Mental Health Nursing
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
mental health
state of wellbeing where people reach their potential, cope with normal stressors, work productively, and contribute to society
mental illness
significant dysfunction in mental state related to development, biology, or psych disturbances
Diathesis-Stress Model
most psych disorders result from combo of genetic vulnerability and negative environmental stressors
Mental Health Parity Act
equal insurance coverage for mental health care as physical health care
epidemiology
study of distribution of mental disorders to identify high-risk groups and factors
incidence
# of new cases in a given timeframe
prevalence
# of current cases regardless of when they began
lifetime risk
risk one will develop a disease in the course of life
DSM-5
guidelines on clinical manifestations of disorders from APA, influenced by multiprotection clinical field trials
International Classification for Nursing Practice (INCP)
provides standardized nursing diagnoses
International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10)
clinical descriptions of disorders and associated codes
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
abuse; violence against a parent; living w/ someone w/ substance use disorders, mental illness, or ever incarcerated
these people are more sensitive to stress later in life
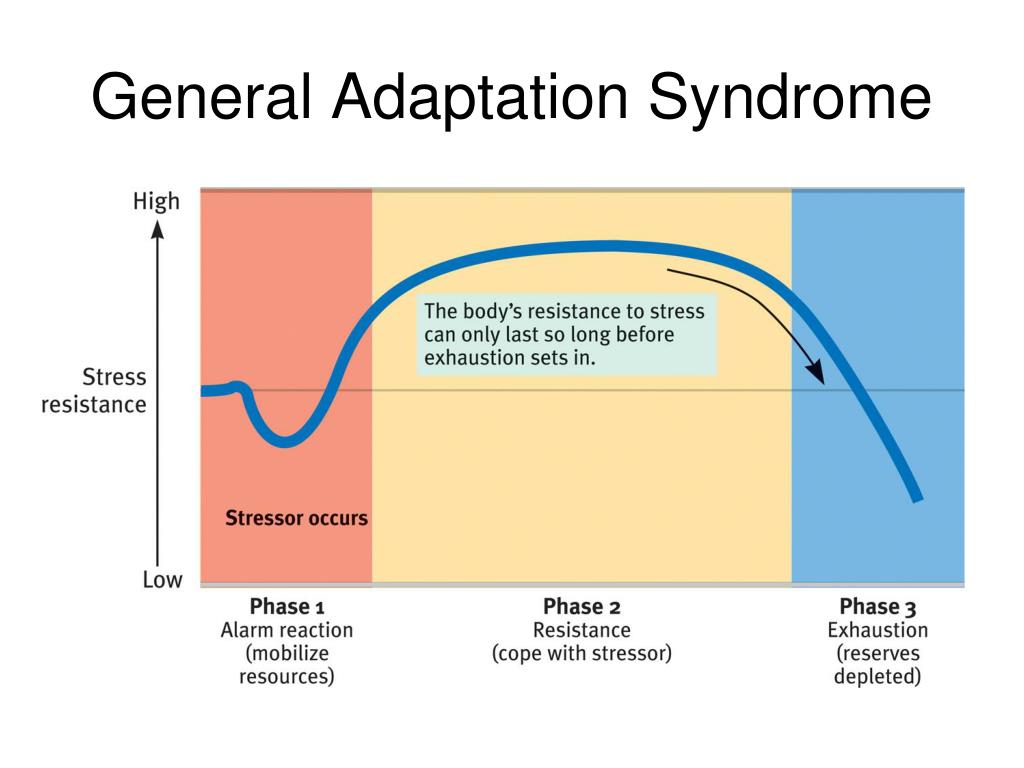
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
alarm / acute stress stage - symp nervous system activates, on alert
resistance / adaptation stage - sustained resistance, may be able to renew and repair under stress
exhaustion - resources depleted, stress becomes chronic
tend and befriend stress response
stress response of tending for children and leaning on social support networks - more common in women
stress mediators
perception, temperament, social support, culture, religion
reactive attachment disorder
consistent pattern of inhibited, emotionally withdrawn behavior, unresponsive to caregiver offering support
disinhibited social engagement disorder
no normal fear of strangers, unfazed by separation from caregivers
attachment disorders (treatment and consequences of not treating)
treatment: individual and family therapy
consequences w/o treatment: lack of trust, relationship insecurity
PTSD
seen as flashbacks, hypervigilance, avoidance, mood alterations, sleep problems, self-blame, detachment, loss of interest
polyvagal theory (threat response)
myelinated ventral vagal response - “on”, not overwhelmed
unmyelinated ventral vagal response - fight or flight arousal
dorsal vagal response - dampens sympathetic nerve system to curb overwhelm
myelinated ventral vagal response
“on”, not overwhelmed
unmyelinated ventral vagal response
fight or flight arousal
dorsal vagal response
dampens sympathetic nerve system to curb overwhelm (sleep, mind-numbing, depression)
PTSD treatment
provide safety/support system
Regulate emotions & arousal
Catch up on social skills (development in children)
PTSD meds
antidepressants, SSRIs
PTSD diagnosis timeframe
3 days-1 month after trauma typically
acute stress disorder
shorter timeframe of manifestations than PTSD, very similar in many ways - treated similarly
dissociative amnesia
inability to recall important personal info, traumatic or stressful nature
depersonalization
(self) being an observer of one’s own body & mental processes
derealization
(outside world) surroundings are unreal/distant; walking in fog, bubble, or dream
dissociative disorder treatment goals
personality integration:
increase personal identity
increase role performance
decrease anxiety
ethics
philosophical beliefs of right and wrong
bioethics
healthcare related ethical dilemmas - conflict between to actions with favorable and unfavorable consequences
principles of bioethics
autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, fidelity, veracity
pharmacogenetic testing
helps to identify what medication to use on a specific patient based on genetic testing
psych admissions
voluntary - patient has the right to leave
involuntary - law enforcement related
emergency - can’t leave without medical clearance, may have been committed by court
writ of habeus corpus
formal written order to free the person
least restrictive alternative doctrine
choosing the least drastic action
discharge
unconditional
release AMA (against medical advise)
conditional
assisted outpatient
unconditional discharge
no other treatment required for discharge
release AMA (against medical advise) discharge
only for non-court ordered admissions; worse health outcomes, increased readmission, delayed care, and higher costs
conditional discharge
requires other out-patient treatment
assisted out-patient discharge
court ordered, similar to conditional discharge
patient rights
right to treatment, right to refuse treatment, right to informed consent
mental capacity
ability to make informed decisions
competency
degree of mental soundness to make decisions
advance directives
wishes for medical treatment, may include DNR orders and proxy assignment
restraint
can be utilized in an emergency, needs new orders every time and requires check-ins every 15 minutes
chemical restraints
medications to help sedate / subdue
confidentiality
ethical responsibility prohibiting information disclosure without patient consent
confidentiality exceptions
duty to warn and protect third parties
tort law
wrongful acts that result in injury to others, can be intentional or unintentional
intentional tort examples
assault, battery, false imprisonment, invasion of privacy, defamation
unintentional tort examples
negligence, malpractice
factors to prove negligence
duty, breach of duty, cause in fact (actual cause), proximate cause (legal cause), damages, institutional policies and practices
reporting process for negligence, irresponsibility, and impairment
document clearly and accurately beforehand
supervisor intervenes, if unavailable, then you do
patient can review record
record belongs to the institution
retrospective record reviews
used in lawsuit, abuse, disability, and workers comp cases
forensic nursing
appointment of nursing principles in court, nurse educates court and provides medical opinions
minorites
racial/ethical/culturally distinct groups that coexist but are subordinate in some way to the dominant group
minority status
not always fewer in numbers, but lacking in political and social power
race
defined biologically, anthropologically, or genetically; can be based on physical characteristics
ethnicity
common heritage, shared worldview
culture
shared beliefs, values, and practices
western tradition [science]
values individuality, autonomy, and self-reliance; mind and body separate; time is linear; success through preparation for the future
eastern tradition [balance]
values family; body/mind/spirit are one entity; time circular/recurring; duty to comply to fate; disease caused by opposing forces
indigenous culture [harmony]
values identity in tribe; places significance on place of humans in natural world; disease due to lack of harmony w/ the environment
enculturation
transmission of culture’s beliefs to members
ethnocentrism
universal tendency to think one’s beliefs are the only correct/ natural way
cultural imposition
people/groups try to impose beliefs and behaviors on others out of a superiority complex
cultural barriers
communication, stigma, misdiagnosis, genetic variations
culture-based at risk populations
immigrants (choose to move), refugees (forced to leave homeland), cultural minorities
acculturation
learning beliefs, values, and practices of the new cultural setting
assimilation
adaptation to and implementation of the new culture
culturally congruent practice
applying evidence based care that corresponds with patient values, practices, and worldviews
cultural competence
process of demonstrating culturally congruent practice
includes cultural awareness, knowledge, encounters, skills, and desire