UAB Bio Lab exam 3
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
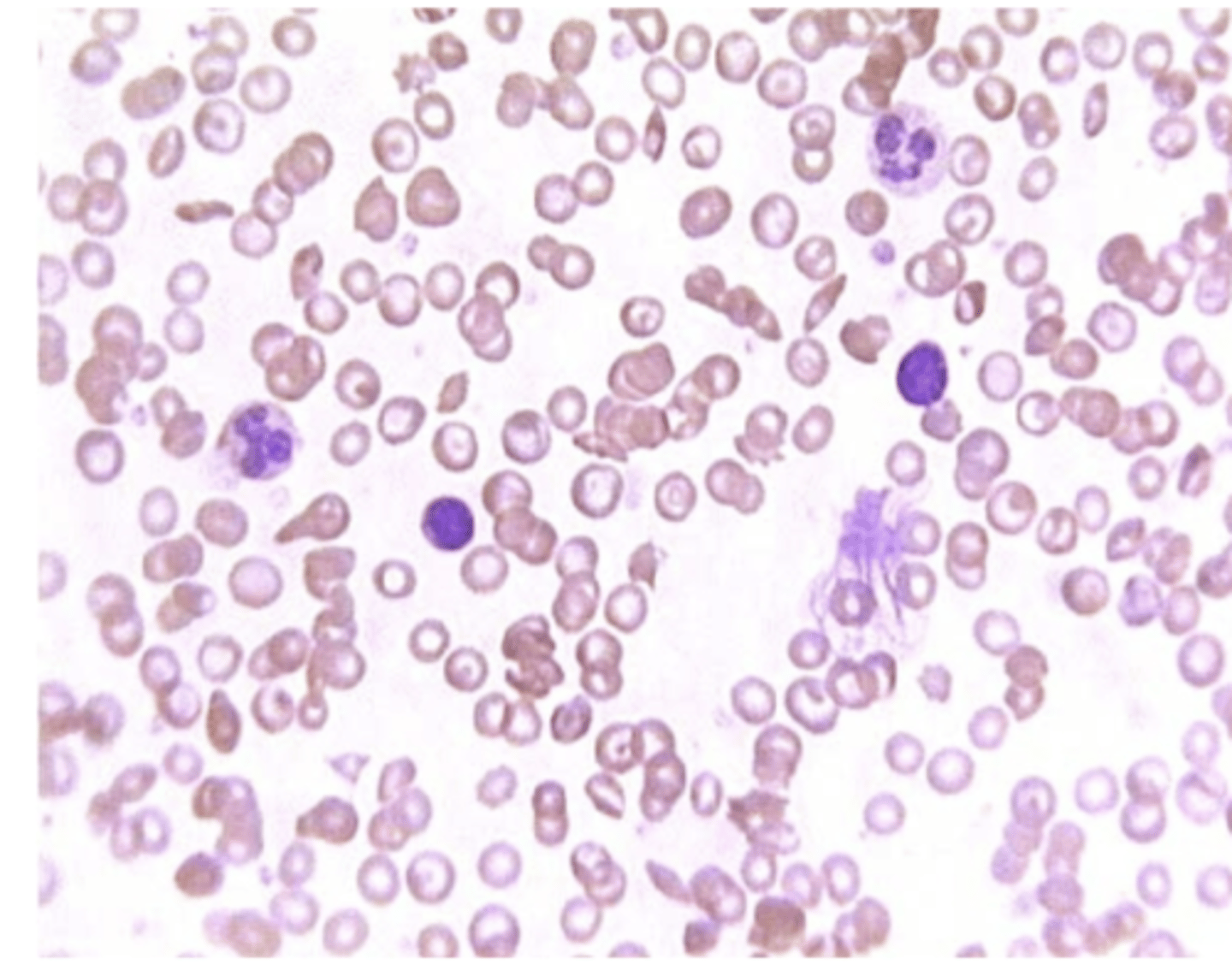
Sickle Cell
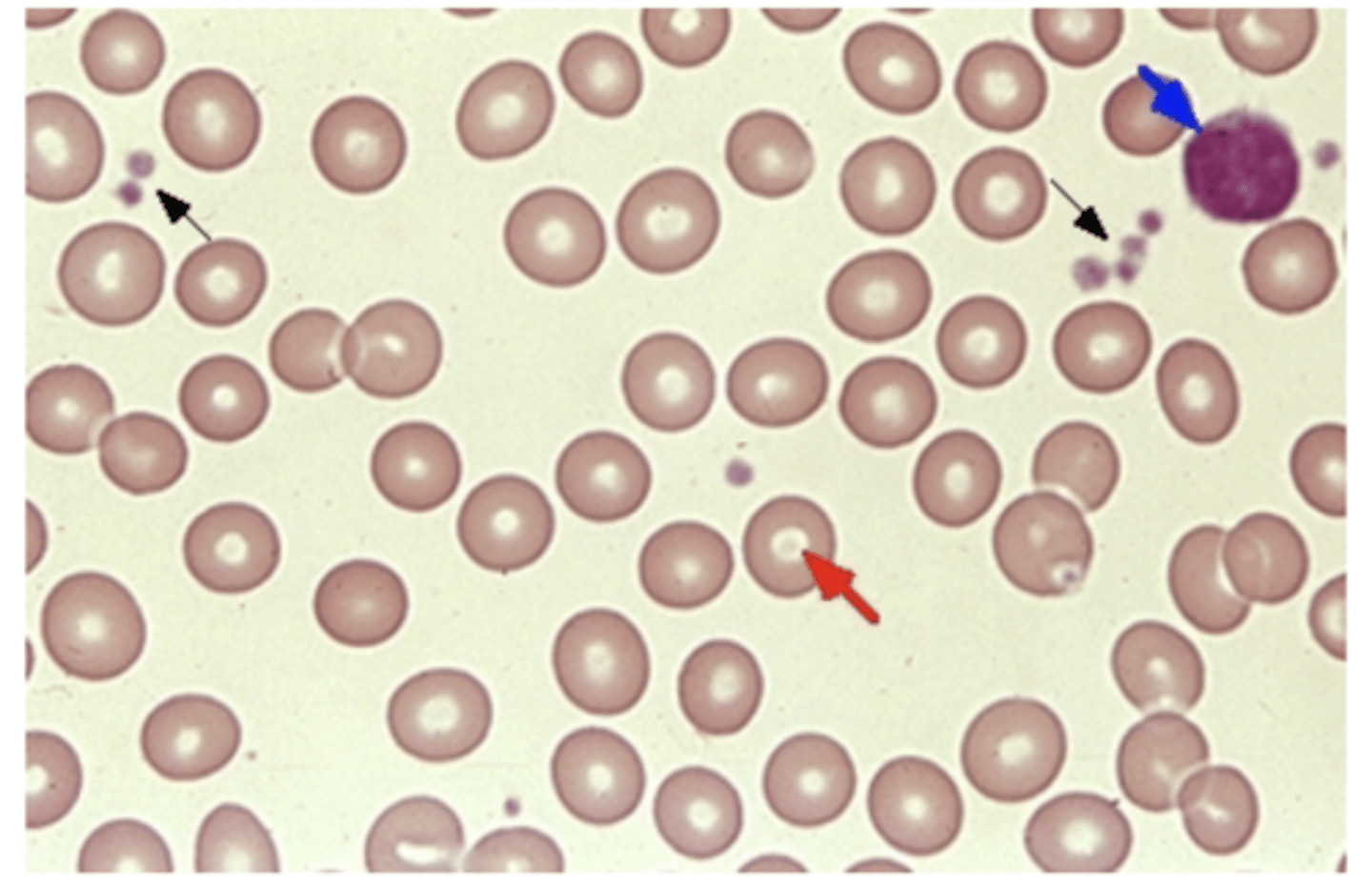
Normal Blood
What is a karyotype?
A picture of all condensed chromosomes inside of a cell.
Why is the correct amount of genetic information important for cells?
Having too little or too much genetic information can be extremely problematic for cell and organism function.
What is the basic definition of biological sex in this course?
XX = female and XY = male, but more accurately referred to as assigned female at birth or assigned male at birth.
What are Barr bodies?
Condensed, inactive X chromosomes found in cells with more than one X chromosome, ensuring only one X remains active.
What is nondisjunction?
The failure of two chromosomes to properly separate during metaphase, occurring in Meiosis I or II.
What is Trisomy 21 commonly known as? Extra copy of chromosome 21
Down Syndrome-nondisjunction, distinct facial features, intellectual disability
What is Trisomy 18 commonly known as? Extra chromosome on 18
Edwards syndrome-delays- heart and organ defects, low birth weight, life-limiting
What is the first step in DNA isolation?
Homogenization, which involves blending strawberries with detergent to break apart cell membranes.
What is the purpose of deproteinization in DNA isolation?
To strip histones away from DNA by adding meat tenderizer.
What is the role of alcohol in DNA isolation?
To precipitate DNA, making it insoluble so it can be isolated.
What are the components of a nucleotide?
A phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
What is Chargaff's rule?
The content of adenine (A) equals thymine (T) and the content of guanine (G) equals cytosine (C).
What is the direction of DNA replication?
DNA polymerase reads in the 3' to 5' direction and synthesizes in the 5' to 3' direction.
What are Okazaki fragments?
Short segments of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
DNA polymerase I
removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA
What is the function of ligase in DNA replication?
To create covalent bonds between DNA fragments, acting as molecular glue.
What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA: ATCG bases, double-stranded, contains deoxyribose sugar
RNA: AUCG bases, single-stranded, contains ribose sugar
What is transcription?
Process where DNA is copied into mRNA, which carries genetic instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
What are the three stages of transcription?
Initiation, elongation, and termination.
What is a codon?
A sequence of three nucleotides that codes for one amino acid.
What is the start codon and what does it code for?
AUG, which codes for methionine.
What are the stop codons?
UGA, UAG, UAA, which signal termination of translation.
Gene
coding for a particular trait
Allele
different variations of a gene
Gene pool
sum of genes within a population
Genotype
genetic make-up, alleles present on your chromosome
Homozygous
AA, aa having the same allele for a gene
Heterozygous
Aa having different alleles for a gene (dominant allele will be expressed)
Homozygous dominant
AA (having the dominant alleles)
Homozygous recessive
aa (having the recessive alleles, only expressed when they are homozygous)
Phenotype
the visual characteristics that are being expressed
Phenotypic frequency
individuals within population with a certain phenotype
Allelic frequency
the percentage of any specific allele in the gene pool
Genotypic frequency
the proportion of a given genotype within a population
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
Population is not changing/evolving
Gel electrophoresis
Technique to separate molecules based on charge
Sickle cell hemoglobin
Will have a different charge than normal hemoglobin protein
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies from one generation to the next, especially in small populations.
Founder effect
New population from a few individuals
Bottleneck effect
Drastic reduction in an existing population
Gene flow
The transfer of alleles into or out of a population due to the movement of fertile individuals or their gametes
Taxonomy
domain-> kingdom-> phylum/Division->Class->Order->Family->Genus->Species
Prokaryotic
Cells without a nucleus; simpler cell structure.
Archarea
Prokaryotes that live in extreme environments and have unique cell chemistry.
Bacteria
Prokaryotic organisms found everywhere; some helpful, some harmful.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that builds new DNA strands by adding nucleotides during replication.
Primase
Enzyme that makes short RNA primers to start DNA synthesis
Helicase
Enzyme that unwinds and separates DNA strands by breaking hydrogen bonds.
What is Triple X Syndrome?
• Cause: Female has an extra X chromosome from nondisjunction.
• Impacts: Usually normal development; may be taller, slight learning/language delays.
Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY)
• Cause: Male has an extra X chromosome due to nondisjunction.
• Impacts: Reduced testosterone, less body hair, possible infertility, some learning difficulties.
Turner Syndrome (X)
• Cause: Female missing one X chromosome (monosomy X).
• Impacts: Short stature, infertility, some physical/medical issues, normal intelligence.
Jacob’s Syndrome (XYY)
• Cause: Male has an extra Y chromosome from nondisjunction.
• Impacts: Often taller, normal fertility, possible mild learning or behavioral challenges.
In which direction is mRNA synthesized?
5' to 3' direction
What is the reading direction of DNA during mRNA synthesis?
3' to 5' direction
What are the base pairings for adenine in DNA?
Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T)
What is the start codon for protein synthesis?
AUG (methionine)
What should be done when base pairs before the start codon do not match?
Ignore them and look for the AUG pair (TAC)
How are codons structured in mRNA?
Codons are letters of 3
What happens when a stop codon is reached during translation?
Detachment occurs and no amino acid is associated
What are the three sites in a ribosome where tRNA moves?
A (attach amino acid), P (polypeptide chain), E (exit)
DNA polymerase II
DNA repair 3-->5
DNA polymerase III
synthesizes new DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction, replication fork process
Mutation
Change in nucleotide sequence of DNA
allelic frequency equation
p + q = 1
genotypic frequency equation
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
p
dominant allele
q
recessive allele
p2
homozygous dominant
2pq
heterozygous
q2
homozygous recessive
Anticodons
Three letters on tRNA that match a codon mRNA
5 assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg
no mutations, random mating, large population size, no gene flow, no natural selection
Gram-positive bacteria
purple-thick cell wall
Gram-negative bacteria
pink
Barr bodies in males
0 (XY)
Barr bodies in females
1 (XX)
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil
Bacterial shapes
cocci, bacilli, spirilla
Archaea: Halophiles
salt loving
Archaea: Thermoacidophiles
Extreme temperature and acid loving
Bacteria: Kingdom Proteobacteria
Gram negative bacteria- e.coli, salmonella, and rhizobium
Bacteria: Kingdom Chlamydia
Sexually transmitted, survives only in animal cells, no peptidoglycan
Bacteria: Kingdom Spirochetes
uses flagella to spiral themselves through environment
Bacteria: Kingdom Cyanobacteria
Blue-green, photosynthetic