Digestive System
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Type of cell tissue found in digestive track
simple columnar and goblet
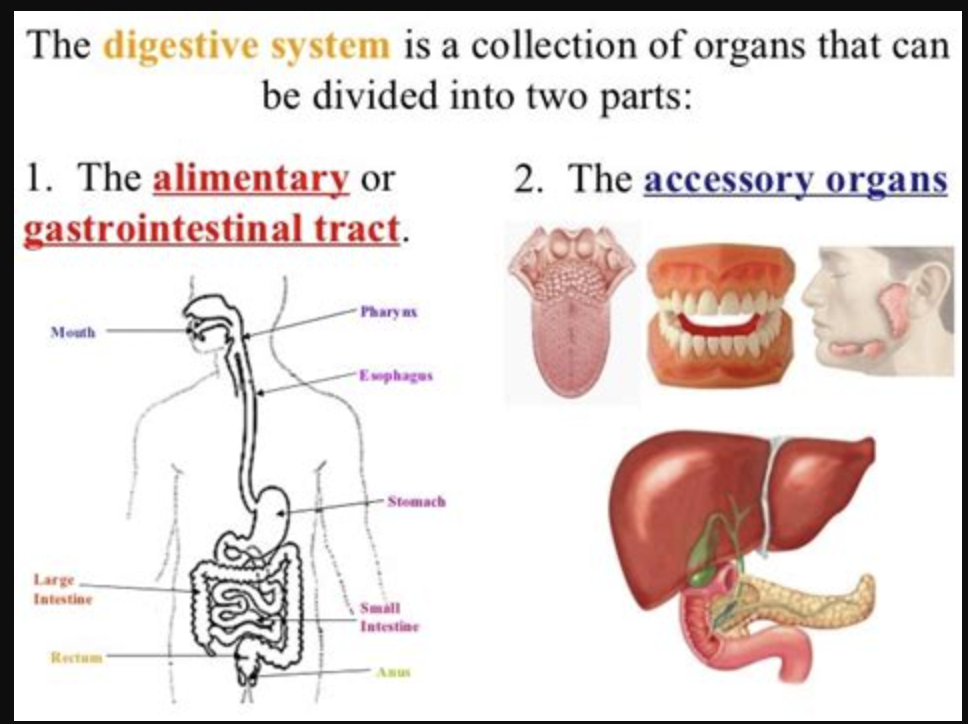
Two main groups of organs in digestive system
alimentary canal: continuous hollow coiled tube (GI tract), about 30ft. Long (cadaver)
accessory digestive organs: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, large/small intestine, anus
Oral Cavity (mouth)
• vestibule: space between lips externally and teeth and gums internally
• Oral cavity: area contained by the teeth
• Tongue: attached to hyoid and style if processes of the skull and by lingual frenulum
• Tonsils:
• Mastication: chew
• mixing food with saliva
• Initiating swallowing by tongue
• allowing for the sense of taste
Lingual frenulum
lingual frenulum is the small fold of mucous membrane that anchors the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth.
Hard palate
hard palate is the bony front part of the roof of the mouth, and it serves several important functions:
Separates the oral and nasal cavities – so you can breathe and chew at the same time.
Helps in speech – provides a rigid surface for the tongue to press against when forming certain sounds.
Assists in chewing – provides a firm surface against which the tongue can mash food during mastication.
Supports suction in infants – important for effective breastfeeding.
vestibule
vestibule: space between lips externally and teeth and gums internally
Deglutition (swallowing) phases
• buccal phase
• Pharyngeal-esophageal phase
buccal phase
buccal phase: voluntary; occurs in the mouth, food is formed into a bolus; bolus is forced into the pharynx by the tongue and soft palate
Pharyngeal-esophageal phase
• Pharyngeal-esophageal phase: involuntary transport of bolus;
all other passageways except to the stomach are blocked;
tongue blocks off the mouth;
soft palate (uvula) blocks the nasopharynx;
epiglottis blocks the larynx;
peristalsis moves bolts toward stomach
Cardioesophageal sphincter opens when food presses against it
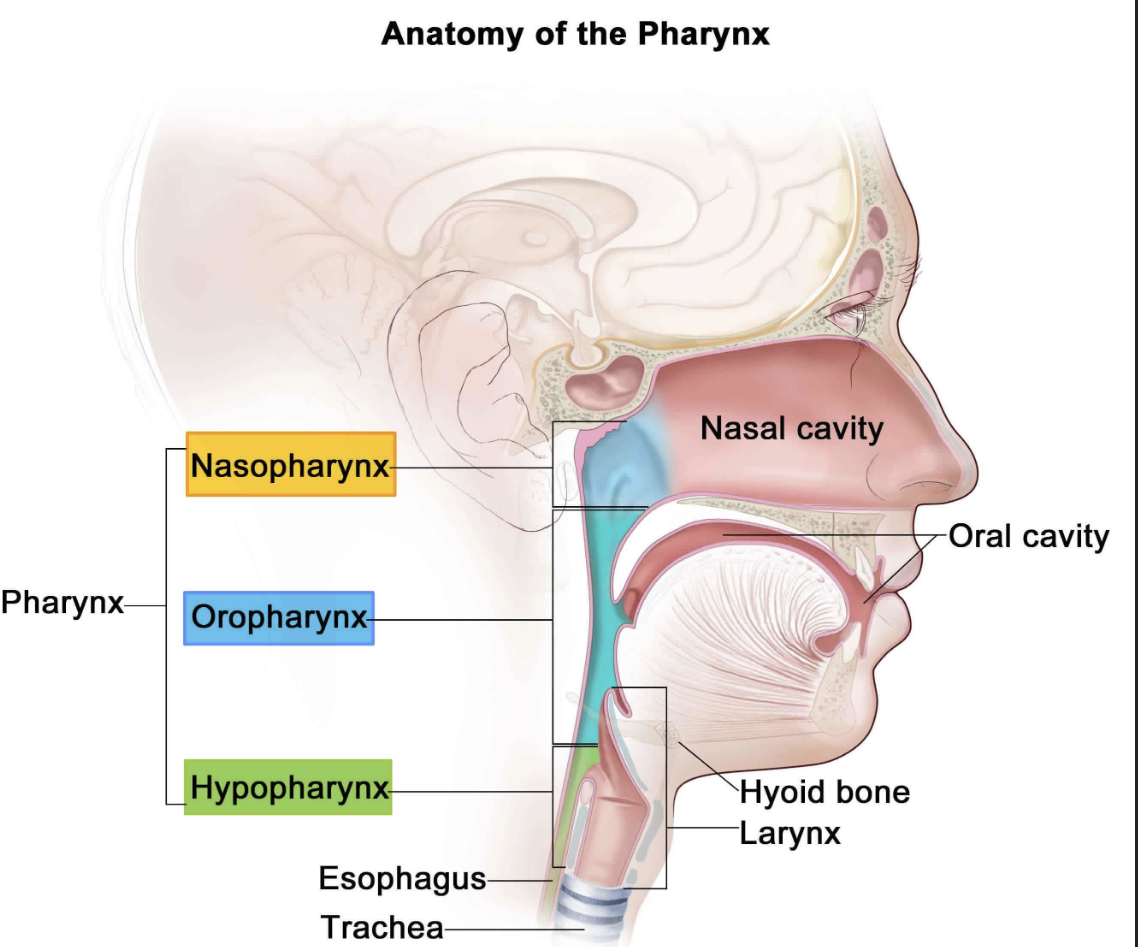
Pharynx function
• serves as a passageway for food and air
• Food is propelled to the esophagus by two muscle layers; longitudinal inner layer; circular outer layer
• Food movement by alternating contractions of muscle layers (peristalsis)
peristalsis
Food movement by alternating contractions of muscle layers
Peristalsis begins in the esophagus, not ends there. It starts in the esophagus and continues throughout the rest of the digestive tract, helping move contents toward the rectum for elimination.
esophagus (gullet)
• pharynx to stomach through diaphragm
• 10in long
• Peristalsis
• Food only
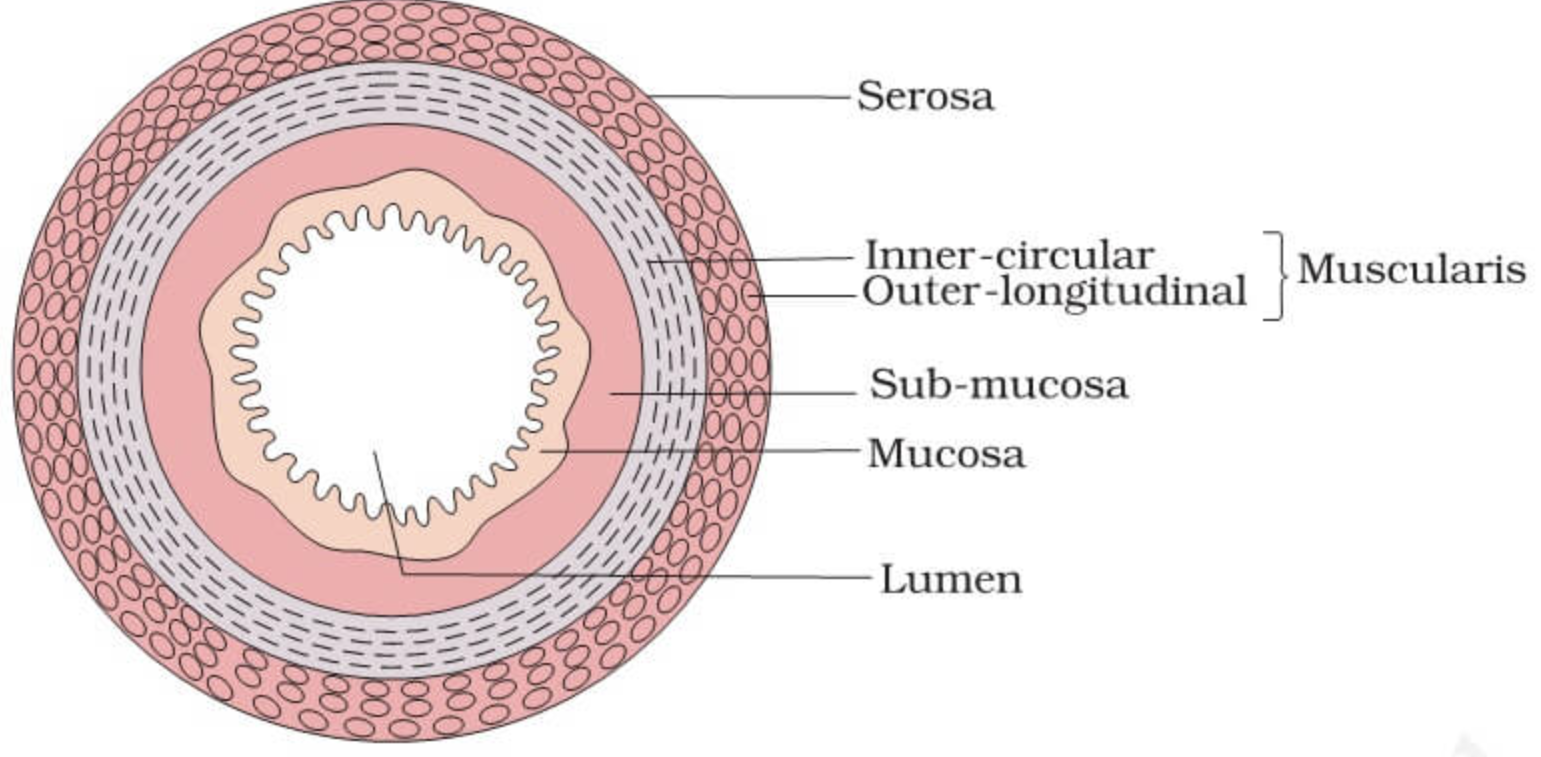
layers of alimentary canal organs (small intestine)
• mucosa: inner most layer ; moist membrane; surface epithelium ; small amount of connective tissue (lamina propia); small smooth muscle layer
• submucosa: soft connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve endings, and lymphatics
• Macular is external- smooth muscle; inner circle layer; outer longitudinal layer
• Serosa: outermost layer- visceral Peritoneum; layers of serous guild-producing cells
alimentary canal nerve plexus
• contains two important nerve plexuses: submucosa nerve plexus, myenteric nerve plexus, associated with the automatic nervous system
Stomache anatomy- regions
Regions of the stomach: fundus, body, pylorus- funnel shaped terminal end
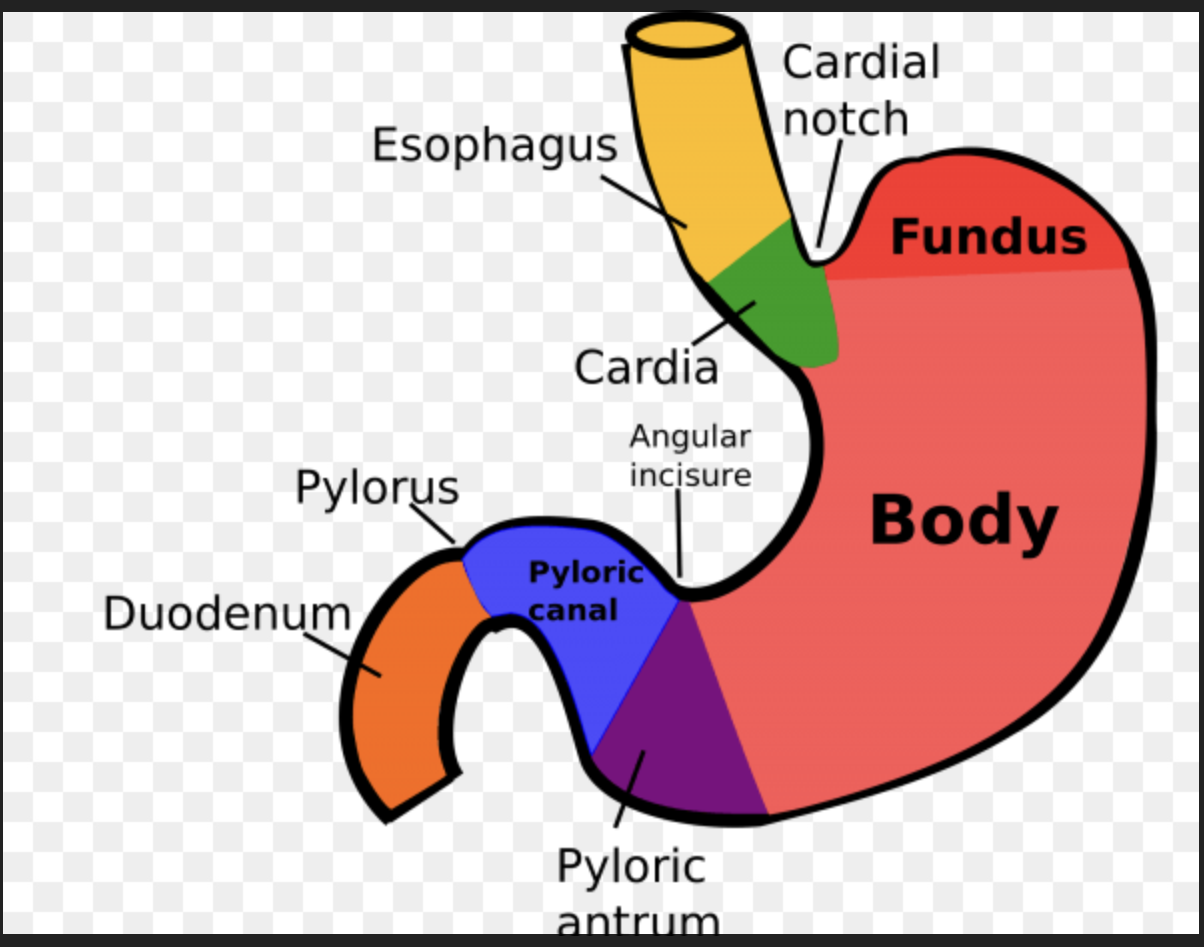
Location of stomache and where food enters it
• located on the left side of the abdominal cavity
• Food enters at the cardio esophageal sphincter
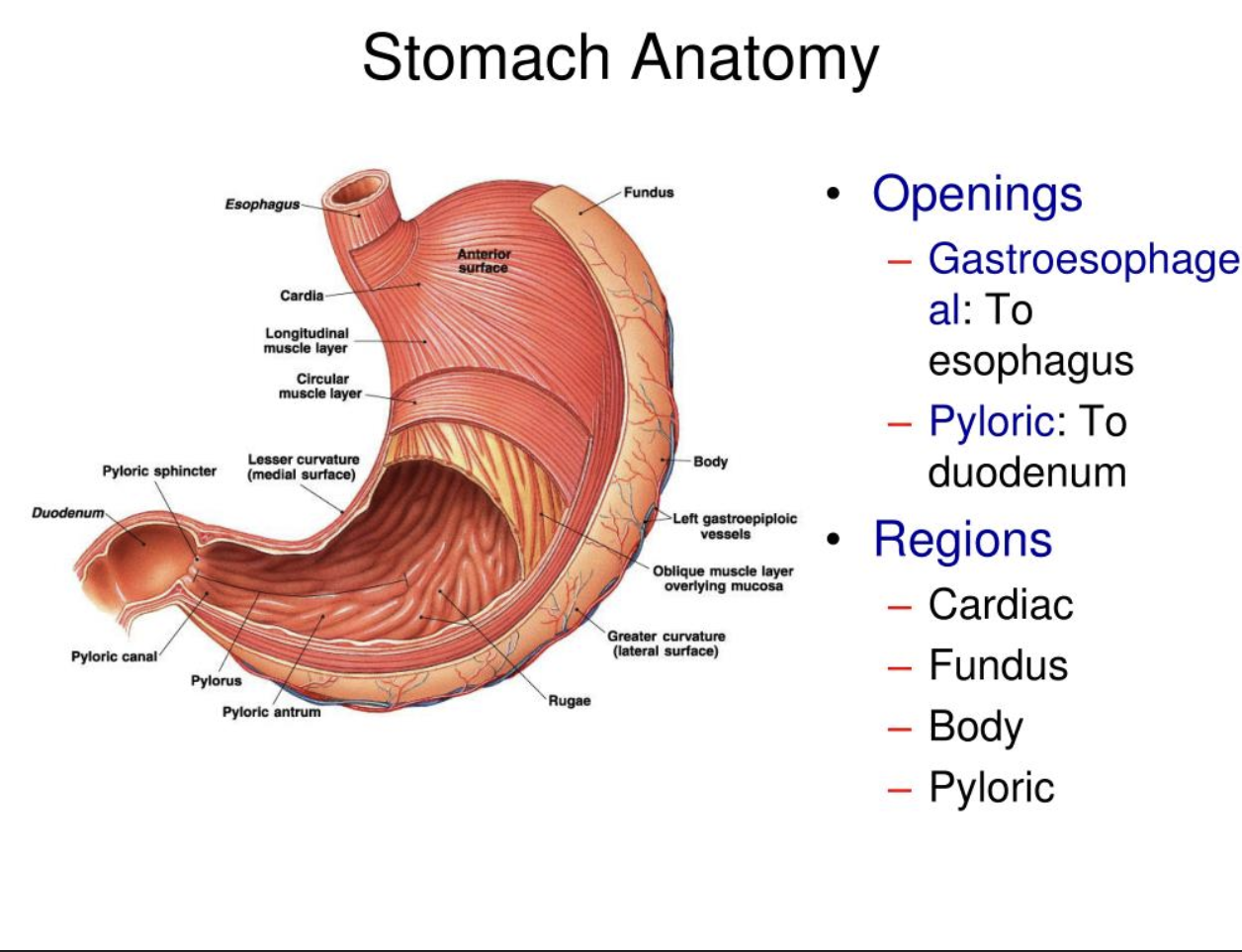
Where does food empty from stomache into small intestine
Pyloric sphincter: A muscular valve that controls the release of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, which is the first part of the small intestine.
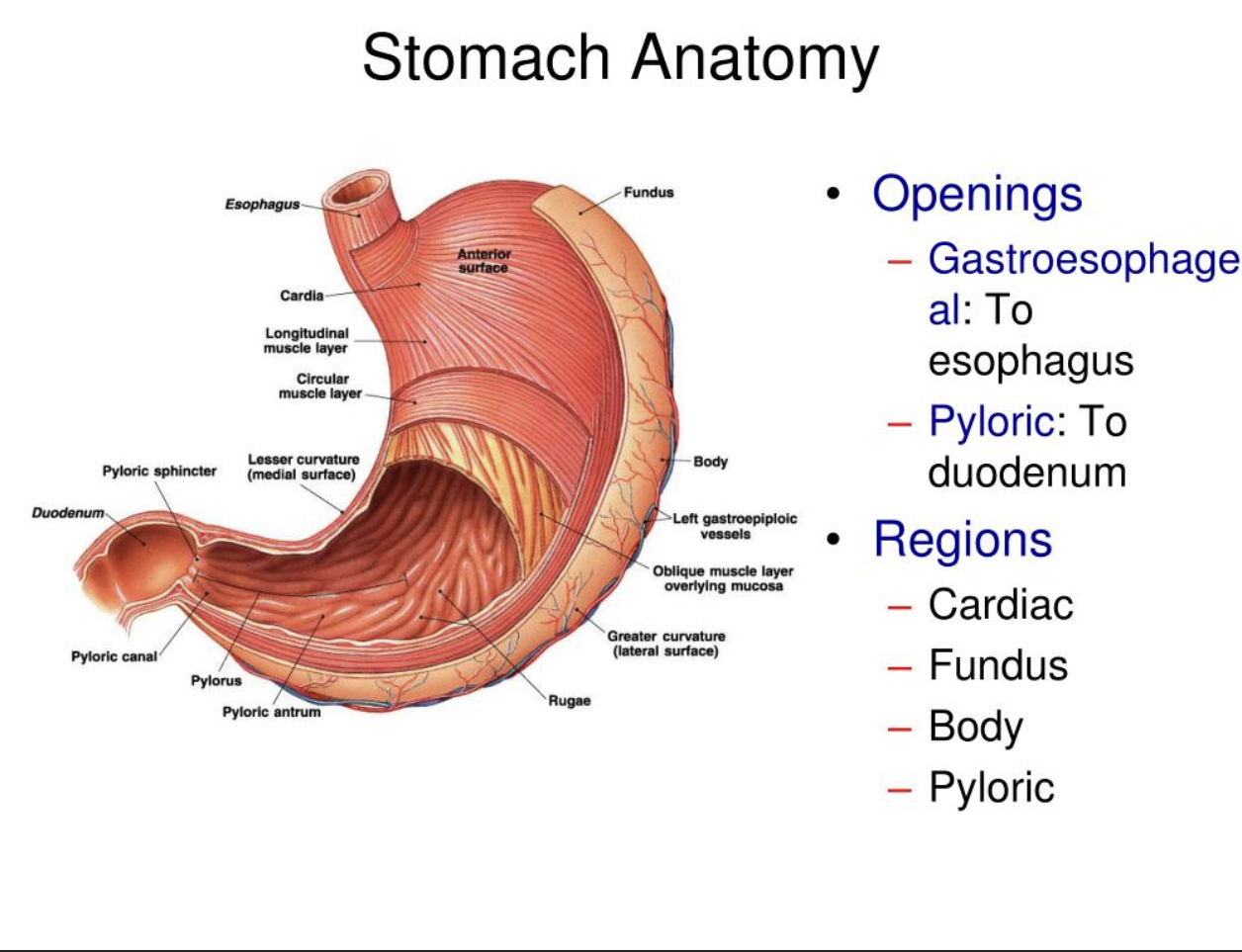
Rugae
Rugae- internal folds of the mucosa
External regions of stomache
lesser and greater curvature
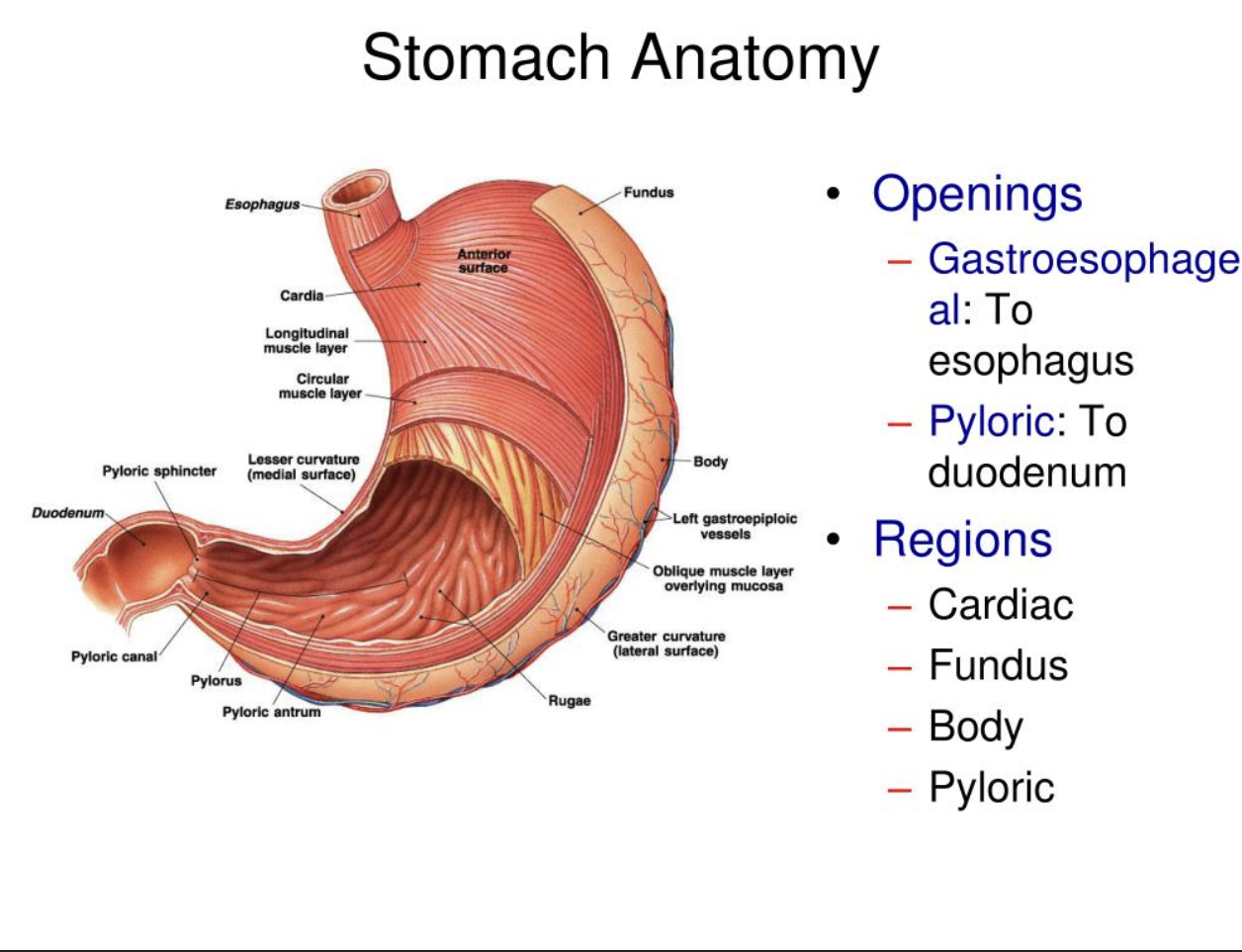
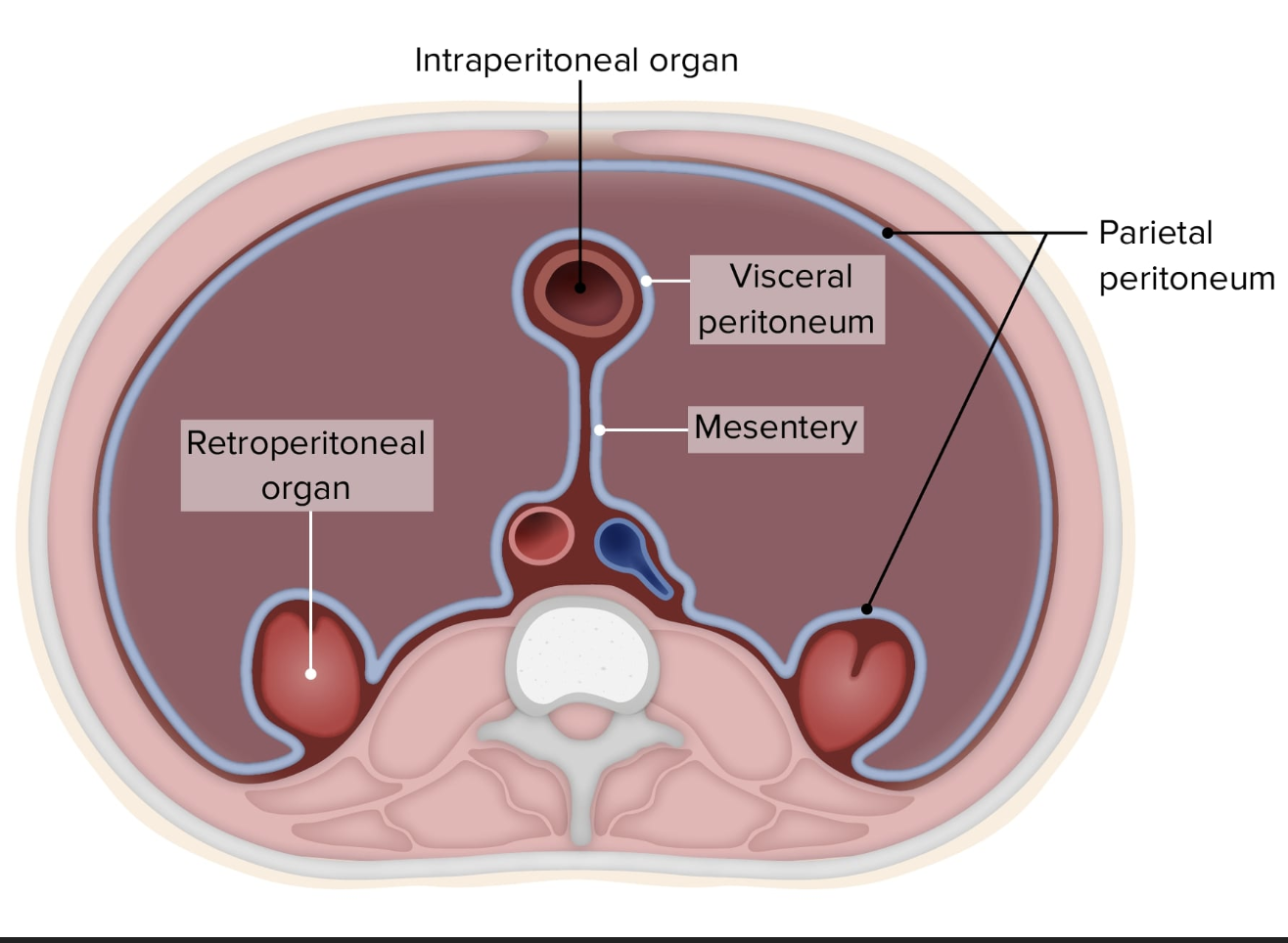
layers of peritoneum attached to the stomach:
lesser omentum attaches to the lever to the less curvature, greater omentum attaches the greater curvature to the posterior body wall, contains fat to insulate, cushion, and protect abdominal organs
stomach functions
• storage for food
• Site of food breakdown
• Chemical breakdown of protein begins
• Delivers chyme (processed food) to the small intestine
specialized mucosa of the stomachs (cells)
simple columnar epithelium:
• mucosa neck cells- produces a sticky alkaline mucous
• gastric glands- secrete gastric juice
• chief cells- produce protein digesting enzymes
(pepsinogens):
• parietal cells- produce hydrochloride acid
• endocrine cells - produce gastrine
(pepsinogens)
produced by cheif cells for protein break down
Small intestine
• body’s major digestive organ
• Site of nutrient absorption
• Extends from the pyloric sphincter to ileocecal valve
• Suspended from the posterior abdominal wall bymesentery
Hepatic portal circulation
system of blood vessels that carries blood from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, including the small intestine, to the liver
Mesentery
mesentery is a fold of tissue that attaches the small intestine (and parts of the large intestine) to the abdominal wall and provides support, holding these organs in place.
Regions of small intestine
•duodenum: attaches to the stomach and curves around the head of the pancreas
• Jejunum: attaches anteriorly to the duodenum
• Ileum: extends from jejunum to large intestine
chemical digestion in the small intestine
• source of enzymes that are mixed with chyme
• Intestinal cells and pancreas
• Bile enters from the gall bladder
Villi of the small intestine
• finger like structures formed by mucosa
• Give the small intestine more surface area
microvilli in the small intestine
• small projections of the plasma membrane
• Found on absorptive cells
structures involving in absorbing nutrients
• absorptive cells
• Blood capillaries
• Lacteals (specialized lymphatic capillaries)
folds of the small intestine
• circular folds called plicae circulares
• Deep folds in the mucosa and submucosa
• do not disappear when filled either food
• Submucosa has peyer’s patches (collection of lymphatic tissue)
large intestine
• larger in diameter but shorter than the small intestine
• Frames the internal abdomen
functions of the large intestine
• absorption of water
• Eliminates indigestible food from the body as feces
• Does not participate in digestion of food
• Goblet cells produce mucus to act as a lubricant
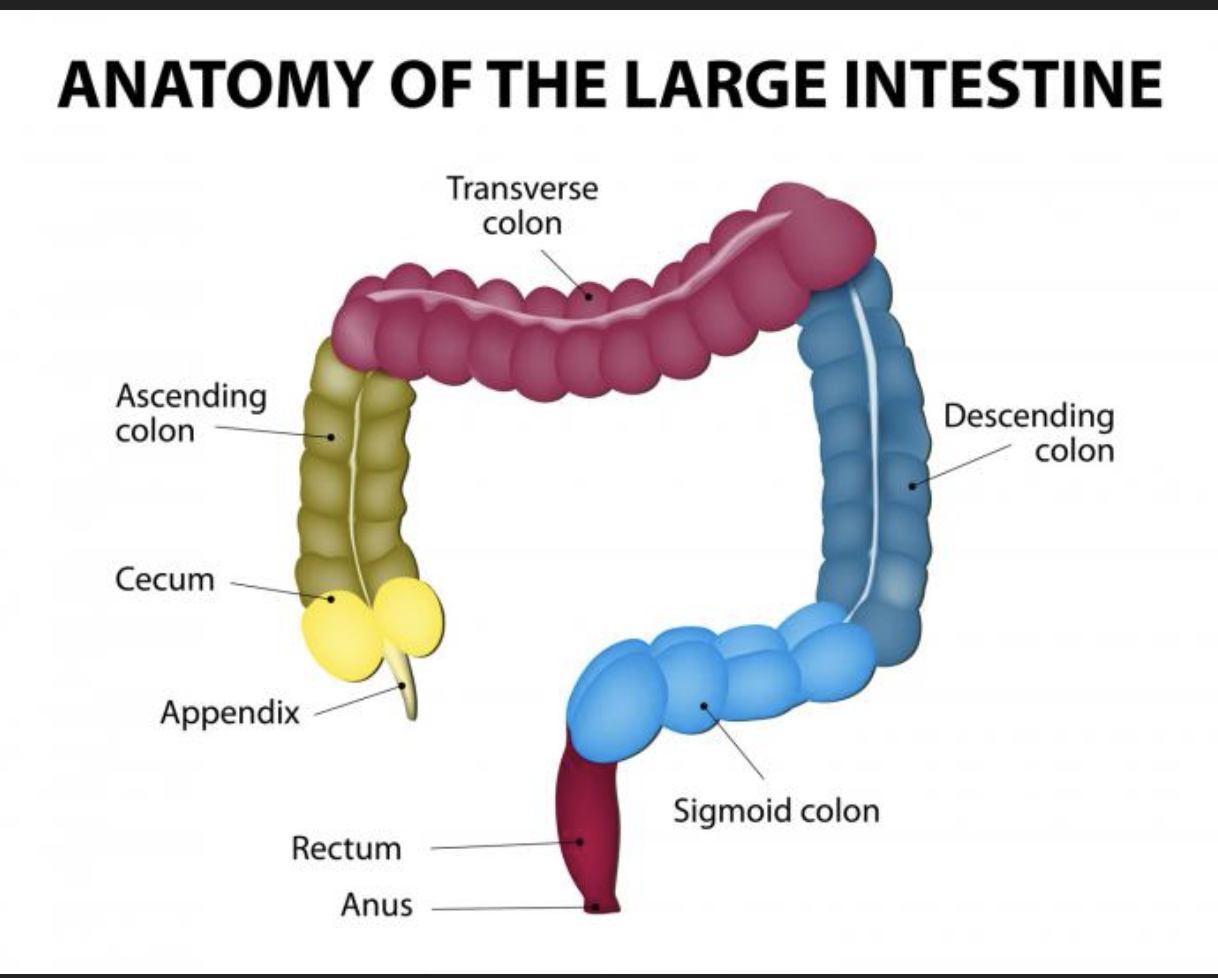
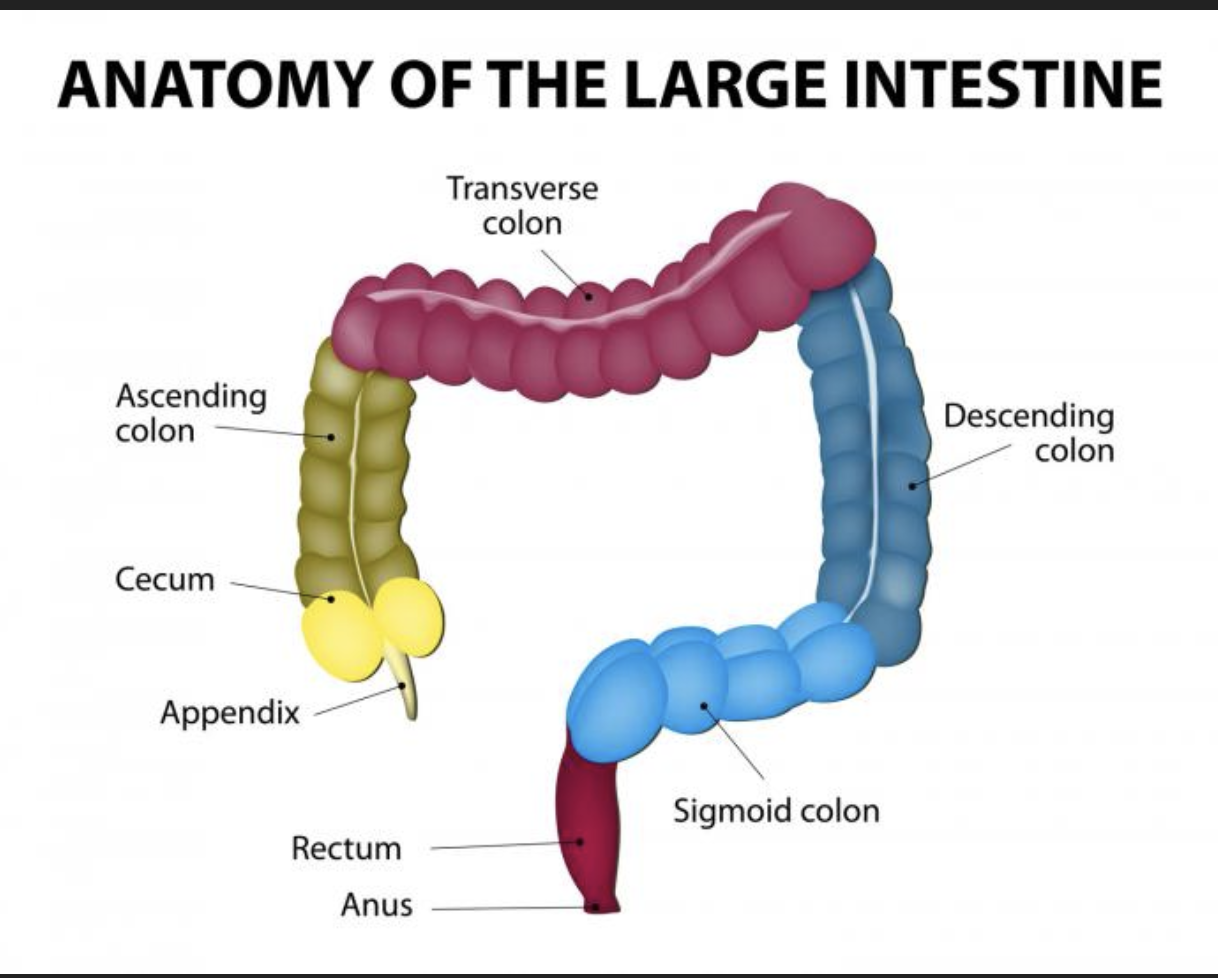
Structures of the large intestine
• cecum - saclike first part of the large intestine
• Appendix - accumulation of lymphatic tissue that sometimes becomes inflamed (appendicitis)
• Colon - ascending, transverse, descending, s-shaped sigmoidal
• Rectum
• Anus- external of the body
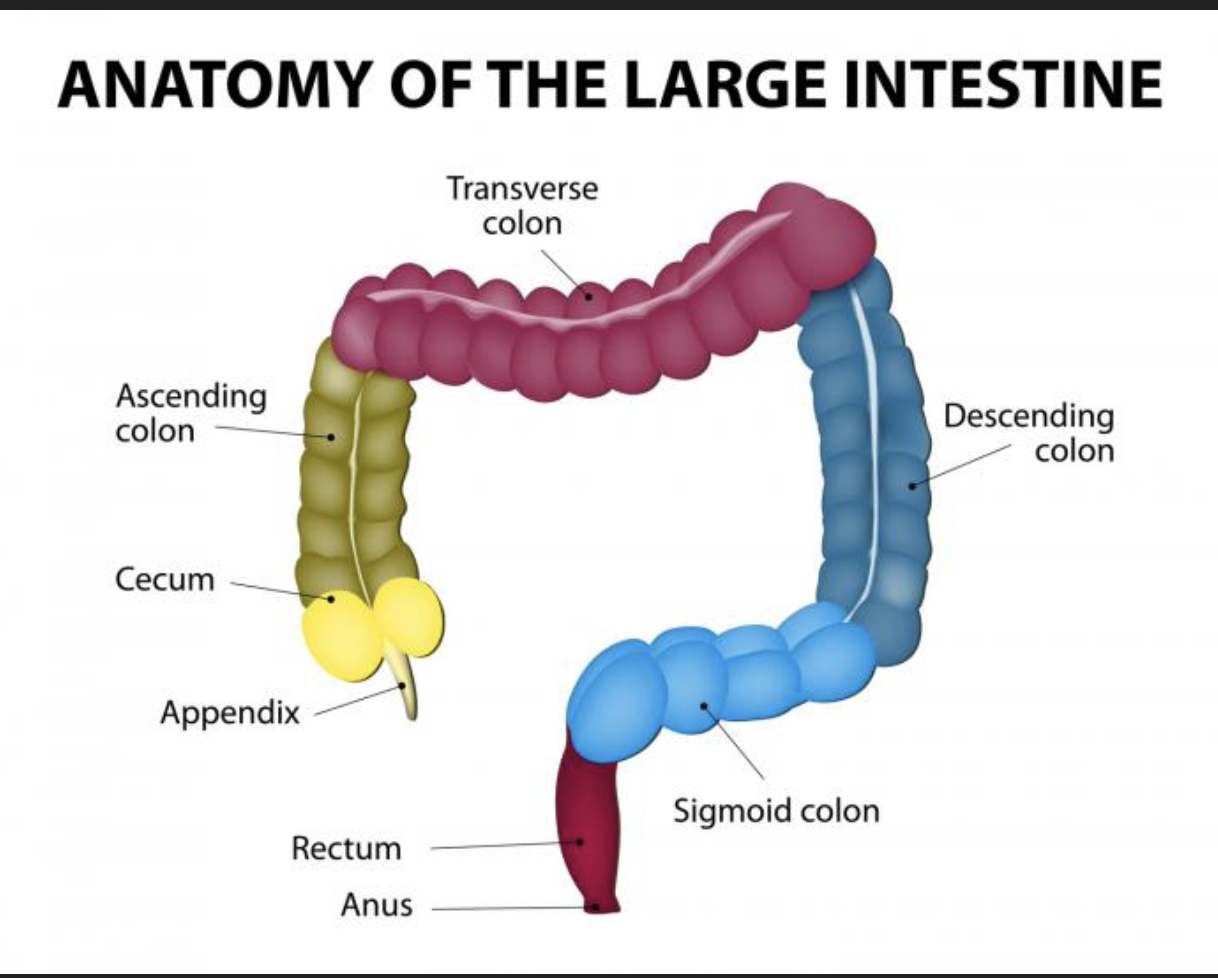
Function of the Ileocecal Valve:
valve between large and small intestine
cecum
• cecum - saclike first part of the large intestine
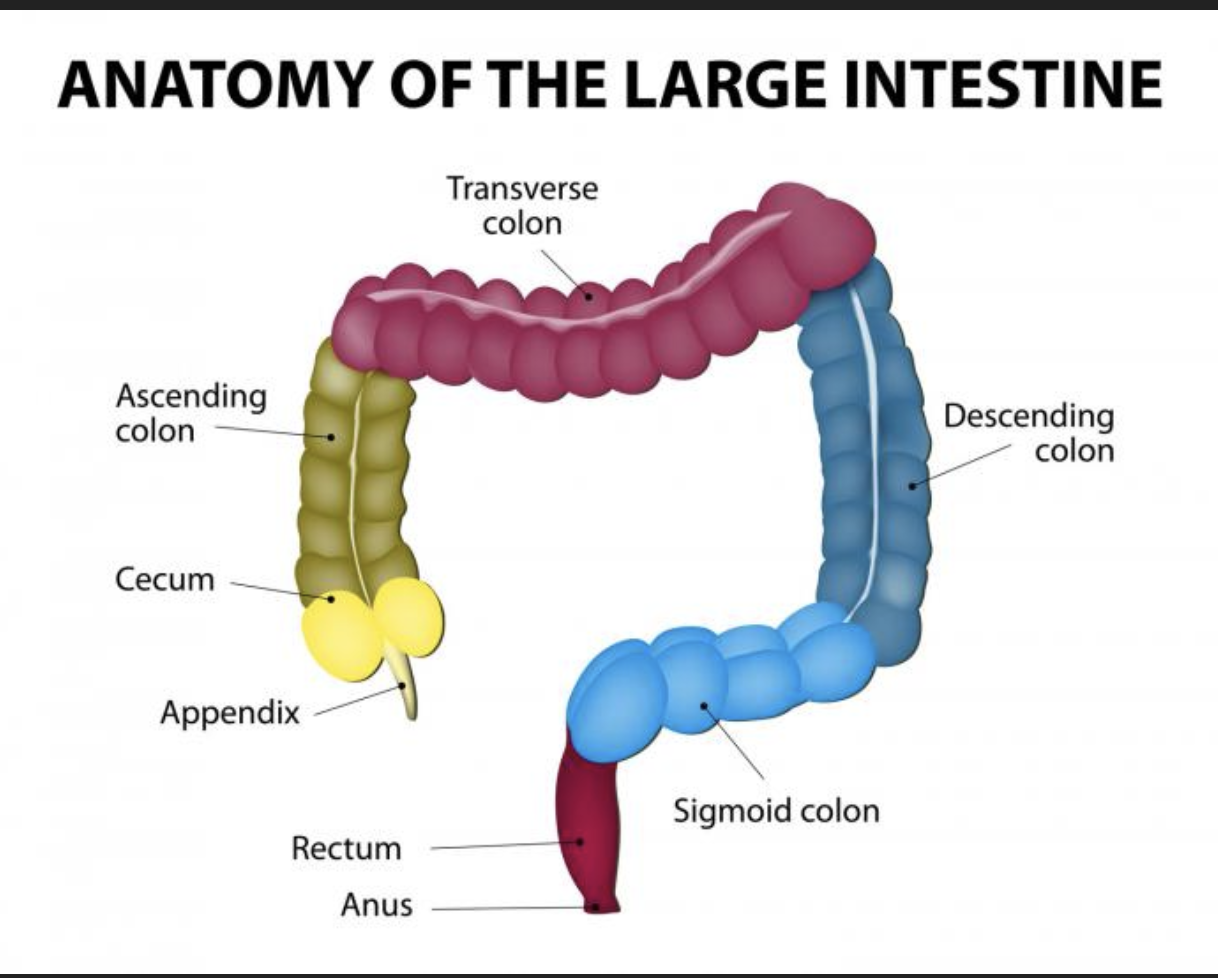
Appendix
• Appendix - accumulation of lymphatic tissue that sometimes becomes inflamed (appendicitis)
hangs off the cecum, typically at the junction of the ileum (end of the small intestine) and the cecum.
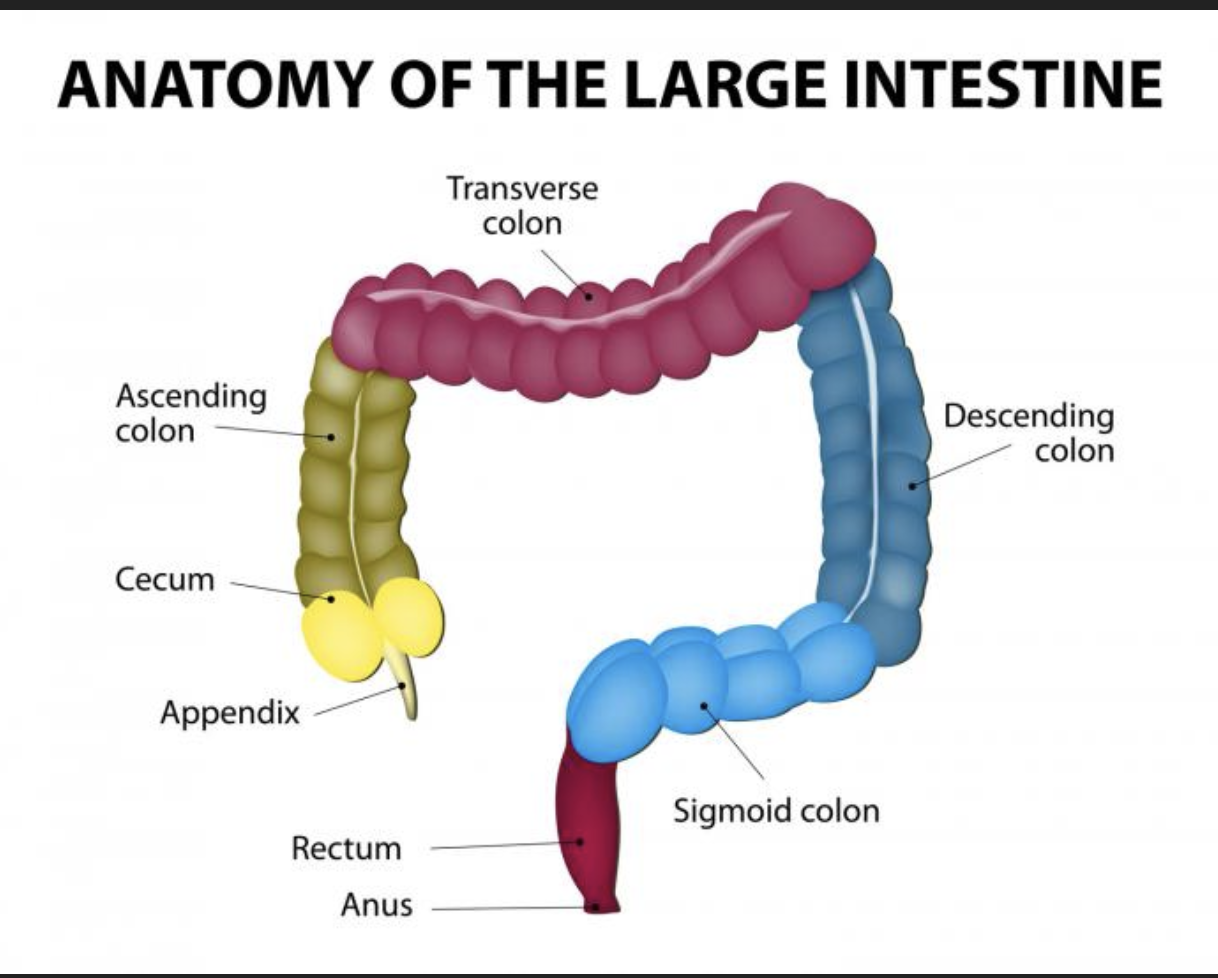
Colon
• Colon - ascending, transverse, descending, s-shaped sigmoidal
smooth muscle is reduced to three bands
(teniae coil)
• Bands have some degree if tone
Walls are formed into pocket-like sac called ____ in large intestine
haustra
salivary glands
saliva producing glands:
parotid glands- located anterior to the ear;
submandibular glands;
sublinguinal glands
Saliva
• mixture of mucus and serous fluid
• Helps form food bolus
• Contains salivary amylase to begin starch digestion
• Dissolves chemicals so they can be tasted
catabolism
substances are broken down to simple substances
Energy is released during catabolism to make APT
Anabolism
larger molecules are built from smaller ones
basic nutrients
• Carbs- increase the bulk in stool and aid in dedication
• Lipids- meat, dairy, and some plants (coconut).
unsaturated fats- seeds, nuts, vegetables oil
Cholesterol - egg yolk, meat
Protein- egg, milk, meat
Water- solvent Nutrient- substance used by body for growth, maintenance, and repair
kcal
Energy value of foods is measured in units
categories of nutrients
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, mineral, water
bile
Made by the liver and stored in the gall bladder to break down fats
Sphincters of stomach
1. Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) – also called the cardiac sphincter
Location: Between the esophagus and the top of the stomach
Function: Prevents stomach acid and contents from flowing back into the esophagus (prevents acid reflux)
2. Pyloric Sphincter
Location: Between the stomach and the duodenum (first part of the small intestine)
Function: Controls the release of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the small intestine
Fundus
The fundus is the rounded, upper portion of the stomach, located above the level of the esophageal opening.
It often contains trapped gas that can be seen on X-rays.
It plays a role in temporary food storage and helps in mechanical digestion by churning food with gastric juices.
Function of Pepsinogen (in gastric juice)
Pepsinogen is an inactive enzyme secreted by chief cells in the stomach.
In the acidic environment of the stomach (due to hydrochloric acid, or HCl), pepsinogen is converted into pepsin, its active form.
Pepsin is a protease enzyme that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides
Function of salivary amylase
Breaks down starch (a complex carbohydrate) into maltose and smaller sugar units.