ap bio unit 3 ch19-25
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
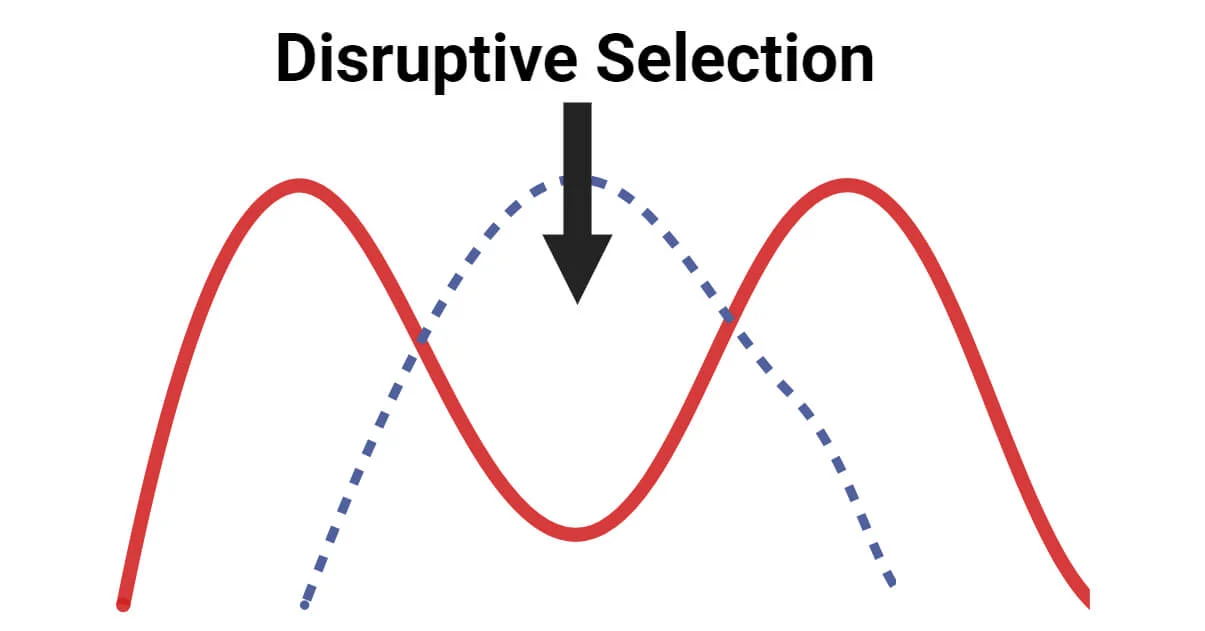
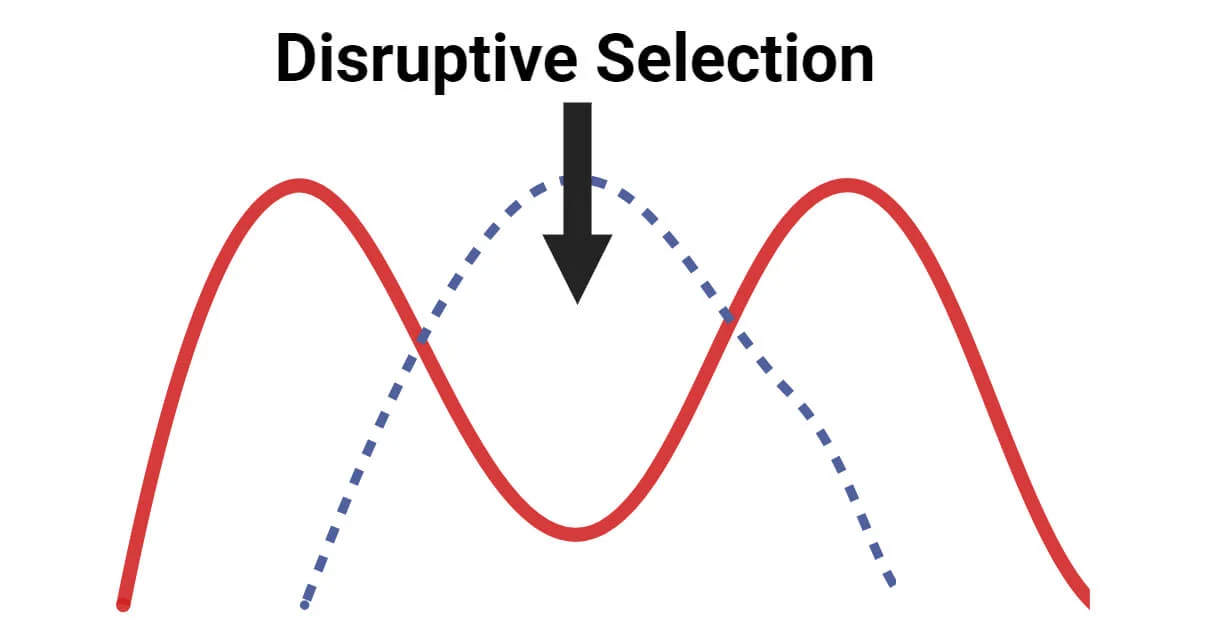
disruptive selection
both of the extremes are favored
stabilizing selection
the majority is favored
hetero zygote advantage
since you have both alleles, you can pass on the favorable one to your offspring so they will be successful
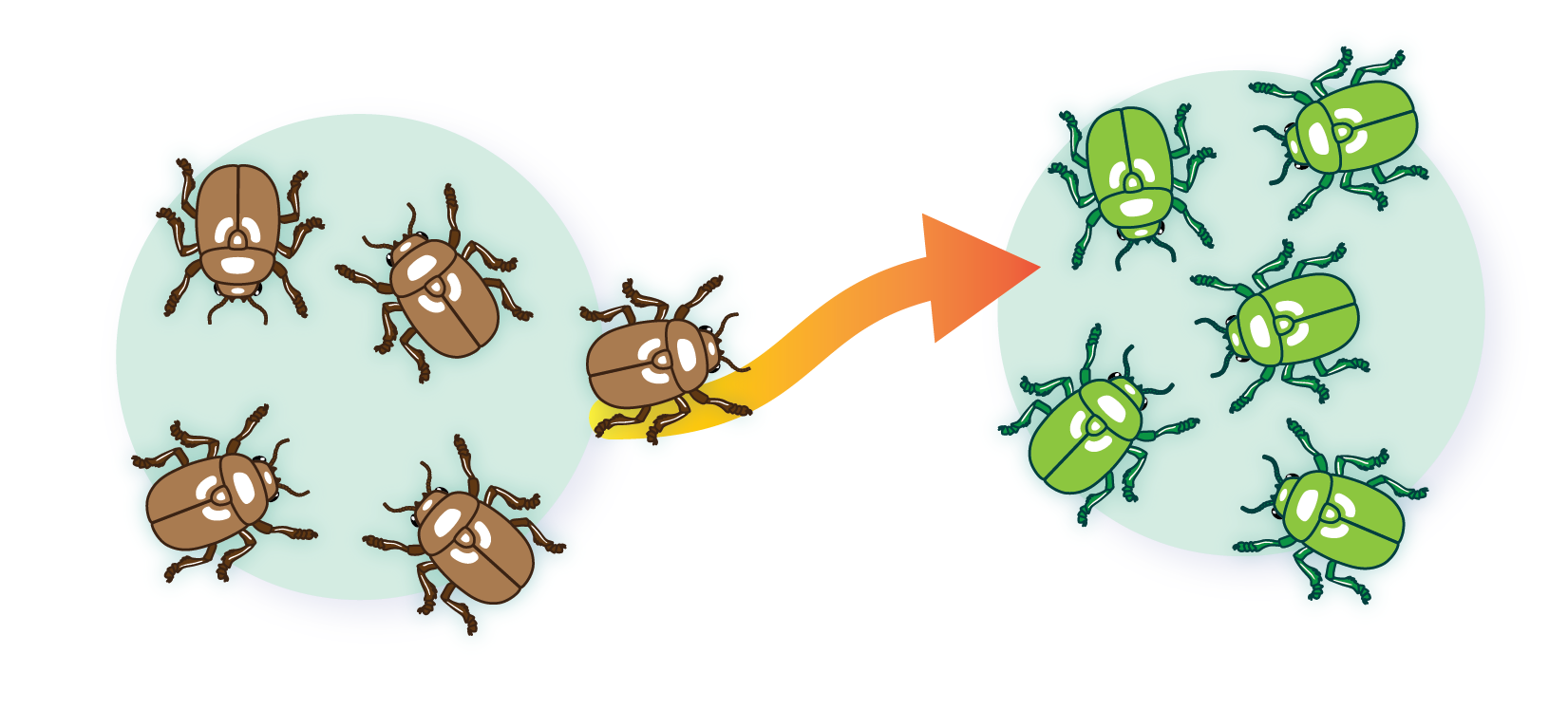
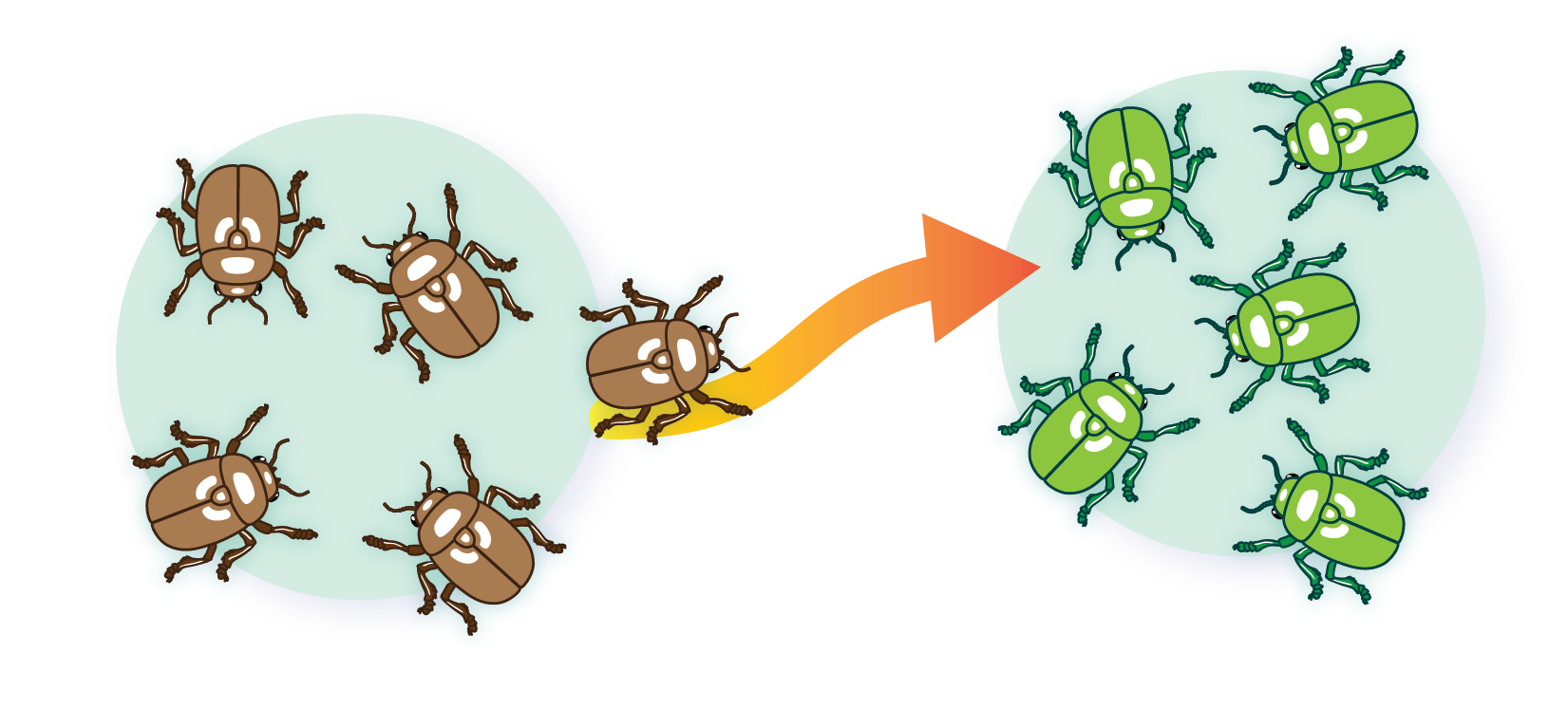
genetic flow
transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another, migration and emigration can causes this
genetic drift
chance that the frequency of an allele changes
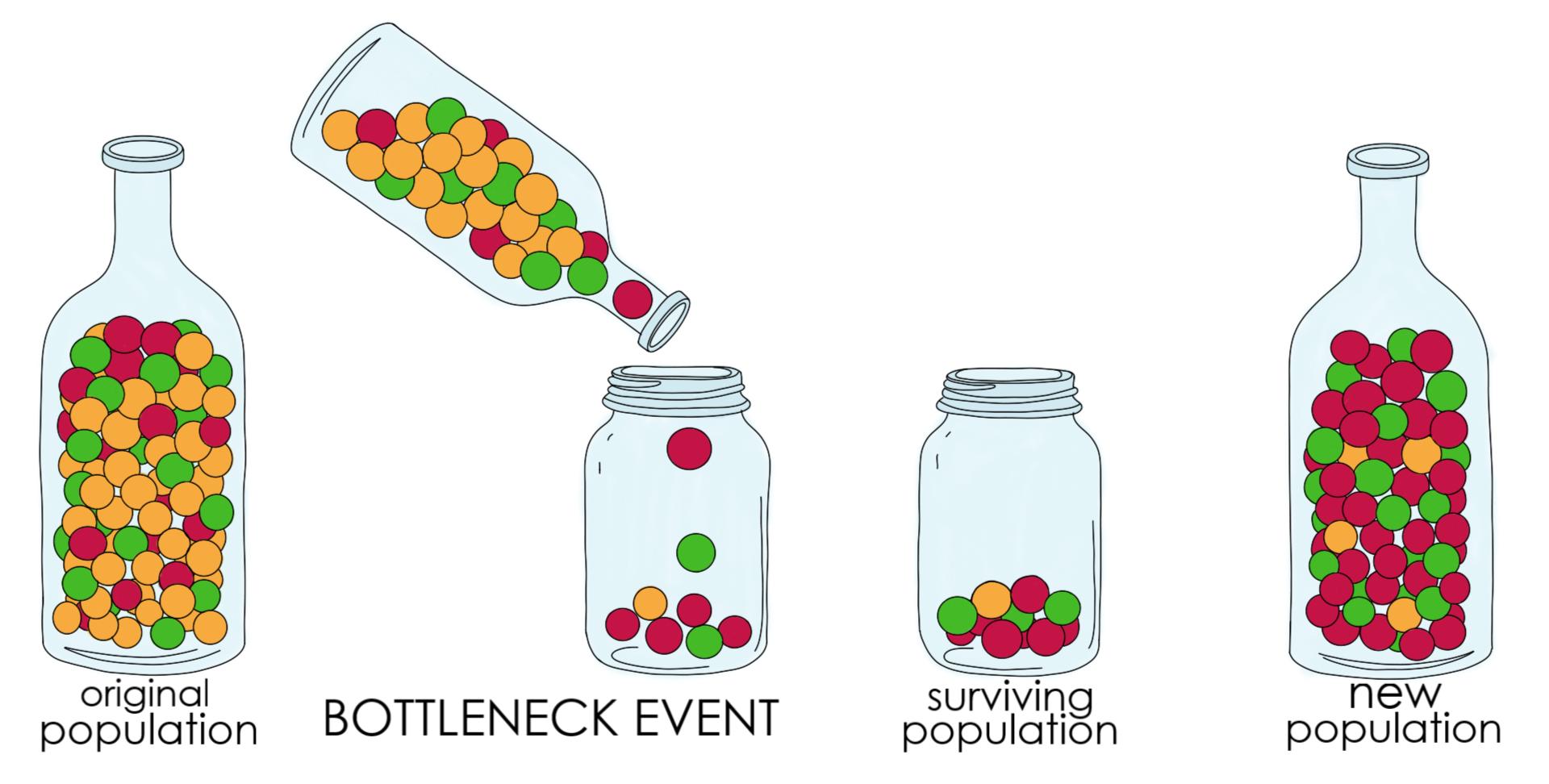
bottleneck effect
some type of catastrophe wipes out a large segment of a population and survivors are not a representation of the original population
mutations
creates new alleles, advantageous alleles will increase over generations
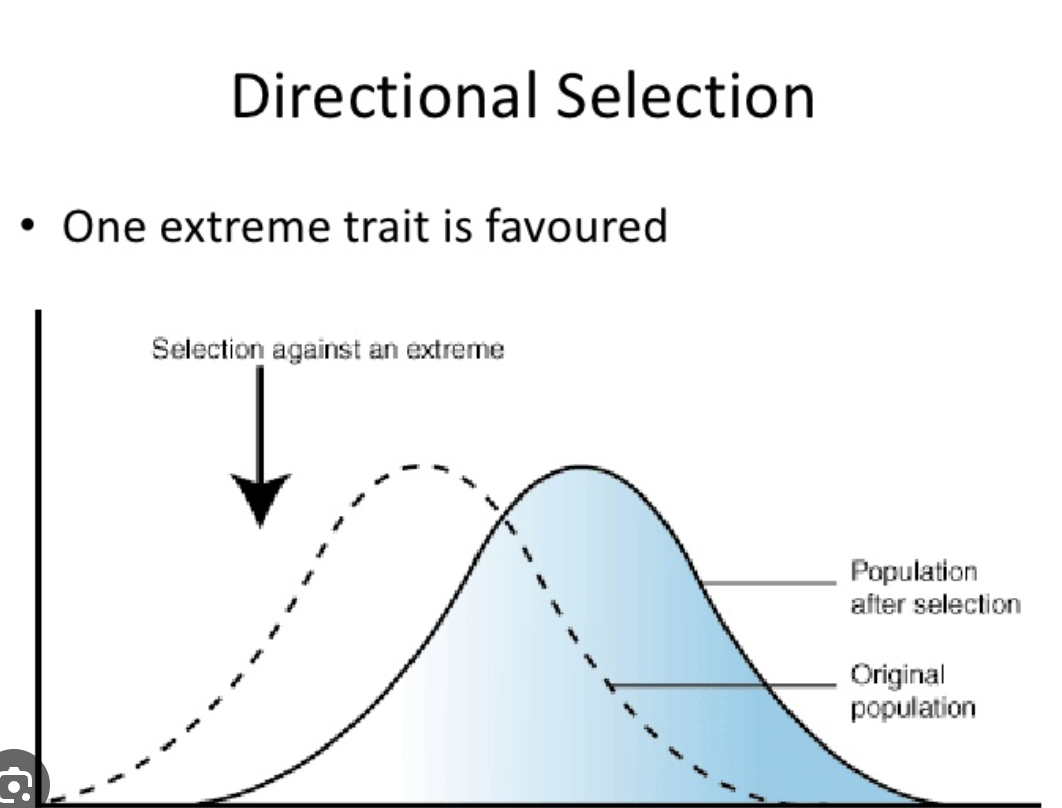
directional selection
one of the extremes are favored
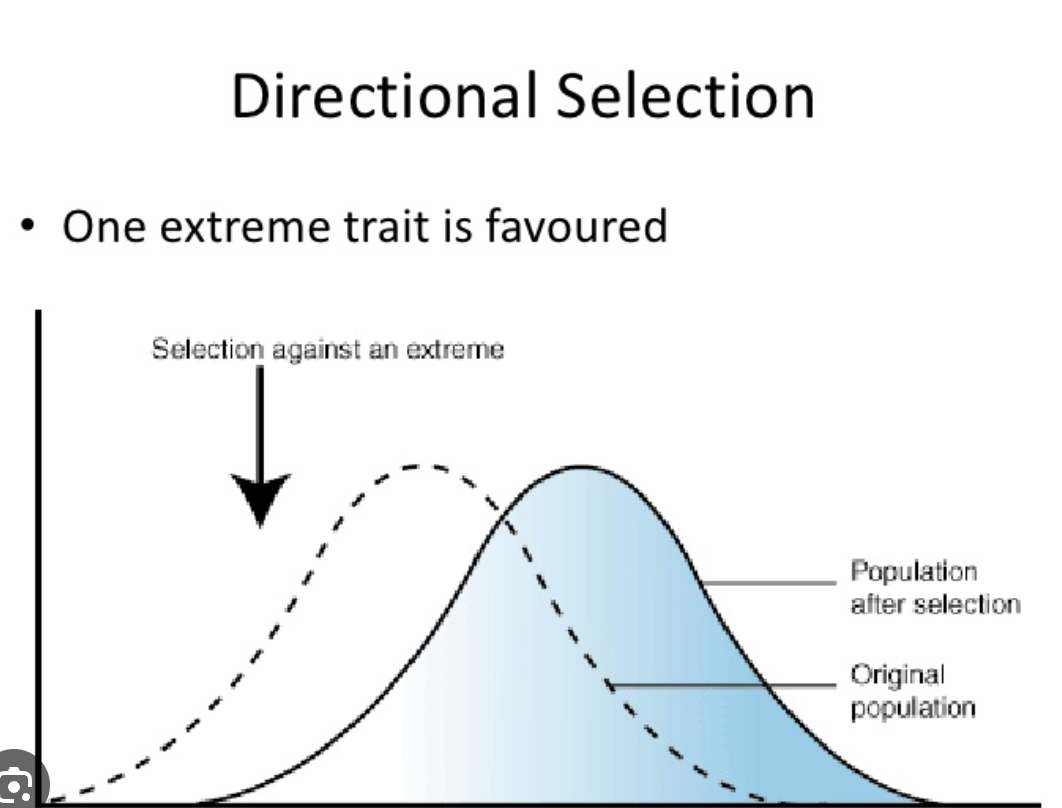
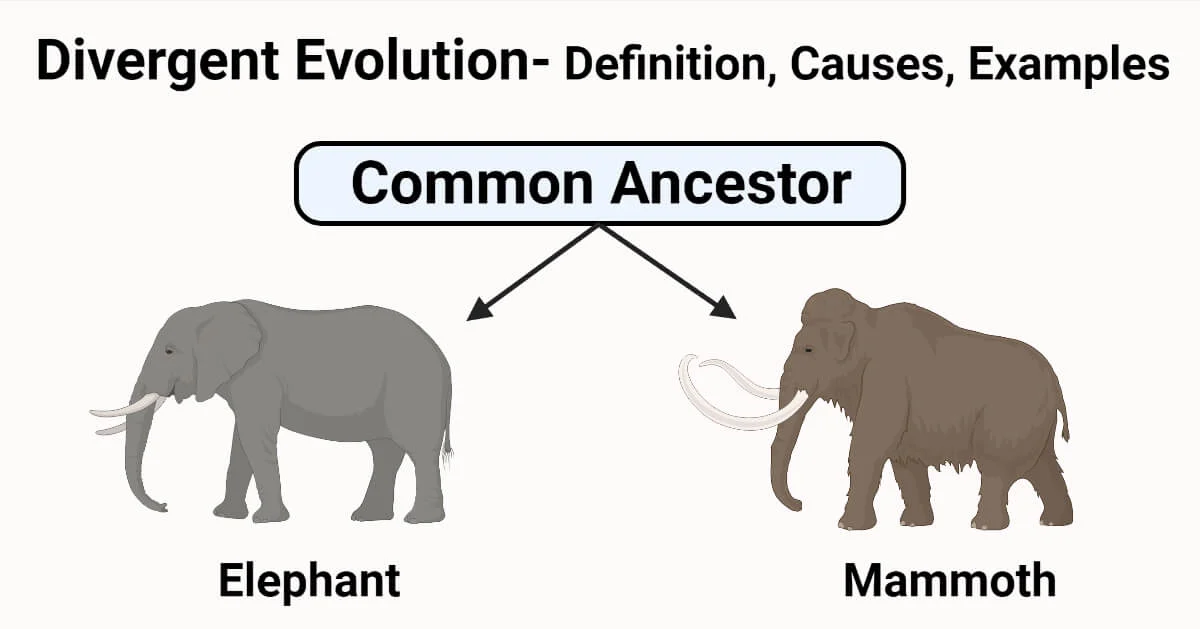
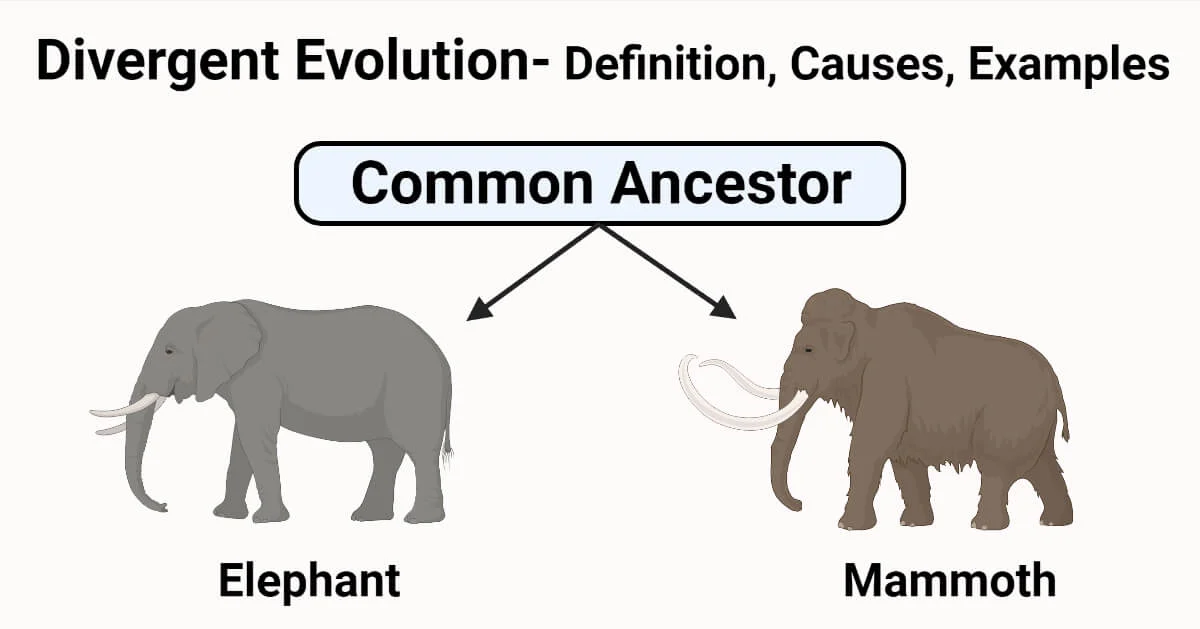
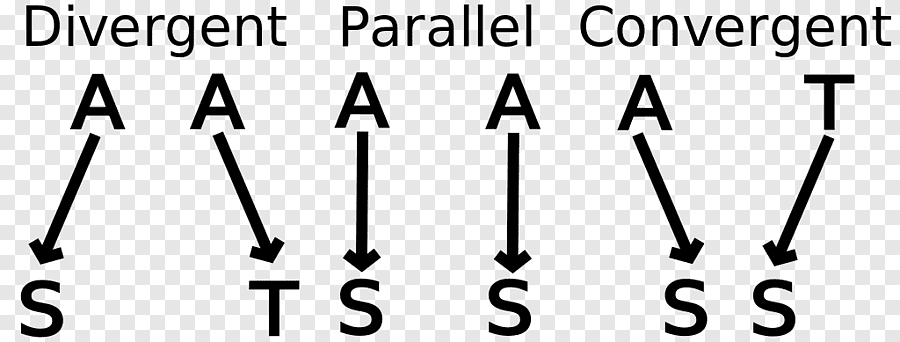
divergent evolution
one species goes 2 different ways and becomes 2 different species, usually due to environment changes
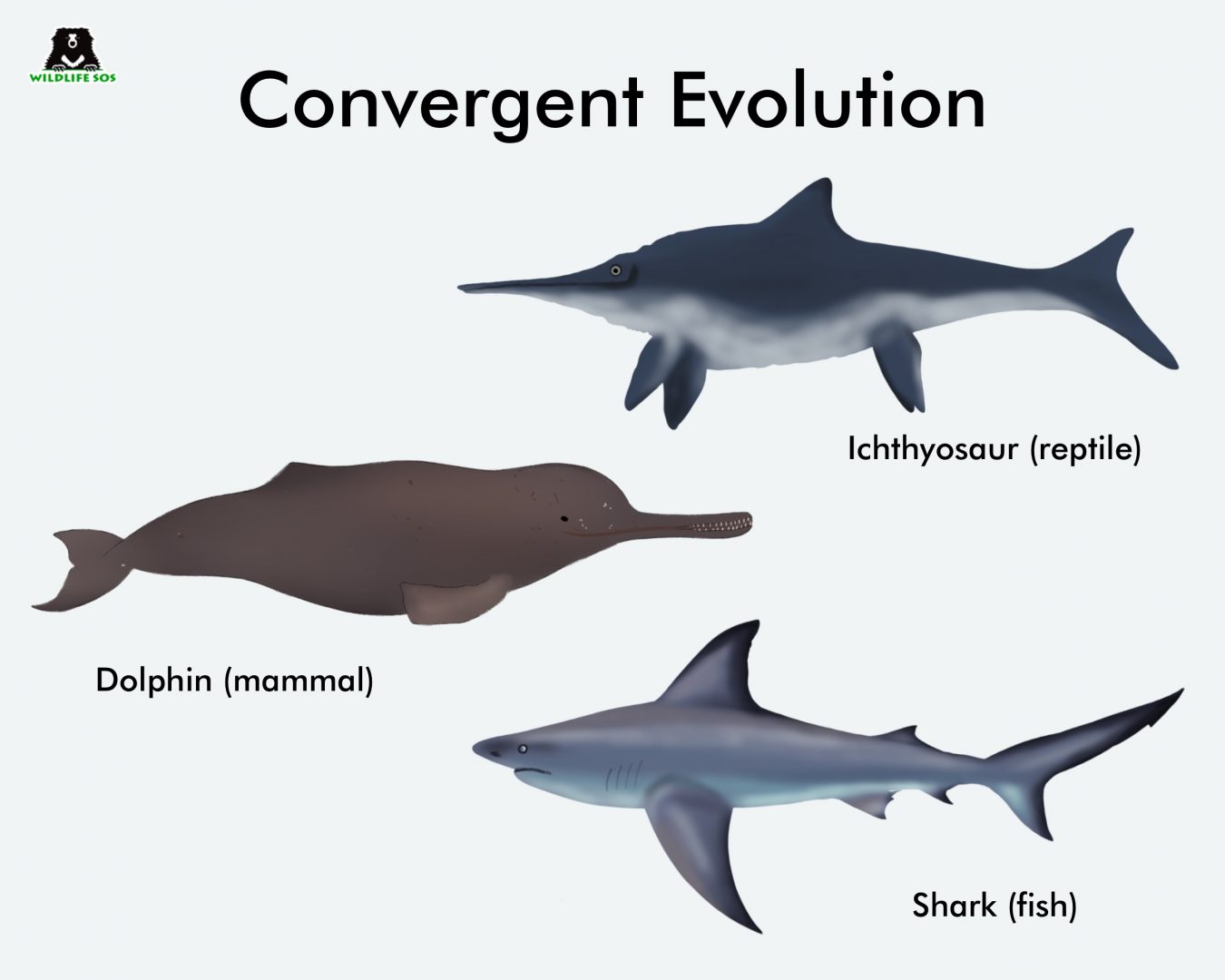
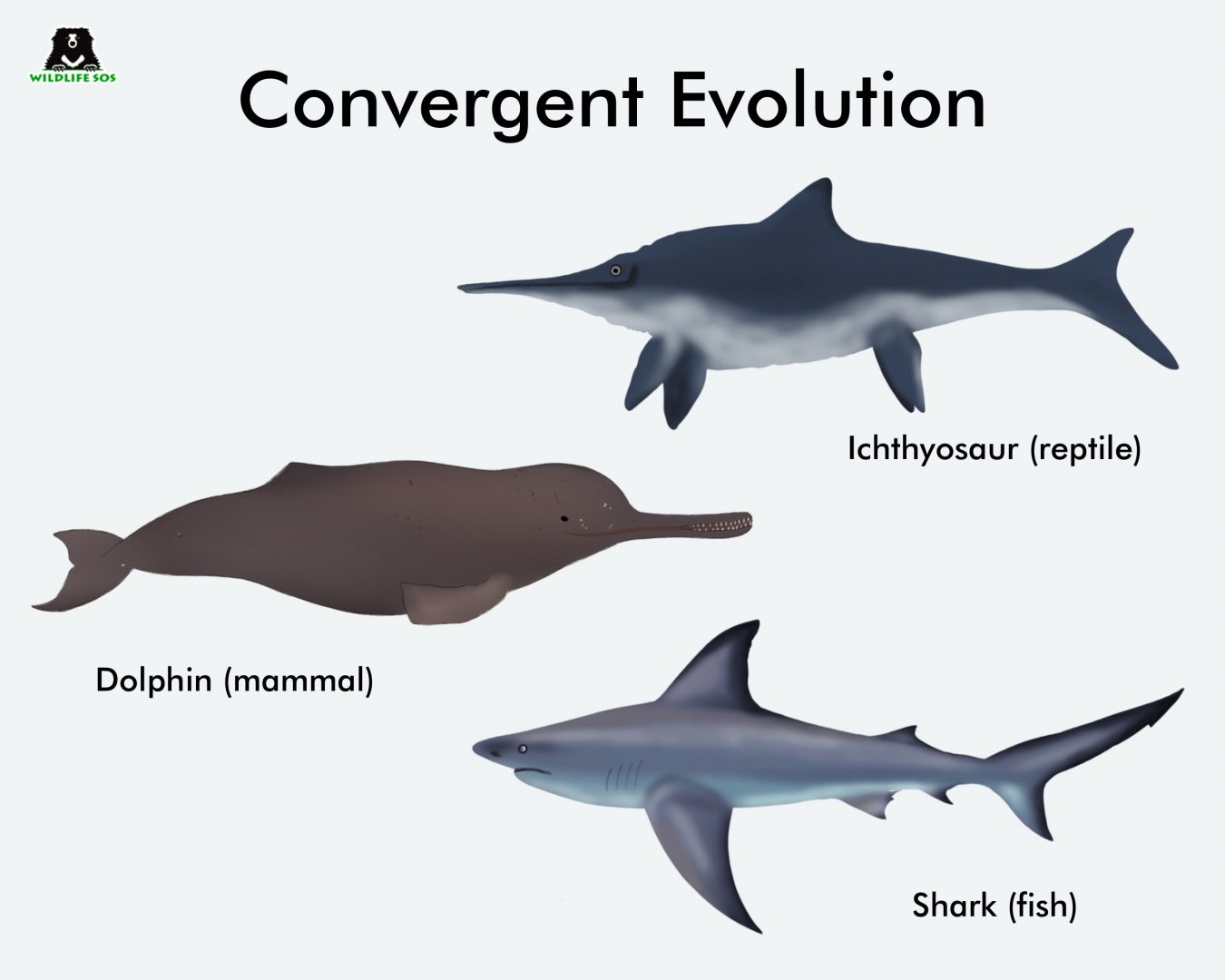
convergent evolution
2 species comeback together to create 1 species, usually due to environment changes
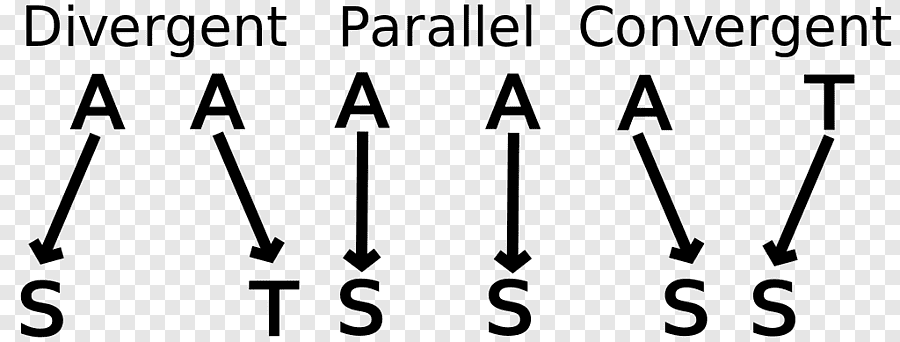
parallel evolution
2 species stay the same over time
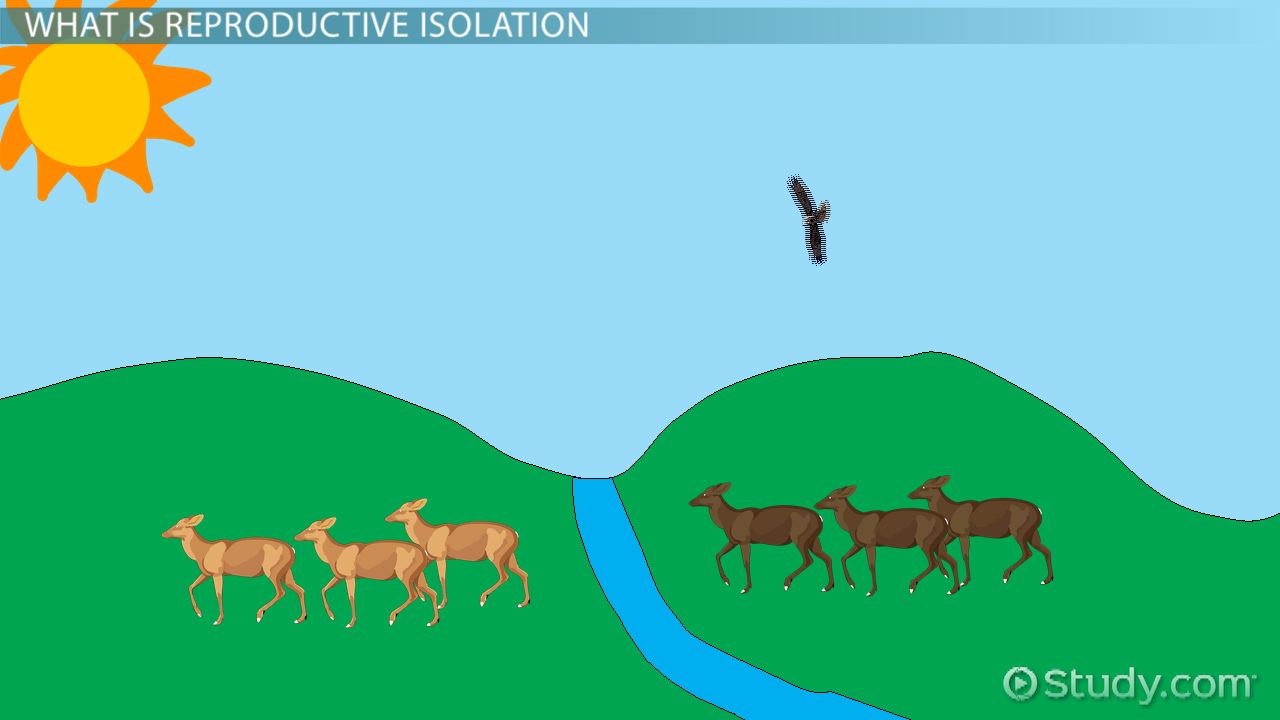
Habitat (geographic) isolation
different environments (prezygotic)
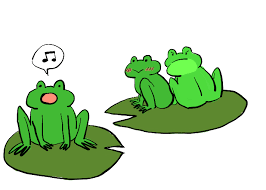
behavioral isolation
different mating rituals (prezygotic)
temporal isolation
time of year of breeding (prezygotic)
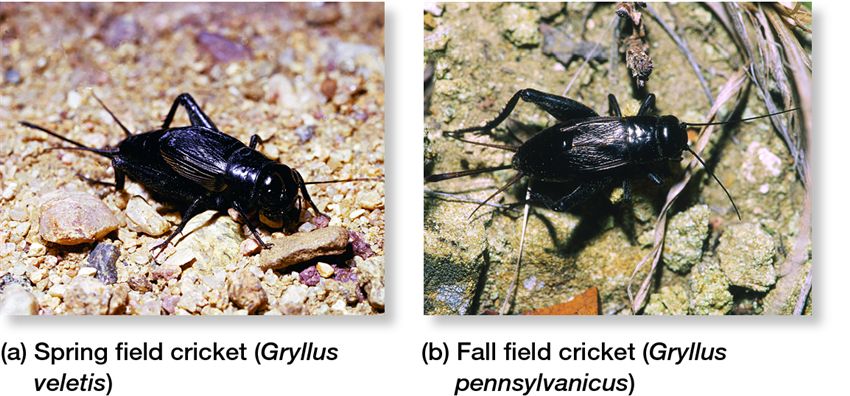

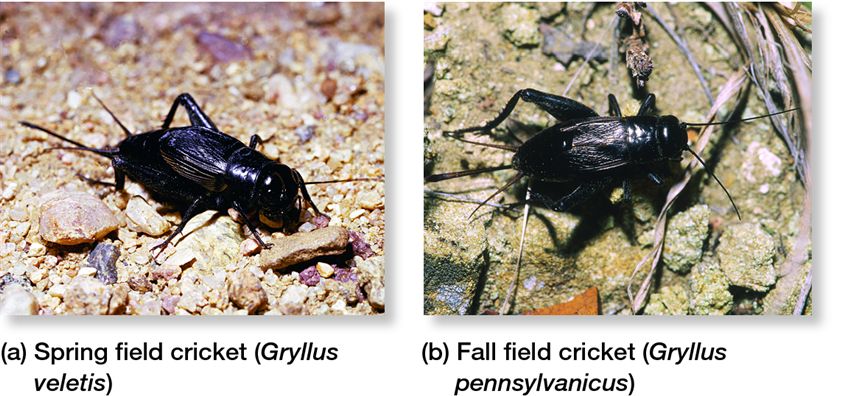
mechanical isolation
reproductive parts do not fit (prezygotic)

gametic isolation
sperm can not fertilize egg (prezygotic)

hybrid inviability
offspring dies during development (postzygotic)
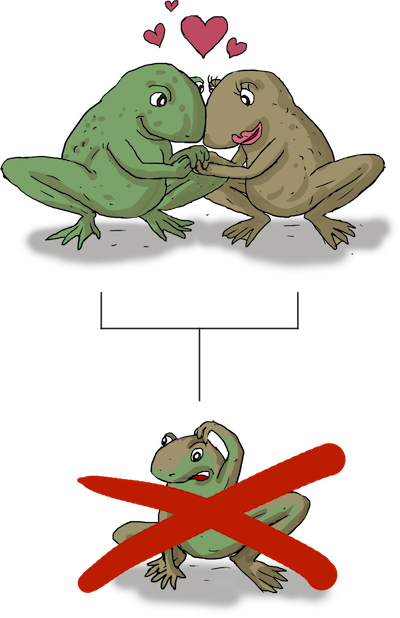

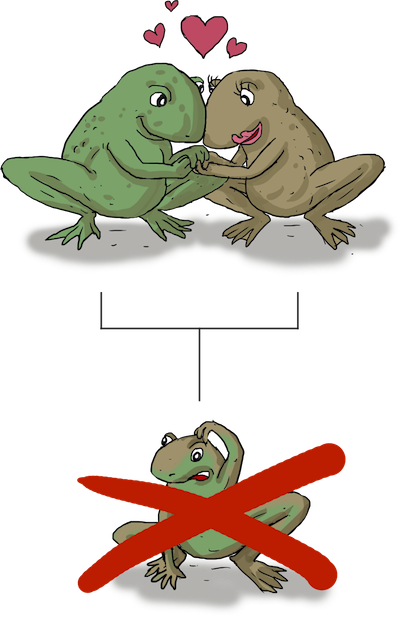
hybrid breakdown
offspring of the hybrid can not reproduce; sterile (postzygotic)
briefly explain what Darwin called "descent with modification"
favorable traits are passed on (natural selection)
how is the Darwinism view of life like a tree
all organisms have a common ancestor and from the ancestor evolution occurred and different species filled different niches
explain differential reproductive success as it relates to the struggle for existence
more successful you are at reproducing, the more you will pass on your genes and your offspring will be fit
explain why an individual organism can not evolve
populations evolve because the changes have to be passed on through generations
explain how natural selection is more of an editing force than a creating force
it does not create favorable genes, it slowly edits out bad genes and keeps good genes in
explain what homologous structures are and give 2 examples
they are bones or aspects of an organism that are similar/the same in other organisms
the arm of a human and a wing of a bat
homologous structure
the flipper of a whale and a arm of a cat
homologous structure
4 conditions to be met for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg genetic equilibrium
No mutations, large population, random mating (no sexual selection), no immigration or emigration, and no natural sleecti
how can gene flow affect genetic equilibrium in a population
if more organisms come or more leave, then there can be more organisms or less organisms and can change the frequency of alleles and effect equilibrium
how can cline lead to speciation
a cline is when a species looks different because they live in different environments and this can lead to speciation because a new species can be created
how does the term differential reproductive success relate to natural selection
if you are more successful at reproducing then natural selection will be successful and the offspring will be fit
describe how selection pressures can change allelic frequencies
if there is a catastrophe and you are only able to mate with an organism with certain genes, then the allelic frequencies will change because then there will be more of one gene and less of another
can an individual organism adapt to its environment
no because if an organism is not born with the genes then it can not make a gene in order to survive, only a population can adapt because mutations can occur and then will pass that gene along and then adaption will occur
what are 4 types of evidence that can be used to determine common ancestry
structural evidence (homologous and analogous) structures,
molecular evidence (DNA sequencing, amino acid sequencing, and RNA types)
fossils
using darwins terms be able to explain the adaptive radiation of the finches and how they filled different niches
overproduction could have occurred and there was an abundance of food and the finches filled that niche
allopatric speciation
new species is created due to geographic barriers
sympatric speciatin
new species is created within the orginial population
how can frequencies change
bottleneck effect, founder effect, genetic drift
differential reproductive success
natural selection acts on ___, not ____
populations not individuals
natural selection acts on frequencies
gene
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck’s theory of evolution
Use and disuse, inheritance of acquired traits, innate drive to become more complex
Use and disuse (Lamarck)
Parts of the body that are used extensively become larger and stronger, while those that are not used deteroriate
inheritance of acquired traits (Lamarck)
an organism could pass these modfications to their offspring
descent with modification
2 main ideas by Darwin
Evolution explains life’s unity & diversity and natural selection is a cause of adaptive evolution.
Darwin’s first observation
The more succesfful offspring, the more the population will increase
Darwin’s second obversation
populations tend to be stable in size, except for seasonal fluctuations
Darwin’s third observation
Resources are limited
Darwin’s fourth observation
Members of a population aren’t identical in appearance or characteristics
Darwin’s fifth observation
Much of this variation is heritable
Darwins first inference
Production of more individuals than the environment can support leads to a struggle for existence among individuals of a population, with only a fraction of their offspring surviving
Darwin’s second inference
Survival depends in part on inherited traits; individuals whose inherited traits give them a high probability of surviving and reproducing are likely to leave more offspring than other individuals
Darwins third inference
This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to a gradual change in a population, with favorable characteristics accumulating over generations
What are phylogenetic trees?
it shows the evolutionary history with branch lengths representing evolutionary change or time,
What are cladograms?
show hypothetical evolutionary relationships (clades) based on shared derived characteristics.
shared derived characteristics
Hardy-Weinberg equation
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1.