Week 7 Quiz - 25-2: Insertion of Long-Term Indwelling Central Venous Catheter
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the primary purpose of a long-term indwelling central venous catheter?
a) To monitor blood pressure continuously
b) To facilitate long-term intravenous administration of medications and fluids
c) To measure cardiac output
d) To provide short-term blood sampling
b. To facilitate long-term intravenous administration of medications and fluids
Venous catheters are a type of central indwelling catheter that is placed to facilitate the long-term intravenous (IV) administration of:
Chemotherapy
Antibiotic therapy
Hemodialysis
IV fluids
Pain medications
The catheter allows for the patient to infuse IV fluids and pain medications at home.
What equipment is required in all insertions of long-term indwelling central venous catheters?
Fluoroscopy (C-arm)
Which of the following is NOT a type of central venous catheter commonly used for long-term insertion?
a) Groshong catheter
b) Hickman catheter
c) Broviac catheter
d) Foley catheter
d. Foley catheter
What is the primary purpose of the micropuncture device during central venous catheter placement?
a) To flush the catheter lumen with saline
b) To change from a 0.035-in. guidewire to a 0.050-in. guidewire
c) To change from a 0.018-in. guidewire to a 0.035-in. guidewire
d) To inject contrast for vessel visualization
c) To change from a 0.018-in. guidewire to a 0.035-in. guidewire
12F Groshong, Hickman, and Broviac are types of __________ _________catheters?
central venous
Which of the following is included in the typical equipment for the insertion of a long-term central venous catheter?
a) Minor instrument set
b) Major laparotomy set
c) Cardiopulmonary bypass machine
d) Endoscopic stapler
a. Minor instrument set
What type of catheter size is typically used for a Groshong central venous catheter?
a) 8F
b) 10F
c) 12F
d) 14F
c. 12F
A 12 French (12F) catheter is commonly used for Groshong central venous catheters, especially the double-lumen or tunneled types designed for long-term use such as:
Chemotherapy
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
Long-term antibiotic therapy
Frequent blood draws
📌 Why 12F?
Larger lumen size allows for:
Higher flow rates
Simultaneous infusion and withdrawal
Groshong catheters have a valve at the tip that eliminates the need for a heparin flush and reduces the risk of air embolism — but this design needs a catheter large enough to accommodate the valve mechanism.
What position is the patient placed in during the insertion of a long-term central venous catheter to increase the diameter of the subclavian vein?
a) Prone with head turned to the right
b) Supine with slight Trendelenburg, head turned left
c) Supine with slight right head rotation
d) Supine with slight Trendelenburg, head turned right
b. Supine with slight Trendelenburg, head turned left
Position: Supine with slight Trendelenburg to increase the diameter of the subclavian vein; head slightly turned to the left, away from the operative site
Reasons for preferring the right subclavian vein:
More direct route to the superior vena cava (SVC):
The right subclavian vein has a straighter, shorter path into the SVC and right atrium compared to the left side, which reduces the risk of catheter kinking or malposition.
What type of anesthesia is typically used for the insertion of a long-term central venous catheter?
a) General anesthesia
b) Spinal anesthesia
c) Local anesthesia with monitored anesthesia care (MAC)
d) Epidural anesthesia
c. Local anesthesia with monitored anesthesia care (MAC)
Why is the skin prepped on both sides of the neck and down to the mid-chest during this procedure?
a) To reduce infection risk only on the operative side
b) To allow access to the contralateral side if the original side cannot be accessed
c) To prepare for a possible emergency tracheostomy
d) To cover the entire chest for any vascular access
b. To allow access to the contralateral side if the original side cannot be accessed
What is the typical draping used during the insertion of a central venous catheter?
a) Large laparotomy drape
b) Small fenestrated drape from catheter tray or surgeon’s preference
c) Whole-body drape
d) No drape used
b. Small fenestrated drape from catheter tray or surgeon’s preference
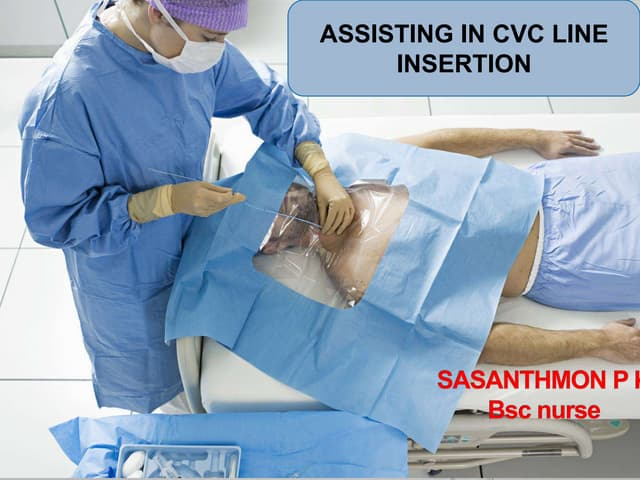
Where is the insertion site for the long-term central venous catheter in relation to the clavicle and first rib?
a) 1–2 cm medial to the insertion of the clavicle and first rib
b) 1–2 cm lateral to the insertion of the clavicle and first rib
c) Directly on the clavicle
d) 3–5 cm inferior to the clavicle
b. 1–2 cm lateral to the insertion of the clavicle and first rib
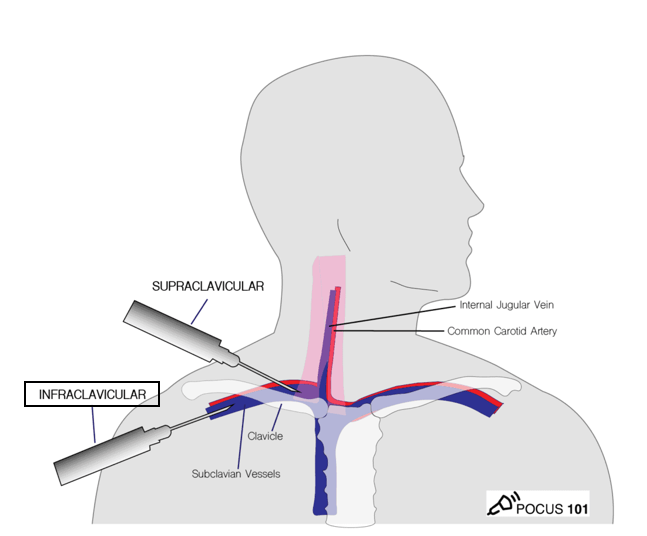
What device is used for the initial venous puncture to decrease the risk of pneumothorax during catheter insertion?
a) 18-gauge introducer needle
b) 21-gauge introducer needle with micropuncture device
c) 25-gauge hypodermic needle
d) Standard intravenous catheter
b. 21-gauge introducer needle with micropuncture device
The micropuncture technique uses a 21-gauge introducer needle followed by a small, flexible guidewire and dilator system to access the vein.
Procedural Consideration: A micropuncture device allows the use of the 21-gauge introducer needle for the initial venous puncture instead of the larger 18-gauge needle that is provided in the catheter kit. The use of the 21-gauge needle decreases the risk for pneumothorax and bleeding from an accidental puncture of the subclavian vein. The device also allows for the placement of a 0.035-in.-diameter guidewire into a vessel later in the procedure.
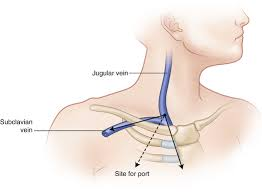
What does it indicate if the guidewire curves upward in a “J” shape during insertion of the CVC line?
a) It is correctly placed in the superior vena cava
b) It has entered the jugular vein and must be repositioned
c) The catheter is in the right atrium
d) The guidewire has punctured the vessel wall
b. It has entered the jugular vein and must be repositioned
A 0.018-in. guidewire is inserted through the needle and advanced into the superior vena cava. A challenge with inserting the guidewire is to prevent it from traveling cephalad into the jugular vein. If this occurs, the guidewire will curve upward, looking like a “J,” meaning it has entered the jugular vein. The surgeon will carefully withdraw the guidewire from the jugular vein and reposition into the superior vena cava.
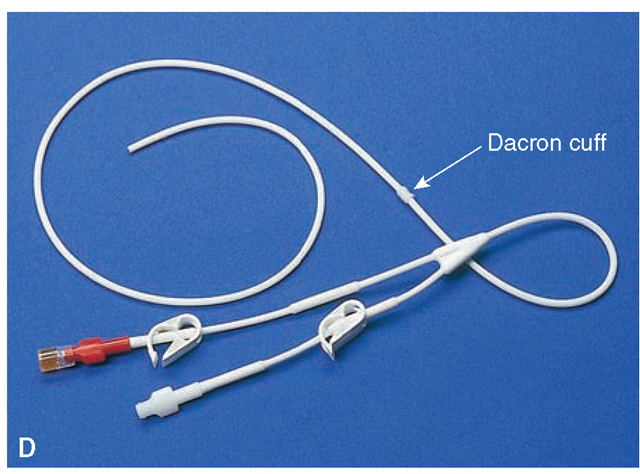
What is the purpose of the Dacron cuff attached to the catheter?
a) To filter blood clots
b) To help prevent catheter migration or accidental removal
c) To deliver medications locally
d) To prevent infection at the insertion site
b. To help prevent catheter migration or accidental removal
Procedural Consideration: The cuff helps to prevent the catheter from migrating inward or being pulled out.
Which of the following sutures is typically used to secure a central venous catheter to the skin until the cuff becomes embedded in the subcutaneous tissue layer?
a) 2-0 Vicryl
b) 3-0 or 4-0 silk
c) 5-0 Prolene
d) 2-0 chromic gut
b) 3-0 or 4-0 silk
Silk sutures are commonly used for temporary external fixation of central venous catheters because they are nonabsorbable, strong, and easy to handle. The catheter is secured for approximately 2 weeks, giving time for the Dacron cuff to embed in the subcutaneous tissue, creating a barrier against infection.
How long is the catheter typically secured with silk sutures to allow the cuff to embed in subcutaneous tissue?
a) 3-5 days
b) 1 week
c) Approximately 2 weeks
d) 4 weeks
c. Approximately 2 weeks
Which complication involves accidental puncture during this procedure?
a) Cephalic placement of catheter
b) Subclavian artery puncture
c) Air embolus during removal of sheath
d) Infection at insertion site
b. Subclavian artery puncture
What immediate postoperative imaging may be done in the OR to exclude pneumothorax?
a) Ultrasound
b) Chest X-ray
c) MRI
d) CT scan
b. Chest X-ray
When can a patient typically return to normal activities after uncomplicated catheter insertion?
a) Same day
b) 2–3 days
c) 1 week
d) 1 month
b. 2–3 days
All of the following are possible complications of long-term indwelling central venous catheter insertion except:
a) Subclavian artery puncture
b) Pneumothorax
c) Cephalic placement of the catheter unnoticed during insertion
d) Deep vein thrombosis
d) Deep vein thrombosis
Venous catheters, a type of central indwelling catheter, are used for all of the following except:
a) Long-term intravenous administration of chemotherapy
b) Antibiotic therapy
c) Hemodialysis
d) Short-term emergency blood transfusions
d) Short-term emergency blood transfusion