IID 21: Therapeutics of C. difficile and Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is diarrhea
Unusual passage of loose/watery stool at least 3 times in 24h
type 6: fluffy pieces with ragged edges and mushy stool
type 7: watery, no solid pieces, entirely liquid
Complications of diarrhea
Dehydration
Hypovolemia (critical reduction in circulating blood of fluid volume)
Electrolyte disturbances
Malabsorption of nutrients
Definition of a c diff infection present
presence of diarrhea/megacolon w/o other known etiology AND lab confirmed presence of c diff
diagnosis of typical pseudo-membrane on sigmoidoscopy/colonoscopy
histological (study tissues under microscope) diagnosis of c diff w/ or w/o diarrhea
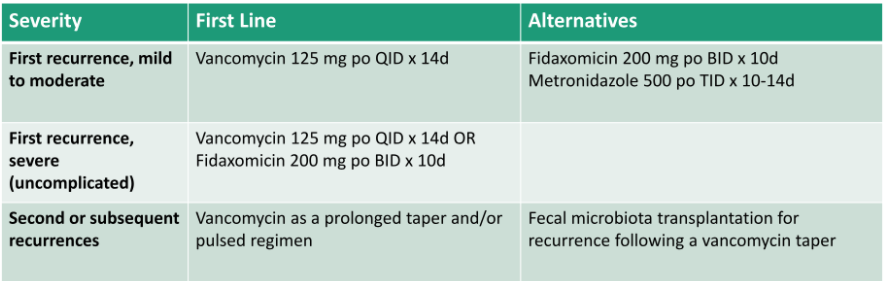
Definition of recurrent c diff infection
resolution of symptoms following therapy, followed by reappearance of symptoms and pos c diff test withing 8 weeks
more common in ppl w/ risk factors
How is c diff transmitted
spores shed in feces
contamination on surfaces (can last up to 5 months)
ingestion of spores
Risk factors for c diff
over 65yr, immunocompromised, history of inflammatory bowel disease, pt using antimicrobials, hospitalized, history of previous c diff
Pathophysiology of c diff inside host
person ingests both spore and vegetative cells
vegetative cell killed in stomach acid but spore remains
spore germinate in small intestine when in contact w/ bile acid
c diff multiplies in colon
immunocompromised gut mucosa esp helps adherence to colonic epithelium
Pathophysiology of how c diff causes harm
vegetative form releases 2 potent exotoxins → diarrhea + colitis
toxin A: activates neutrophils to cause inflammation
toxin B: more potent, cause colonic mucosal damage
Complications of c diff
diarrhea
pseudomembranous colitis
toxin-induced ulcers on mucosal surface of intestine (raised yellow plaques)
toxic megacolon
prolong hospitalization
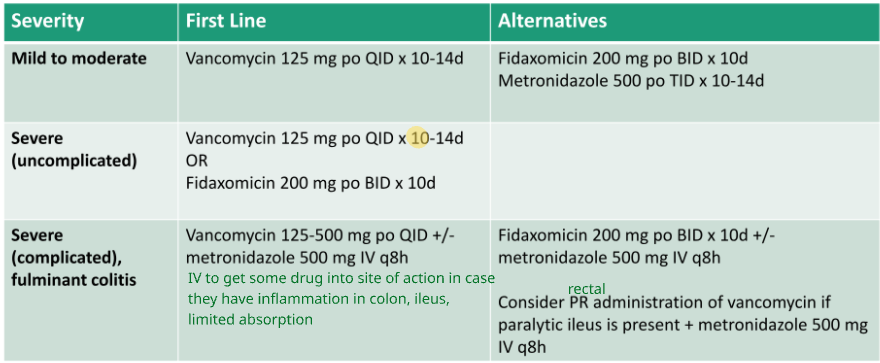
Mild to moderate c diff
WBC <= 15 × 10^9 per L and SCr < 133 umol/L (or < 1.5x increase from baseline)
Severe c diff
WBC >= 15 × 10^9 per L and SCr > 133 umol/L (or 1.5x increase from baseline)
Severe, complicated c diff
WBC >= 15 × 10^9 per L and SCr > 133 umol/L (or 1.5x increase from baseline)
AND
hypotension, shock, toxic megacolon
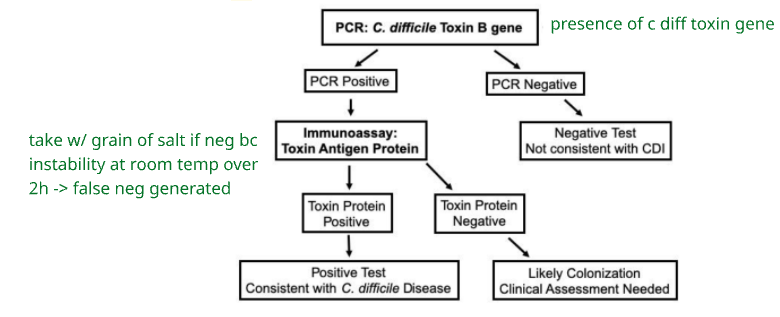
What is the 2 step testing algorithm for c diff
Treatment principles of c diff
discontinue concomitant antimicrobials
hydration
correct electrolyte abnormalities
discontinue laxatives
tube feed in needed
infection control measures
monitor w/ stool chart
Antimicrobial treatment options for c diff
metronidazole 500mg po/IV TID x 10 days
vancomycin 125mg po QID x 10 days
fidaxomicin 200mg po BID x 10 days
Monoclonal antibody treatment for c diff
bezlotoxumab 10mg/kg IV x 1
human monoclonal antibodies that bind to toxin B and prevent it from entering GI: no colonic damage
not for ppl w/ history of heart issues
used in conjunction w/ antimicrobials
prevent recurrent c diff in high risk pts
Fecal microbiota transplant for c diff
transfer of stool from healthy donor to a recipient w/ recurrent c diff to introduce healthy microbiota
injected right into pt colon as a slurry, oral capsule, nasal tube into stomach into colon
for pts with two or more recurrent episodes
not for treatment, only for prevention of further reoccurrences
Which antimicrobial agent is better for what severity
metro and vanco same for mild/moderate c diff
vanco better than metro for severe c diff
fidaxo and vanco same for curing c diff
fidaxo resulted in lower rates of recurrence of c diff
Approach to treating initial episode of c diff
Approach to treating recurrent episode of c diff
Pt w/ 2 or more recurrences should be considered for FMT to prevent further recurrences
Are antidiarrheal agents recommended in c diff
Can be used prn in pts with mild c diff being treated
Avoided in untreated c diff and pt w/ severe c diff
Should PPIs be used in c diff
increased risk of primary and recurrent c diff reported with gastric acid suppression (vegetative cells killed in acid)
Prevention measures for c diff
no probiotics
no prophylaxis therapy
yes isolation precautions
full-barrier gown and gloves
spore resistant to hand sanitizers: must use soap/water
yes antimicrobial stewardship
right drug at right dose for right duration
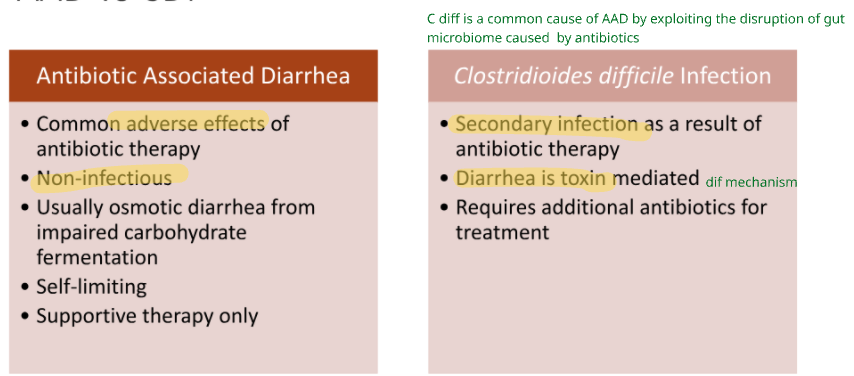
Antibiotic associated diarrhea vs c diff