Biology (topic 6) Homeostasis (without nephron) (2)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is glycogenesis?
Conversion of glucose to glycogen
What does insulin binding to receptors result in?
Chemical signal which causes vesical with channel proteins for glucose to fuse with membrane of target cell
What do increased channel proteins in muscle and liver cells do?
Make membrane more permeable to glucose as a result of transport proteins fusing
What happens after a decrease in blood glucose levels are detected by the pancreas ?
a cells in pancreas secrete glucagon
Glucagon causes an increase in blood glucose by :
Activates enzymes that
They convert amino acids to glucose (Gluconeogenesis)
And that convert glycogen to glucose (glycogenolysis)
What is gluconeogenesis?
The synthesis of glucose from non carboyhdrate molecules e.g amino acids
What is glycogenolysis ?
Breaking down glycogen to produce glucose
What activates the enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis?
Glucagon
What is the second messenger model?
When a hormone (First messenger)
triggers the production of a second messenger which is the enzymes involved in glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
Describe the steps in the second messenger model.
Glucagon binds to receptors on target cell
Activates G protein
G protein activates adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase catalyzes conversion of ATP to cAMP (second messenger)
cAMP activates enzyme protein kinase A
Which initiates a cascade of reactions resulting in activation of enzymes that do Glycogenolysis
What do G proteins activate in the second messenger model ?
Adenylate cyclase
What does Adenylate cyclase do in the second messenger model?
Catlyises the conversion of ATP to cAMP
What does cAMP activate in the second messenger model?
Enzyme protein kinase A
What does protein kynesis A do in the second messenger model ?
Initiates a cascade (chain) of reactions that results in the activation of enzymes
The enzymes break down glycogen to glucose (glycogenolysis)
what hormones are involved in the second messenger model?
Glucagon and Adrenalin
What’s the difference between the second messenger model where glucagon or adrenalin is the first messenger?
Same mechanism
Glucagon:
Is released when blood glucose is low
Is released to restore levels
Adrenalin:
Is released during fight or flight
Is released for rapid energy
Less gluconeogenesis than glucagon
What is diabetes?
When homeostatic control of glucose has failed or deteriorated
What is type one diabetes?
Pancreas fails to produce or does not produce enough insulin
Caused by autoimmune attack on B cells
Occurs during childhood
What is the treatment for type one diabetes?
Insulin injection that are calculated on the basis of insulin intake and exercise
What is type 2 diabetes?
Insulin receptors are no longer responsive to insulin
Occurs in adults
Risk factors : obesity , high carbohydrate diet, age, family history
What is treatment for type two diabetes?
Low carbohydrate diet
Exercise
Medication
How can the rise in type 2 diabetes be combated?
Promotion of eating well
Reduced intake of processed food
Approaching food industrys to reformulate products reducing sugar and fat contents
What is a calibration curve?
Graph used to identify concentrations of unknown solutions
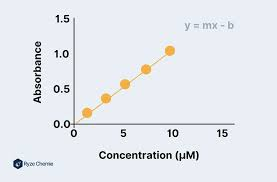
What is colorimetry?
When colorimeter is used to determine concentration of substances
Light passes through a sample , the transmission or absorbance of light is measured
Describe the practical: colourimetry usage to determine concentration of glucose
Add quantitative benedicts reagent to glucose solution
The solution starts blue , a loss of blue colour indicates a high concentration of glucose
(Dark blue = low glucose)
(colourless = high glucose)
Dark blue colour allows less transmission of light
Colorimeter is set to red
Make a calibration curve with a dilution serious of none glucose concentrations
Plot the glucose concentration
Find the percentage of light transmission that matches the sample
What colour is the light in the colorimetry practical determining the concentration of glucose and why?
Red
Because it is complementary to blue so the blue solution will be absorbed by red light
(blue light would be reflected)
What is added to glucose in the colorimetry practical to determine concentration of glucose?
Quantitative benedicts reagent