exam 1 - part 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
helping infant mortality rates
breastfeeding → decreased risk of infection, reduces obesity risk, lowers risk of allergic disease, celiac and IBD
safe sleep → place infant on their back, no bed sharing, reduces SIDS
parental support → postpartum depression, parenting education, improves outcome for both parent and baby
if there is a family with a different culture what should the nurse do first
assess your biases first
caring for people of different cultures
put away your biases
try and figure out what will work best for pt
help them find resources
ask the pt
be willing to learn something new - even if it does not make immediate sense to you (and even if it defers from your values)
informed consent
decision maker must be legal
info must be simple and understandable
decision must be voluntary
witness pt sign
witness signs form
women 35 years or older are at higher risk of
birthing/pregnancy complications
family centered care
the pt and the family are partners in care
family centered care - who does it effect
the pt, the family, nurses, the HC team, the HC system, long-term community health
site of fertilization
outer third of the ampulla of the fallopian tube which leads to the formation of a zygote. The zygote undergoes cleavage, eventually implanting in the endometrium about 7 to 10 days after conception.
hormone responsible for ovulation
luteinizing hormone (LH)
FH stimulates the ovarian follicle to mature, estrogen rises (powered by the developing follicle) high estrogen levels triggers an LH surge which causes the follicle to rupture and release the egg
secretion of the seminal vesical
fructose rich (provides food for sperm to give them energy to live and swim), alkaline fluid containing prostaglandins and clotting factors that nourish sperm, enhance mobility, and protect them from acidic environments (the vagina)
amniotic fluid is essential for
fetal lung development
the placenta
protects the fetus from immune attack by the mother, removes waste products from the fetus, induces the mother to bring more food to the placenta, and, near the time of delivery, produces hormones that mature fetal organs in preparation for life outside the uterus.
oligohydramnios
a deficiency of amniotic fluid
associated with uteroplacental insufficiency and fetal renal abnormalities
genetic counseling
involves evaluation of an individual or a family. Its purpose is to confirm, diagnose, or rule out genetic conditions, identify medical management issues, calculate and communicate genetic risks to a family, discuss ethical and legal issues, and assist in providing and arranging psychosocial support.
Preconception screening and counseling can raise serious ethical and moral issues for a couple. The results of prenatal genetic testing can lead to the decision to terminate a pregnancy
X linked diseases
disorders are those associated with altered genes present on the X chromosome. They can be dominant or recessive. X-linked recessive inheritance is associated with disorders such as hemophilia
umbilical cord
AVA - two arteries and 1 vein
Warton jelly
autosomal dominant inheritance disorder
occurs when a single gene in the heterozygous state is capable of producing the phenotype. Huntington disease is an example of an autosomal dominant inheritance disorder
down syndrome
a chromosomal abnormality involving the number of chromosomes (trisomy numeric abnormality), in particular chromosome 21, in which the individual has three copies of that chromosome.
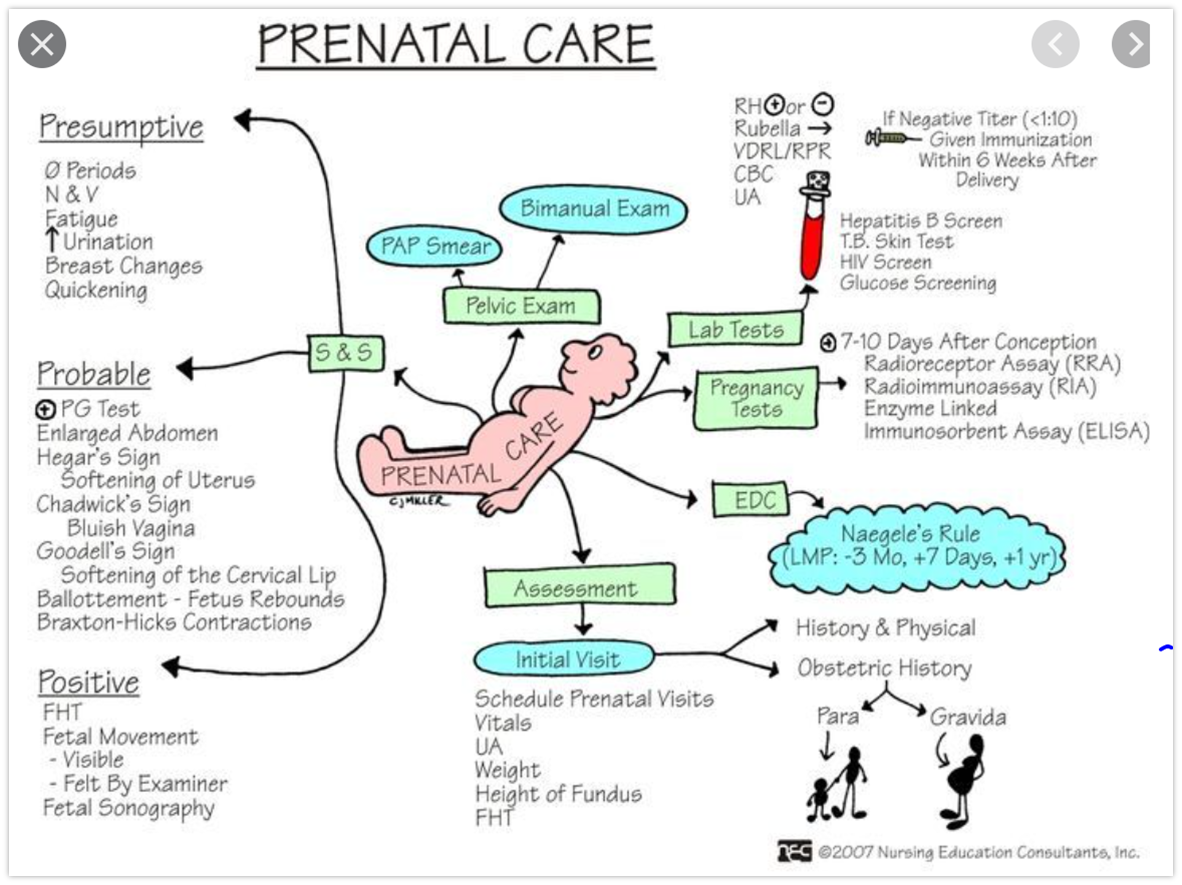
presumptive signs of pregnancy
reported by the women
ex. Fatigue, Breast tenderness, Nausea and vomiting, Amenorrhea, Urinary frequency, Hyperpigmentation of skin, Fetal movements (quickening), Uterine enlargement, Breast enlargement
probable signs of pregnancy
objective and observed by the HCP
ex. Braxton Hicks contractions, Positive pregnancy test, Abdominal enlargement, Ballottement, Goodell’s sign, Chadwick’s sign, Hegar’s sign → can all be detected on a physical exam
Hegar’s sign
softening of the lower uterine segment or isthmus
Goodell sign
softening of the cervix
Chadwick sign
blue-ish purple coloration of vaginal mucus and cervix
ballottement
examiner pushes against the women’s cervix during a pelvic exam and feels a rebound from the floating fetus
positive signs or pregnancy
ultrasound verification of embryo or fetus, Fetal movement felt by experienced clinician, Auscultation of fetal heart tones via Doppler
food that women should avoid during pregnancy
high traces of mercury
ex. shellfish, shark, swordfish, king mackerel, tuna, tilefish
nutrient needed in pregnant women to prevent neural tube defects
folic acid - found in dark green vegetables, baked beans, black-eyed peas, citrus fruits, peanuts, and liver.
Folic acid supplements are needed to prevent neural tube defects
pica
compulsive ingestion of nonfood substances. Suspect pica when the woman exhibits anemia although her dietary intake is appropriate. Ask about her usual dietary intake, and include questions about the ingestion of nonfood substances. Consider the potential negative outcomes for the pregnant woman and her fetus, and take appropriate action
quickening
The mother’s first perception of fetal movement, it is commonly described as a gentle fluttering
Perception of fetal movement typically begins in the second trimester, and occurs earlier in multiparous women versus nulliparous women.
supine hypotensive syndrome
main reason why pregnant women should avoid laying flat
occurs when the heavy gravid uterus falls back against the superior vena cava in the supine position. The vena cava is compressed, reducing venous return, cardiac output, and blood pressure, with increased orthostasis.
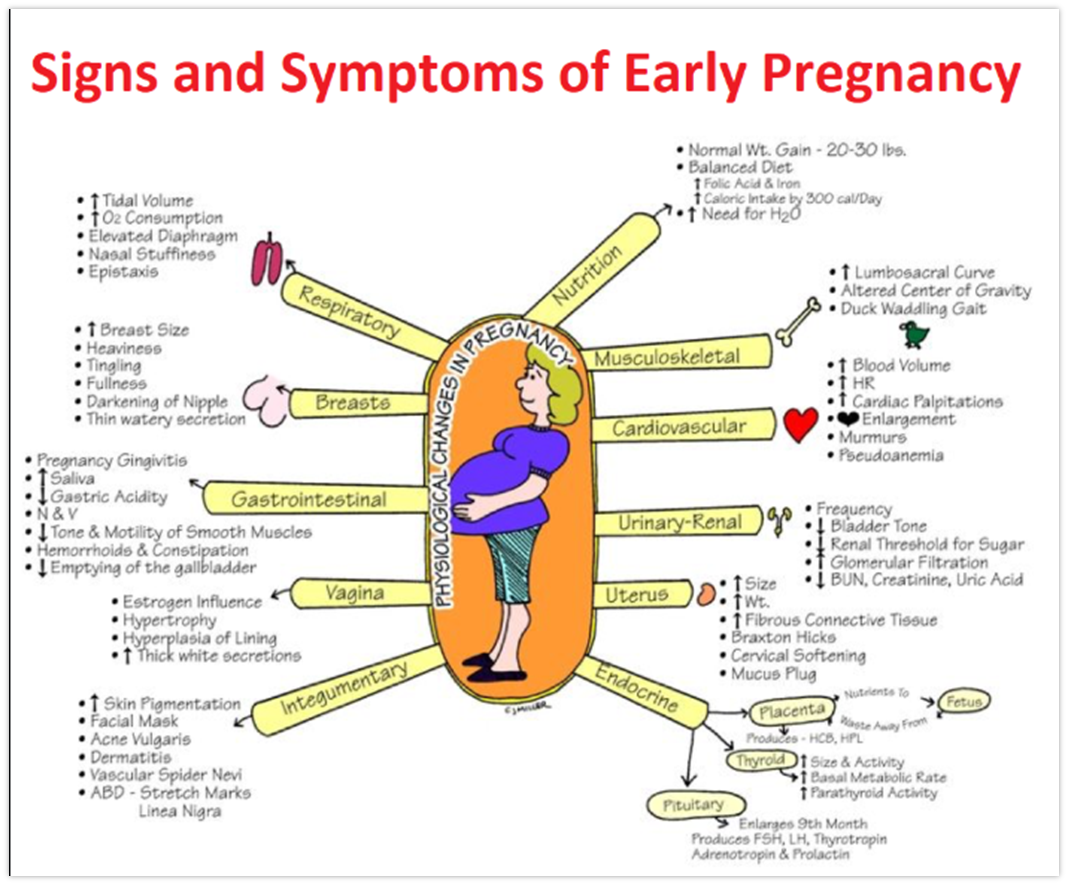
linea nigra
The skin in the middle of the abdomen may develop a pigmented line, which extends from the umbilicus to the pubic area
stria gravidarum
aka stretch marks
they are irregular reddish streaks that appear on the abdomen, breasts, and buttocks in up to 90% of pregnant women. Striae are most prominent by 6 to 7 months. They result from genetics, reduced connective tissue strength resulting from the elevated adrenal steroid levels, and stretching of the structures secondary to growth. They are more common in younger women, women with larger infants, and women with higher body mass
melisma (face melisma)
increased pigmentation that occurs on the breasts and genitalia also develops on the face to form the “mask of pregnancy”
It occurs in up to 70% of pregnant women. There is a genetic predisposition toward melasma, which is exacerbated by the sun, and it tends to recur in subsequent pregnancies. This blotchy, brownish pigment covers the forehead and cheeks in dark-haired women.
Most facial pigmentation fades as the hormones subside at the end of the pregnancy, but some may linger.
vascular spiders
small dilated blood vessels that appear on the skin and look like a spider
they have a central red dot, the blanch if you press on the center
usually due to an increase in estrogen
hPL
hormone produced by the placenta that decreases maternal insulin sensitivity (causes blood sugar to be higher), causes insulin resistance and increased maternal blood glucose levels
mom must produce more insulin the overcome resistance
if mom has DM, her insulin would need to increase to meet those demands
respiratory adaptations
breathing more diaphragmatic then abdominal due to increase in diaphragmatic excursion, chest circumference and tidal volume
increase in oxygen consumption
congestion secondary to increased vascularity
maternal weight gain

healthy BMI → first trimester 3.5 - 5 lbs, second and third trimesters 1 lb/wk; overall 25-35 lbs
low BMI → first trimester 5 lbs, second and third trimester 1+ lb/wk; overall 28-40 lbs
BMI >25 → first trimester 2 lbs, second and third trimesters 2-3 lbs/wk; overall 15-25 lbs
couvade syndrome
sympathy and pain that men feel when women is pregnant
men can go through post-partum depression too
prenatal care
signs and sx of early pregnancy
biophysical profile (BPP)
parental test that checks fetal well being using and ultrasound and a nonstress test (NST); it looks for signs of hypoxia in baby
biophysical profile scoring components
a total score of 10 is possible if NST is used
a score of 8-10 is considered normal if the amniotic fluid volume is adequate
a score of 6 or less is suspicious, possibly indicating a compromised fetus and further investigation will be needed
Nagele’s rule
used for calculating EDD based on LMP - This date is within plus or minus 2 weeks (margin of error).
calculation formulas:
best used when LMP was April - December
subtract 3 months from LMP date
add 7 days
add 1 year
important to consider the amount of days in each month:
28 days → Feb.
30 days → Sept., April, June, Nov.
31 days → Jan., March, May, July, Aug., Oct., Dec
maternal serum Fetal alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP)
AFP screening is 16 to 18 weeks of gestation
elevation → open neural tube defect, underestimation of gestational age, the presence of multiple fetuses, gastrointestinal defects, low birth weight, oligohydramnios, maternal age, diabetes, and decreased maternal weight.
GTPAL
an acronym used to assess pregnancy
G → gravidity: # of time a women has been pregnant (includes current)
T → term births: # born at 37 weeks +
P → preterm births: # born at 20-37 weeks (includes alive or stillborn)
A → abortions or miscarriages: the number of pregnancies ending at 20 weeks or before, regardless of outcome
L → living children: # of currently living children (twins/triplets count individually for this one but as one for all the others)
changes in the cardiovascular system during pregnancy
occur early during pregnancy to meet the demands of the enlarging uterus and the placenta for more blood and more oxygen
include an increase in heart rate (25%); cardiac output increases by 30% to 50% and peaks at 25 to 30 weeks gestation; reduced total peripheral resistance; increased blood volume; increased plasma volume which leads to physiologic anemia. Perhaps the most striking cardiac alteration occurring during pregnancy is the increase in blood volume
Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling
diagnostic tests that may confirm a genetic anomaly in a developing fetus, but they are all invasive techniques A fetal nuchal translucency test, seen on ultrasound, may suggest the presence of trisomy 21 or Down syndrome if increased nuchal thickness is found
chronic villus sampling (CVS)
an invasive procedure involving an 18-gauge needle stick through the abdomen or passage of a suction catheter through the cervix under ultrasound guidance. This test is used to obtain a sample of the chorionic villi from the placenta for prenatal evaluation of chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome or cystic fibrosis, enzyme deficiencies, and fetal gender determination and to identify sex-linked disorders such as hemophilia, sickle cell anemia, and Tay–Sachs disease CVS is generally performed 10 to 13 weeks after the LMP
amniocentesis
needle is inserted into the amniotic sac wo w/d amniotic fluid to confirm a genetic abnormality in a developing fetus
done at 15- 20 weeks
vaccines a pregnant women should get
hep c
influenza
tetanus (Tdap)
RSV
covid
Rho(D) immune globulin injection
RhoGAM
IM injection given to women who are Rh negative (have a negative blood type) and have the potential to give birth to a positive blood type and if the baby comes out as a positive blood type then mom has to have the injection once more to prevent attacking in future pregnancies
this only effects Rh negative moms
when its given:
at 28 weeks
within 72 hours after birth if baby is Rh-positive
after miscarriage, abortion, trauma, amnio, bleeding, etc.