolio Diversification
The practice of spreading investments among various financial instruments, industries, and other categories to reduce risk.
Institutional Investors
Organizations that invest on behalf of their members, such as pension funds, insurance companies, and endowments.
High-Yield Bonds
Bonds that are rated below investment grade and offer higher returns due to increased risk.
Lower Market
Refers to companies with smaller revenue or capitalization that may seek funding through private debt.
Floating Rate Structures
Loans where the interest rate can change based on changes in a benchmark rate.
High-Yield Premium
Extra yield offered by private debt investments to compensate for risks not present in traditional investments.
Types
Direct lending, Senior / Junior debt, Mezzanine