PLANNING FOR DENTAL HYGIENE CARE
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What is assessment?
The step in the dental hygiene process of care that involves collecting and analyzing systemic and oral health data with the purpose of identifying a patient or client’ s needs
What are some assessment instruments?
explorer
mirror
air water syringe
Four basic steps when PLANNING patient care
• Collect and analyze assessment information
• Establish the diagnosis
• Select treatment and education interventions
• Develop a formal plan of care
Clinical assessment findings play a key role in…
the development of the dental hygiene diagnosis and dental hygiene care plan
Chief Complaint:
the patient’s statement regarding the reason for seeking dental and dental hygiene care
It is a significant concern expressed by the patient, such as pain; and is addressed before initiating dental treatment.
Risk factors
increase the patients potential for diminished oral health status
Anticipatory guidance through preventive education and counseling is
an essential component of the care plan for a patient exhibiting one or more risk factors
Individual risk factors for periodontal diseases
• Diabetes (poorly controlled)
• Cigarette smoking
• Age (not direct but can effect)
• Inflammatory burden
Current research suggest the presence of periodontal infection is associated with a variety of systemic conditions including:
• Cardiovascular disease
• Diabetes Mellitus
• Metabolic Syndrome
• Obesity
• Respiratory Disease
• Adverse Pregnancy outcome
• Osteoporosis
Risk factors for dental caries
• Heavy biofilm
• Dietary factors
• Low fluoride exposure
• Visible caries or white spot lesions
• Recent restorative treatment
• Tooth morphology and position
• Xerostomia
• Recreational drug use
• Orthodontic Appliances
• Low health literacy/low socioeconomic status
• Children (primary caregiver has current/recent history dental caries)
Risk factors of oral cancer
• Tobacco use of any kind
• Betel quid and gutka
• Heavy alcohol use
• Excessive sun exposure
• Exposure to the human papillomavirus
• Male gender
• Older than 55 years
• Genetic susceptibility
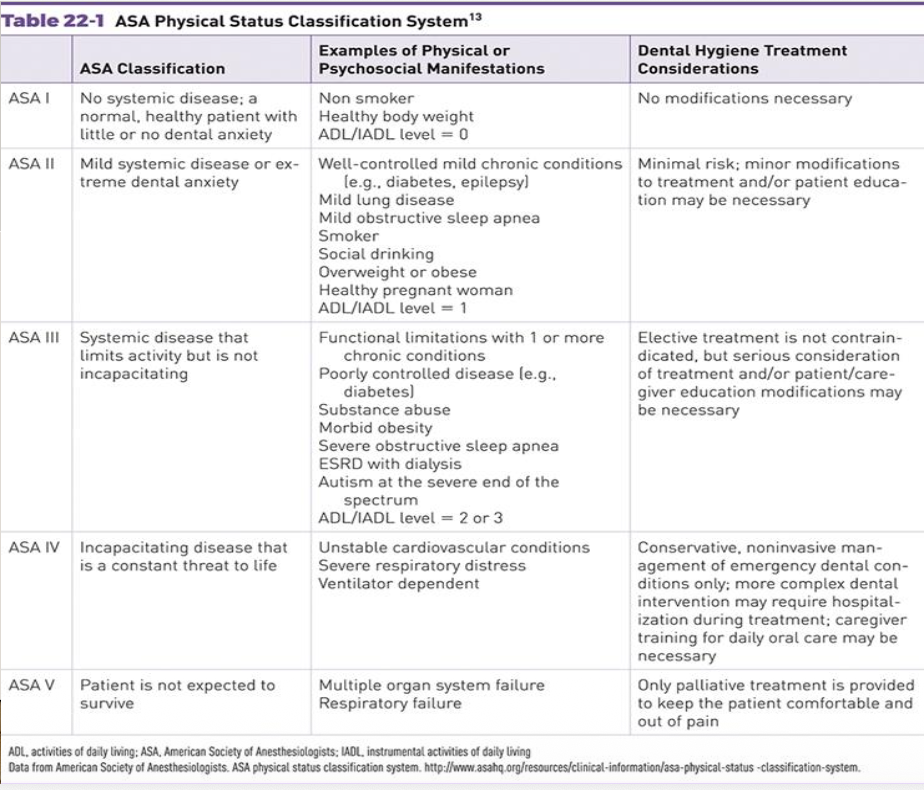
Physical Status
The extent of the patient’s medical, physical, and psychological risk determines modifications necessary during treatment
Systemic approaches to assess physical status: ASA Classification System and OSCAR Planning Guide
ADPIED
assessment
diagnose
plan
implement
evaluate
document
Tobacco Use
Tobacco in all forms affects oral status and dental hygiene treatment outcomes
Review ASA classifications
view image
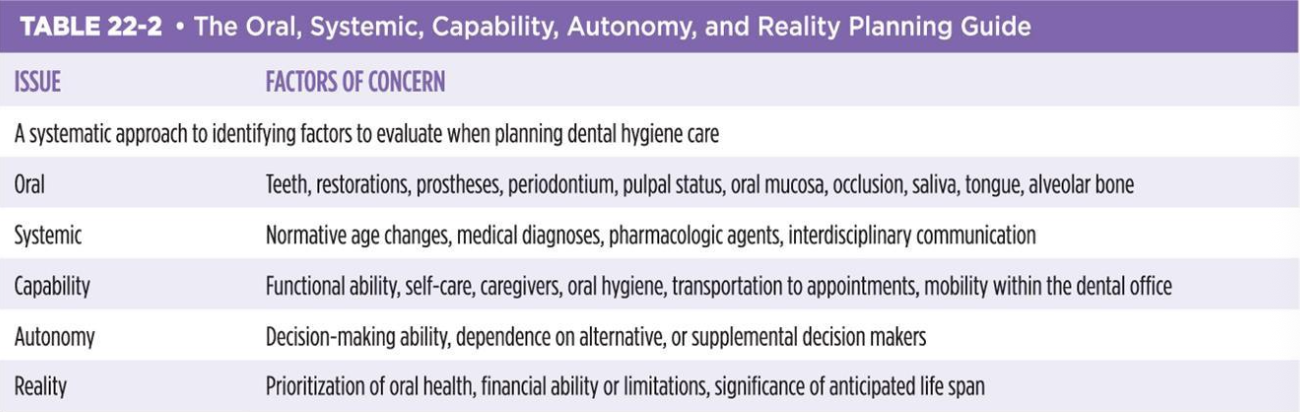
OSCAR planning guide
oral, systemic, capability, autonomy, and reality planning guide
Assessment findings also determine…
• Oral Healthcare Literacy Level of Patient
• Patient’ s Self-Care Ability
Measures of patient functioning
know levels
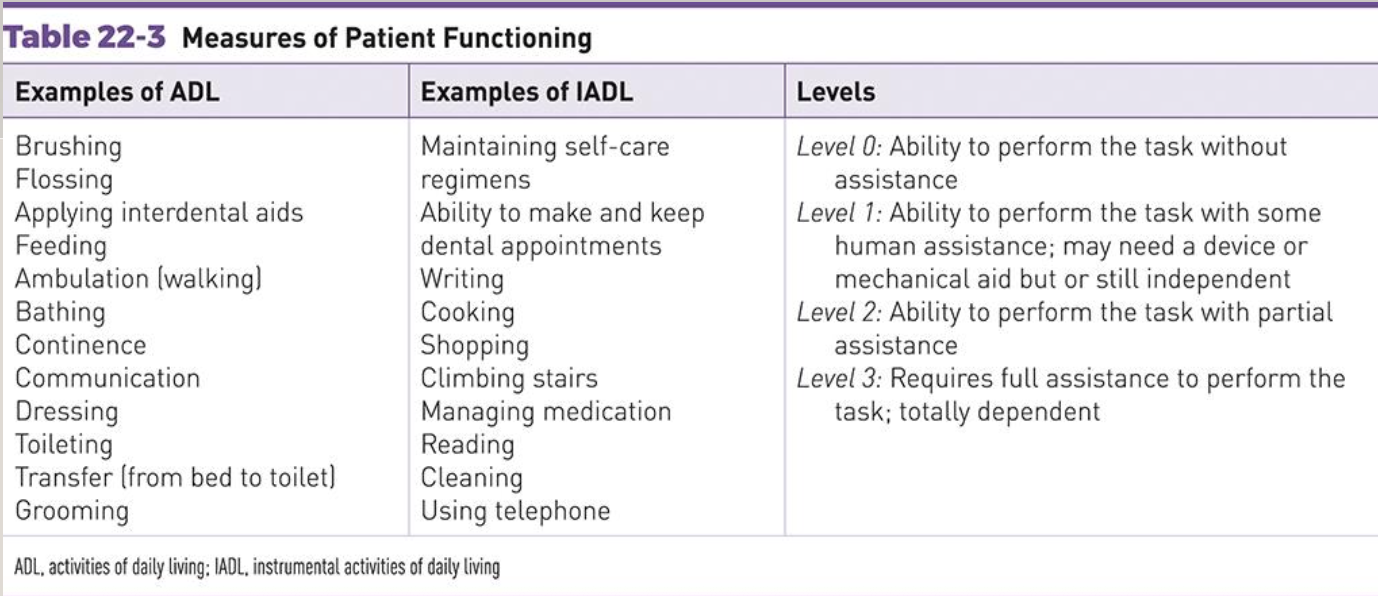
level 0 (patient functioning)
ability to perform the task without assistance
level 1 (patient functioning)
ability to perform the task with some human assistance
may need some divide
level 2 (patient functioning)
level 3 (patient functioning)
Planning for the number and length of appointments in a treatment sequence is influenced by:
• Patients modifiable risk factors
• Periodontal diagnosis
Dental caries risk level
Diagnosis and restorative treatment of caries is provided by the dentist or dental therapist
The plan for dental hygiene care includes interventions aimed at managing risk factors for dental caries- hygienist
dental hygiene diagnosis
Fundamental component of medical and dental care
Part of the process of care, involving the use of evidence based analysis of the assessment findings to determine the patient’s or community’s dental hygiene needs
Provides a basis for the dental hygiene care plan (therapeutic and preventive)
basis for diagnosis
• Patient interview data
• Physical assessment data
• Radiographic series
diagnosis statements provide…
the basis for development of the care plan that focuses on education, oral self- care, prevention, dental hygiene treatment within the scope of dental hygiene practice and referral
Diagnostic statements include the diagnosis and the risk factors contributing to the conditions diagnosed
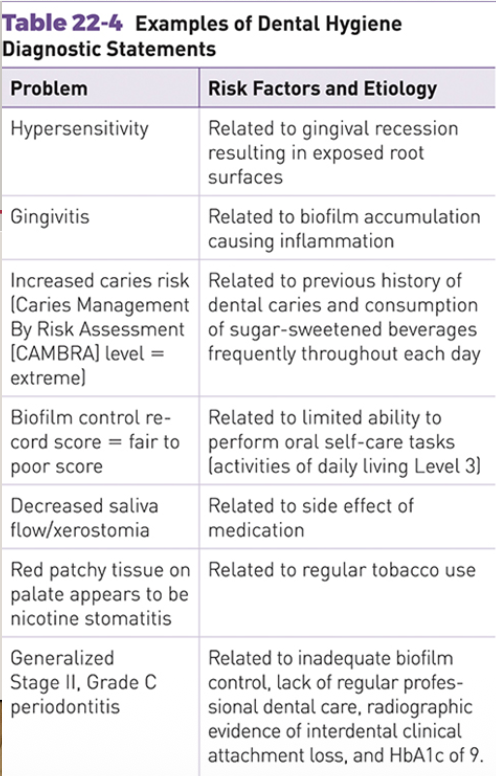
examples of dental hygiene diagnosis statement
view image
Prognosis
forecast of the outcomes of a disease or condition
component of the medical and dental care
Dental hygiene process of care prognosis refers to the following:
A look ahead to an anticipated outcome or endpoint expected from the dental hygiene intervention selected for an individual patient
Expressed in general terms for either and individual tooth or the overall prognosis for the patients teeth
(overall prognosis will be determined in consultation with dentist)
Based on treatment and self-care behavior goals agreed upon by patient and clinician during planning phase of care
the steps all together:
1. Evaluation of the Assessment Data
2. Selection of Dental Hygiene Interventions
3. Dental Hygiene Care Plan
the dental hygiene care plan is
A formal, written, evidence based dental hygiene care planis an essential component of the comprehensive dental treatment plan
Dental Hygiene Care Plan Objectives
Address patient needs identified from assessment data
Reassess previous treatment goals and identify barriers to success
Develop treatment goals in collaboration with the patient to address problems and modifiable risk factors
Identify treatment option interventions and recommendations based on current scientific evidence include need for referral
Prioritize sequence of education, preventive services and treatment in the care plan
Collaborate with dentist to integrate the dental hygiene care plan into the comprehensive dental treatment plan
patient =
client
A dental hygiene care plan:
may be written in a variety of formats
software for electronic records include a treatment plan template that can be used to develop a dental hygiene care plan
components of a written care pan (10):
Individual Patient Considerations
Assessment Findings and Risk Factors
Medical, social and dental history
Health risk factors
Periodontal Classification
Caries Risk
Diagnosis
Patient Centered Oral Health Goals
Planned Interventions
Expected Outcomes
Re-evaluation
Appointment Sequence
Individual Patient Considerations
• Basic demographic information
• Chief complaint
• Social determinants of health
• Health and oral beliefs/cultural beliefs
Medical, Social, and Demographic Data
ASA Classification
Systemic diseases and conditions (current and past)
Medications
Health behaviors
Dental Anxiety
Cultural Factors
Functional Assessment
Health risk factors
Increased risk of systemic disease due to oral infection
Potential for compromised treatment outcomes
Periodontal Classification is based on…
stage and grade
Use patient’s caries risk level to guide…
preventive aspects in dental hygiene care plan
Ex.) oral self care, sealants, fluoride….
Dental Hygiene Diagnosis (DHDX): The ADHA defines dental hygiene diagnosis as…
the identification of an individual’s health behaviors, attitudes, and oral health care needs for which a dental hygienist is educationally qualified and licensed to provide
Problem (Diagnostic Statement)
Part of the process of care involves the use of evidence-based analysis of the assessment findings to determine the patient’s dental hygiene needs.
Provides a basis for the dental hygiene care plan (therapeutic and preventive)
Provides the basis for development of the dental hygiene care plan that focuses on education, oral self- care, prevention, dental hygiene treatment within the scope of dental hygiene practice, and referral
In the diagnostic statement…
There may be multiple diagnoses based on analysis of assessment data
Provides basis for dental hygiene care plan
Is a two-part statement which describes an oral condition & possible etiology
statement of problem, statement of cause, as evidenced by statement of defining characteristics
ex.) inflamed gingiva related to heavy biofilm
Diagnostic statements based on the diagnosis (from assessment findings) require the creation of patient-specific goals linked to dental hygiene disease status and modifiable risk factors
Goals are broad
Goals must address the problem
the goal is to resolve the oral health problem
Prioritize the modifiable risk factors for oral health disease.
Addresses cognitive, psychomotor, affective aspects of the patient specific oral health care needs
Example of goals related to dental caries:
• Absence of any new demineralized areas
• No new carious lesions
• Change dietary habits
Problem statement example:
Palatal irritation related to wearing dentures all night as evidenced by self report and tissue tenderness
Goal statement example:
To resolve denture oral tissue irritation/trauma