unit 1: basic economic concepts
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12th grade ap economics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
economics
how an individual in society experiences limitless wants, and chooses to allocate its limited resources to satisfy wants
microeconomics
study of individual decisions and markets
macroeconomics
study of national and global economies
economic resources
- means of producing goods and services
- all natural, human, and manufactured resources that go into the production of goods and services
utility
any good or service that gives pleasure/satisfaction/usefulness
fundamental economic questions
- FOR WHOM will it be produced?
- WHAT will be produced?
- HOW will it be produced?
market economies/capitalism
- no government regulation
- decisions of individual producers and consumers largely determine what, how, and for for whom to produce
- problem: unequal distribution of power and wealth
command economies/communism
- total government regulation
- industry is publicly owned and a central authority makes production and consumption decisions
mix economies/free enterprise
government regulation and private business control the factors of production
karl marx
favored government control (command economy//communism)
john maynard keynes
favored a mixed economy
adam smith
favored a market economy (lassiez-faire)
positive statements
- objective (non-opinionated) statements that can be tested even if not true
- economists use this
normative statements
subjective (opinions) statements that can't be tested
ceteris paribus
all things stay constant
factors of production
- capital: capital goods and human capital
- entrepreneurial ability: decision maker
- land: natural resources
- labor: physical and mental talents
circular flow diagram
- product market: firms sell, households buy
- factor/resource/labor market: firms buy, households sell
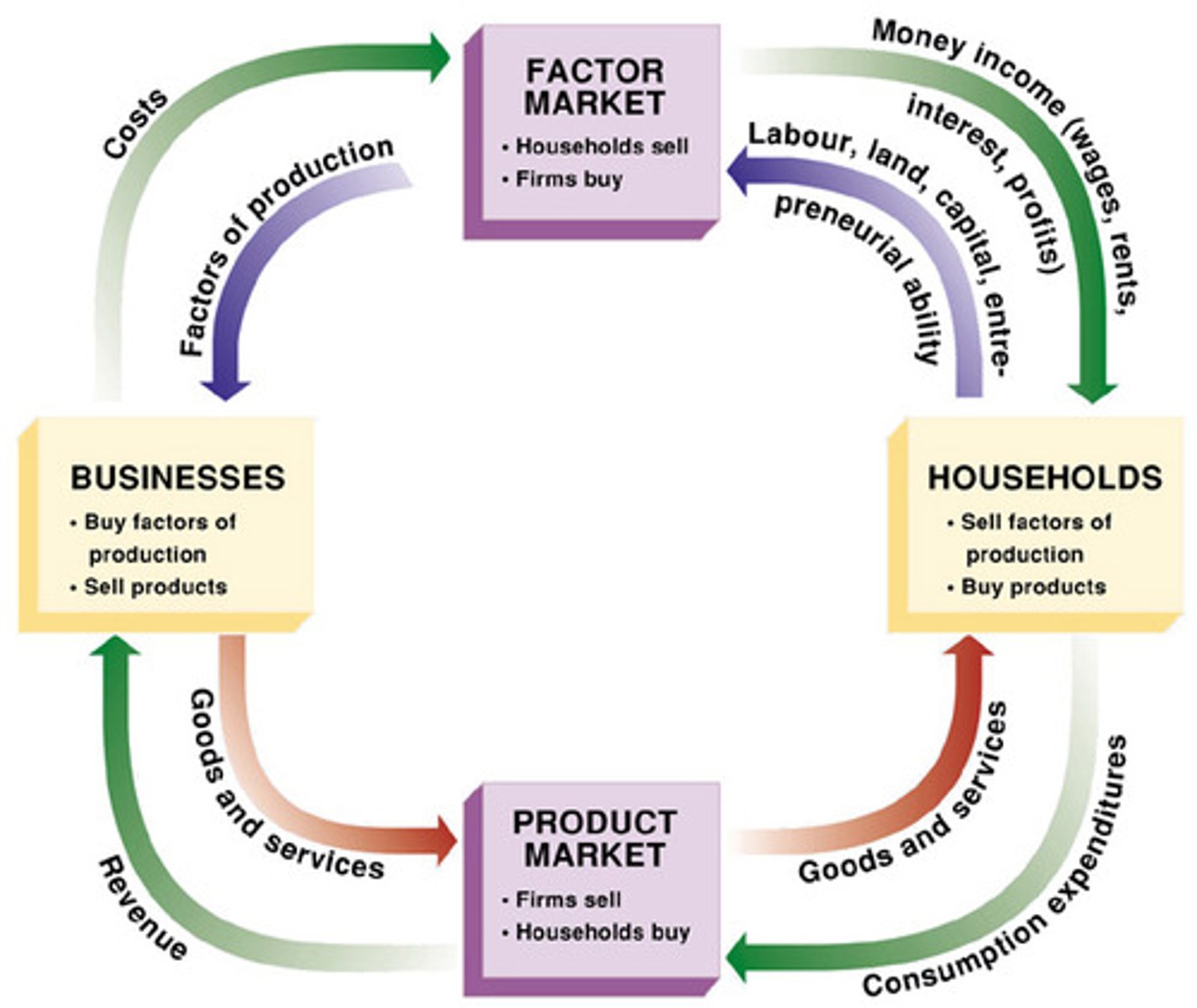
households
consumers
firms
businesses/producers
powers of economic thinking
- decisions/resources cost more than you think
- all decisions are made at the margin (MC=MB)
- all decisions are rational
- the answer to most economic questions is "it depends"
- all people/businesses are maximizers
opportunity cost
- the second best option
- what one sacrifices in order to obtain what one wants
production possibility curve
- illustrates the tradeoffs facing an economy that produces only two goods
- recessions and depressions does not affect curve
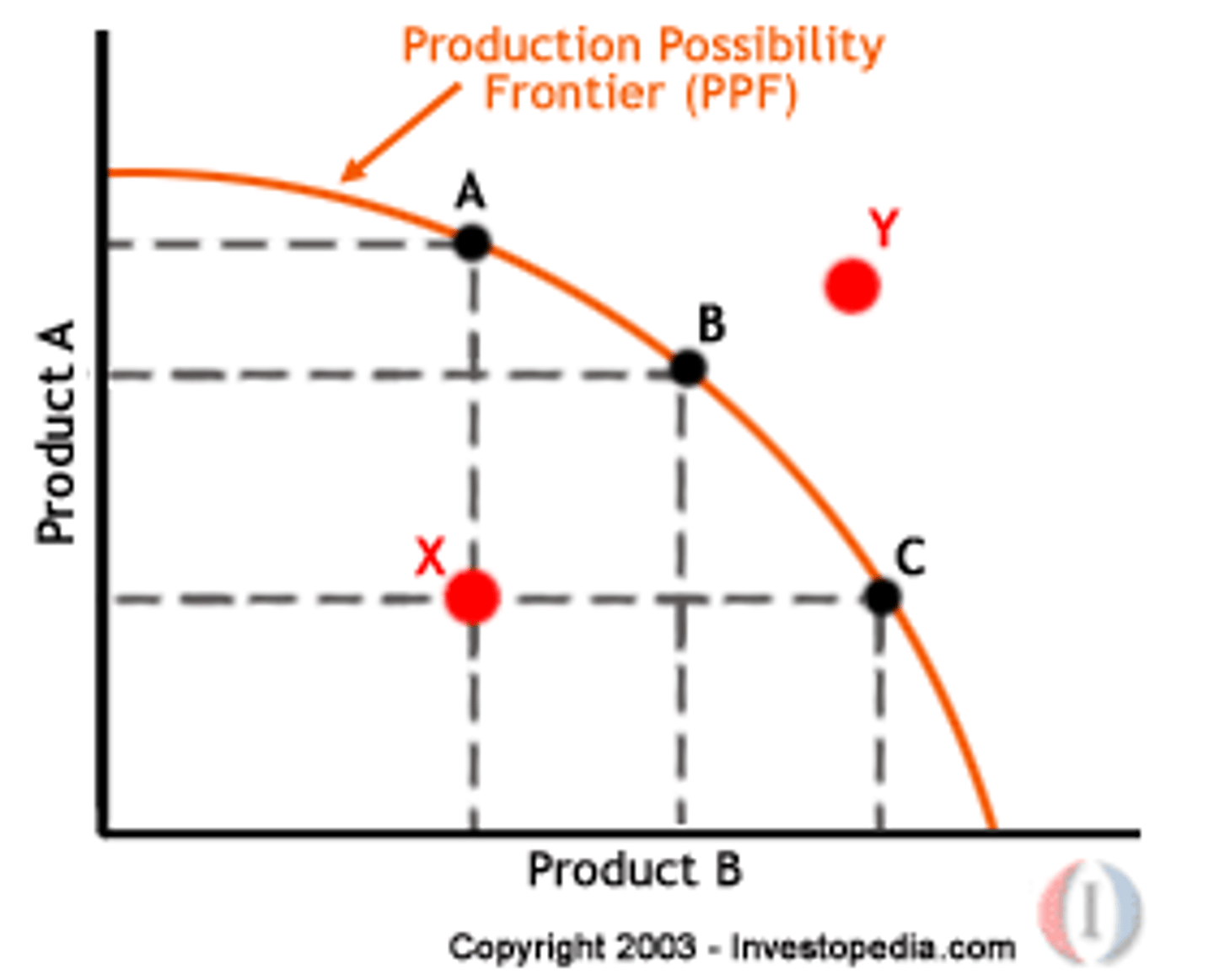
productive efficiency
- producing goods and services for the lowest cost
- no resources unused
- on the curve
allocative efficiency
- more concerned with the distribution and allocation of resources among society's wants/needs
- below curve
shifters of the PPC
- resources (more=outward)
- technology
- change in trade
- investments
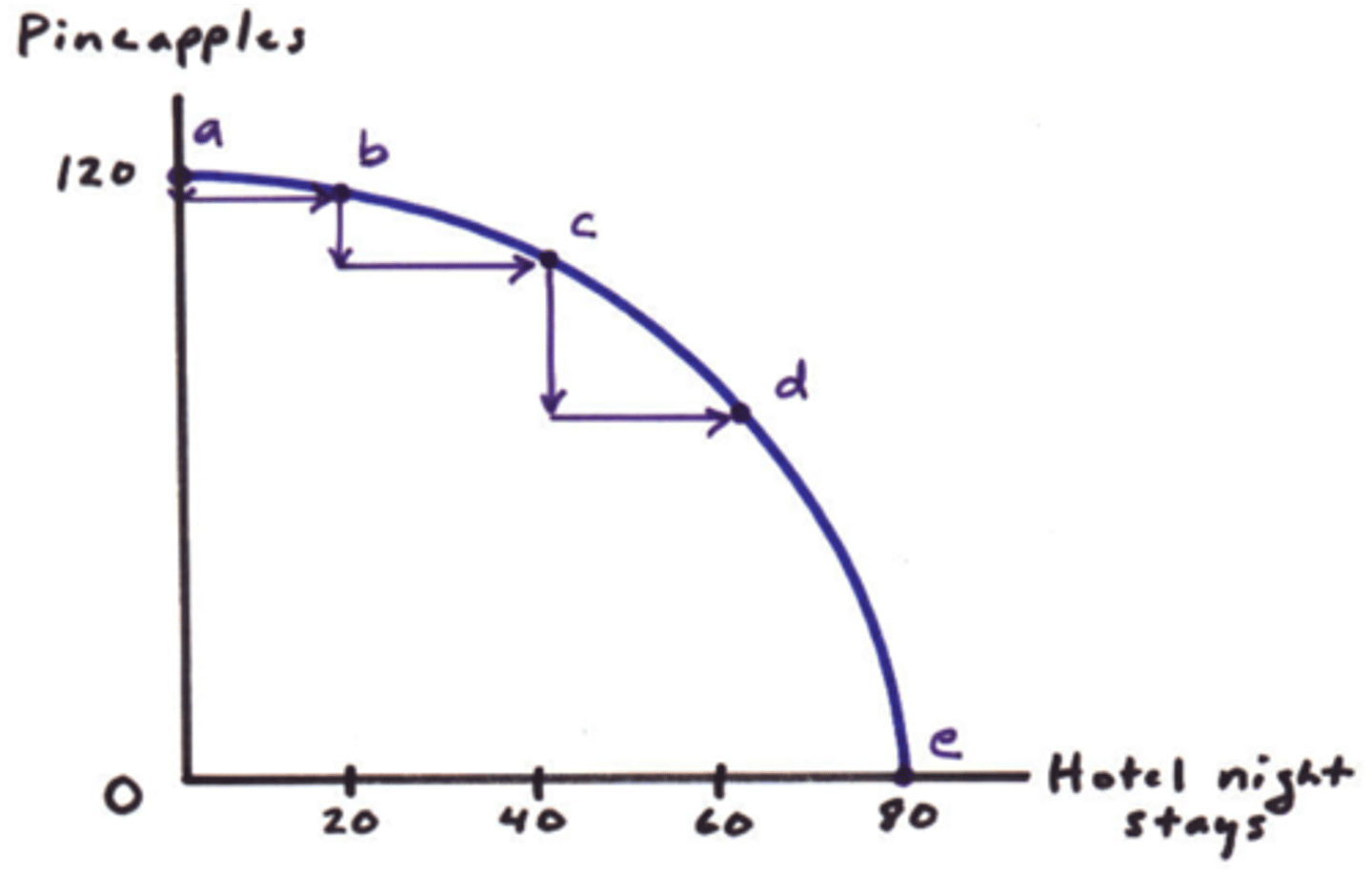
increasing opportunity cost
- resources are not balanced between two goods
- producing more of one good requires giving up an increasing amount of production of the other good
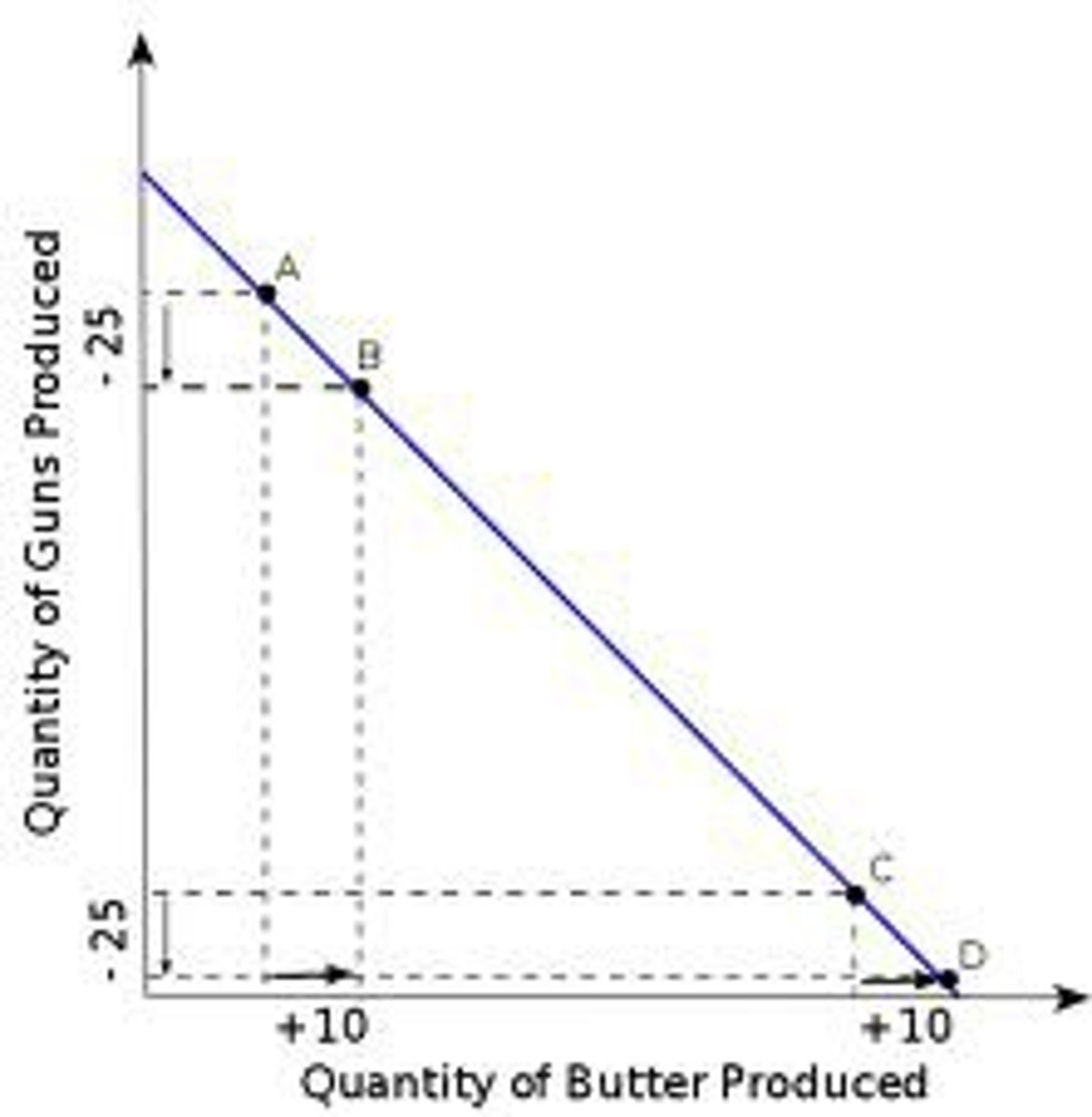
constant opportunity cost
- resources are balanced between two goods
- resources are easily adaptable for producing either good
absolute advantage
- ability to producing a good with fewer resources than another producer
- input/labor/factor market: smallest #
- output/goods/product market: largest #
comparative advantage
- ability to produce a good with the lowest opportunity cost
- input/labor/factor market: cross-add/smallest #
- output/goods/product market: cross-add/largest #
output opportunity cost
Other goes Over (OOO)
input opportunity cost
Other goes Under (IOU)
theory of consumer choice
- consumer is rational
- consumer is affected by diminishing marginal utility
- consumer faces constraints of income
utility maximizing rule
- should be equal to obtain greatest utility/happiness
- inequality: buy less of product with lower MUx/Px and more of product with higher MUx/Px
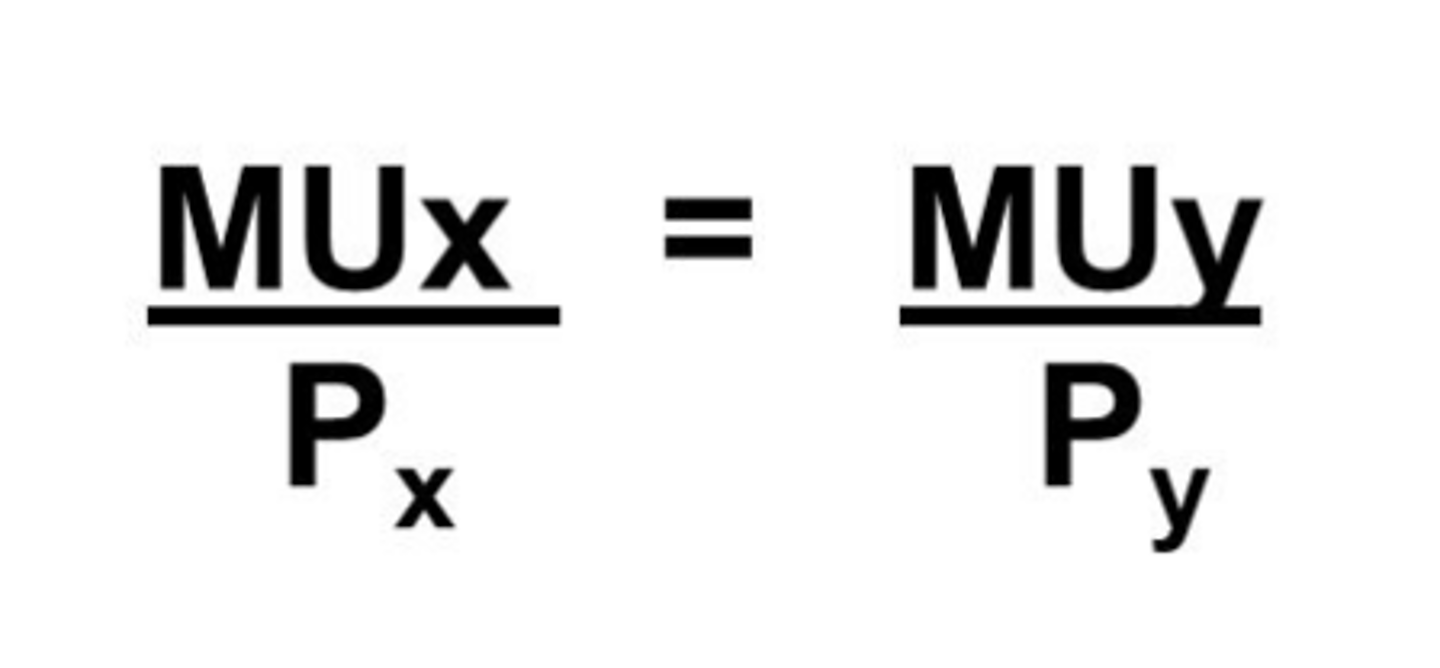
total utility
total amount of satisfaction obtained from consumption of a good or service
marginal utility
satisfaction or usefulness obtained from acquiring one more unit of a product
factor/resource market
where resources (capital and labor) are bought and sold
product market
goods and services are bought or sold
capital goods
goods that produce other goods for future use
consumer goods
products and services that satisfy human wants directly
marginal analysis
involves comparing marginal benefits and marginal costs