PSIO 107 Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:22 PM on 3/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
1
New cards
What color is Blood
Hemoglobin (red)- iron
Vanabin (yellow)- vanadium
cholorocruorin (green)
Hemocyanin (blue)- copper
Hemerythrin (purple) - no heme component
Vanabin (yellow)- vanadium
cholorocruorin (green)
Hemocyanin (blue)- copper
Hemerythrin (purple) - no heme component
2
New cards
Functions of blood
* carry oxygen and carbon dioxide
* provide capability of defense by carrying immune cells and antimicrobial chemicals
* carry blood clotting cells and substances
* carry nutrients and wastes
* provide capability of defense by carrying immune cells and antimicrobial chemicals
* carry blood clotting cells and substances
* carry nutrients and wastes
3
New cards
composition of blood
formed elements
* erythrocytes (red blood cells)
* Leukocytes (white blood cells)
* thrombocytes (platelets)
plasma
* erythrocytes (red blood cells)
* Leukocytes (white blood cells)
* thrombocytes (platelets)
plasma
4
New cards
Erythrocytes
RBCs
contain hemoglobin
* binds oxygen (and CO2)
* each hemoglobin can carry 4 oxygen molecules
* approximately 250,000 hemoglobin molecules per RBC
contain hemoglobin
* binds oxygen (and CO2)
* each hemoglobin can carry 4 oxygen molecules
* approximately 250,000 hemoglobin molecules per RBC
5
New cards
Mature RBCs do not have a nucleus
maximizes oxygen-carrying capability
sacrifices ability to repair self
* life span \~ 120 days
sacrifices ability to repair self
* life span \~ 120 days
6
New cards
RBC concentration stays constant
RBCs are replaced from red bone marrow by demand
* process of erythropoiesis
* process of erythropoiesis
7
New cards
Red Blood Cell Pathologies: Too few RBCs
Anemia
* nutritional problems
* sickle cell anemia
* kidney problems
* blood loss
* iatrogenic issue
* nutritional problems
* sickle cell anemia
* kidney problems
* blood loss
* iatrogenic issue
8
New cards
Too many RBCs
Polycythemia
* tumor-causing overproduction
* respiratory disease compensation
* performance-enhancing practice
* tumor-causing overproduction
* respiratory disease compensation
* performance-enhancing practice
9
New cards
Leukocytes
WBCs
10
New cards
Granulocytes
* basophils
* produce heparin and histamine
* Neutrophils
* phagocytes
* Eosinophils
* respond to parasites or allergens
* produce heparin and histamine
* Neutrophils
* phagocytes
* Eosinophils
* respond to parasites or allergens
11
New cards
Agranulocytes
* monocytes
* turn into macrophages when activated
* lymphocytes
* T-cells and B-cells
* Control immunity
* turn into macrophages when activated
* lymphocytes
* T-cells and B-cells
* Control immunity
12
New cards
Leukocyte Functions
* vital for immune response to pathogens and host defenses
* neutrophil engulfing bacterium (very cool)
* neutrophil engulfing bacterium (very cool)
13
New cards
Platelets
* originate from megakaryocytes
* mediate part of the clotting process
* mediate part of the clotting process
14
New cards
Hemostasis consists of three parts
Vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, coagulation
15
New cards
vascular spasm
serotonin induced vasoconstriction
16
New cards
Platelet plug formation
* sticky platelets attach to exposed collagen
* net of platelets contract to reduce size of gap
* net of platelets contract to reduce size of gap
17
New cards
Coagulation
* “clotting cascade”- inactive substances are activated to induce the formation of the clot
* positive feedback cycle which culminates in cessation of leaking blood
* final step of cascade is fibrinogen converted to fibrin
* positive feedback cycle which culminates in cessation of leaking blood
* final step of cascade is fibrinogen converted to fibrin
18
New cards
inappropriate clotting
* plaque formation can activate platelets
* blood pooled in varicose veins can coagulate
* thrombus formation → embolus
* blood pooled in varicose veins can coagulate
* thrombus formation → embolus
19
New cards
too little clotting
* hemophilia
* hereditary (genetic link) - lack of clotting factor
* multiple sub-types
* hereditary (genetic link) - lack of clotting factor
* multiple sub-types
20
New cards
Hematopoiesis
blood cells form from stem cell pop. in red bone marrow
* also, yolk sac, liver and spleen during development
RBC formation stimulated by erythropoietin
WBC and platelet formation due to similar factors
* also, yolk sac, liver and spleen during development
RBC formation stimulated by erythropoietin
WBC and platelet formation due to similar factors
21
New cards
Plasma
92% water
remaining composition is:
* plasma proteins (albumin, globulins, clotting factors, fibrinogen)
* electrolytes (0.9% NaCl, K, Ca, phosphate, and others)
* nutrients (carbs, lipids, amino acids, vitamins)
* metabolic wastes (urea, ketoacids, bilirubin)
* respiratory gases (O2, CO2)
* hormones
plasma without clotting is called serum
\*coconut blood can serve as a substitute, FOR PLASMA
remaining composition is:
* plasma proteins (albumin, globulins, clotting factors, fibrinogen)
* electrolytes (0.9% NaCl, K, Ca, phosphate, and others)
* nutrients (carbs, lipids, amino acids, vitamins)
* metabolic wastes (urea, ketoacids, bilirubin)
* respiratory gases (O2, CO2)
* hormones
plasma without clotting is called serum
\*coconut blood can serve as a substitute, FOR PLASMA
22
New cards
ABO system
Type A, B, AB, O
23
New cards
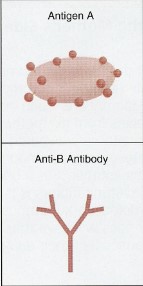
Type A
has A anitgen, B antibody
24
New cards
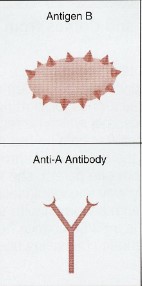
Type B
has B antigen, A antibody
25
New cards
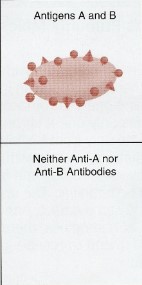
Type AB
has both A and B antigens ( no antibodies)
26
New cards
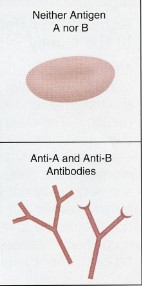
Type O
has both A and B antibodies (no antigens)
27
New cards
Rh factor
* Also called D antigen, identified from Rhesus Monkey blood
* Rh+ blood contains the Rh-antigen
* Rh- blood does not contain the antigen
* NOTE: must be exposed to Rh antigen before producing an anti-Rh antibody
* this becomes relevant for pregnant patients and their developing fetuses
* Common nomenclature: ABO type followed by Rh factor status
* Ex: O-, A+, etc.
* Rh+ blood contains the Rh-antigen
* Rh- blood does not contain the antigen
* NOTE: must be exposed to Rh antigen before producing an anti-Rh antibody
* this becomes relevant for pregnant patients and their developing fetuses
* Common nomenclature: ABO type followed by Rh factor status
* Ex: O-, A+, etc.
28
New cards
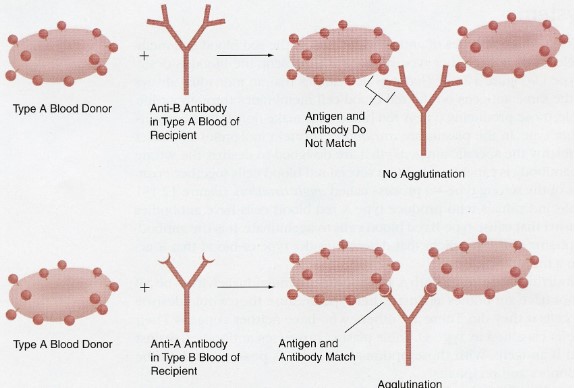
Blood transfusion reactions
agglutination will occur if incompatible blood types are mixed
29
New cards
Someone with Type A blood cannot receive type B blood transfusion. What component int the type A blood makes it so that they can’t receive a type B blood infusion?
Anti-B antibody; because if we anti-B antibody in the Type A blood, the B antigens in Type B blood would cause agglutination, causing improper clotting.
30
New cards
Which blood is the best donor blood
Type O, but Type O recipients can only receive Type O blood
31
New cards
Which blood type is least picky or can accept both Type A or Type B
AB, just dont give an AB type O blood
32
New cards
CV system
* heart
* dual-sided, 4-chamber pump
* Arteries and veins
* conduction vessels (conduits)
* Arterioles and venules
* resistance vessels (regulate blood flow)
* Capillaries
* Nutrient exchangers with high-surface area
* Closed circuit w/ 2 “sides”
* pulmonary loop
* systemic loop
* dual-sided, 4-chamber pump
* Arteries and veins
* conduction vessels (conduits)
* Arterioles and venules
* resistance vessels (regulate blood flow)
* Capillaries
* Nutrient exchangers with high-surface area
* Closed circuit w/ 2 “sides”
* pulmonary loop
* systemic loop
33
New cards
Heart overview
Sits in mediastinum of thoracic cavity
4 chambers
* 2 atria
* 2 ventricles
4 major vessels
* Vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, Aorta
Coronary circulation (supplies cardiac cells)
heart wall is layered
* epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
4 chambers
* 2 atria
* 2 ventricles
4 major vessels
* Vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, Aorta
Coronary circulation (supplies cardiac cells)
heart wall is layered
* epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
34
New cards
Pericardium
double-walled serous membrane surrounding the heart
* visceral pericardium
* parietal pericardium
anchors and suspends heart
* shock-absorption and freedom of movement
provides lubrication during movement
* visceral pericardium
* parietal pericardium
anchors and suspends heart
* shock-absorption and freedom of movement
provides lubrication during movement
35
New cards
Pericardial fluid
fills the “potential space” inbetween visceral and parietal pericardium
* can become pathologic if fluid builds up → becomes pericardial effusion
* can become pathologic if fluid builds up → becomes pericardial effusion
36
New cards
Coronary Circulation
* right coronary artery
* \~25% of heart tissues
* left coronary artery
* \~75% of heart tissues
* some exceptions because not all hearts have the same coronary artery dominant pattern
* \~25% of heart tissues
* left coronary artery
* \~75% of heart tissues
* some exceptions because not all hearts have the same coronary artery dominant pattern
37
New cards
Major blood vessels associated with the Heart
1. superior/inferior Vena Cava
2. Pulmonary Trunk
3. Pulmonary Veins
4. Aorta
38
New cards
Superior/inferior Vena Cava
venous return (of deO2 blood) from systemic circulation
39
New cards
Pulmonary Trunk
deO2 blood to lung circulation
40
New cards
Pulmonary Veins
O2 blood from lung circulation
41
New cards
Aorta
O2 blood to systemic circulation
42
New cards
Internal anatomy of heart
4 Heart Chambers
* right atrium and ventricle
* left atrium and ventricle
4 valves
* right and left atrioventricular valves
* tricuspid and mitral valves
* right and left semilunar valves
* pulmonic and aortic valves
* right atrium and ventricle
* left atrium and ventricle
4 valves
* right and left atrioventricular valves
* tricuspid and mitral valves
* right and left semilunar valves
* pulmonic and aortic valves
43
New cards
Heart valves
function as one-way doors to prevent backwards blood flow
* Open/close determined by pressure gradient of blood in vessels and heart chambers
* Open/close determined by pressure gradient of blood in vessels and heart chambers
44
New cards
Pacemakers
set rate of heartbeat
* Sinoatrial node (SA node) (75 bpm; sets the pace normally, since its the fastest)
* atrioventricular node (40 bpm)
* purkinje fibers (25 bpm)
pattern of impulse is dependent on where the impulse is started
* Sinoatrial node (SA node) (75 bpm; sets the pace normally, since its the fastest)
* atrioventricular node (40 bpm)
* purkinje fibers (25 bpm)
pattern of impulse is dependent on where the impulse is started
45
New cards
Conduction pathway
SA node → atrial syncytium → AV node → Bundle of His → Left/Right bundle branches → Purkinje Fibers
* SA node depolarizes atrium
* Bundle of His depolarizes ventricular septum
* Purkinje Fibers depolarizes ventricular free walls
* SA node depolarizes atrium
* Bundle of His depolarizes ventricular septum
* Purkinje Fibers depolarizes ventricular free walls
46
New cards
Electrocardiograms
Aka EKG or ECG
* no-invasive, diagnostic meas. of the electrical activity of the heart
* no-invasive, diagnostic meas. of the electrical activity of the heart
47
New cards
What do EKGs determine:
* cardiac metrics (P-R interval, R-R interval, etc) and orientation of heart
* Extent/location of ischemic damage
* effect of pharmaceuticals or other drugs and electrolyte disturbances
* Extent/location of ischemic damage
* effect of pharmaceuticals or other drugs and electrolyte disturbances
48
New cards
Which of these heart electrical components
signals frst in the the normal cardiac cycle?
signals frst in the the normal cardiac cycle?
Sinoatrial (SA) node
49
New cards
The sinoatrial (SA) node normally sets the pace
of the heartrate around which value?
of the heartrate around which value?
75 bpm
50
New cards
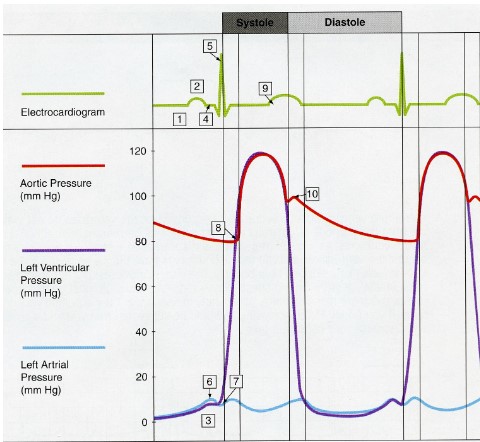
Wiggers Diagram
a visual representation of the events throughout a complete heartbeat sequence (cardiac cycle)
51
New cards
Cardiac Cycle
each half of the heart ejects the same amount of blood
52
New cards
Cardiac cycle stage 1
atrial systole: atria contract, AV valves open, semilunar valves closed
53
New cards
Cardiac cycle stage 2
Early Ventricular Systole: atria relax, ventricles contract AV valves forced closed, semilunar valves still closed
54
New cards
Cardiac cycle stage 3
Late Ventricular Systole: atria relax, ventricles contract, AV valves remain closed, semilunar valves forced open
55
New cards
Cardiac cycle stage 4
Early Ventricular Diastole: atria and ventricles relax, AV valves and semilunar valves closed, atria begin passively filling with blood
56
New cards
Cardiac cycle stage 5
Late Ventricular Diastole: atria and ventricles relax, atria passively fill with blood as AV valves open, semilunar valves closed
57
New cards
Which of these sets of valves opens as the
ventricles begin to contract in the the normal
cardiac cycle?
ventricles begin to contract in the the normal
cardiac cycle?
aortic and pulmonic valves
58
New cards
Cardiac output (mL/min) =
HR (bpm) X Stroke volume (mL/beat)
* 5040mL = 72 bpm X 70 mL/beat)
* 5040mL = 72 bpm X 70 mL/beat)
59
New cards
Stroke volume is a function of venous return and cardiac contractility
* \~70mL per beat average
* Altered through muscular pumping, venous return
* sympathetic nerves increase this too
* Altered through muscular pumping, venous return
* sympathetic nerves increase this too
60
New cards
Frank - Starling Law of the Heart
* the normal heart will pump out most of the volume that is returned to it, including increases
* increased venous return → increase stroke volume
* increased venous return → increase stroke volume
61
New cards
Low BP
Sympathetic input → increased heart rate and contractility
Sympathetic effects SA node and motor neurons
Sympathetic effects SA node and motor neurons
62
New cards
High BP
Parasympathetic output → reduced heart rate
63
New cards
A person stands up quickly and feels dizzy for a few
seconds before steadying. Knowing that the
autonomic nervous system helps maintain BP, what
type of response did this standing trigger?
seconds before steadying. Knowing that the
autonomic nervous system helps maintain BP, what
type of response did this standing trigger?
sympathetic
64
New cards
Cardiac output is infuenced by stroke volume. Which
of the following factors/actvites increases stroke
volume?
of the following factors/actvites increases stroke
volume?
* leg muscles pumping while walking
* adrenaline rush from seeing a bear on a hike
* adrenaline rush from seeing a bear on a hike
65
New cards
Blood vessels
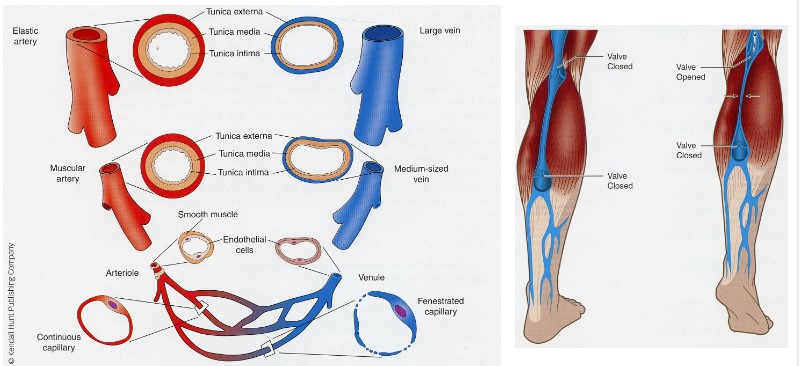
66
New cards
arteries
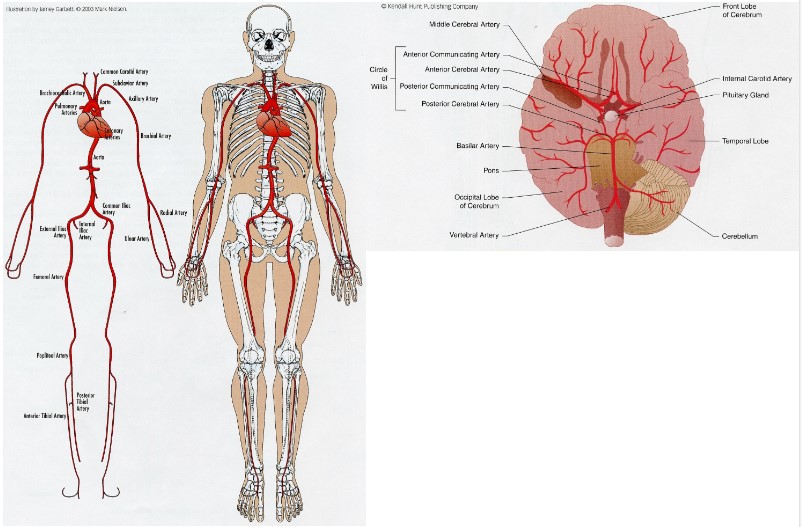
aorta branches into 3 parts
* Right side: Brachiocephalic Artery
* right common carotid artery
* Left common carotid artery
* subclavian artery
* Right side: Brachiocephalic Artery
* right common carotid artery
* Left common carotid artery
* subclavian artery
67
New cards
veins
know portal circulation?
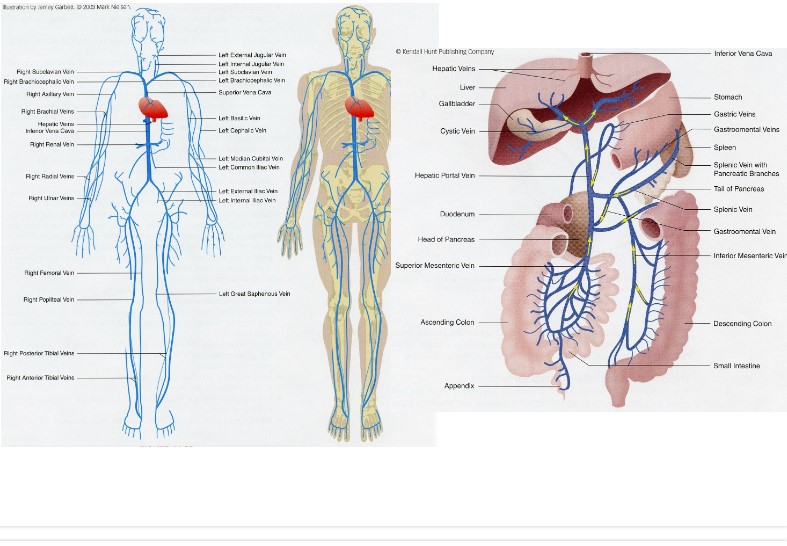
68
New cards
Fetal circulation
Contains shunts which redirect blood to systemic circulation
* foramen ovale
* ductus arteriosus
* foramen ovale
* ductus arteriosus
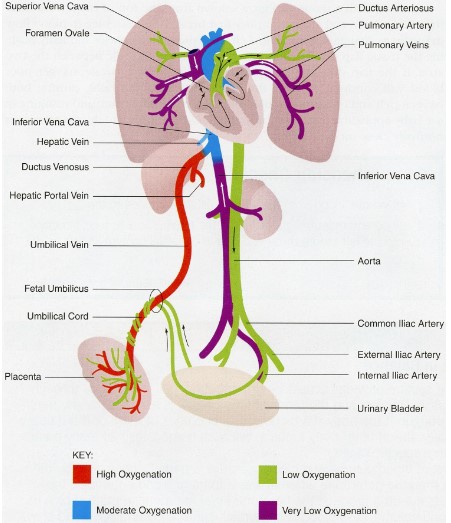
69
New cards
Which of the following structures have one-
way valves?
way valves?
veins
70
New cards
In the fetal circulaton, which has the highest
oxygen concentraton in the blood it contains?
oxygen concentraton in the blood it contains?
umbilical vein
71
New cards
Describe the layered appearance, from top to bottom, of a tube of blood that has been centrifuged to obtain a hematocrit.
Plasma, buffy coat, red blood cells
72
New cards
Mature erythrocytes do not have a nucleus.
true
73
New cards
An individual may have an infection is his buffy coat is thicker than normal.
TRUE
74
New cards
Which fluid associated with blood does not contain clotting factors?
Serum
75
New cards
An embolism is
a thrombus that has gotten loose and become stuck in the vasculature
76
New cards
The condition whereby there are too many erythrocytes (RBCs) is
polycythemia
77
New cards
Which of the white blood cells are the phagocytic cell largely responsible for removing debris?
neutrophils
78
New cards
The end event of the clotting cascade and subsequent formation of a blood clot is the conversion of
fibrinogen to fibrin
79
New cards
Mothers who have type A- blood that are pregnant with their second type A+ child will have to worry about erythroblastosis fetalis (Rh antibody reaction with Rh antigen).
TRUE
80
New cards
The cells that are responsible for cell- and antibody-mediated immunity are
lymphocytes
81
New cards
Platelets are best defined as
cytoplasmic fragments of cells
82
New cards
Which of the white blood cells are important with parasitic infection?
eosinophils
83
New cards
Which step in hemolysis is caused by the release of serotonin from vascular wall cells?
vascular spasm
84
New cards
Which of the white blood cells are important in the specific defense mechanisms (immunity)?
lymphocytes
85
New cards
What characteristic is shared by eosinophils and basophils?
they are granulocytes
86
New cards
Which hematocrit value would likely be seen with anemia?
35%
87
New cards
Which of the following is an example of a specific body defense mechanism?
immunity
88
New cards
When the heart contracts, into what type of vessel is blood pumped first?
arteries
89
New cards
Heart valves open because of specialized valve muscles that pull them open.
false
90
New cards
A normal heart is governed only by its pacemakers and not by nervous or endocrine input.
false
91
New cards
Which blood vessels serve as the "body's resistance vessels"?
arterioles
92
New cards
Which of the following would enhance blood return to the heart?
skeletal muscles pumping
93
New cards
Which heart chamber receives blood from the peripheral circulation?
right atrium
94
New cards
Arteries have thicker walls than veins.
TRUE
95
New cards
Which heart chamber sends blood to the peripheral circulation?
Left ventricle
96
New cards
In which part of the vasculature does nutrient and waste exchange occur with the body's tissues?
capillaries
97
New cards
Depolarization of a cardiac muscle cell is similar to skeletal muscles with the exception of the movement of which ion across the membrane to lengthen the duration of the action potential?
Calcium
98
New cards
Identify the type of vessel that sits between two capillary beds, such as between the intestines and liver capillaries.
portal vein
99
New cards
The blood pressure in the systemic arteries is greatest during
ventricular systole
100
New cards
Metabolically active tissues have more extensive capillary networks.
TRUE