Peripheral Nervous System
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
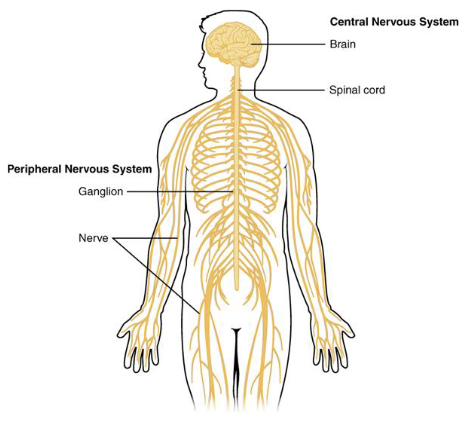
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
• Connects the CNS to the
rest of the body
• Includes nerves and
ganglia
• Transmit sensory input
and motor output
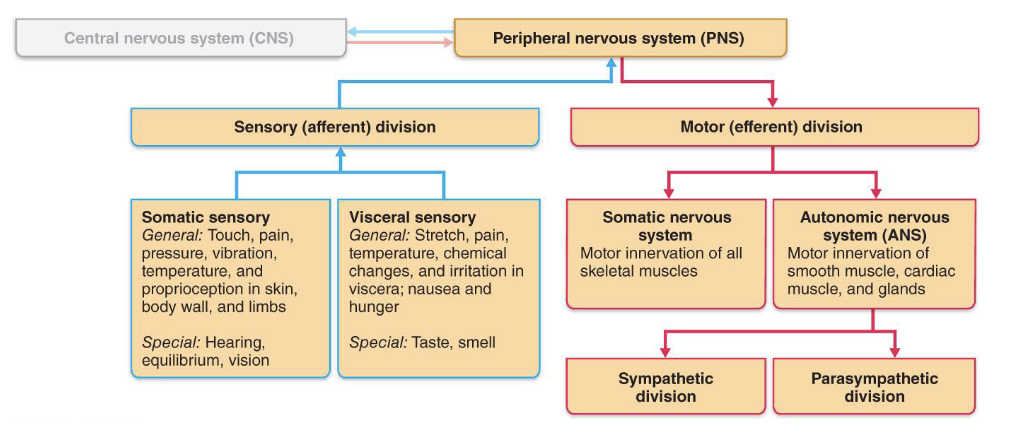
Functional Divisions of the PNS
• Divided into sensory (input) and motor (output)
pathways
• Somatic (body surface, muscles) and visceral
(internal organs)
• General (widespread) and special (localized senses)
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
• General visceral motor division of the PNS
• Regulates involuntary functions (ex. heart rate,
digestion)
• Main divisions:
1. Parasympathetic: rest and digest
2. Sympathetic: fight or flight
PNS Pathway Picture
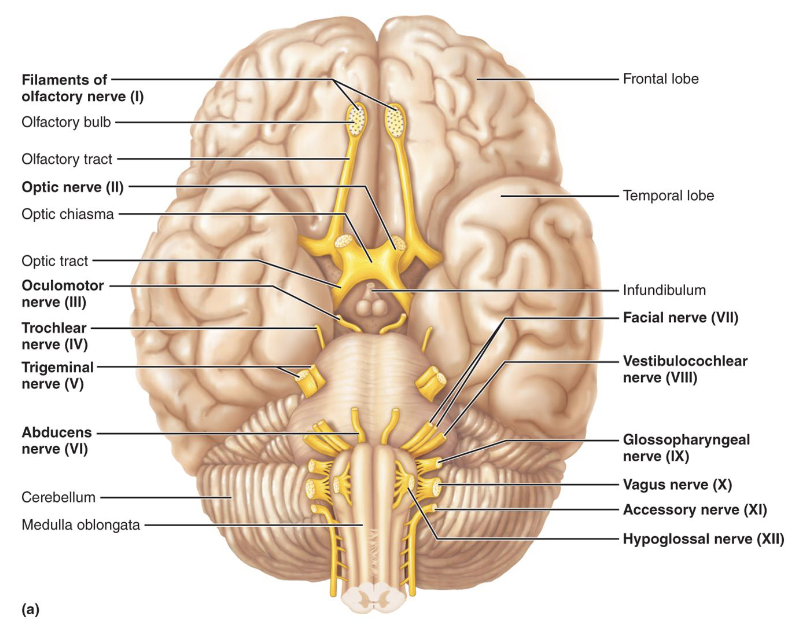
Cranial Nerves
• Originate from the brain and pass through specific
foramina of the skull
• Numbered from I-XII
• Cranial nerves I and II: attach to the forebrain
• Cranial nerves III–XII: attach to the brainstem
• Serve head and neck structures
• Only vagus nerve (X) extends into the abdomen
Cranial Nerves Table
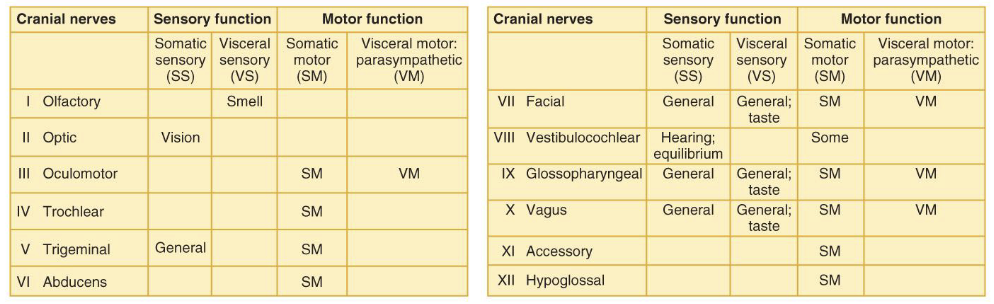
Cranial Nerves Mnemonic
Open One Or Two Textbooks And Find Very Generic Vague Study Habits
1. Open = Olfactory
2. One = Optic
3. Or = Oculomotor
4. Two = Trochlear
5. Textbooks = Trigeminal
6. And = Abducens
7. Find = Facial
8. Very = Vestibulocochlear
9. Generic = Glossopharyngeal
10. Vague = Vagus
11. Study = Spinal Accessory
12. Habits = Hypoglossal
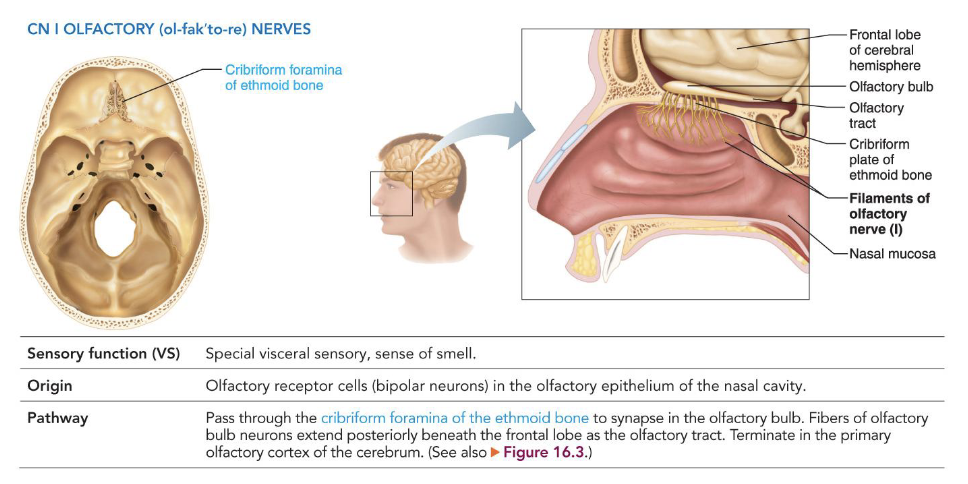
I - Olfactory Nerves
• Special visceral sensory
• Smell
• Origin: olfactory receptor cells located in olfactory
epithelium of nasal cavity
• Pathway: pass through cribriform foramina of the
ethmoid bone
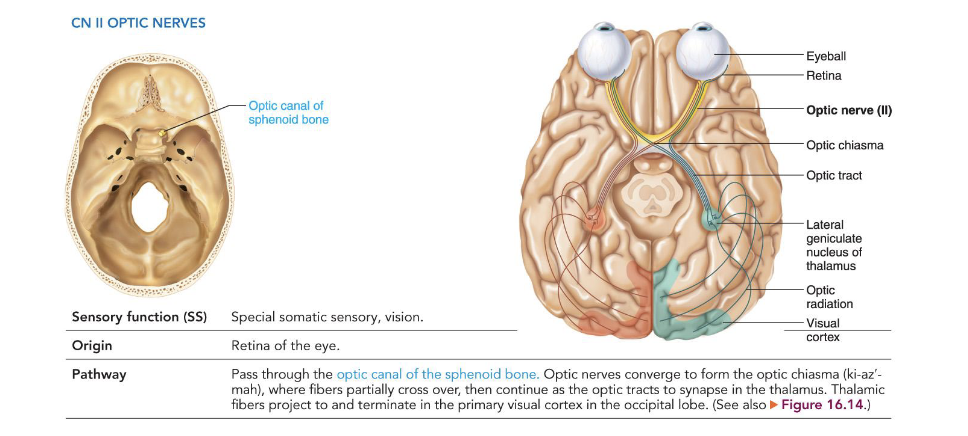
II - Optic Nerves
• Special somatic sensory
• Vision
• Origin: retina of the eye
• Pathway: pass through the optic canals of the
sphenoid bone
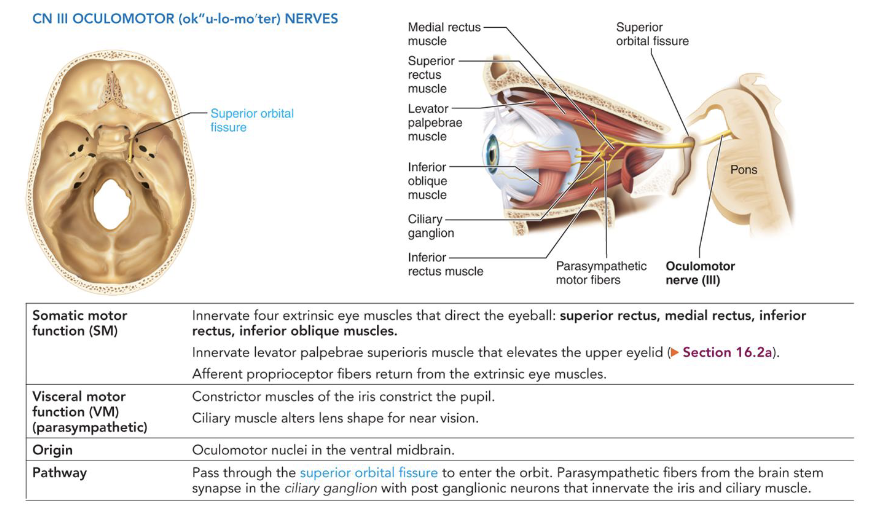
III - Oculomotor Nerves
• Somatic motor: innervates extrinsic eye muscles
1. Superior rectus
2. Medial rectus
3. Inferior rectus
4. Inferior oblique
• Visceral motor: constricts pupil, controls lens shape
• Origin: oculomotor nucleus of midbrain
• Pathway: pass through the superior orbital fissure
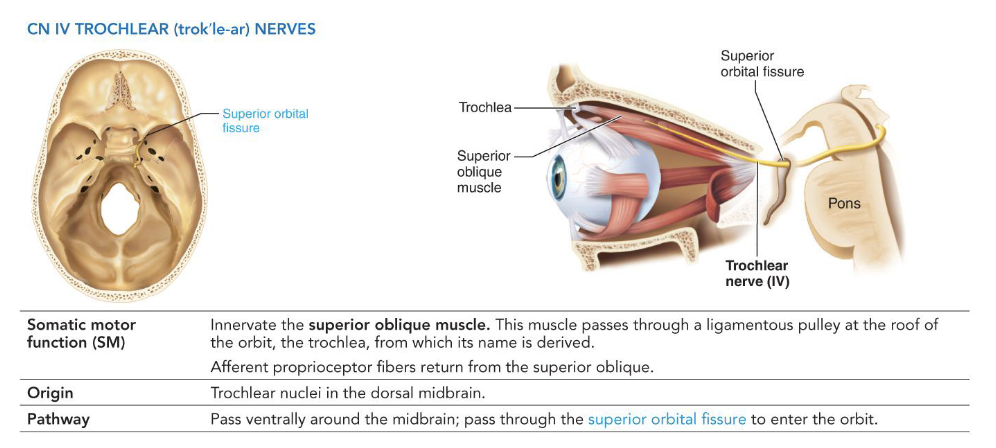
IV - Trochlear Nerves
• Somatic motor
• Innervate superior oblique muscle
• Origin: trochlear nucleus of midbrain
• Pathway: pass ventrally and laterally around midbrain
• Exit through superior orbital fissure
V - Trigeminal Nerves
• Largest cranial nerve, sensory and motor functions
• Ophthalmic Division (V1): sensory, upper face
• Maxillary Division (V2): sensory, midface
• Mandibular Division (V3): sensory and motor,
lower face
• Origin: sensory cell bodies in the trigeminal ganglion
and motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve
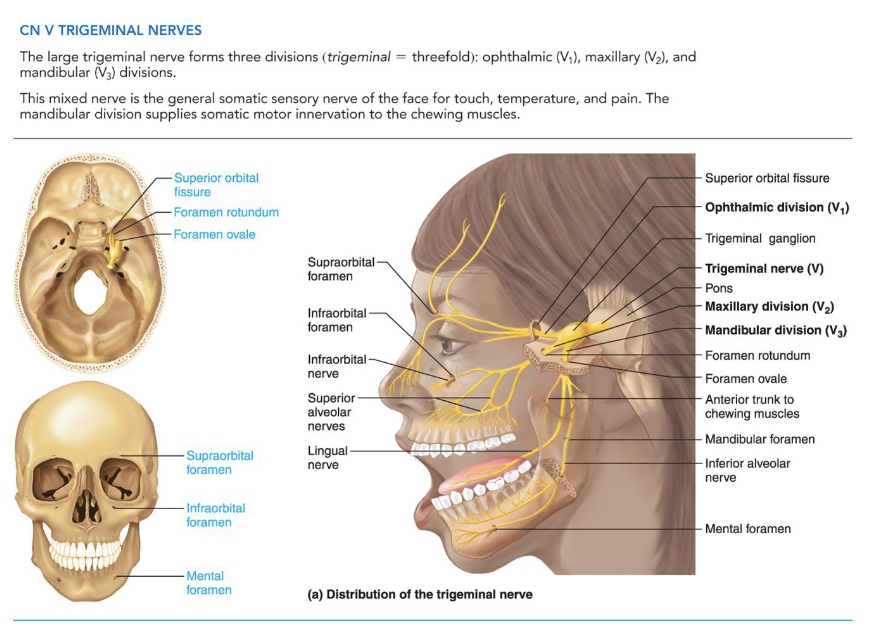
V - Trigeminal Nerve Pathways
• V1 – passes through superior orbital fissure
• V2 – passes through foramen rotundum
• V3 – passes through foramen ovale; enters
mandible through mandibular foramen
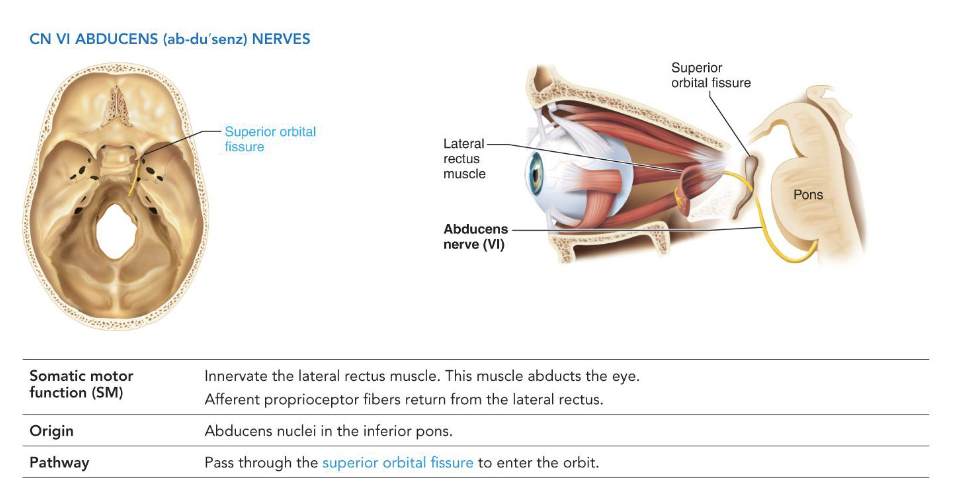
VI - Abducens Nerves
• Somatic Motor
• Innervates the lateral rectus muscle
• Origin: abducens nucleus in the pons
• Pathway: travels through the superior orbital fissure
to the eye
VII - Facial Nerves Somatic
• Special visceral sensory:
• Taste (anterior two-thirds of tongue)
• Somatic motor:
• Innervates five branches of facial muscles
1. Temporal
2. Zygomatic
3. Buccal
4. Mandibular
5. Cervical
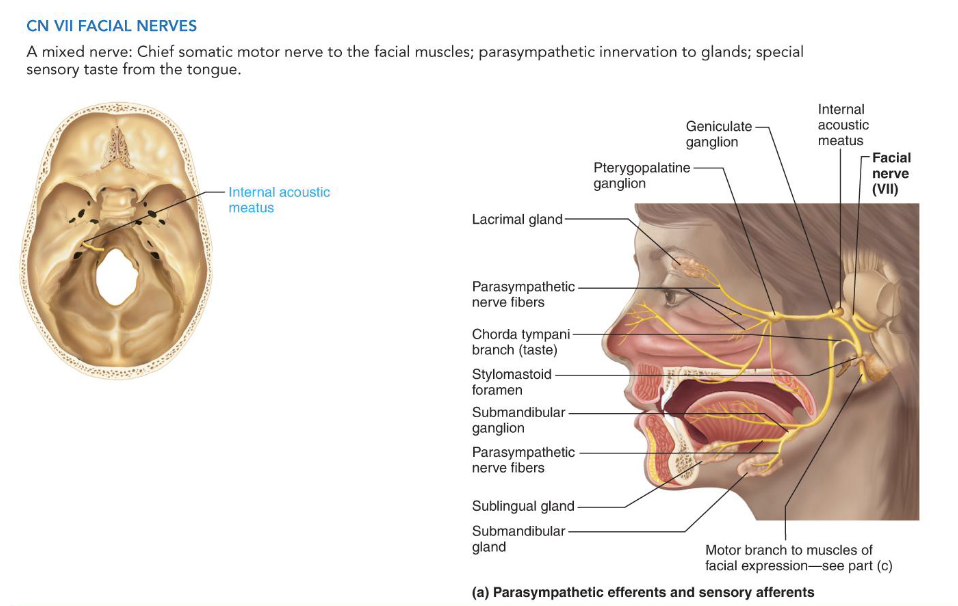
VII - Facial Nerves Visceral
• Visceral motor
• Innervates lacrimal glands, submandibular and
sublingual salivary glands
• Origin: facial nucleus of pons in brain stem
• Pathway: enters temporal bone through the internal
acoustic meatus
• Travels through facial canal to target glands
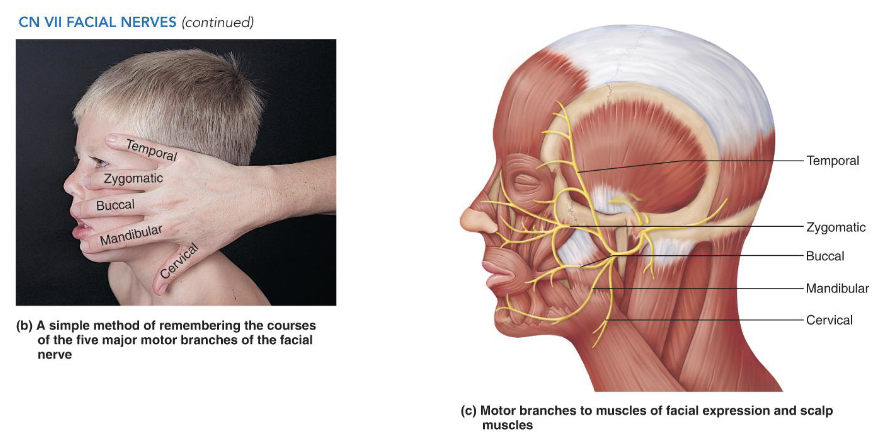
VIII - Vestibulocochlear Nerves
• Sensory nerve for hearing and balance
• Vestibular Branch: equilibrium
• Cochlear Branch: hearing
• Origin: vestibular apparatus and cochlea
• Pathway: Passes through the internal acoustic meatus
to the brainstem
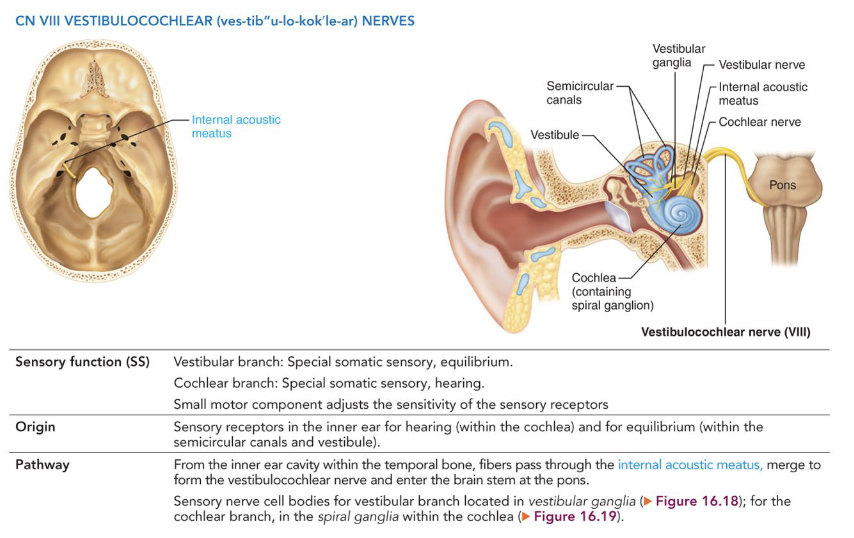
IX - Glossopharyngeal Nerves Sensory
• Posterior third of tongue
Special Visceral Sensory:
• Taste
General Visceral Sensory:
• Pharyngeal mucosa
• Chemoreceptors in the carotid body
• Baroreceptors in the carotid sinus
IX - Glossopharyngeal Nerves Motor
Somatic Motor:
• Elevate pharynx during swallowing
Visceral Motor:
• Innervate the parotid salivary gland
• Origin: Medulla oblongata
• Pathway: fibers exit through the jugular foramen
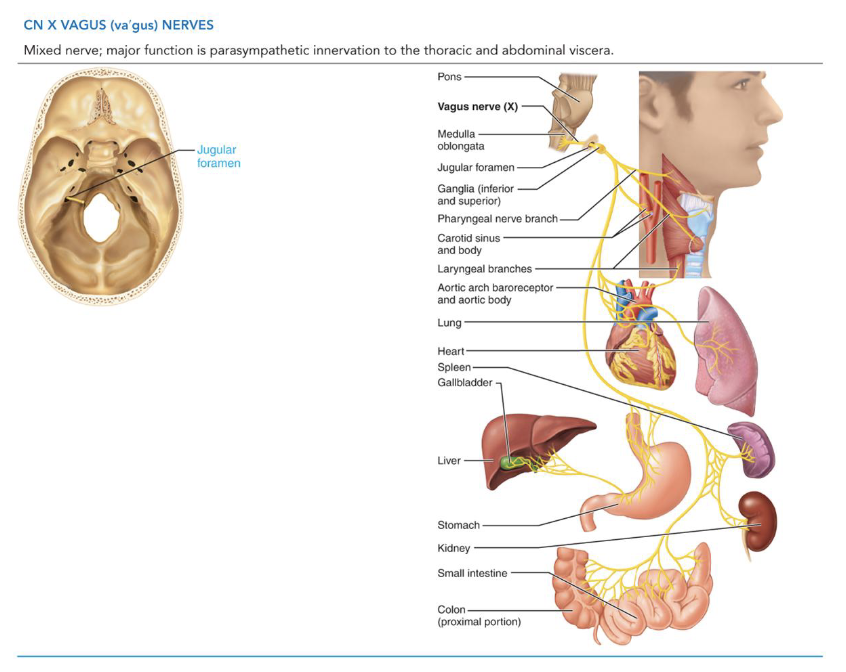
X - Vagus Nerves Sensory
Sensory Functions
• General Visceral Sensory: from thoracic and
abdominal viscera
• Special Visceral Sensory: taste from taste buds on the
epiglottis
X - Vagus Nerves Motor
Somatic Motor Functions
• Innervates skeletal muscles of pharynx and larynx
Visceral Motor (Parasympathetic innervation)
• Heart, lungs, abdominal viscera
• Origin: Medulla oblongata
• Pathway: fibers exit the skull through the jugular
foramen
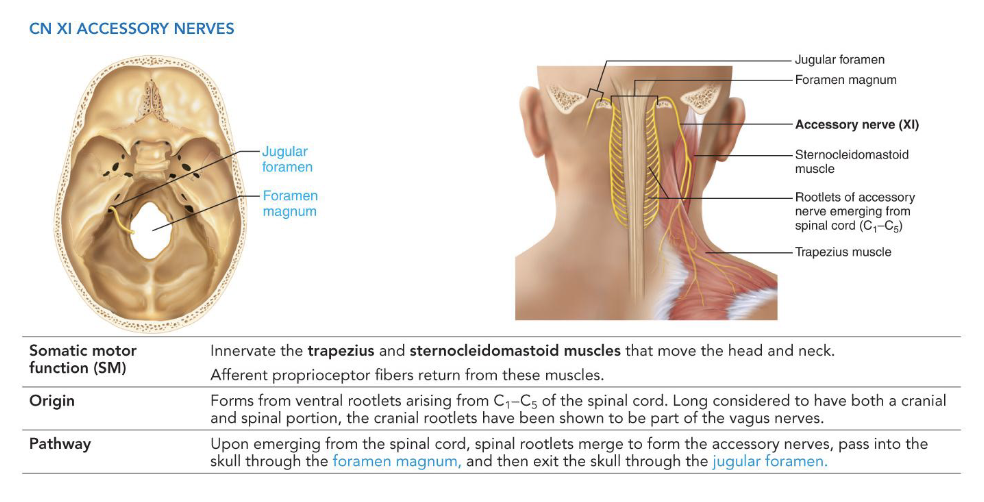
XI - Accessory Nerves
• Somatic motor
• Innervates the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
muscles
• Formed from ventral rootlets of spinal cord (C1–C5)
• Pathway:
• Enter skull through foramen magnum
• Exit skull through jugular foramen
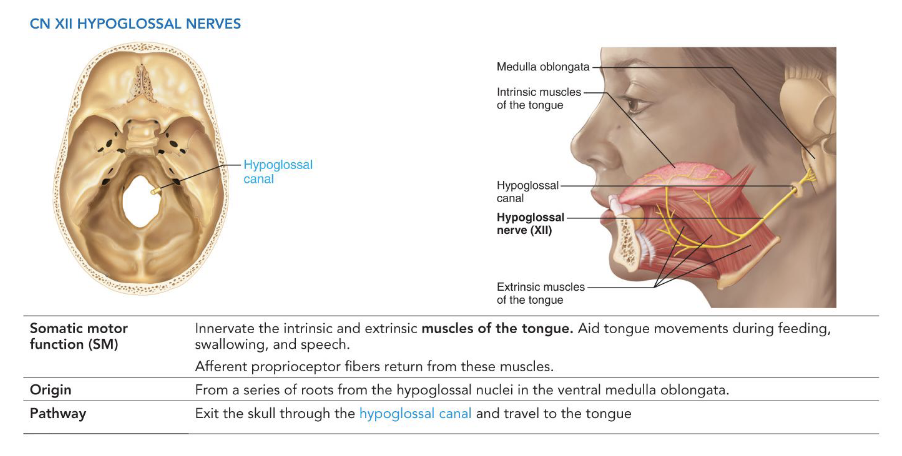
XII - Hypoglossal Nerves
• Somatic motor
• Innervates the tongue muscles
• Formed from ventral rootlets of medulla oblongata
• Pathway: Exits skull through the hypoglossal canal
Cranial Nerve Function Mnemonic

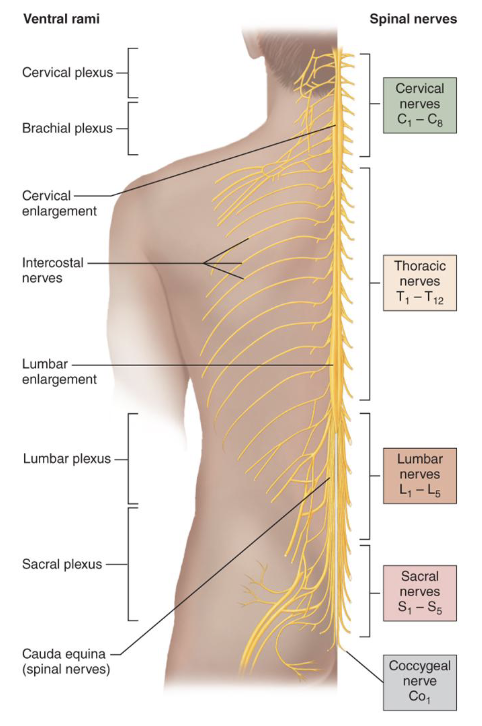
Spinal Nerves
• 31 pairs connect to spinal cord
• Cervical (C1–C8): 8 pairs
• Thoracic (T1–T12): 12 pairs
• Lumbar (L1–L5): 5 pairs
• Sacral (S1–S5): 5 pairs
• Coccygeal (Co1): 1 pair
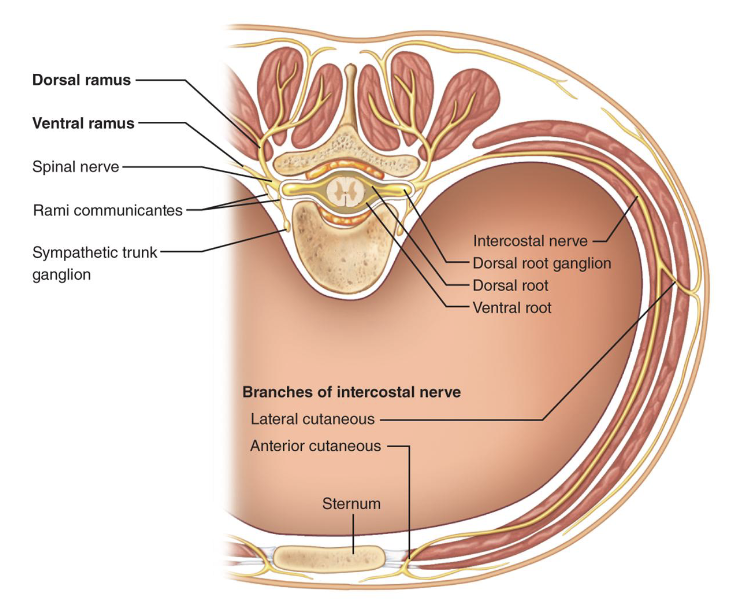
Spinal Nerve Root Connections
• Dorsal Root: sensory fibers, cell bodies in dorsal root
ganglion
• Ventral Root: motor fibers from the anterior gray
column
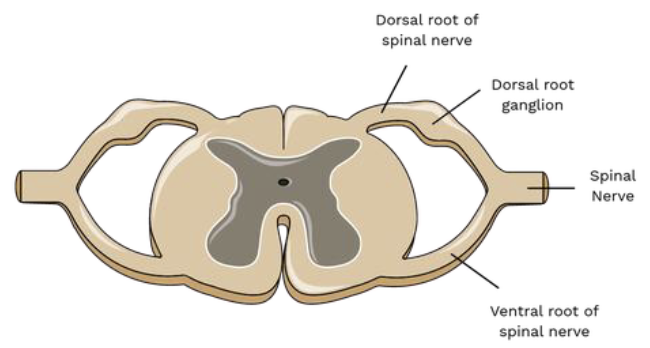
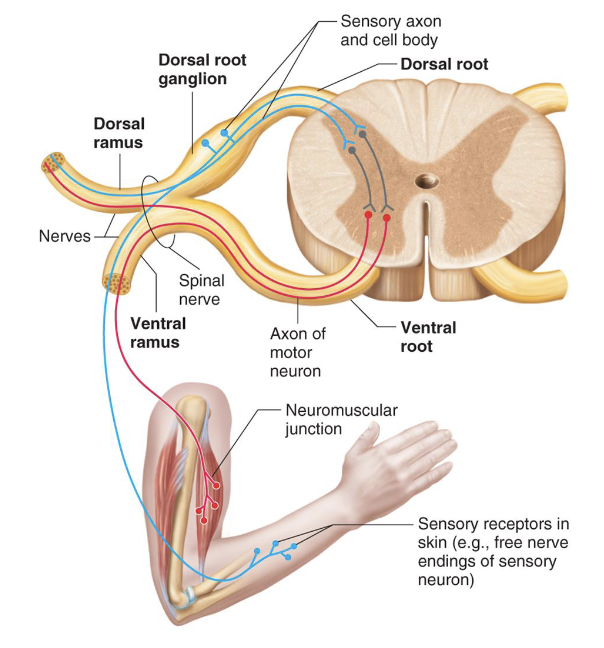
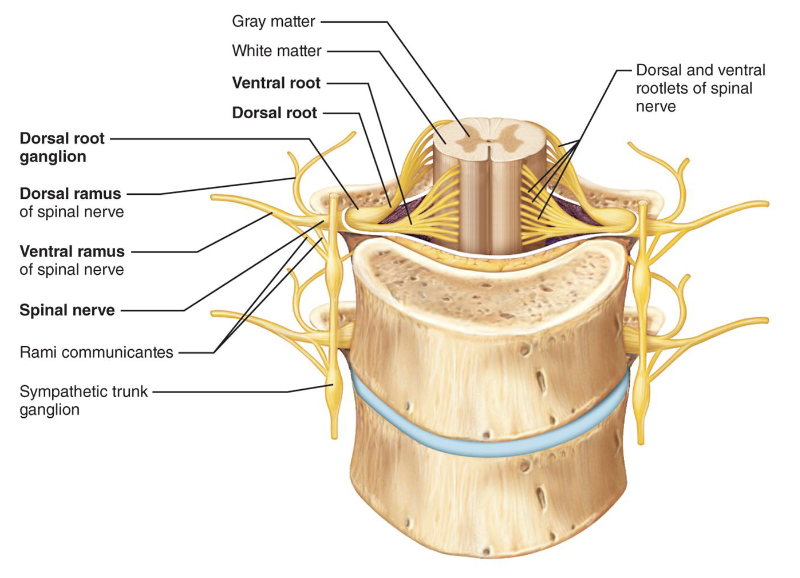
Spinal Nerve Branches
• Dorsal & Ventral Rami: both carry sensory and motor
fibers
• Rami Communicantes: connect ventral ramus to
sympathetic chain ganglia
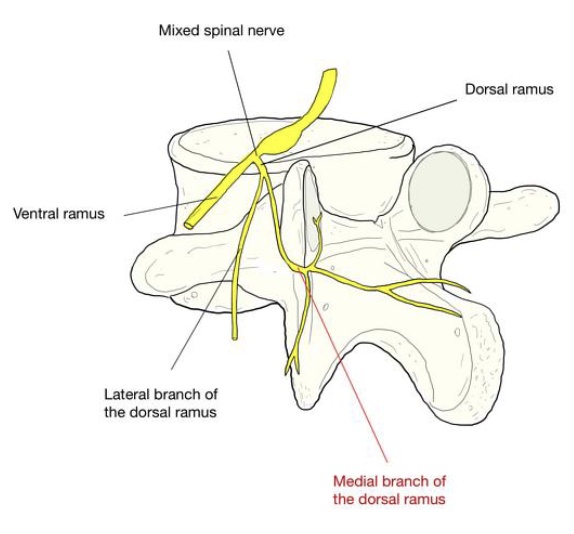
Innervation of the Back
• Dorsal rami supply
back muscles and
skin in segmented
strips
• Follow emergence
points of the
vertebral column
Thoracic and Abdominal Wall Innervation
• Ventral Rami: simple, segmented pattern
• Intercostal Nerves: supply intercostal muscles, skin,
and abdominal wall
• Branches: lateral and anterior cutaneous
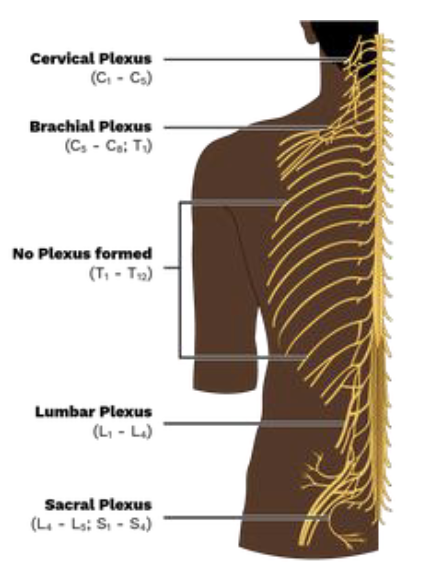
Introduction to Nerve Plexuses
• Networks of ventral rami
(except T2–T12)
• Found in cervical,
brachial, lumbar, and
sacral regions
• Serve limbs; fibers
crisscross for redundancy
The Cervical Plexus
• C1-C4
• Deep to the
sternocleidomastoid
• Mostly cutaneous
nerves; some serve
anterior neck muscles
Cervical Plexus Sensory Branches
• Lesser Occipital Nerve
• Great Auricular Nerve
• Transverse Cervical Nerve
• Supraclavicular Nerves
• Mnemonic: “Let’s Go To Sleep”
Cervical Plexus Motor Branches
• Muscular branches
• Ansa cervicalis
• Phrenic nerve
• Acronym: "MAP"
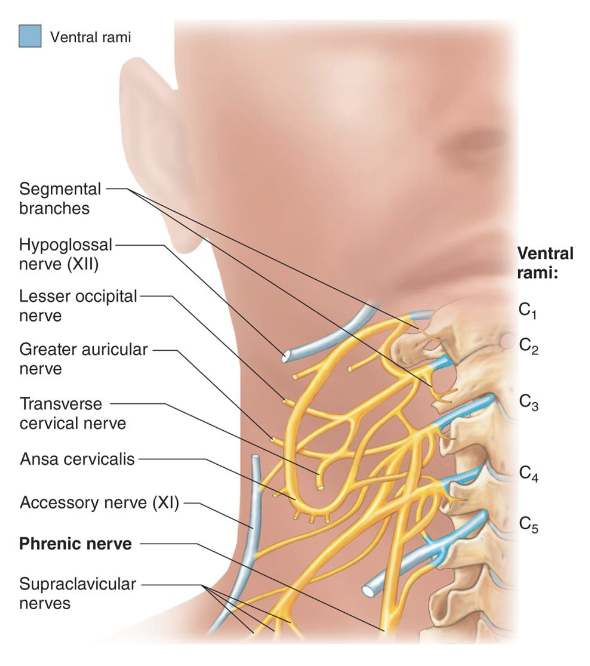
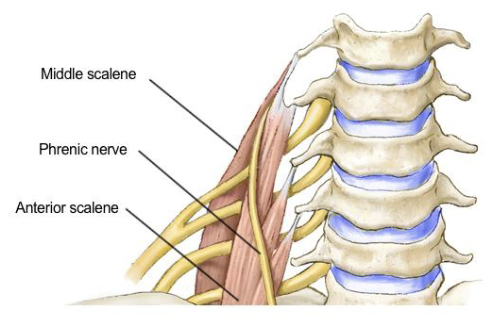
Phrenic Nerve
• Key nerve of the cervical
plexus
• Formed by C3, C4, and C5
fibers
• Controls the diaphragm
• “C3,4,5 keeps the
diaphragm alive”
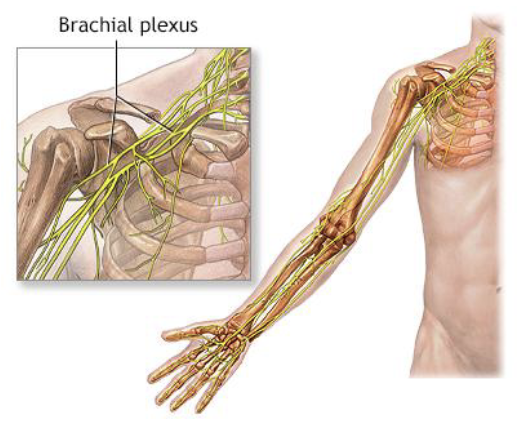
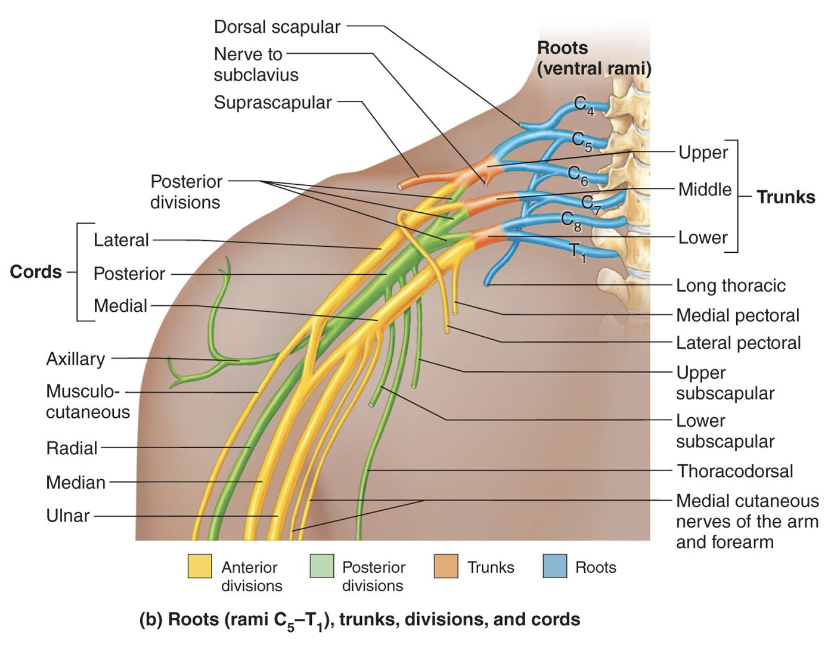
Brachial Plexus
• Located in the neck and
axilla
• Formed by C5–C8 ventral
rami
• Cords give rise to main
upper limb nerves
Upper Limb Innervation
• Components (medial to lateral):
1. Ventral rami
2. Trunks
3. Divisions
4. Cords
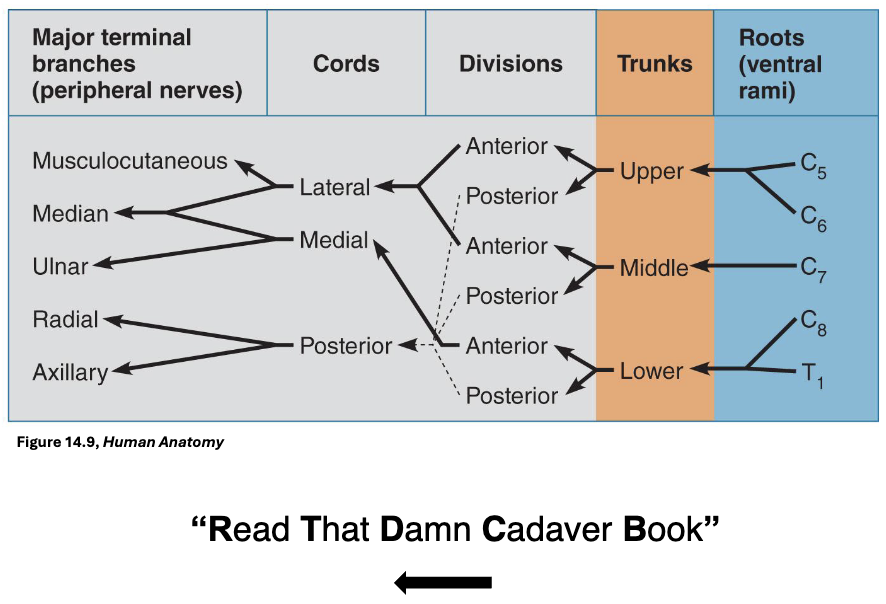
Brachial Plexus Structure
• Ventral Rami: form the roots of the brachial plexus
• Trunks: 3 trunks formed from merging rami
• Divisions: Each trunk splits into anterior and posterior
divisions
• Cords: 6 divisions converge to form 3 cords
Terminal Branches from Lateral and Medial Cords
1. Musculocutaneous: from lateral cord, innervates
biceps brachii and brachialis
2. Median: from lateral and medial cords, innervates
anterior forearm muscles and lateral palm
• Muscular and digital branches
3. Ulnar: from medial cord, innervates intrinsic hand
muscles and medial hand skin
• Dorsal, superficial, and digital branches
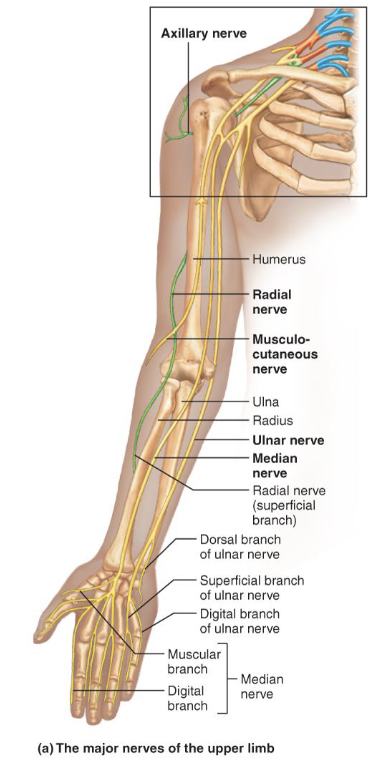
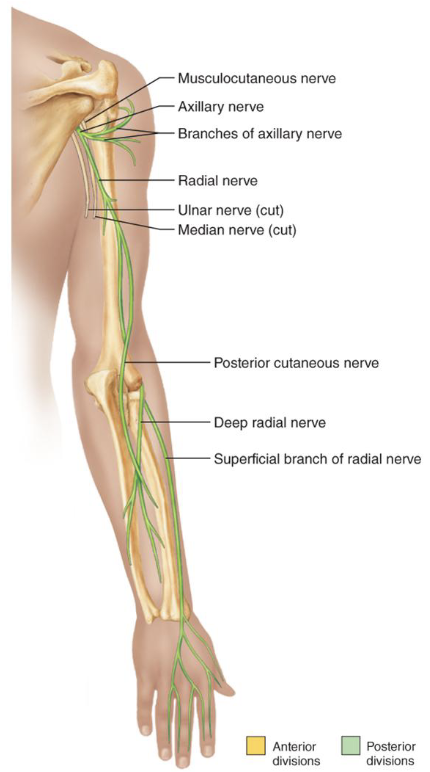
Terminal Branches from the Posterior Cord
• Axillary: innervates deltoid and teres minor
• Deep and superficial branch
• Radial: continuation of posterior cord, largest branch,
innervates posterior upper limb muscles
• Deep and superficial branch, posterior cutaneous nerve
Terminal Branches Mnemonic:
Most Alcoholics Must Really Urinate
Musculocutaneous Axillary Muscular Radial Ulnar
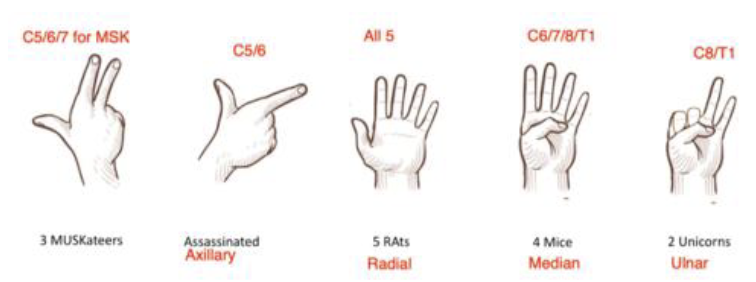
Mnemonic for the Brachial Plexus
3 Musketeers Assassinated 5 Rats, 4 Mice and 2 Unicorns
• C5, C6, C7 fingers = Musculocutaneous nerve
• C5 and C6 form a gun shape = Axillary nerve
• C5 to T1 = Radial nerves
• C6 to T1 = Median nerves
• C8 and T1 = Ulnar nerve
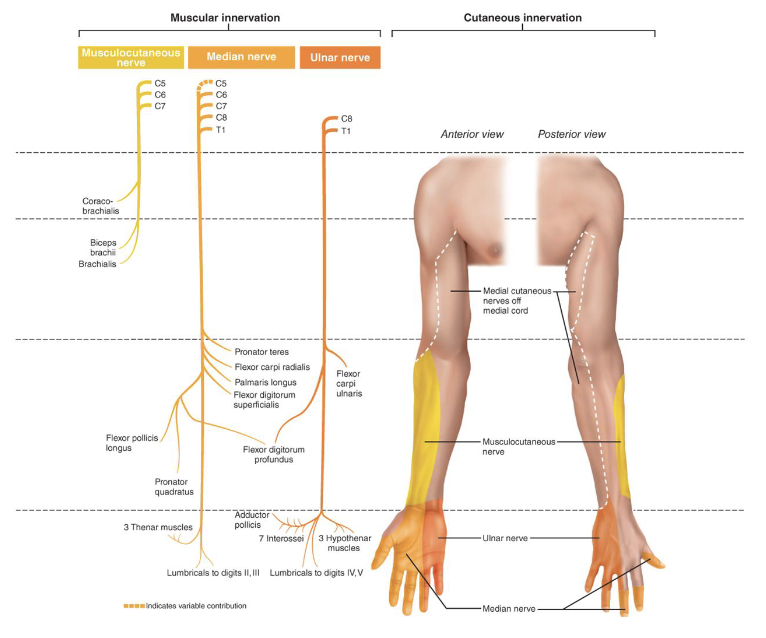
Muscular Innervation of the Upper Limb MME
• Musculocutaneous Nerve: Coracobrachialis, Biceps
Brachii, Brachialis
• Median Nerve: Forearm flexors, 3 Thenar muscles,
Lumbricals (digit 2 and 3)
• Ulnar Nerve: Flexor Carpi Ulnaris, Flexor Digitorum
Profundus, 3 Hypothenar Muscles, Lumbricals (digit 4
and 5)
• Radial Nerve: Triceps, Brachioradialis, Extensors
(Wrist, Digits), Supinator, Abductor Pollicis Longus,
Aconeus
• Axillary: Teres Minor, Deltoid
Cutaneous Innervation of the Upper Limb RAM
• Medial Cutaneous Nerve: sensory input to
Musculocutaneous, Ulnar, and Median Nerves
• Axillary Nerve: provides sensory input to the shoulder
• Radial Nerve: provides sensory input to the posterior
arm, forearm, and hand
Lumbar Plexus
• L1 to L4
• Smaller branches:
innervate posterior
abdominal wall and psoas
muscle
• Femoral Nerve:
innervates anterior
thigh muscles
• Obturator Nerve:
innervates adductor
muscles
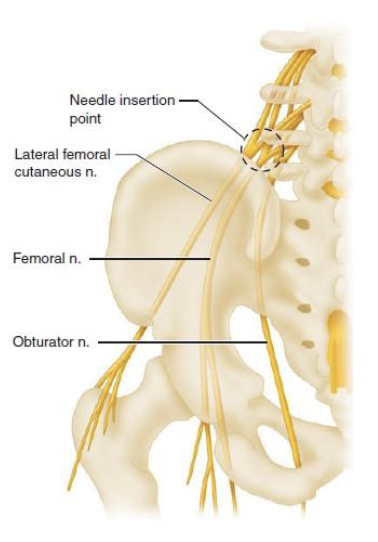
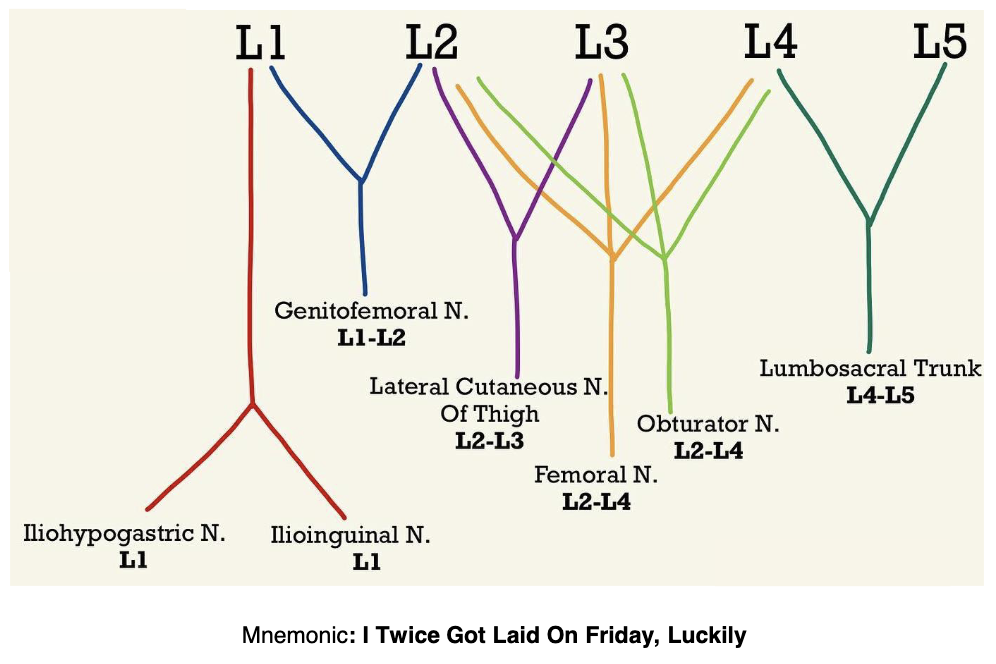
Ventral Rami & Major Branches
• Iliohypogastric: L1
• Ilioinguinal: L1
• Genitofemoral: L2
• Lateral Femoral Cutaneous: L2-L3
• Obturator: L2-L4
• Femoral: L2-L4
• Lumbosacral Trunk: L4-L5
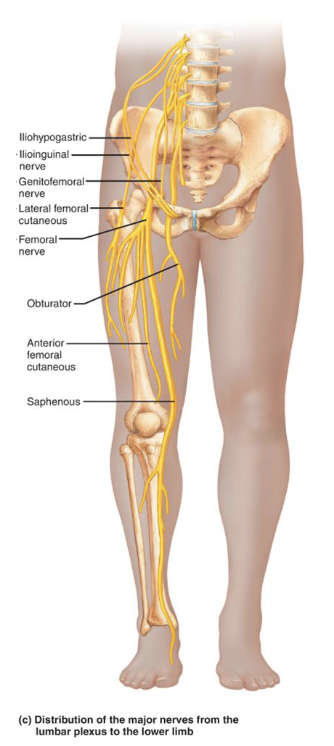
Muscular Innervation of the Lower Limb
Femoral Nerve
• Anterior thigh
• Innervates: Iliacus, Sartorius, Pectineus, Rectus Femoris,
Vastus Lateralis, Vastus Intermedius, Vastus Medialis
Obturator Nerve
• Medial thigh
• Innervates: Pectineus, Obturator Externus, Adductor
Brevis, Adductor Longus, Adductor Magnus, Gracilis
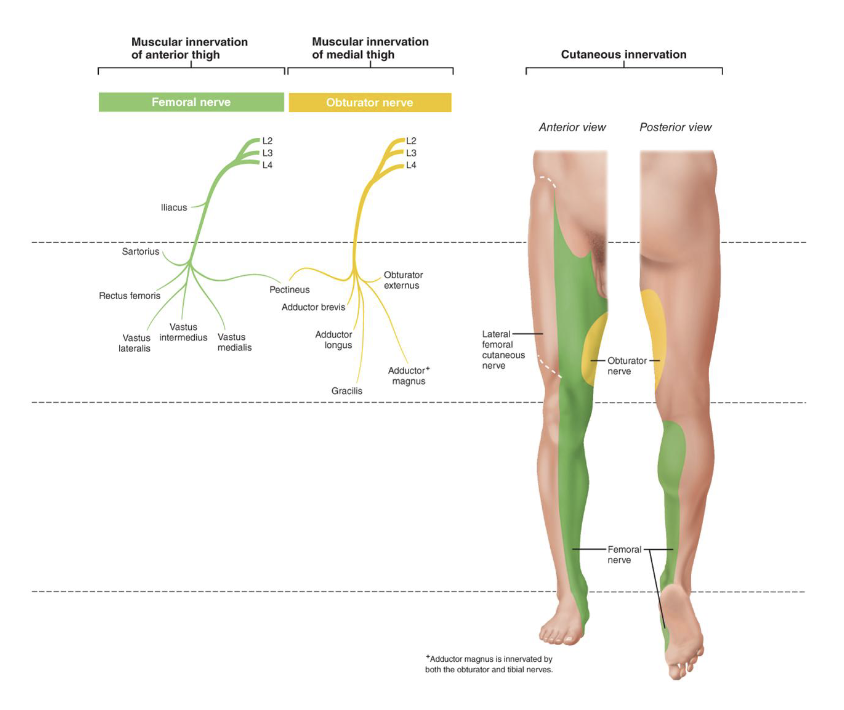
Cutaneous Innervation of the Thigh
• Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve: lateral sensory
innervation
• Obturator Nerve: medial sensory innervation, upper
thigh
• Femoral Nerve: anterior thigh, medial thigh, knee
Sacral Plexus
• Arises from spinal nerves L4–S4
• Located caudal to the lumbar
plexus
• Often considered together with
the lumbar plexus
• “Lumbosacral plexus”
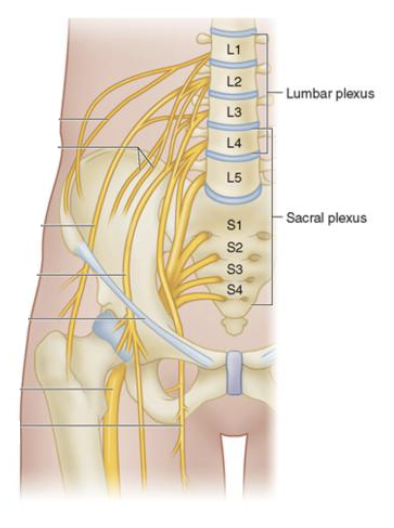
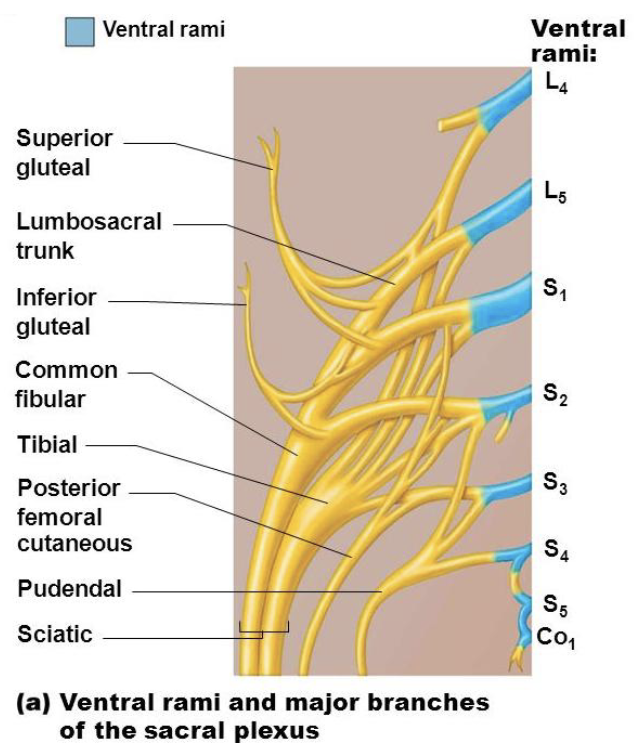
Ventral Rami and Major Branches
• Superior Gluteal Nerve: L4-S1
• Inferior Gluteal Nerve: L5-S2
• Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve: S1-S3
• Sciatic Nerve: L4–S3
• Pudendal Nerve: S2-S4
• Nerve to Quadratus Femoris: L4-S1
• Nerve to Obturator Internus: L5-S2
Mnemonic: Some Irish Sailors Pester Polly Quite Often
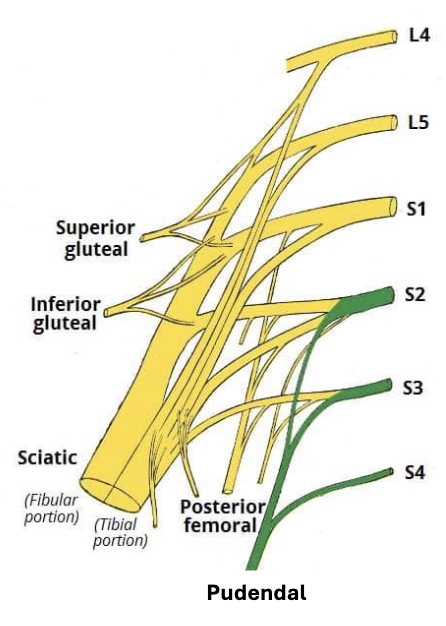
Innervation of the Pelvis
• Superior and Inferior
Gluteal Nerves:
innervate gluteal
muscles
• Superior: gluteus
medius, minimus,
and tensor fasciae
latae
• Inferior: gluteus
maximus
• Pudendal Nerve:
innervates perineum
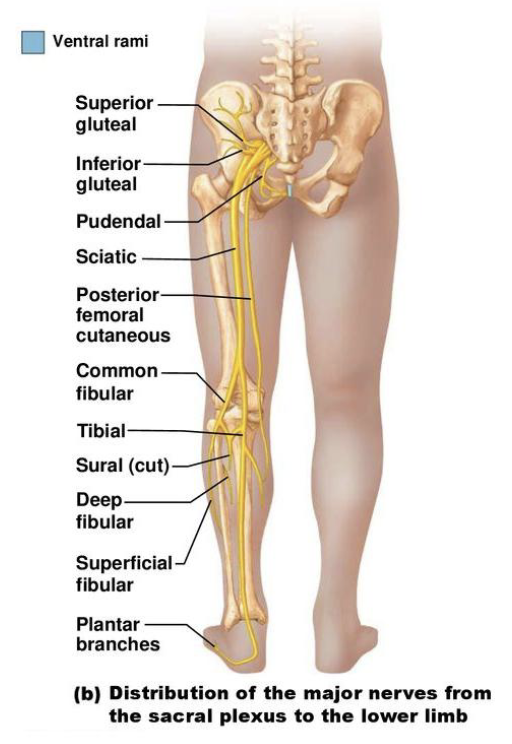
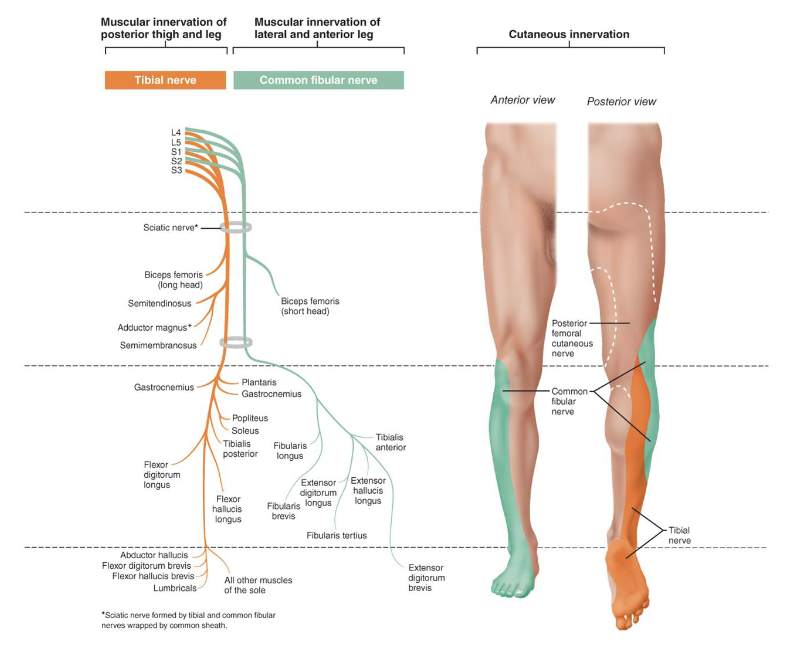
Innervation of the Lower Limb
• Sciatic Nerve
• Largest nerve of the sacral
plexus
• 2 nerves in one sheath:
1. Tibial Nerve:
innervates posterior
lower limb
2. Common Fibular
(Peroneal) Nerve:
innervates
anterolateral leg
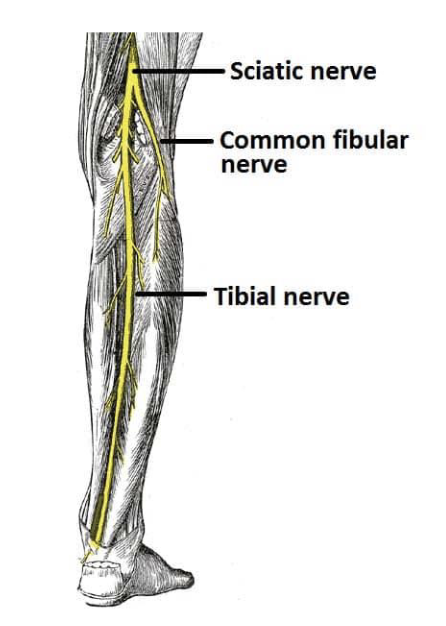
Tibial Nerve
• Passes through popliteal fossa, innervates posterior leg
and foot muscles and skin
• Divides into:
• Medial Plantar Nerve
• Lateral Plantar Nerve
Common Fibular Nerve
• Innervates anterolateral leg
• Divides into:
• Superficial Fibular Nerve: Fibularis Longus and
Fibularis Brevis
• Deep Fibular Nerve: Tibialis Anterior, Extensor
Hallucis Longus, Extensor Digitorum Longus, and
Fibularis Tertius
Cutaneous Innervation of the Lower Leg
• Common Fibular Nerves: dorsum of foot and
anterolateral leg
• Tibial Nerve: posterior leg and sole of foot
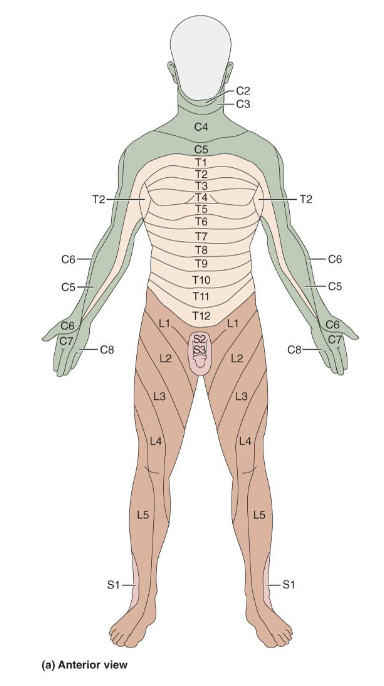
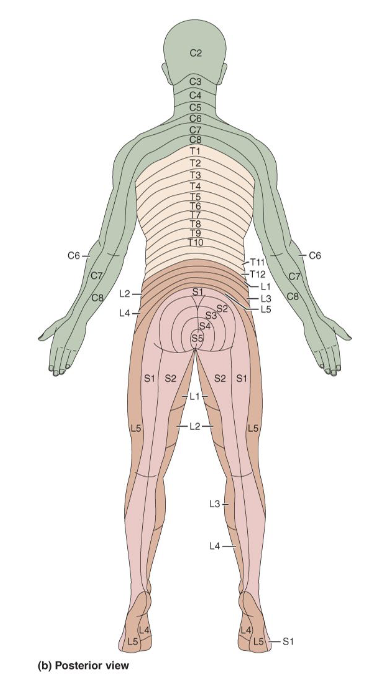
Innervation of the Skin
• Dermatome: area of skin innervated by cutaneous
branches of a single spinal nerve
• Pain along dermatome indicates nerve root damage
• General pattern similar, precise area innervated unique
like fingerprints