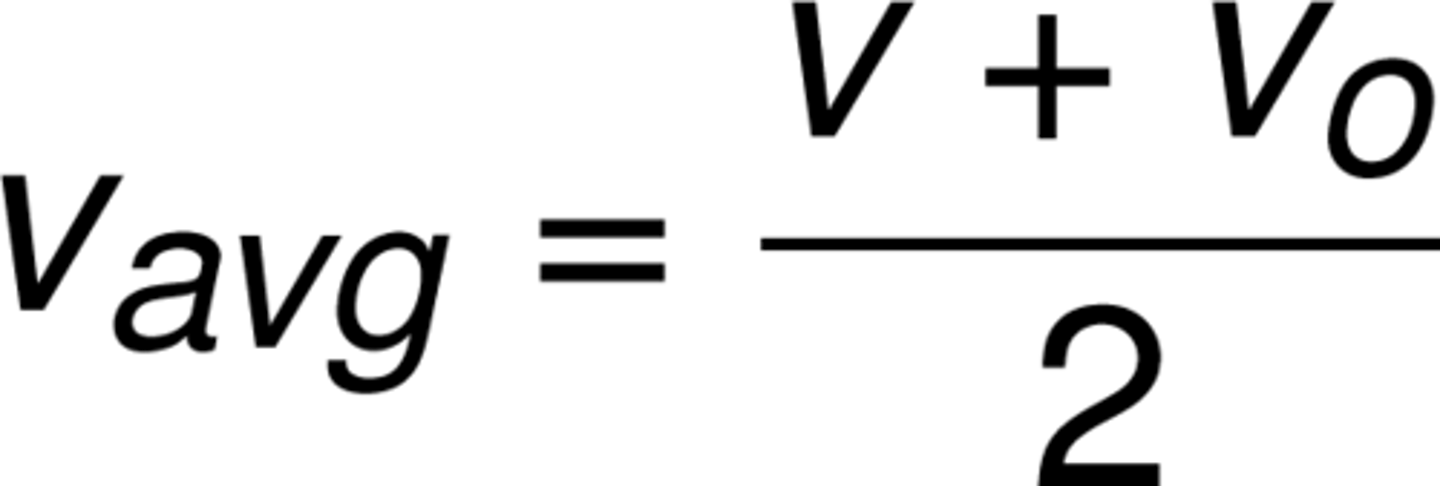Physics I Lesson 1: Vectors
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
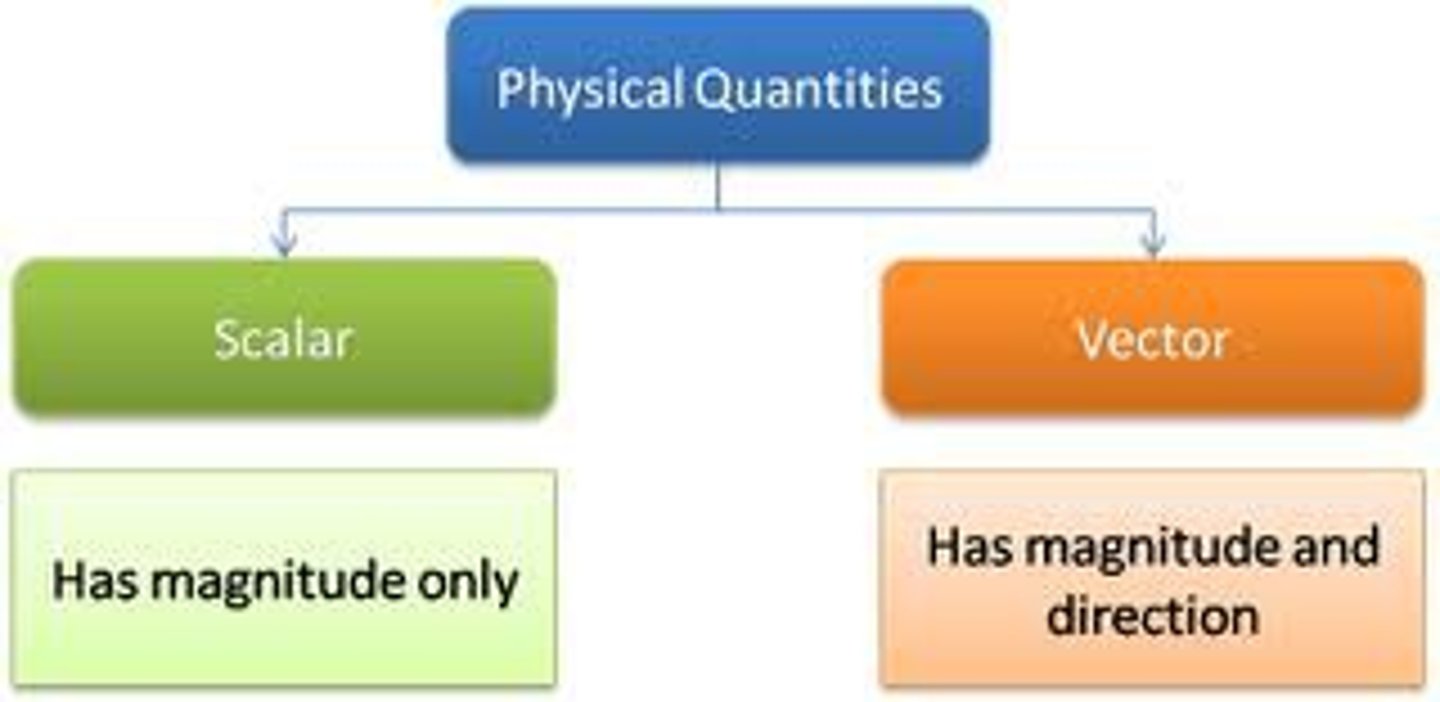
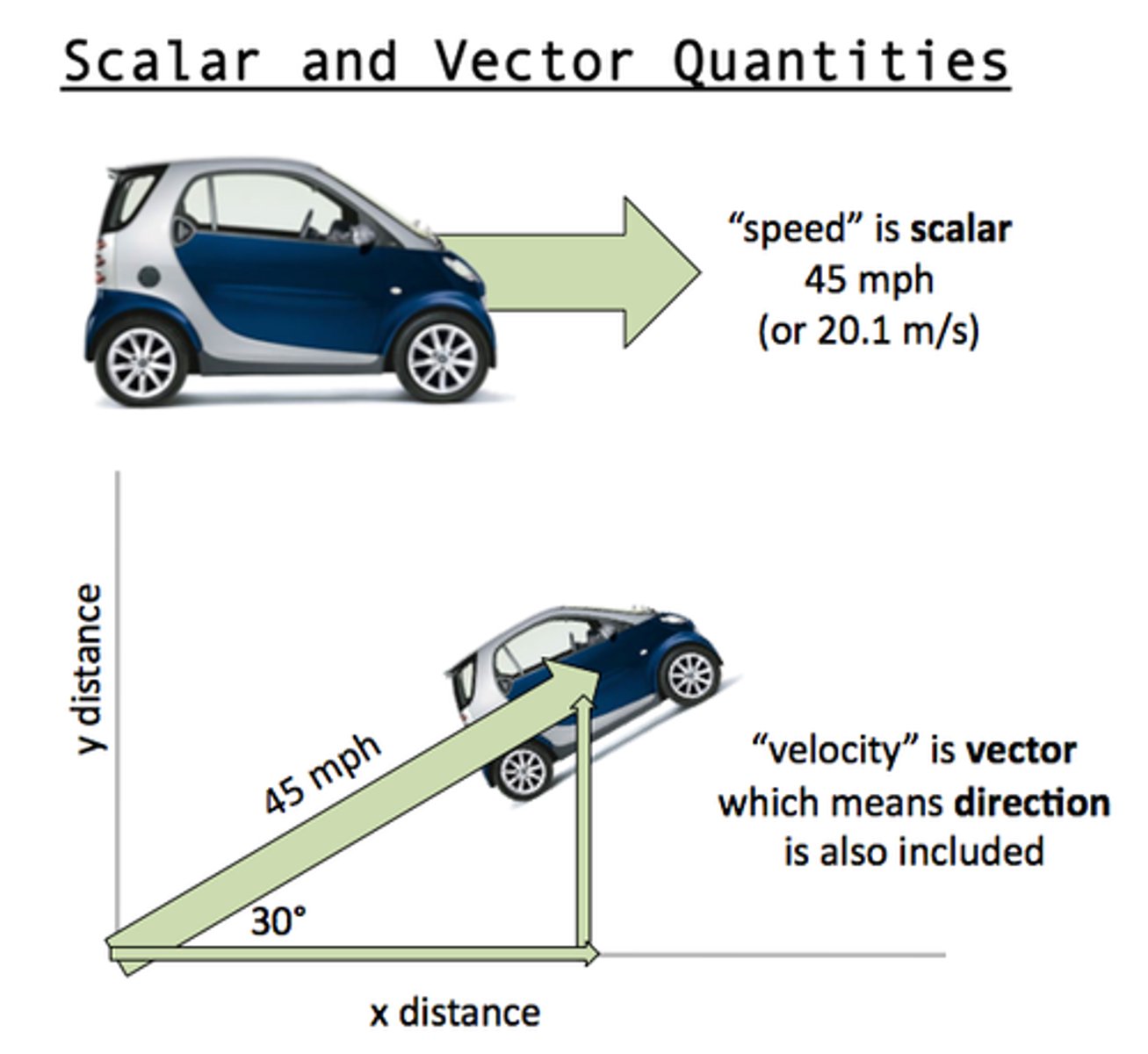
What is the difference between a vector and a scalar?
Vectors have magnitude AND direction. Scalars just have magnitude.
CRB Draw out how to add vectors using the head-to-tail method.
CRB True or false? When multiplying a vector by a positive (n>0) number, the magnitude of the vector will change, but not its direction.
True. When multiplying a vector by a positive (n>0) number, the magnitude of the vector will change, but not its direction.
Scalar is to ____________ as vector is to___________.
(A) distance, distance
(B) distance, displacement
(C) displacement, displacement
(D) displacement, distance
(B) distance, displacement
Displacement includes a direction and a quantity; therefore, it is a vector quantity.
Distance, on the other hand, is a scalar quantity as it only entails a quantity.
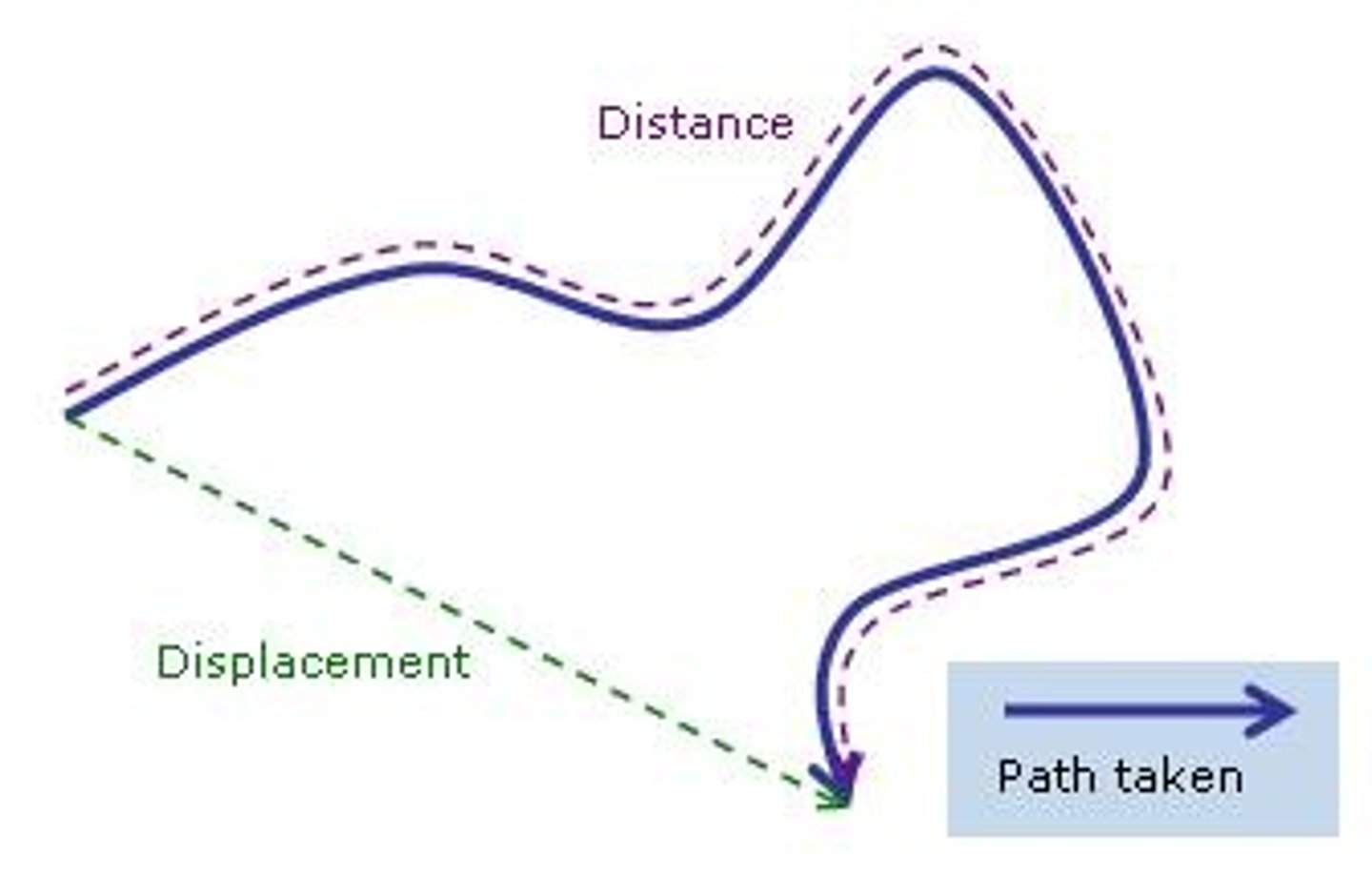
What is the difference between velocity and speed?
Velocity is a vector quantity, while speed is a scalar quantity. Speed = absolute value of velocity.
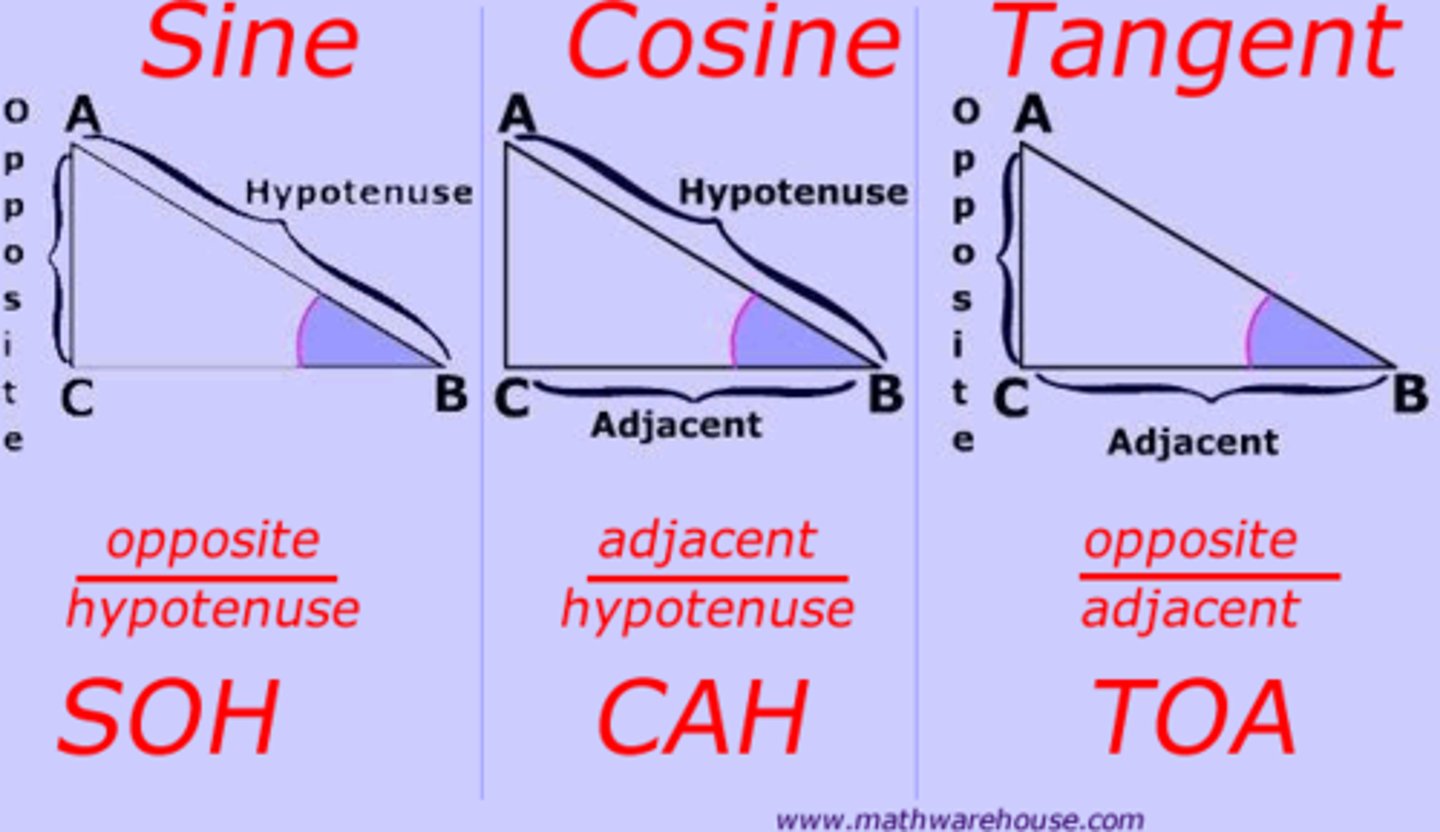
What does soh cah toa stand for?
Sinθ = opposite/hypotenuse
Cosθ = adjacent/hypotenuse
Tanθ = opposite/adjacent
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
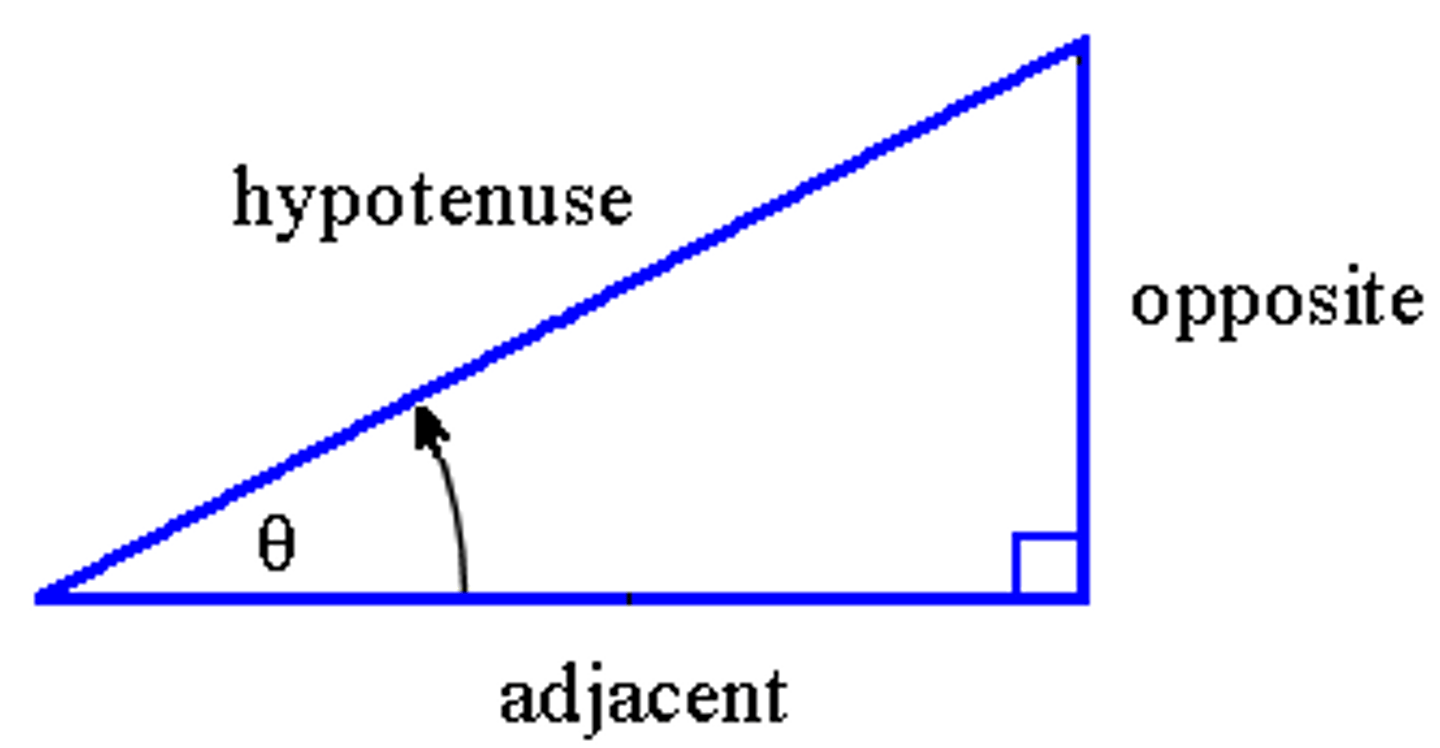
If we know the angle of a vector and adjacent horizontal vector, how can we use that to find the length of the original vector (the hypotenuse)?
By using cosθ = adjacent/hypotenuse
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
If Max got in his car and traveled northwest, with a 63.2° angle between his direction and due west, how far west (in miles) would he have gone if he went 26.6 miles in the northwest direction?
(A) 4.6
(B) 12.0
(C) 16.8
(D) 34.2
(B) 12.0
cosθ = adjacent/hypotenuse
cos63.2 = adjacent/26.6
adjacent = (26.6)(cos63.2)
adjacent = (26.6)(approx. .5 (actual: .451))
adjacent = (approx. 13.3 (actual: .12.0))
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Match the following xyz-plane directions with their corresponding unit vectors.
I. x
II. y
III. z
(A)h^
(B)î
(C)ĵ
(D)k^
I (B) x: î
II (C) y: ĵ
III (D) z: k^
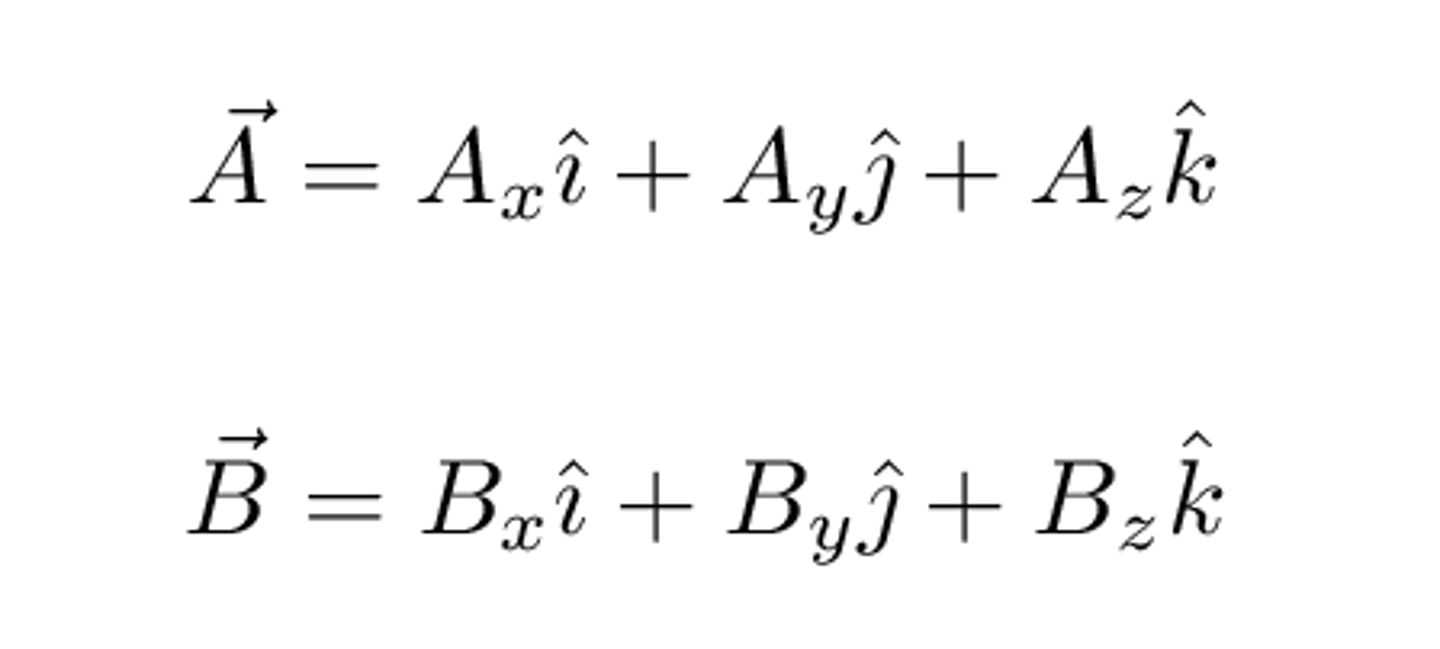
What does vector b̂ = 4î + 3ĵ mean?
Vector b can be broken down into a horizontal vector of length 4 and a vertical vector of length 3.
How is average velocity calculated from displacement?
Average velocity = displacement/change in time
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
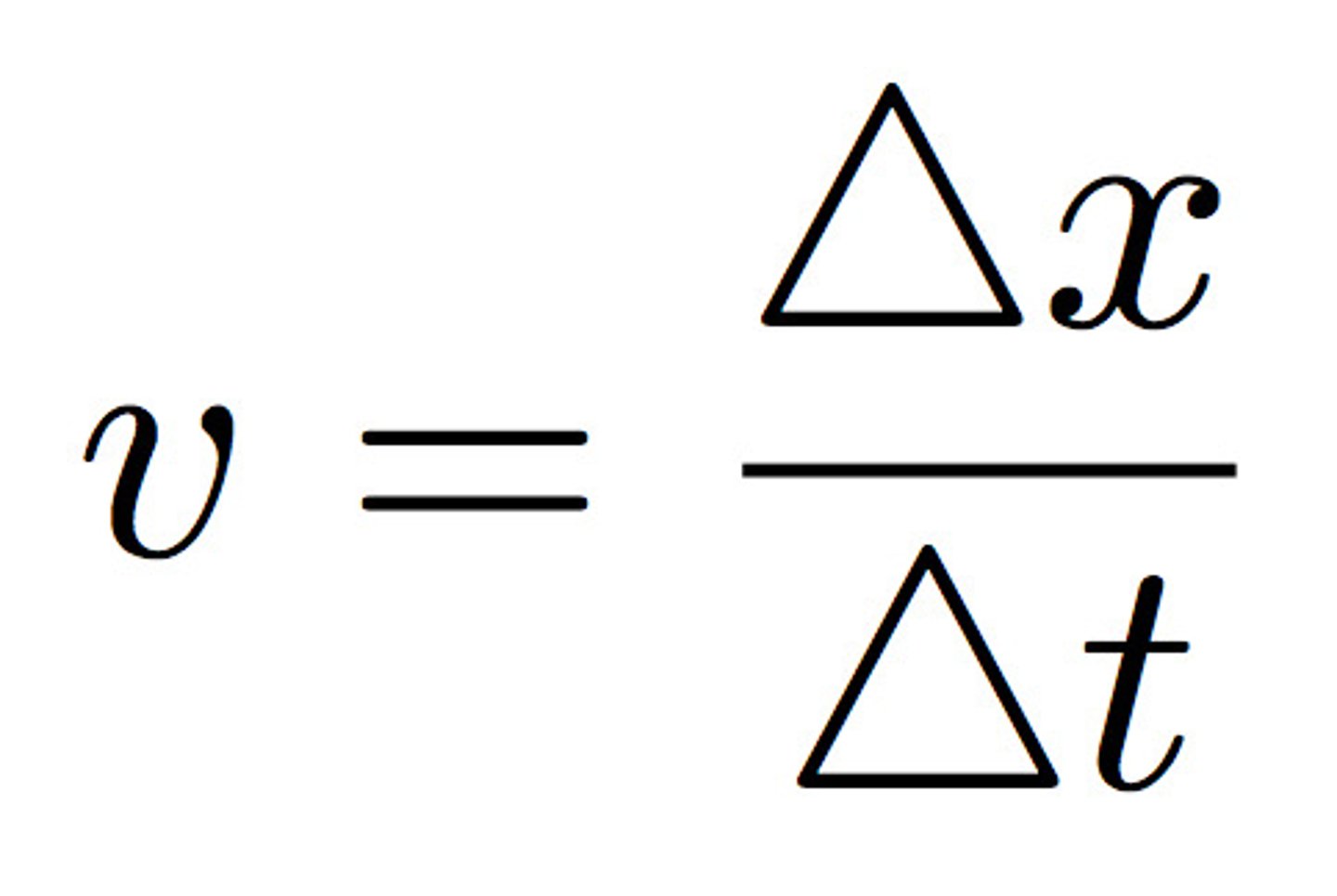
CRB In order to use the above equation, you need to know the displacement. How do you calculate displacement?
Displacement = Final Position - Initial Position = Net Distance (in some direction)
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB Rusev started on an xy-plane at (-0.5, 3). He walks so that his final position is (-0.5, -3). What is Rusev's displacement?
(A) -6 units
(B) 6 units
(C) -3 units
(D) 3 units
(A) -6 units
Displacement = Final Position - Initial Position = Net Distance (in some direction)
X-displacement = -0.5 - (-0.5) = 0
Y-displacement = (-3) - 3 = -6
Total displacement is 6 units due South.
CRB If there is displacement in multiple directions (for example, in both the x and y directions), then the distance formula will be needed. Write out the distance formula for 2- and 3-dimensional movement.

CRB In which of the following examples could you calculate the missing variable from given information?
I. Given Distance and Initial Position, find Final Position.
II. Given Final Position and Distance, find Initial Position.
III. Given Initial Position and Final Position, Find Displacement.
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) I, II and III
(B) III only
If you know the Initial and Final position, you can find Displacement. However, knowing distance cannot help to find Initial or Final Positions, since distance has no direction, only magnitude!
CRB True or false? Displacement, unlike Distance, can be used when knowing one of Final or Initial to find the other because Displacement has both a magnitude and a direction.
True. Displacement, unlike Distance, can be used when knowing one of Final or Initial to find the other because Displacement has both a magnitude and a direction.
Joshua drove 17.45 miles in 23.4 minutes. His total displacement, however, was only 9.44 miles in the north direction. What was his average velocity (in mph)?
(A) 13.5 north
(B) 24.2 north
(C) 43.6 north
(D) 67.2 north
(B) 24.2 north
Average velocity = displacement/change in time
Average Velocity = (9.44 miles) / (23.4/60 hour)
Average Velocity = (9.44 miles) / (approx. 1/3 hour)
Average Velocity = approx. 30 mph (actual: 24.2)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Johnny was traveling at a speed of 14.2 m/s and traveled a total of 345.9 meters. How long did it take?
(A) 13.78 s
(B) 24.36 s
(C) 31.92 s
(D) 55.24 s
(B) 24.36 s
Average velocity = displacement/change in time
14.2 = 345.9 / change in time
change in time = 345.9 / 14.2
change in time = approx. 23 seconds (actual: 24.36)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
CRB What does "instantaneous" mean when referring to velocity (or speed of acceleration, etc)?
It means the velocity at a specific time, not an average over a period of time.
CRB What does the slope at a point on a position vs time graph represent?
The instantaneous velocity at that point.
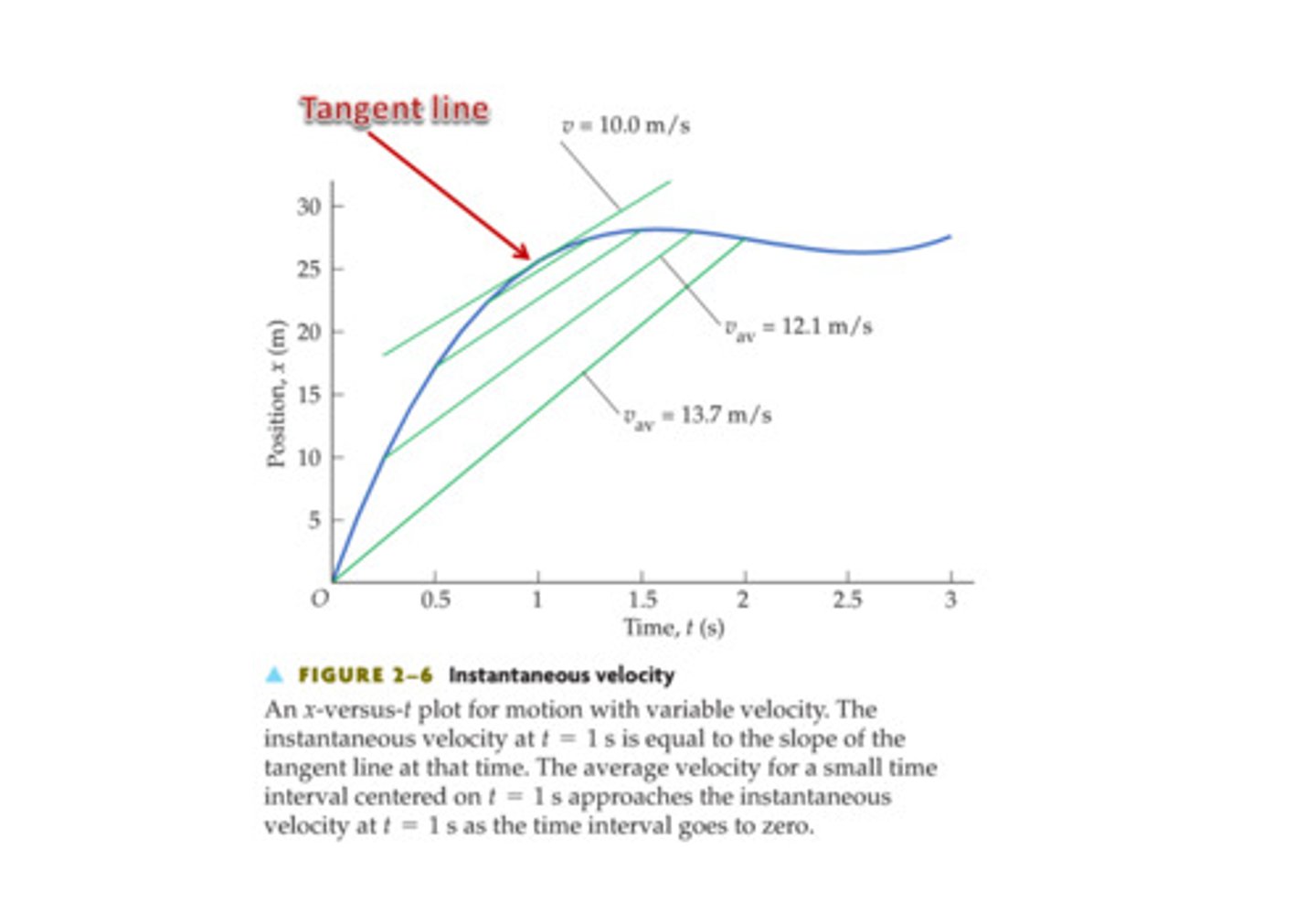
CRB What would the slope of a Velocity vs Time graph represent?
(A) Displacement
(B) Distance
(C) Acceleration
(D) Time Elapsed
(C) Acceleration
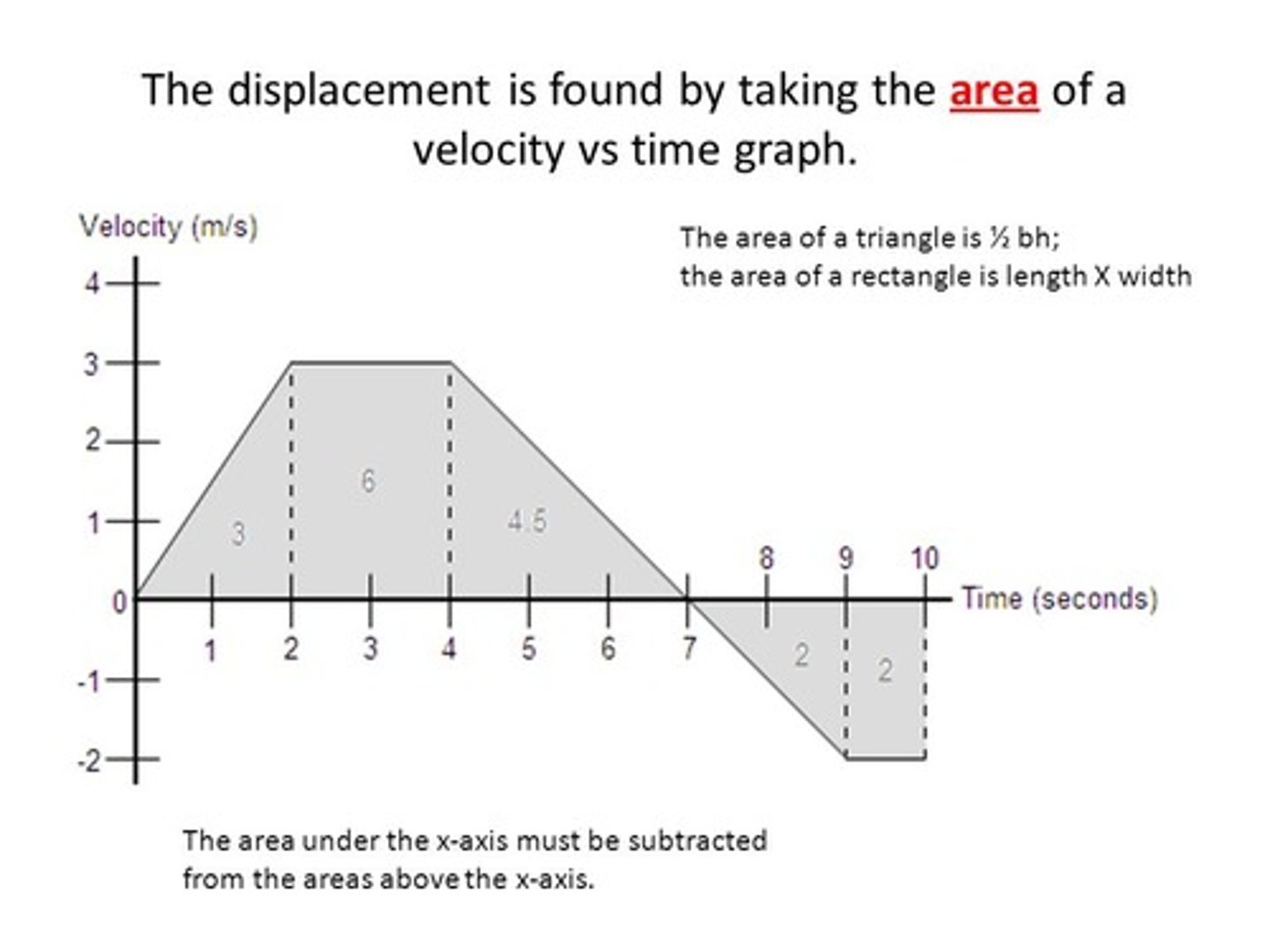
CRB What would the area underneath a Velocity vs Time graph represent?
(A) Displacement
(B) Distance
(C) Acceleration
(D) Time Elapsed
(A) Displacement
How is acceleration calculated from velocity?
Acceleration = change in velocity/change in time
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
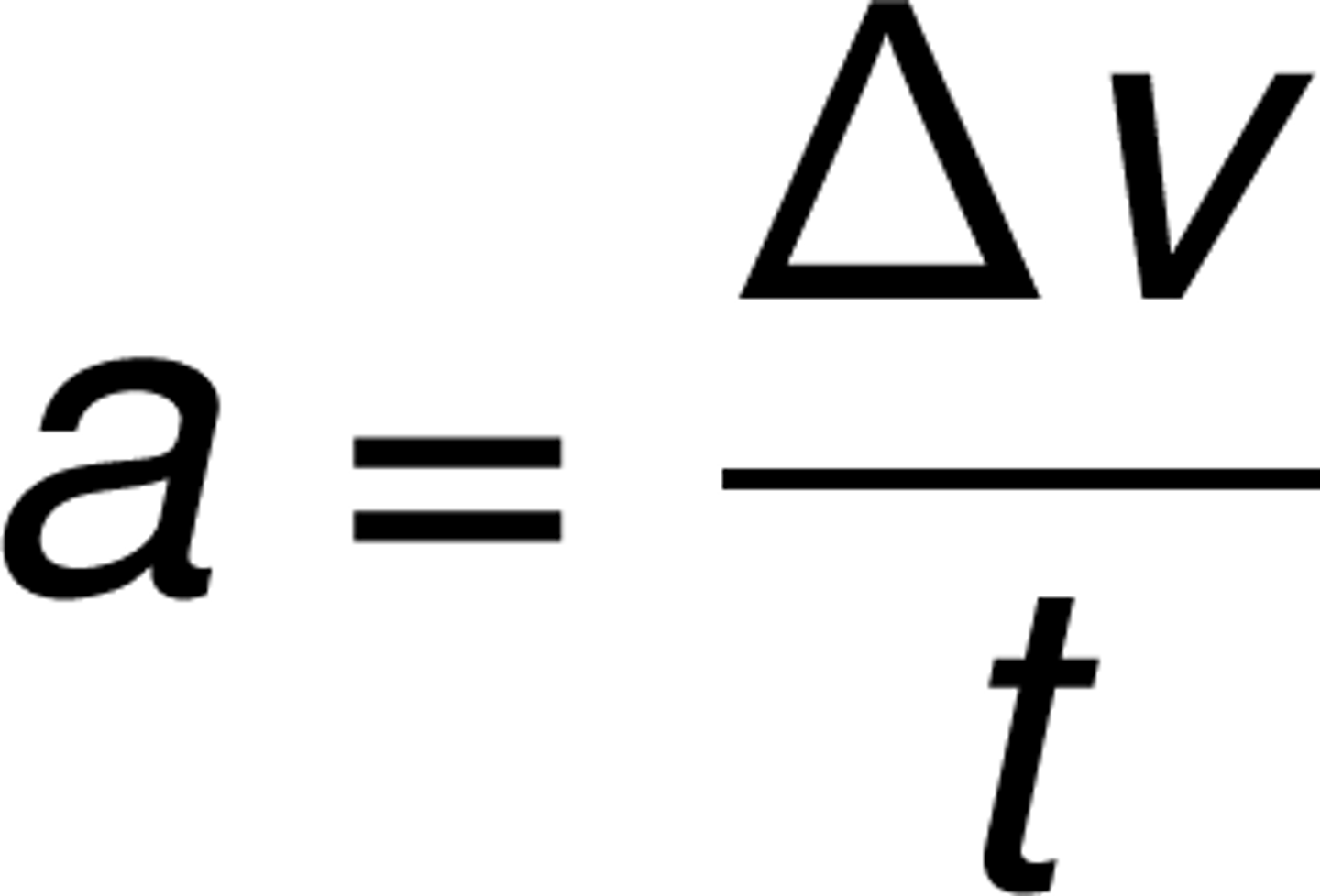
CRB True or false? If an object's velocity is zero, then the object's acceleration must also be zero. If false, provide a counterexample.
False. Even if an object's velocity is zero, the object could still be accelerating. Think of a baseball thrown straight up into the air; there is a split second where the ball is not moving up or down (at it peak height), but gravity is still making the ball accelerate back towards the Earth.
Ali is running at 1.22 m/s in the positive direction. Over 19.44 seconds he increases his speed to 2.31 m/s, what is his average acceleration?
(A) 3.1 m/s^2
(B) 0.52 m/s^2
(C) 0.31 m/s^2
(D) 0.056 m/s^2
(D) 0.056 m/s^2
Acceleration = change in velocity / change in time
Acceleration = ( 2.31 - 1.22 m/s) / (19.44 s)
Acceleration = 0.05 m/s^2 (actual: .056 m/s^2)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
CRB True or false? An object's average acceleration must be in the same direction as the object's net change in velocity. If false, provide a counterexample.
True. An object's average acceleration must be in the same direction as the object's net change in velocity.
What is the mathematical relationship between acceleration and velocity?
a = dv / dt
Acceleration is the derivative of velocity (ie, how quickly velocity changes over time, measured in m/s^2).
v = dx / dt
Similarly, velocity is the derivative of position (how quickly position changes over time).
What are the 2 formulae you need to know for velocity and displacement?
vf = v0 + a Δt
Δd = v0 (t) + 1/2 a (t^2)
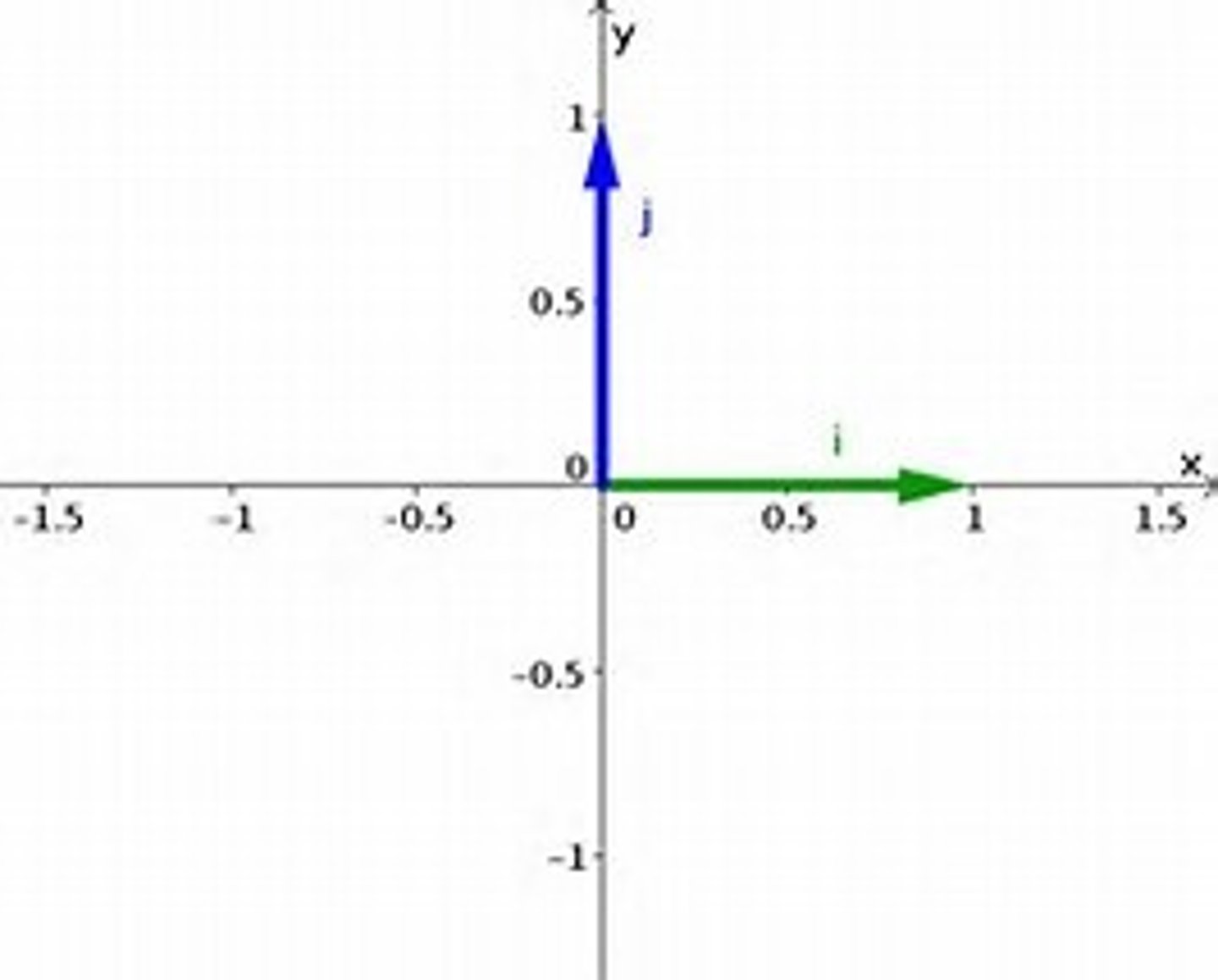
What is the benefit of using i and j vectors?
i and j are unit vectors ( i = x direction, j = y direction)
Any vector can be broken down into its x and y components, and thus, can be written as a sum of i and j vectors.
V = Vx + Vy OR V = ___ i + ___ j
How can we use a graph to determine the instantaneous velocity?
Find the slope of a point on a d-t graph (derivative)
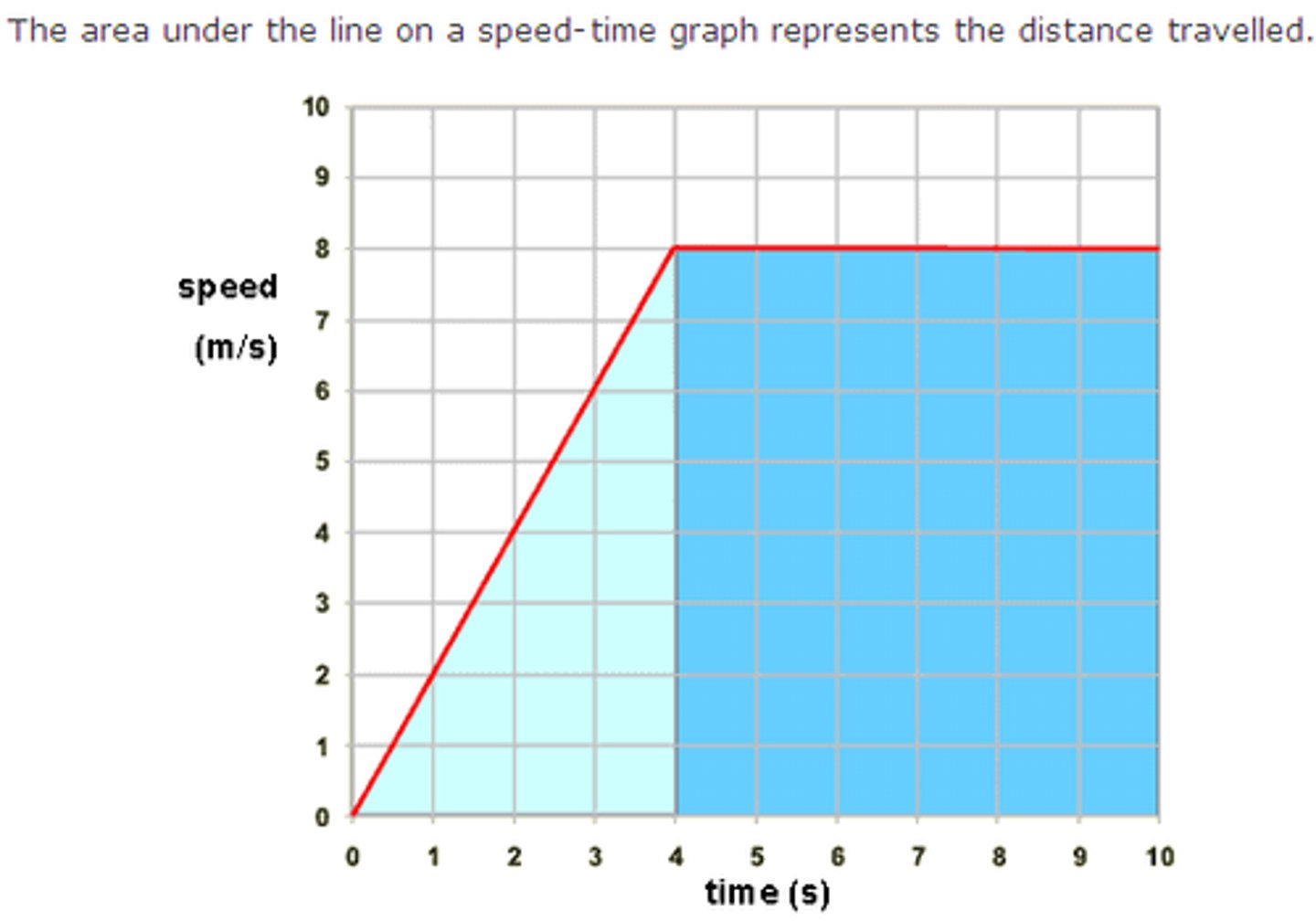
Area under a VT graph tells you...
displacement! (go backwards)
(picture: represents DISPLACEMENT)
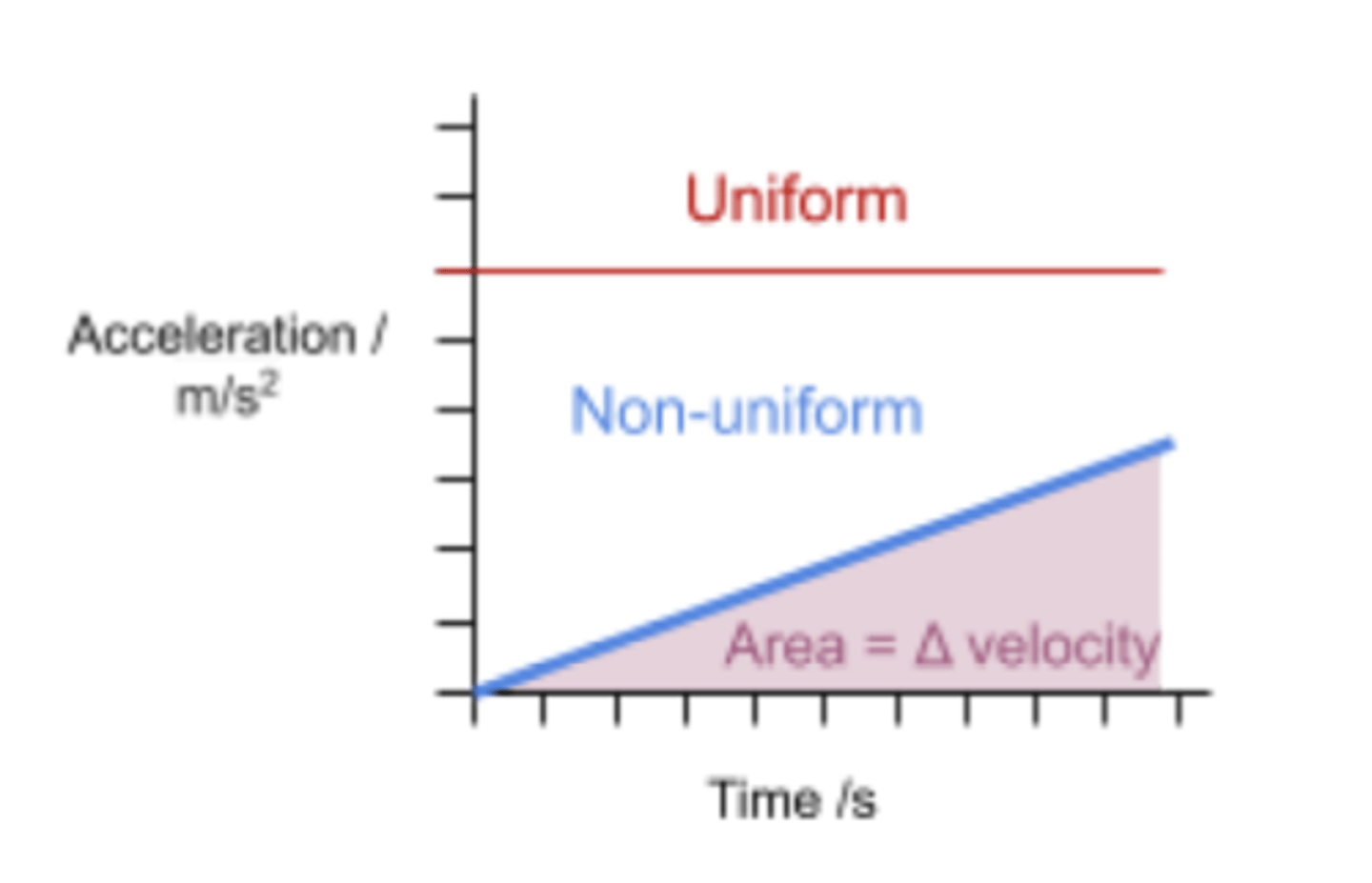
Area under an AT graph tells you...
velocity! (go backwards)
How can you calculate Avg vs Ins acceleration with a vt graph?
Avg A = slope of the vt line between two points on the graph
Inst A = slope of a point on the line
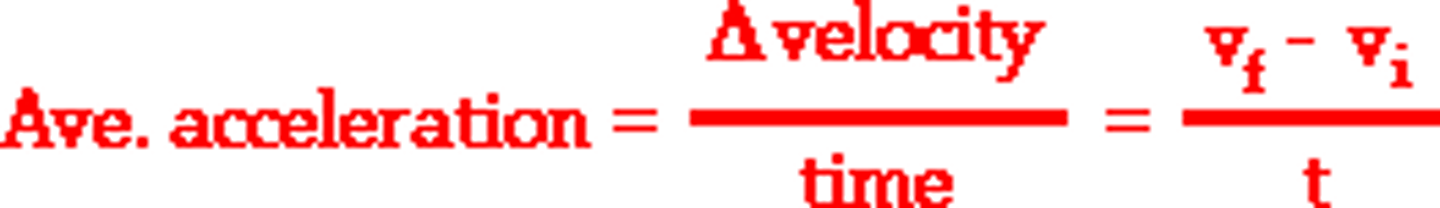
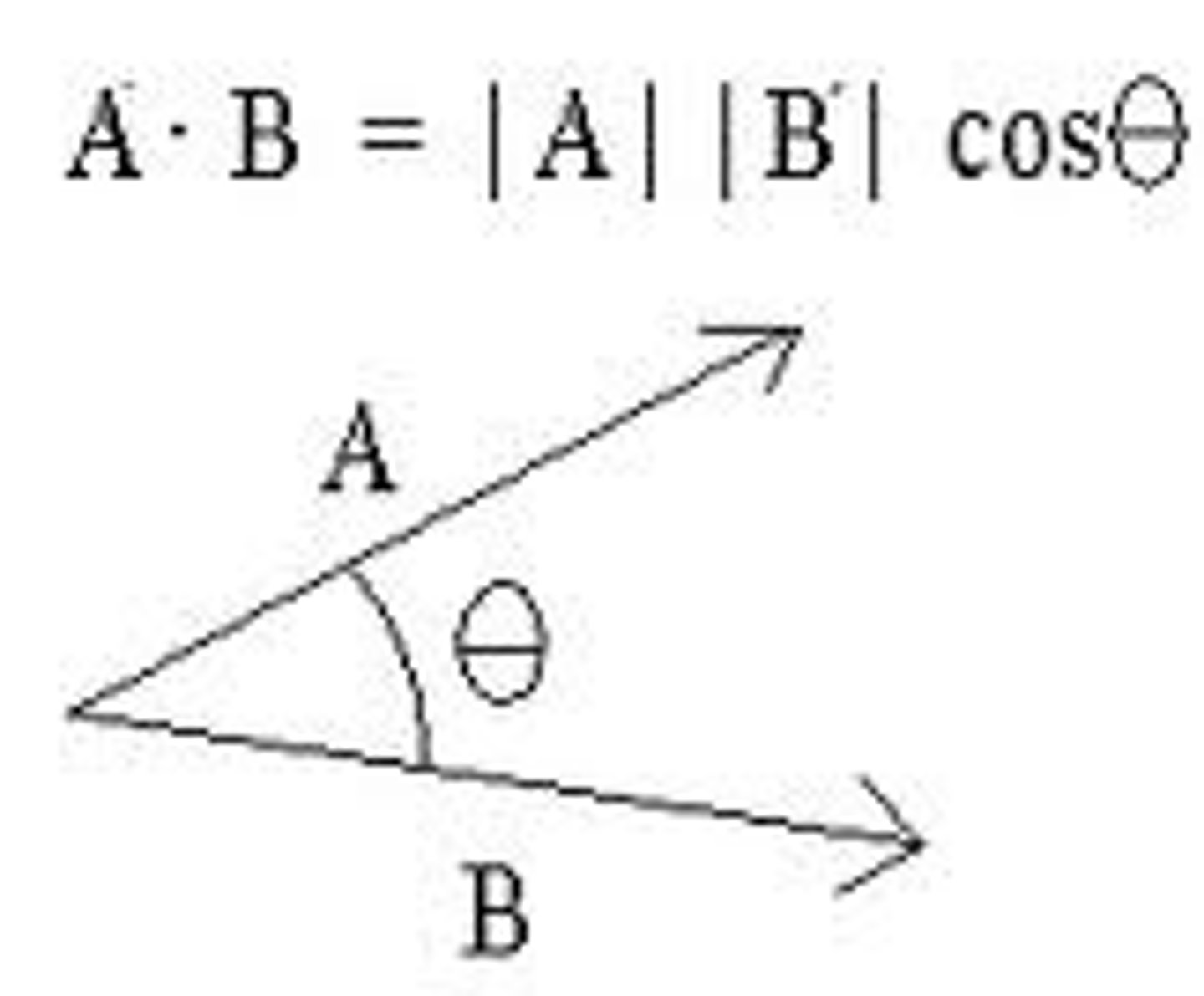
What does the dot product result in?
Scalar quantity (just a number, or magnitude)
What does the cross product result in?
Vector quantity (number, plus use RHR to determine direction)

State the Right Hand Rule for vector multiplication
Resultant Vector = F
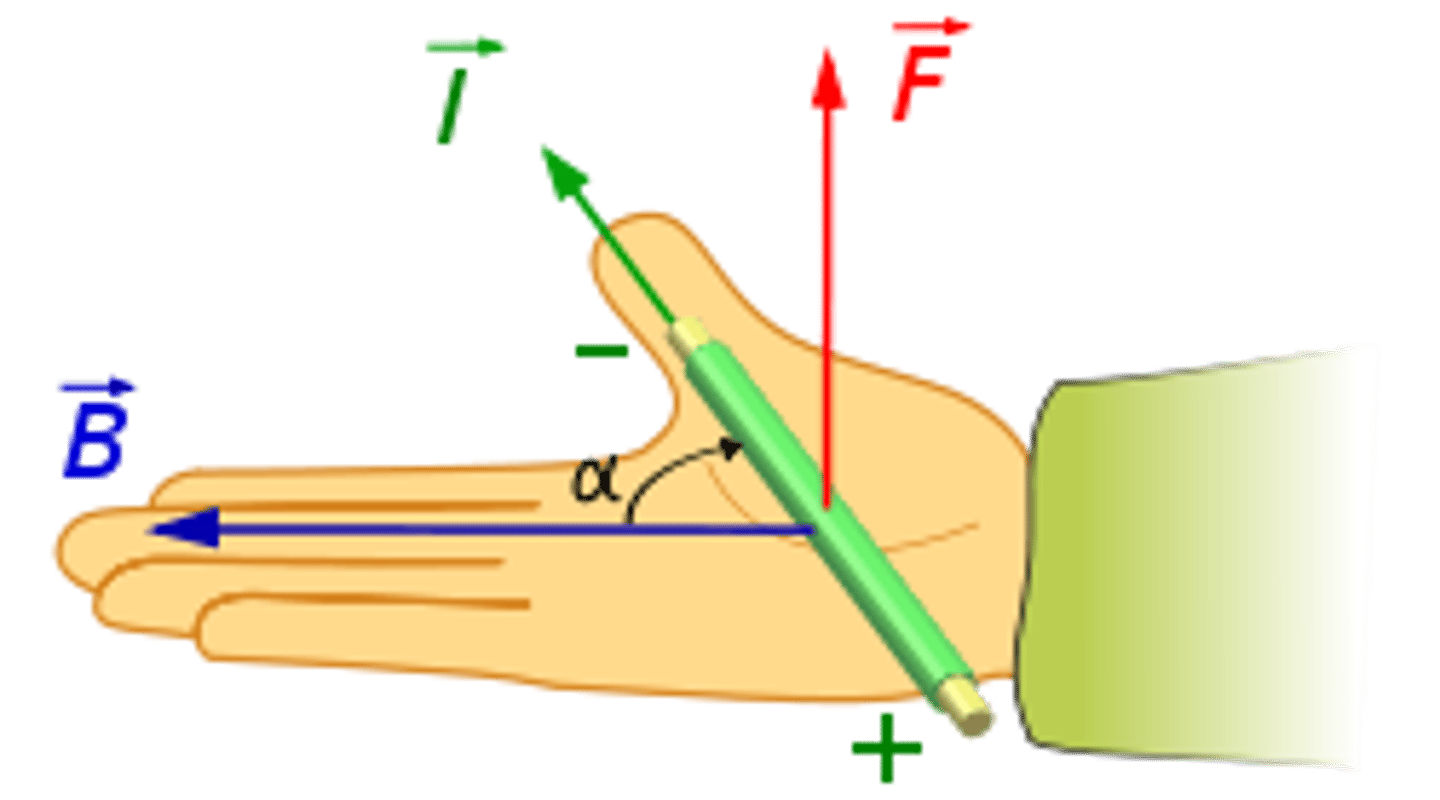
How can we calculate Vinst when acceleration is constant?
we use the formula
Vf = V0 + a t
How can we find Vavg when acceleration is constant?
By taking the average of two velocities given