1. Cardiovascular Disease
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What are the #1 cause of death in men and women in the U.S.?
Cardiovascular disorders
-Hypertension
-Hyperlipidemia (triglycerides and cholesterol)
-Arteriosclerosis
-Atherosclerosis
what is the most modifiable risk factor of stroke
HTN
~50% of all deaths from CVD are from ?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
-atherosclerosis
~33% of deaths are from ?
Cerebral Vascular Accident (CVA)
-15 million people worldwide suffer a CVA annually
-5 million are left permanently disabled
~10% of hypertensive related deaths are due to?
End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
What generates blood pressure?
BP = CO x VR
-Cardiac Output (CO): amount of blood pumped by the ventricle per minute
-VR = peripheral resistance
Chronic elevation of BP is Hypertension
Cardiac Output (CO)
CO= SV x HR
-SV= stroke volume
-Amount of blood ejected from ventricles
-HR= heart rate
VR = peripheral resistance
what impacts it
what is HTN
-Vascular resistance is the resistance of blood vessels to blood flow, which is affected by blood volume and blood vessel size (diameter & length)
-smaller diameter is more resistance, longer length is more resistance and higher viscosity is more resistant
-VR increases with obesity & aging
chronic elevation of blood pressure
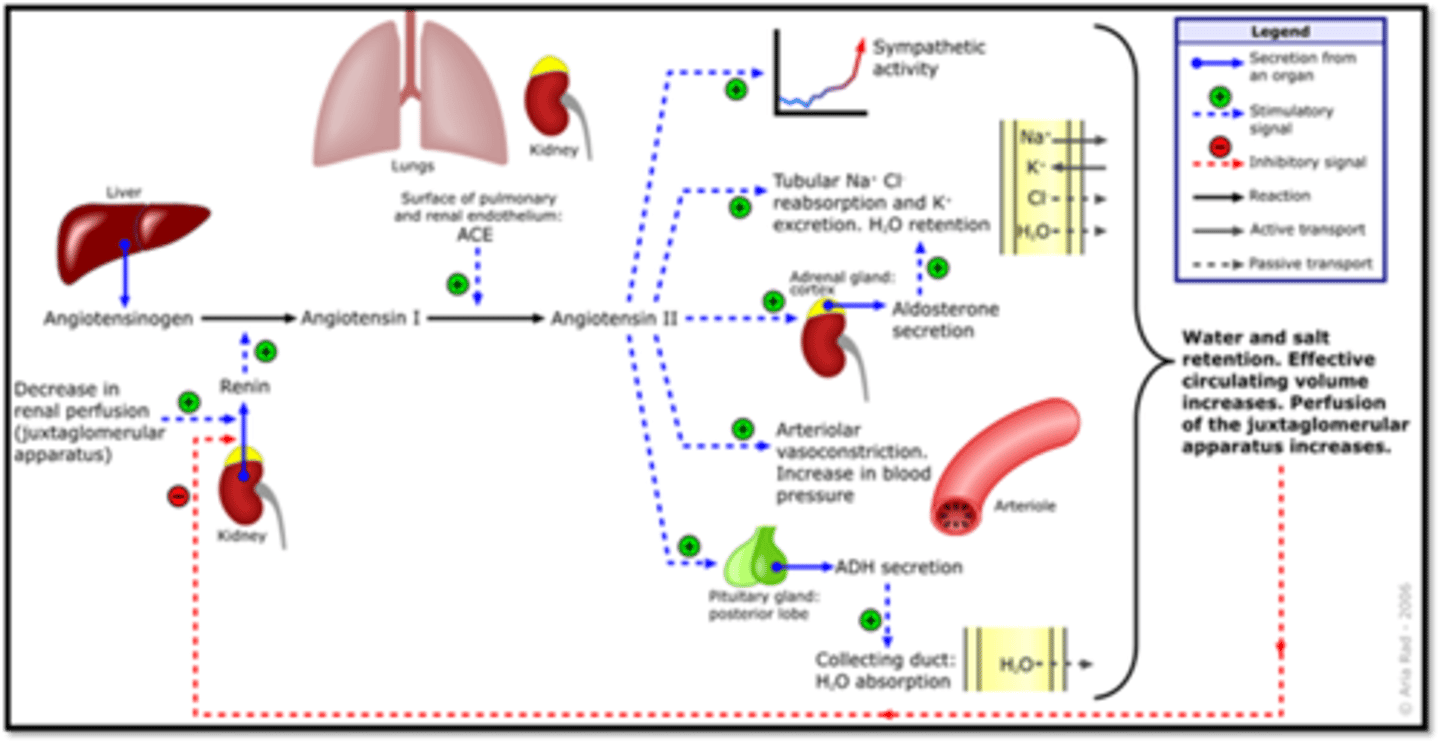
What is a major contributor to the development of primary HTN and secondary HTN?
which 3 thigns increase renin production
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
Angiotensin II has multiple effects
-Obesity increases renin production
-Renin can also be stimulated through sympathetic activation (noradrenaline from adrenal glands)
-Hyper aldosteronism also increases renin production
How common is HTN?
what % are well controlled
Affects 48% of adults in U.S.
-Only ~ 22.5% are adequately controlled
-Geographic, sex, ethnic, and socioeconomic differences
Primary /essential hypertension
-what % of cases
-is it symptomatic
-95% of cases
-Idiopathic
-Asymptomatic "Silent Killer"
Secondary HTN
Increased BP secondary to another cause
-medication, kidney, endocrine disorders, drug use
Hypertensive crisis / malignant hypertension
whcih organs does it impact 4
Acute end-organ damage
-Heart
-Brain
-Retina
-Kidneys
Labile HTN
what is unique about it
-BP that fluctuates repeatedly in response to emotional stress
-HTN medications not effective; usually Rx stress-relieving meds
-Monitor for 24 hours
White Coat Syndrome
amount it increases by
Can increase bp ~20/10mmHg
Gestational/Pregnancy-Induced HTN
when does it return to normal
BP usually returns to normal within 12 weeks of delivery
What is normal BP?
Systolic <120
and
Diastolic <80
What is elevated BP?
Systolic 120-129
and
Diastolic less than 80
Stage 1 HTN
Systolic 130-139
or
Diastolic 80-89
Stage 2 HTN
Systolic 140 or higher
or
Diastolic 90 or higher
Hypertensive crisis
Systolic higher than 180
and/or
Diastolic higher than 120
Consult your doctor immediately
What increases the risk for CV disease 2-fold?
Every 20/10 mmHg increase in BP over 115/75 mmHg
Updated HTN Diagnostic Criteria
in office
24/7
day time
night time
HBPM
ABPM - ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
HBPM - home blood pressure measurement
Whenever possible, the diagnosis should not be made on a single office visit. Usually 2-3 office visits at 1-4-week intervals (depending on the BP level) are required to confirm the diagnosis of hypertension. The diagnosis might be made on a single visit, if BP is ≥180/110 mm Hg and there is evidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD)

What is the difference between HTN urgency & emergency?
Both: Systolic >180 or Diastolic >120
Emergency has end organ damage
HTN Urgency symptoms that DO NOT constitute an emergency 4
-Severe headache
-Shortness of breath
-Nosebleeds
-Severe anxiety
Emergent symptoms
-CVA
-Loss of consciousness
-Memory loss
-MI
-ESRD
-Aortic dissection
-Angina
-Pulmonary edema
-Eclampsia
Hypertension-Risk Factors
-gender
-race
-systemic diseases
-Male gender
-Increased age
-Race: AA
-Family Hx of premature cardiovascular disease
-Sympathetic over-activity
-Sleep apnea
-Concomitant disease
-Lifestyle factors
-BMI: body mass index
What age is a risk for HTN? men vs women
>55 in men; >65 in women
Sympathetic over-activity
what does it cause 4
-stress & pheochromocytoma
-Vasoconstriction, increased heart rate
Concomitant disease
Dyslipidemia, diabetes
Lifestyle factors 5
-Alcohol (moderate to heavy),
-Obesity (BMI>30),
-Sedentary lifestyle
-Cigarette smoking
-Dietary salt intake
BMI: body mass index
= [weight (lb)/height (inches)^2] x 703
= weight (kg)/height (meters)^2
Secondary hypertension manifestations 6
-Edema (pitting)
-Truncal obesity
-Foot ulcers
-Numbness of extremities
-Muscle weakness
-Tachycardia
Blood pressure reading specifications
-Proper size cuff (small cuff = elevated)
-Patient relaxed
-Remove constricted clothing
-No caffeine or tobacco use prior
-At rest for 5 or more minutes
-Feet on floor, legs uncrossed
-Void bladder before
Diagnostic Tests or Procedures Prior to Treatment
-EKG, ECG
-Urinalysis
-Blood glucose
-Hematocrit
-Electrolytes: Na, K, Ca, Chloride, Bicarbonate
-BUN (kidney function)
-Creatinine (or glomerular filtration rate)
-CRP
-Homocysteine
-Lipid profile (total, HDL, LDL, triglycerides)
-Liver profile (Albumin)
C-Reactive Protein
what is it
Inflammation-promoting globulin in blood that is produced when blood vessel walls become damaged
C-Reactive Protein values
normal
moderate
high
-Normal - <0.11 mg/dL
-Moderate - 0.12 to 0.19 mg/dL
-High - 0.20 to 1.50 mg/dL
Factors that increase CRP
-HTN
-Body mass index
-Smoking
-Metabolic syndrome
-Hyperglycemia
-Low HDL/ High triglycerides
-Estrogen/progesterone use
-Chronic infection
-Rheumatoid arthritis
-Genetic mutation
-Vasculitis
Homocysteine
what does it cause 3
Amino acid in blood that converts cholesterol to LDL
-Further damages arterial walls
-Causes blood to clot
-Increases risk of vessel blockage / ischemic stroke
Homocysteine values
normal
increased risk cardiovascular disease
-<12 µmol/L - desirable
-12 to 15 µmol/L - increases risk for cardiovascular disease
Homocysteine treatment
B vitamins (folic acid/B9; cobalamin/B12; pyridoxine/B6)
Hypertension Treatment
Reduce BP gradually (consult with internist)
-First Line Agents
-Second Line Agents
-Lifestyle modifications
First Line Agents 4
which is the preferred treatment for diabetics
-Diuretics: furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide
-ACE inhibitors (preferred treatment for diabetics): captopril
-Angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARB): valsartan
-Ca 2+ channel blockers: diltiazem, nifedipine, verapamil
Second Line Agents
-b-blockers: e.g. metoprolol
-Alpha agonist/antagonist: clonidine, terazosin
-Methyldopa
-Vasodilators: hydralazine
Lifestyle modifications 5
what is a normal BMI
-Weight reduction (normal BMI=18.5-24.9)
-Adopt Mediterranean Diet
-Dietary sodium decrease
-Increase physical activity
-Moderation of alcohol consumption
HTN Effects on Heart Muscle 2
what do they cause
Increased workload
Stronger contractions
-Left ventricular hypertrophy (can lead to left sided heart failure, and then right sided will follow)
-Congestive heart failure (CHF)
stiffening & narrowing of BVs puts stress on heart
Hypertensive Retinopathy
-what is it second to in prevalence
-Second only to diabetic retinopathy in prevalence
-Clinical presentation depends upon severity, duration, and degree of control
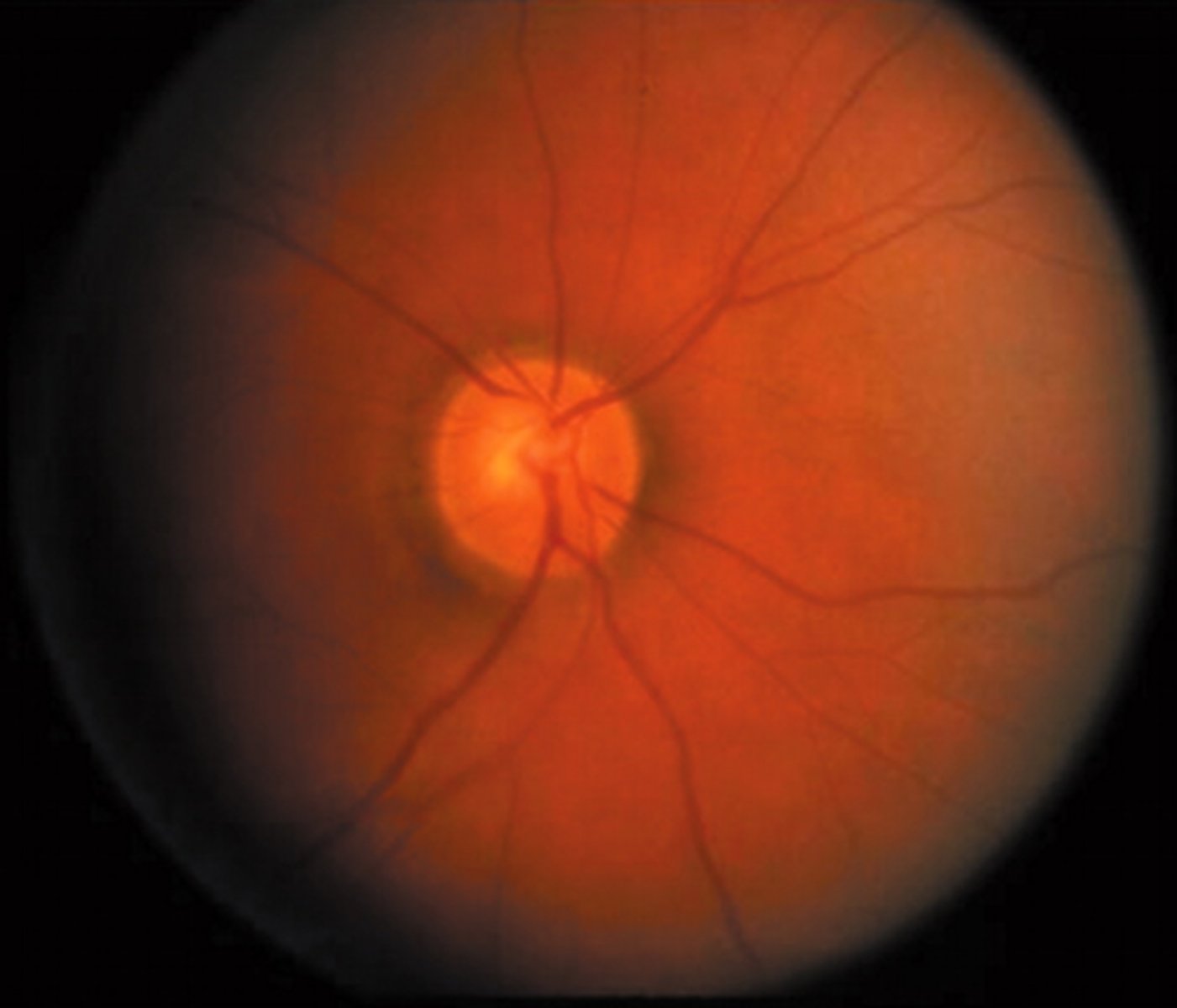
Keith-Wagener-Barker grade 1
Arterial narrowing
-Chronic, asymptomatic hypertension, adequate cardiac and kidney function
-Mild retinopathy does not correlate with mortality and morbidity
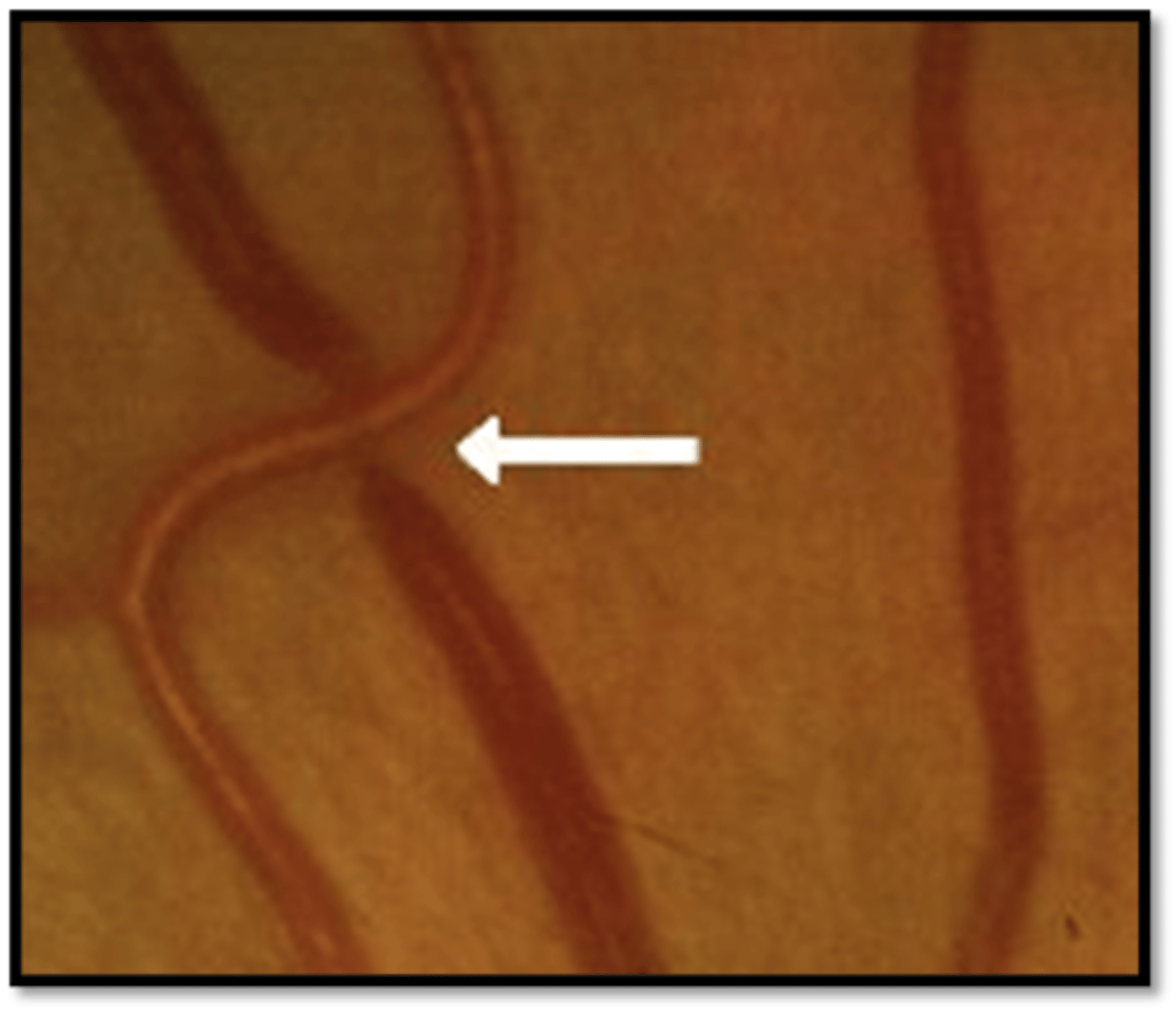
Grade 2: appearance
is it reversible
where
-Irreversible
-Damage and thickening of arterial wall
-Caliber of arterioles is reduced
-Best observed about 1DD out
-Attenuation of arterioles (Normal A/V=2/3)
-Thickening of arterial light reflex (normal ALR=1/3)
Keith-Wagener-Barker grade 2
-Focal arteriolar narrowing (ALR thickening d/t steepening)
-AV crossing changes
AV Nicking & Banking - Grade 2 appearance
-Occurs at AV crossings
-Most common in superior temporal arcade
-Compression of the retinal vein at their common sheath causes venous nicking/banking, dilation, and tortuosity
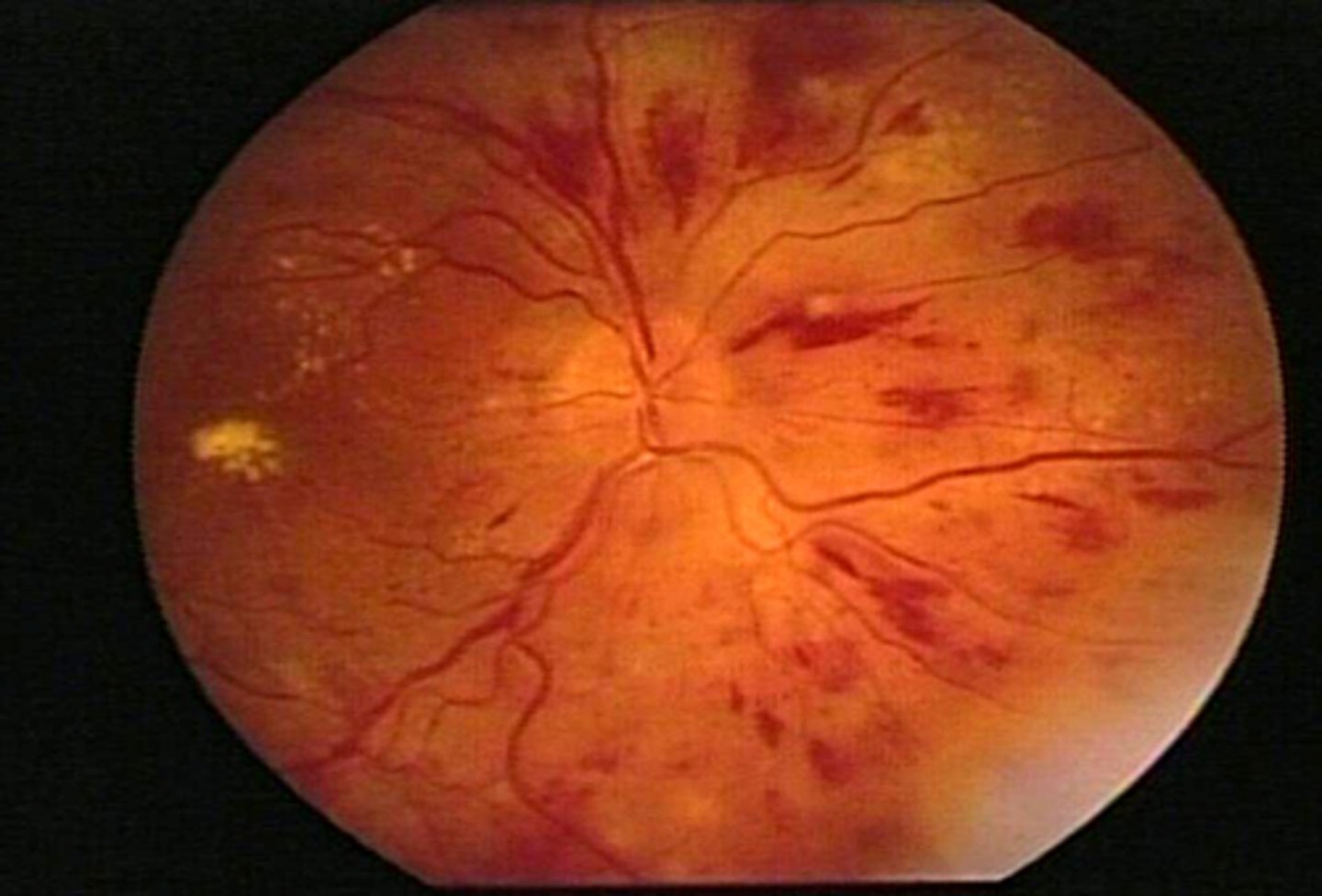
Keith-Wagener-Barker grade 3
Exudates, hemes, CWS, vessel occlusions, microaneurysms, macroaneurysms
Microaneurysms- Grade 3 appearance
where are they usually located
how are they best visualized
Small out-pouch of an capillary wall
May be the direct result of an increase in pressure from a sclerosed arteriole
-Usually near AV crossing change
Often associated with CWS
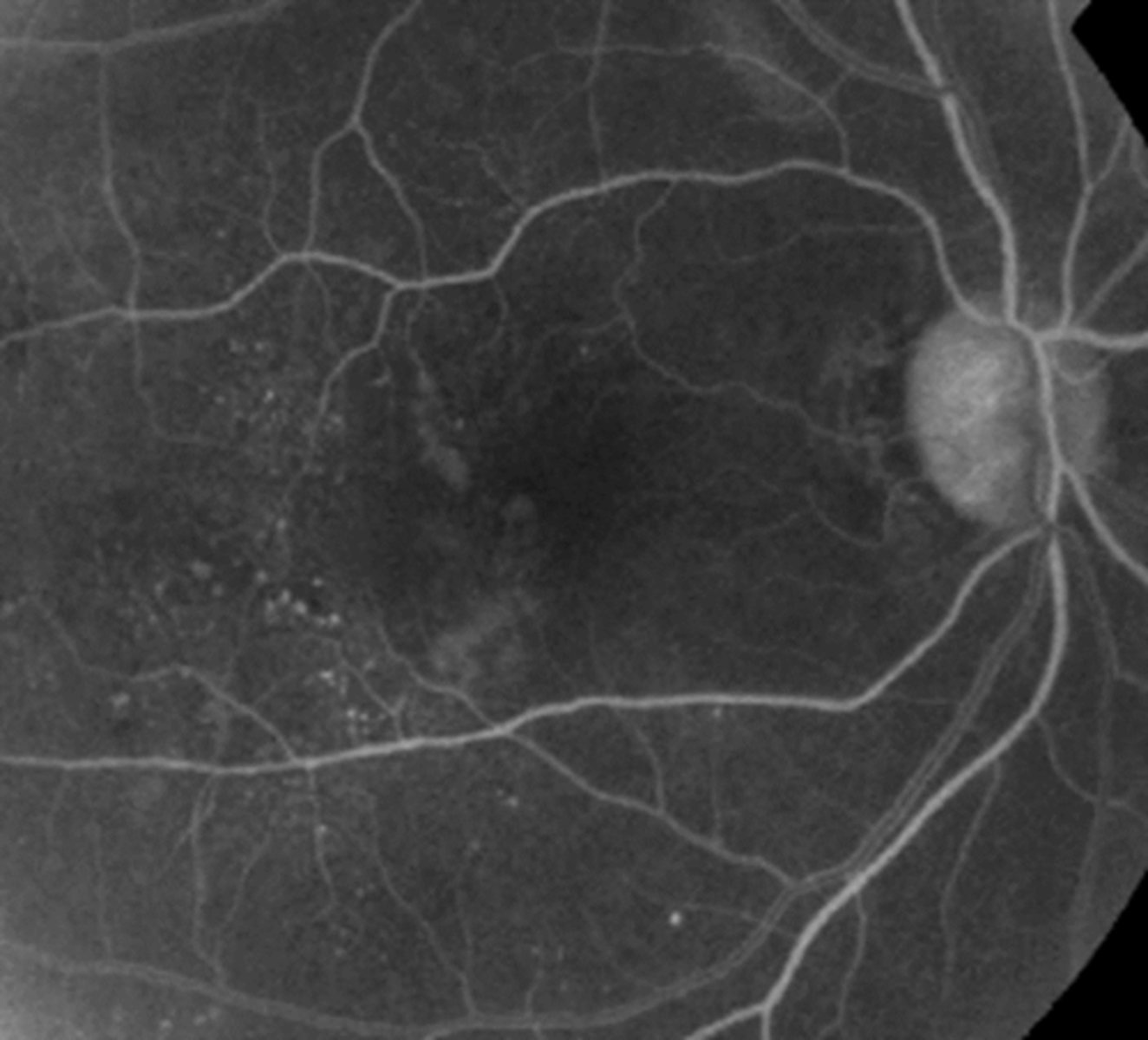
Difficult to visualize
-Best seen with IVFA
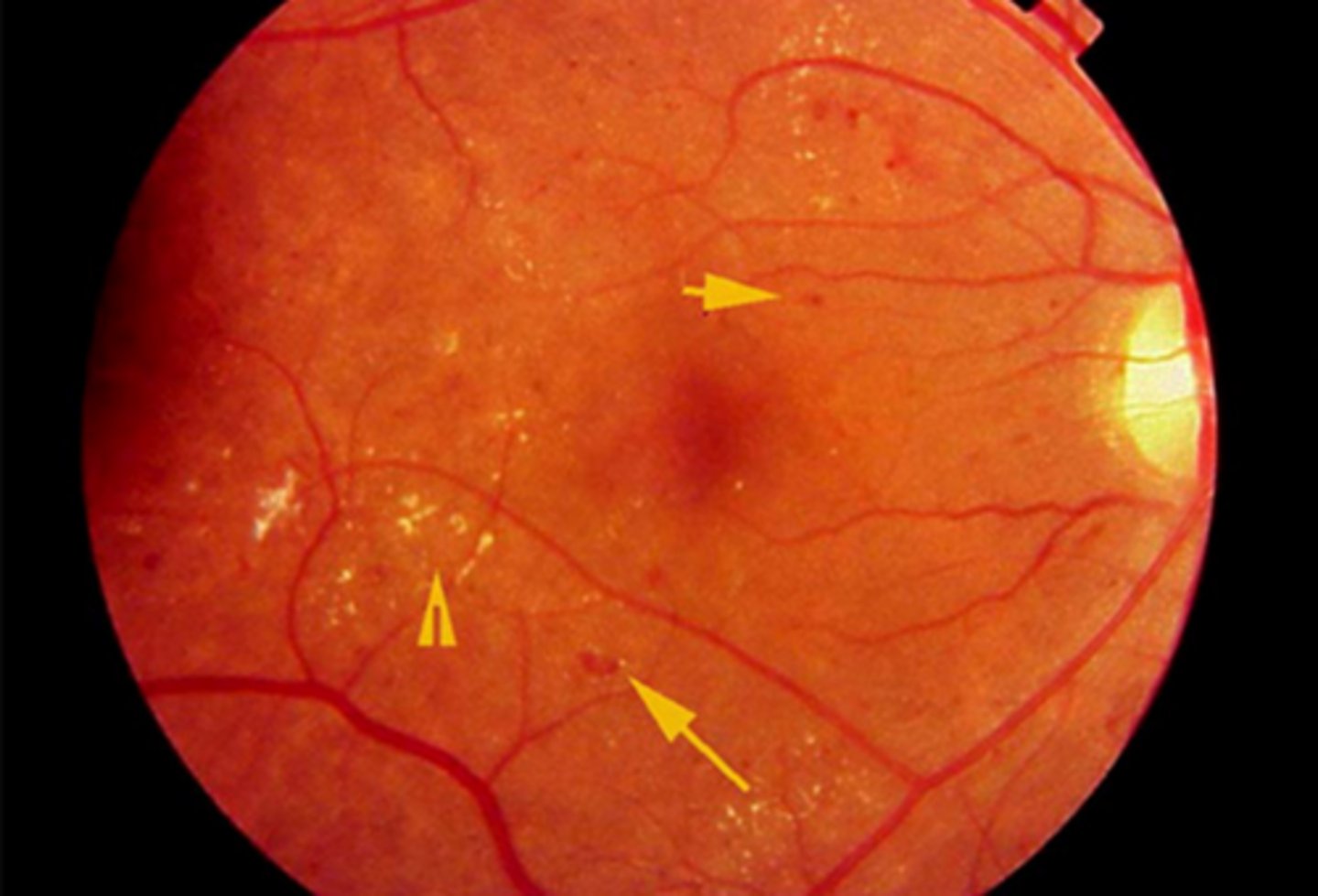
Exudation- Grade 3 appearance
what does it result from
Results from prolonged hypertension or abrupt acute episode
Tight junctions damaged
Blood leaks into retina
-Flame & intraretinal (dot/blot) hemes
Hard exudates
Retinal NFL ischemia (CWS)
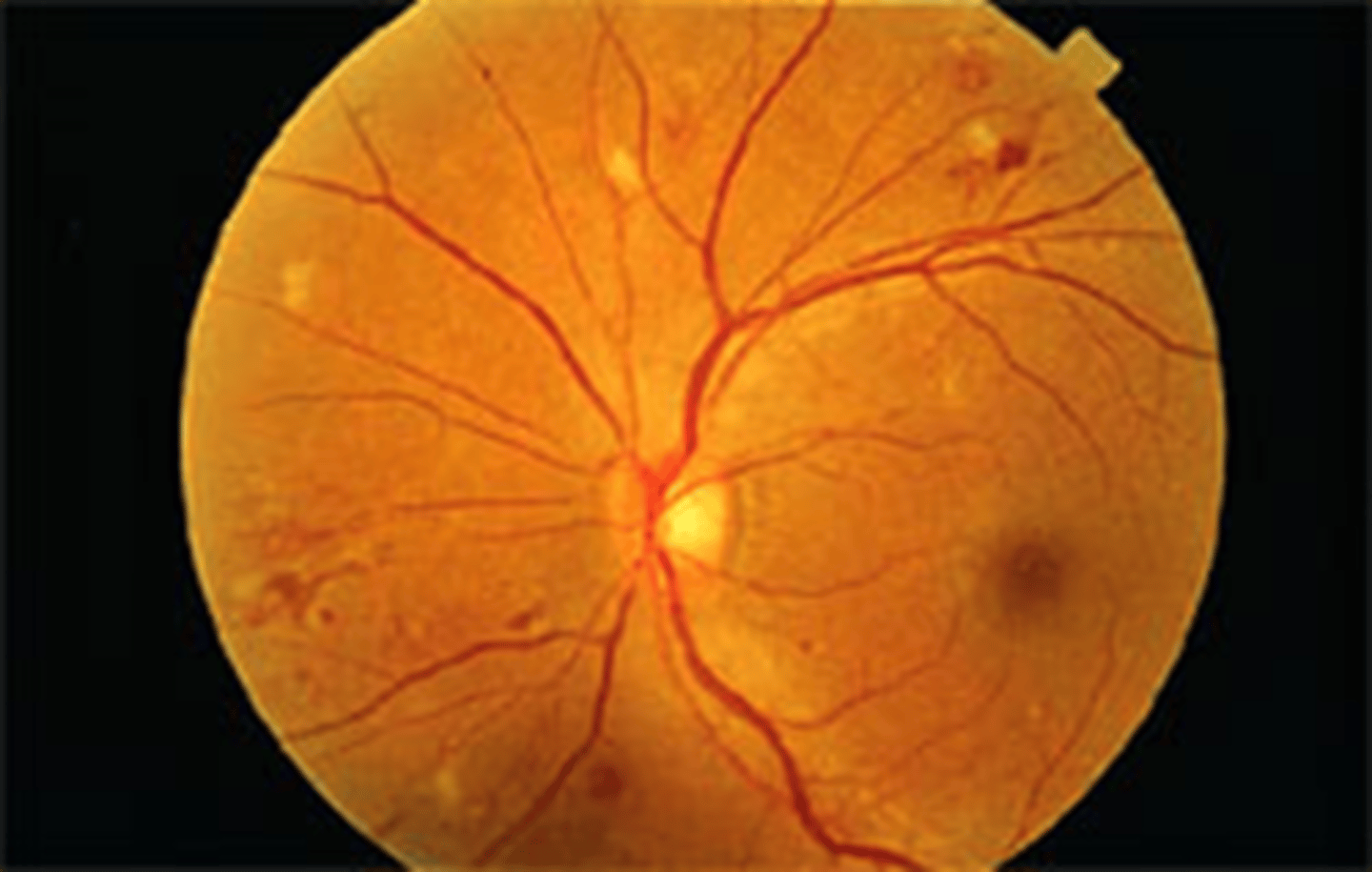
what are the two different type of macroaneurysms and how do they appear
what is the most common location for it
fusiform: spindle shaped and associated with exudation. ruptured ones cause hemorrhage and exudation at any level of the retina
saccular RAM: small sac. more likely to reslut in hemorrhaging
superior temporal arcade
Vascular Occlusion- Grade 3 appearance
-what is this a complication of
-what is it the most common cause of
Complications of retinal arteriosclerosis
-BRVO, CRVO (ischemic vs. non-ischemic): Most common etiology of BRVO
-Retinal, optic nerve, and/or anterior segment neovascularization
-BRAO, CRAO
-Retinal macroaneurysm
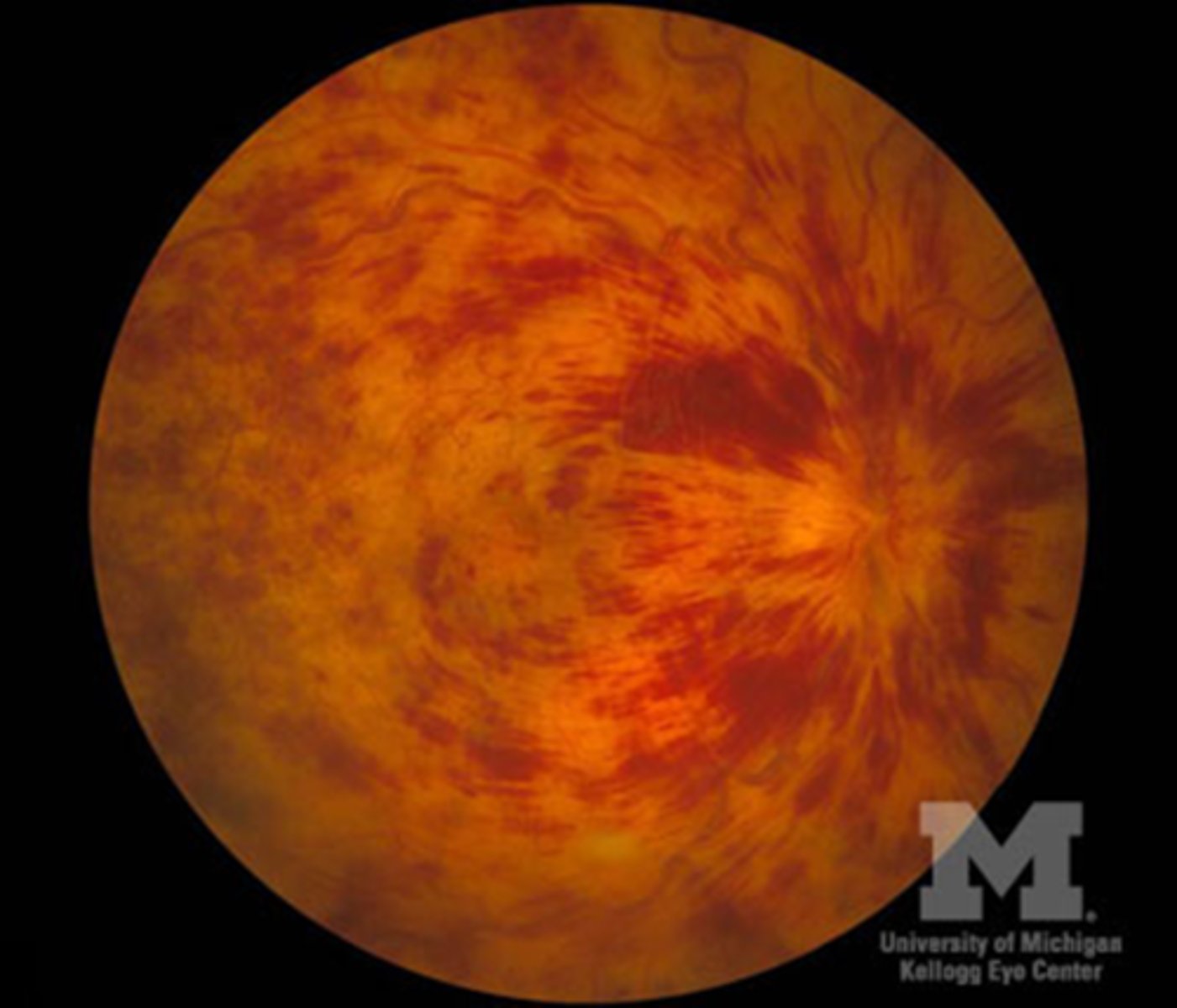
Keith-Wagener-Barker grade 4
what is this called
what is it most commonly associated with
where do exudates form (which layer)
hypertensive encephalopathy/malignant HTN: most commonly associated with acute, severe HTN
Optic nerve head edema, macular edema, venous engorgement and arteriolar constriction
rapid rise in BP damages the small vessel endothelium. Lipid exudates in the outer plexiform layer form a radiating pattern called a macular star