Population
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms

Population
the total number of people living in an area at a period of time
what is population affected by
migration, birth rate and death rate
birth rate
the total number of births per 1000 per year
death rate
total number of deaths per 1000 people per year
migration
the movement of people from one place to another
MEDC birth rate
low
LEDC birth rate
high
factors causing high birth rates
early marriage, high infant mortality, low status/position in society, lack of sex ed, no contraceptives
factors causing low birth rates
late marriage, low infant mortality, high status/position, knowledge of sex ed, adequate contraceptives
natural increase
when the birth rate is higher than death
natural decrease
when the death rate is higher than birth rate
natural increase is calculated
birth rate minus death rate
dtm
demographic transition model
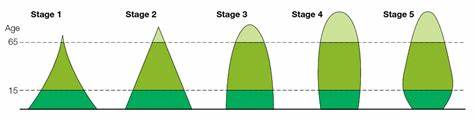
what is dtm
a model which describes how populations change over time as they develop
population structure
the composition of a countries population
resource
anything that is valuable to man and used in the product of goods/services
overpopulation
where there are too many people living in an area relative to natural resources
what can overpopulation lead to
food shortage, high crime, unemployment, insufficient water/energy
examples of overpopulated countries
china, Singapore, monaco
underpopulation
when people are too little
result of underpopulation
high maintenance
examples of underpopulation
greenland, Mongolia, australia
optinum population
a country with a balance of population size and resources available
why is it difficult to reach optinum population
migration, population changes, tech, exploitation of resources
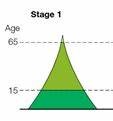
stage 1
high birth rate, low life expectancy, high death rate
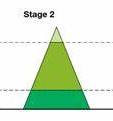
stage 2
birth rate still high, death rate decreasing, higher life expectancy
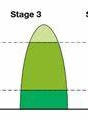
stage 3
falling birth rate, low death rate, higher life expectancy
stage 4
low birth rate, low death rate, high life expectancy
stage 5
low death rate, birth rate is low, very high life expectancy