12: synaptic plasticity
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
115 blair
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
what happens in the correlation test of the inferior olive (IO)
neurons in the IO respond when the US (air puff) is delivered to a naive animal
what happens in the necessity test of the IO
when IO is lesioned, the CR functions as if US is absent
prevent acquisition of CR and extinction
what happens in the sufficiency test of the IO
electrical stimulation of the IO can substitute for the US (CR will still develop with nothing happening)
what are the 2 glutamate receptors in post-synaptic interpositus neurons
AMPA & NMDA
what kind of ion is Mg2+ and what role does it play in interpositus neurons
divalent cation, blocks NMDA receptors
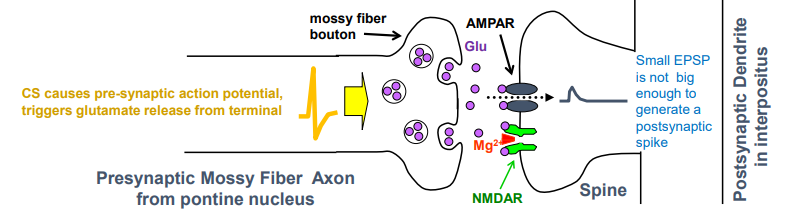
what happens during the pretraining (baseline) neural response to only the CS
pontine neurons fire & release glutamate onto interpositus neurons
glutamate binds to AMPA & NMDA receptors but only AMPA receptors pass current since NMDA is blocked by Mg2+
sodium through AMPA generates EPSP, but too small to trigger AP because there are few AMPA receptors in mossy fiber synapse
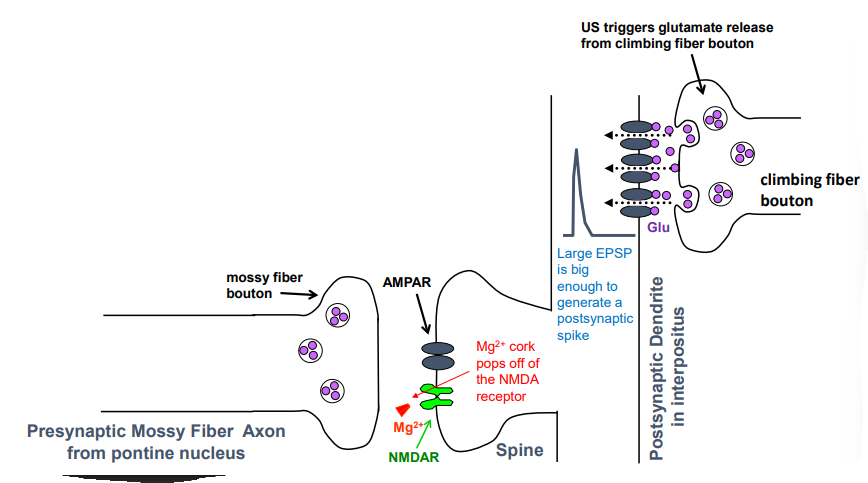
what happens during the pretraining (baseline) neural response to only the US
IO neurons fire & release glutamate onto interpositus neurons which generates EPSP
EPSP triggers AP in interpositus because lots of AMPAR in climbing fiber synapse
depolarization causes Mg2+ off NMDAR at mossy fiber
what happens during the training (CS-US paring) phase
CS causes pontine neurons to fire & release glutamate on weak interpositus synapses while US causes IO to fire & release glutamate on strong synapses
since Mg2+ is no longer on NMDAR, it allows Ca2+ to enter interpositus
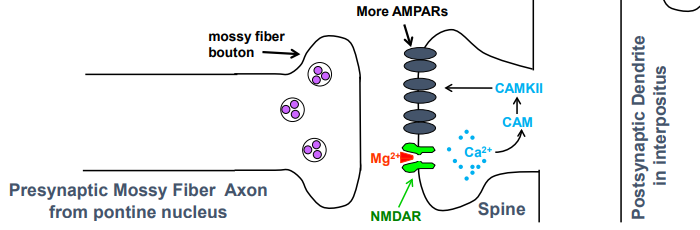
what is the process of long-term potentiation (LTP)
Ca2+ entry through NMDARs activates calmodulin (CAM) which activates CAM kinase II (CAMKII)
CAMKII triggers signaling that leads to insertion of more AMPA receptors into postsynaptic membrane of mossy fiber synapse, making synapse stronger
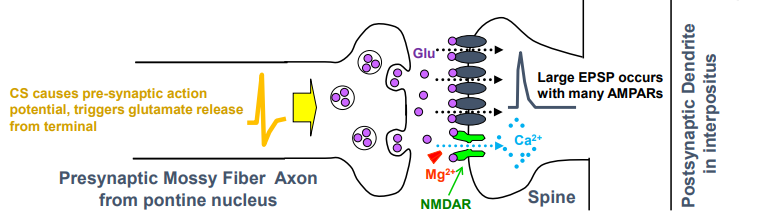
what happens during post-training (testing) neural response to CS
pontine neurons fire & release glutamate onto interpositus
mossy fiber synapse generates large EPSP that triggers AP in postsynaptic (eyeblink) and opens NMDA receptors
hebb’s rule (1949)
when 2 cells are active at same time, the synapse between them becomes stronger & stays stronger for a long time after
what is coincidence detection
part of hebb’s rule that requires a biological mechanism to signal when pre and postsynaptic cell are activated at same time
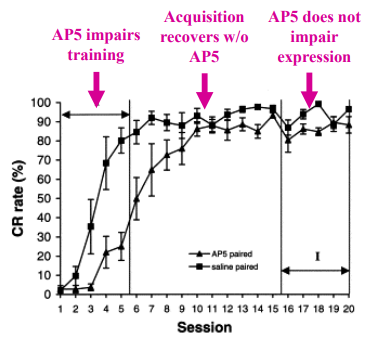
how does NMDA play into the conditioning process
NMDARs are necessary for acquisition but not expression of eyeblink CR when NMDAR antagonist (AP5) is infused into interpositus
where is the amygdala located and what does it control
temporal lobe, controls fear, anxiety, and emotions
what are the 2 parts of the amygdala and what do they consist of
striatal amygdala: inhibitory projection neurons, central (Ce) & medial (M) nuclei
cortical amygdala complex: excitatory projection neurons, lateral (LA), basal (B), accessory basal (AB) nuclei
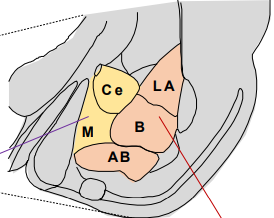
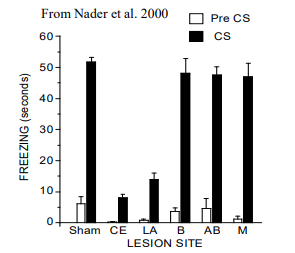
what parts of the amygdala are necessary for learning auditory fear conditioning
lateral and central nuclei
what is the process of synaptic plasticity during auditory fear conditioning
nociceptive inputs by footshock are sent to LA nucleus which excites neurons in Ce nucleus
Ce sends inhibitory projections to ventral periaqueductal gray (vPAG) which disinhibits neurons to drive freezing
what is the difference in the process of conditioning and fear conditioning
presynaptic comes from thalamus or cortex (CS) and postsynaptic is in LA nucleus
what happens when LA neurons are optogenetically stimulated instead of US
rats would learn to freeze from the light rather than an actual shock but it was only about 25% of the time
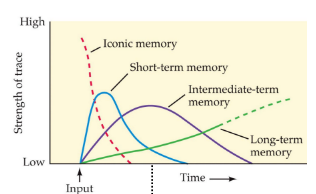
what are the stages of memory in order and how long are they
iconic: briefest, few seconds
short term: aka working memory, one minute
intermediate-term: hours/days
long-term: months, years, lifetime
how are long-term memories made
CAM triggers adenyl cyclase to convert ATP to cAMP which activates protein kinase (PKA)
PKA phosphorylates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)
MAPK goes to soma and enters nucleus of LA, activating CREB
CREB activates gene transcription, producing mRNA that transcribes into new proteins
new proteins are materials for new dendritic spines on the LA neuron
what is anisomycin
a drug that blocks protein synthesis
how does protein synthesis affect fear conditioning
when anisomycin is infused in amygdala, long term memory is impaired for CS-US association (no freezing after a certain amount of time)